Mouse model capable of monitoring NF (nuclear factor)-kB activity in liver by virtue of in-vivo imaging and construction method of mouse model
A mouse model and liver technology, applied in the field of biology, can solve the problems of less research on regulatory mechanisms, lack of real-time, dynamic modeling, convenient use of animal models, difficulties, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. Construction of a mouse model capable of live imaging monitoring of IFN-β activity in the liver
[0036] Using the method of the present invention to construct a mouse model capable of live imaging monitoring of IFN-β activity in the liver, the specific method includes the following steps:
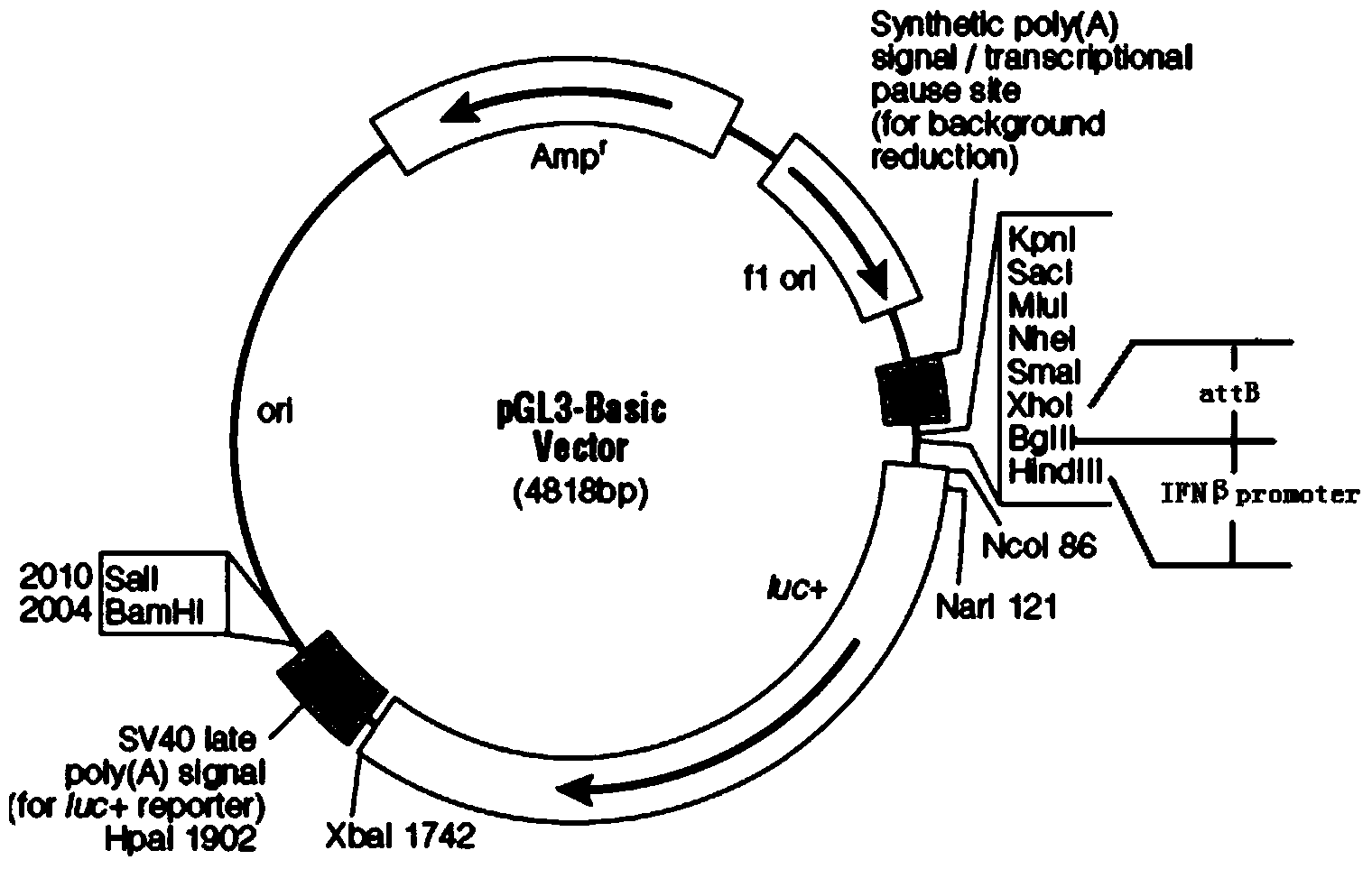
[0037] 1. Construction of recombinant vector pGL3-attB-IFNβ carrying phage integrase recognition site attB gene, IFN-β promoter and firefly luciferase (Fluc) reporter gene
[0038] Using the HepG2 cell genome as a template, the upstream primer IFNBpf:
[0039] AGATCTAATTCTCAGGTCGTTTGCTT and downstream primer IFNBpr:
[0040] Guided by AAGCTTAAAGGTTGCAGTTAGAATGT, utilize high-fidelity PrimeSTAR TM HS DNA polymerase, PCR amplifies the human IFN-β promoter sequence (its nucleotide sequence is as shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing), after the amplification finishes, carry out 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to the PCR amplification product , reclaim and purify the...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2, Evaluation of the activation of the IFN-β promoter using a mouse model that can monitor IFN-β activity with live imaging
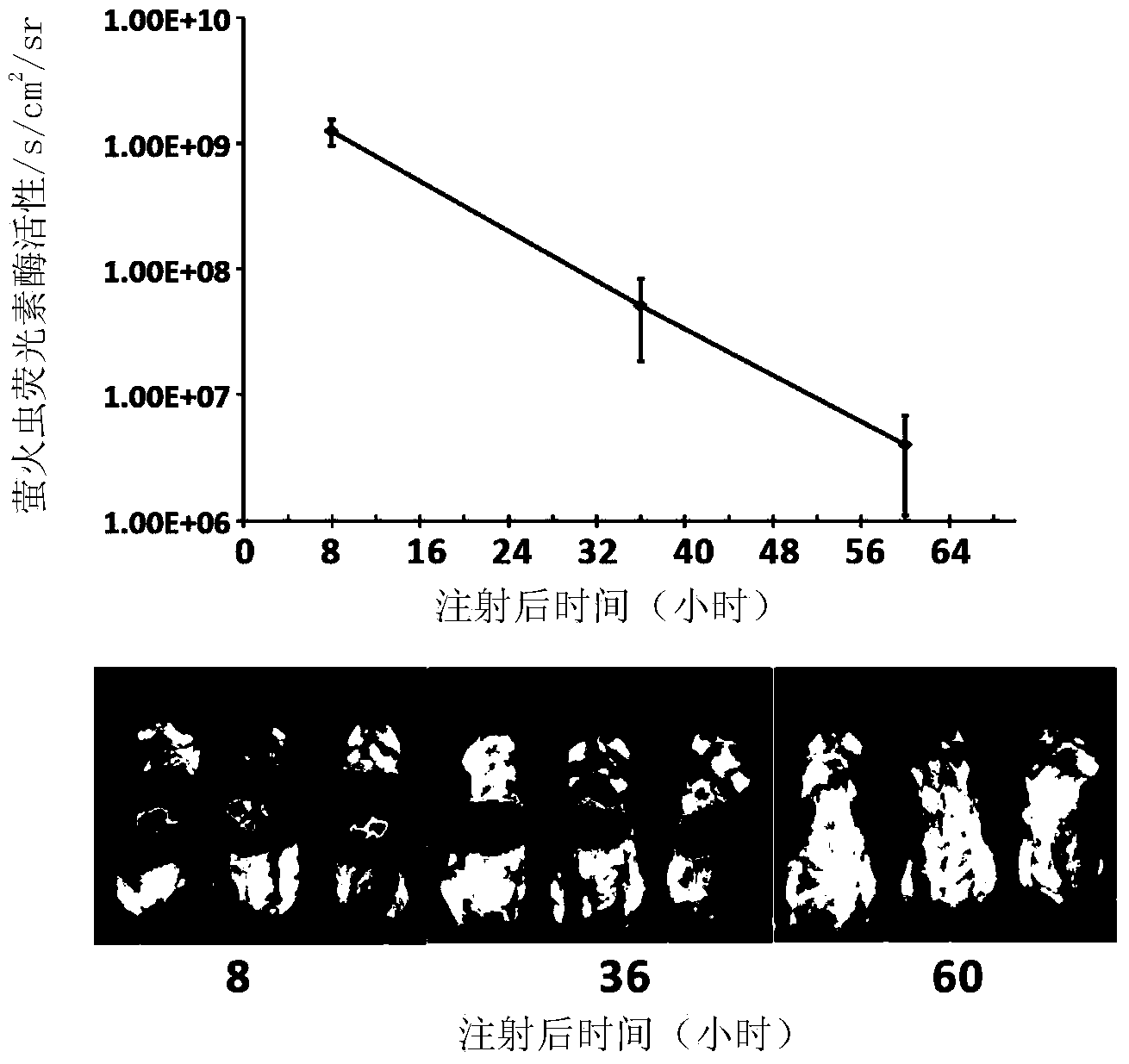
[0072] In order to verify whether the mouse model of live imaging monitoring IFN-β activity in the liver constructed in Example 1 can be used to evaluate the activation of IFN-β in the mouse liver, a pathogen-associated molecular pattern in the signaling pathway produced by IFN-β was selected. poly(I:C) as an inducer. Poly(I:C) was added to normal saline equivalent to 10% of the mouse body weight, and quickly injected (5-8 sec) into the mouse body by hydrodynamic transfection method, and the expression of mouse liver luciferase and The level of IFN-β in serum, specifically: 10 μg of poly(I:C) was delivered to the liver of 3 mice (experimental group), and monitored by live imaging at 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 60 hours Fluorescence activity of mouse liver, and 3 control mice were hydrodynamically injected with normal saline at the same time. ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3. Evaluation of IFN-β Promoter Inhibition Using a Mouse Model That Can Live Imaging Monitor IFN-β Activity in the Liver
[0076]HCV NS3 / 4A protease is a known inhibitor of the IFN-β activation signaling pathway. Studies at the cellular level have demonstrated that HCV NS3 / 4A protease can block the IFN-β activation signal by cleaving MAVS in human cells conduction. The mouse model for monitoring IFN-β activity by in vivo imaging constructed in Example 1 was used to evaluate the inhibitory effect of HCV NS3 / 4A protease on IFN-β. Two groups of plasmids of pCI-neo (control group, purchased from Promega) and pCI-HCV NS3 / 4A (experimental group, constructed by inserting HCV NS3 / 4A into the pCI-neo vector) were transfected into Example 1. In the liver of a mouse model constructed by in vivo imaging to monitor IFN-β activity, 10 μg of poly(I:C) (or normal saline) was used to stimulate IFN-β activation 24 hours later, and fluorescein was monitored by in vivo fluorescenc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com