Method for measuring air specific heat ratio via vibration of drumhead object
A technology of vibration measurement and specific heat capacity ratio, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult realization, rotational uncertainty, lack of simple harmonic vibration, etc., and achieve the effect of simple structure and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
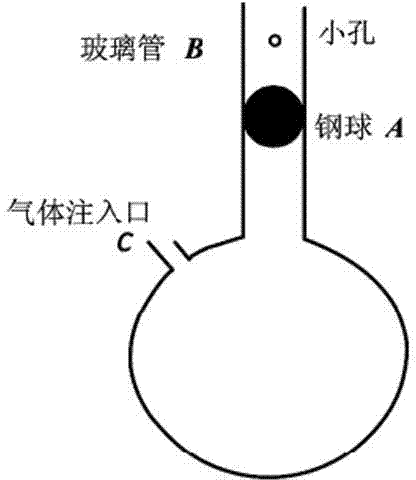
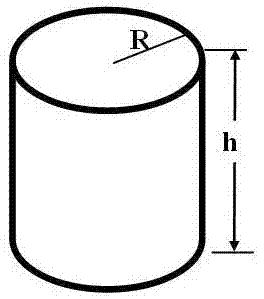
[0012] A cylinder with one end open, its internal radius is R, and the height of the cylinder is h; the open end is covered with a layer of elastic rubber to form the drum head of a leather drum, and a sphere or hemisphere is adhered and fixed in the center of the drum head body or other axisymmetric solids, the mass of the axisymmetric solid is m, relative to the mass of the elastic rubber on the drum surface, the mass of the elastic rubber can be neglected (choose the mass m of the solid, so that m>>the mass of the elastic rubber , when m>99 times the mass of the elastic rubber, it can be considered to meet the previous conditions), and the inside of the cylinder is sealed with air. Press the axisymmetric solid on the drum surface, and then release it, and the axisymmetric solid will vibrate due to the elastic force of the elastic rubber on the drum surface and the elastic action of the air.
[0013] According to the adiabatic equation PV γ =C,
[0014] Among them, P is th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com