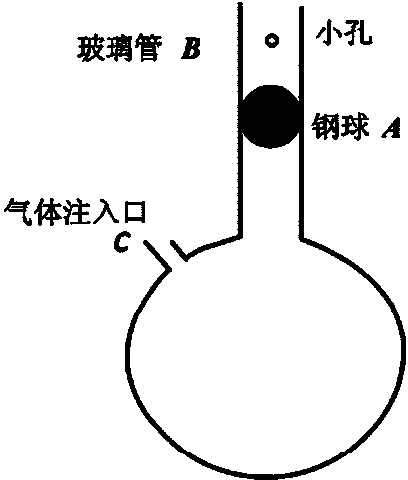
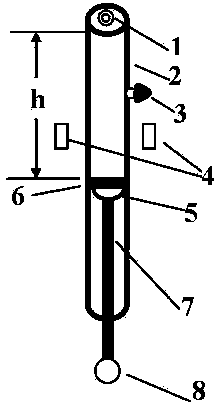
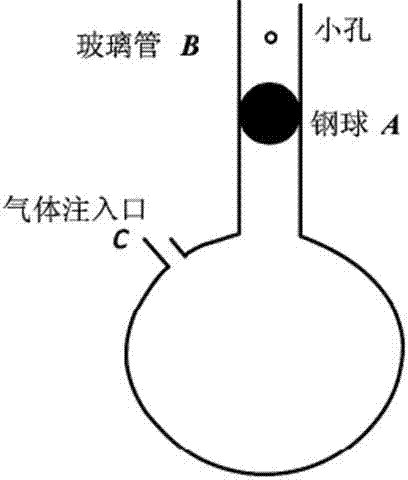
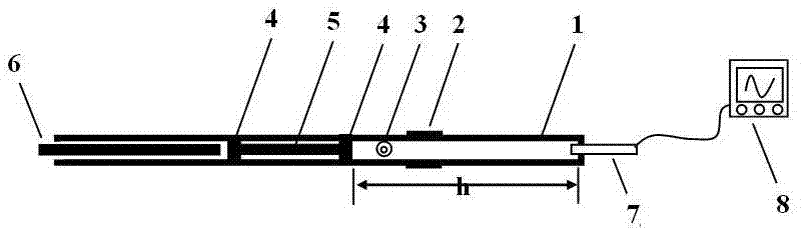
Patents
Literature
32results about How to "No turning phenomenon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
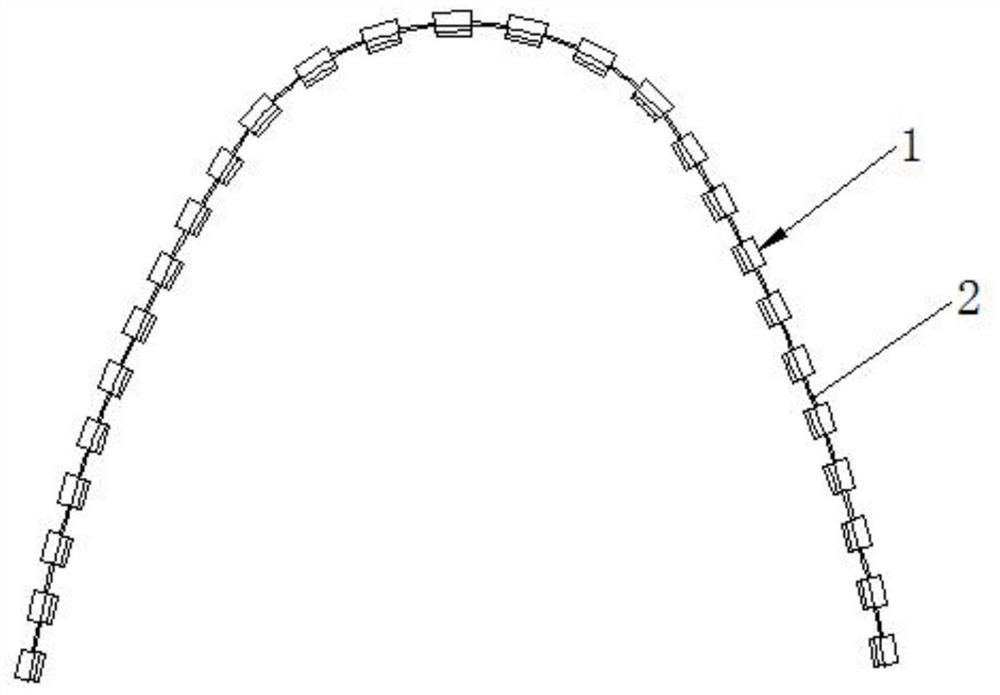
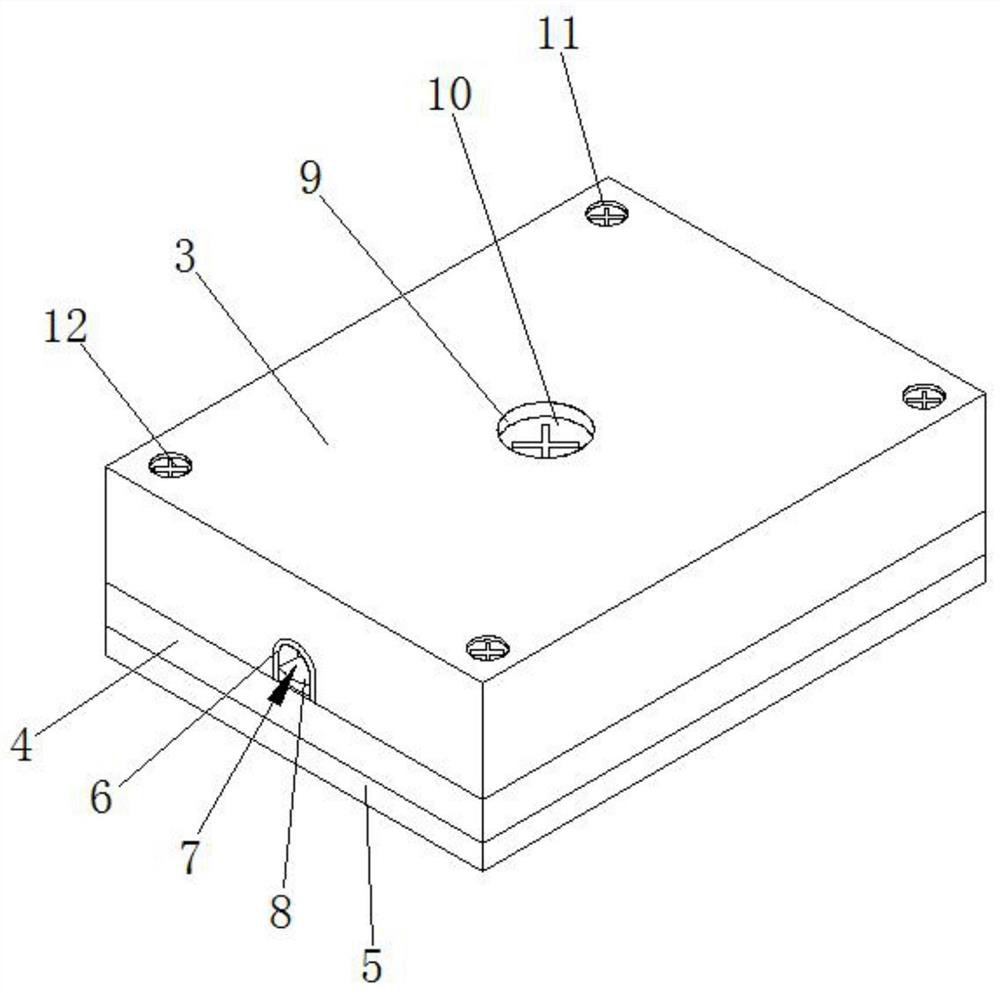
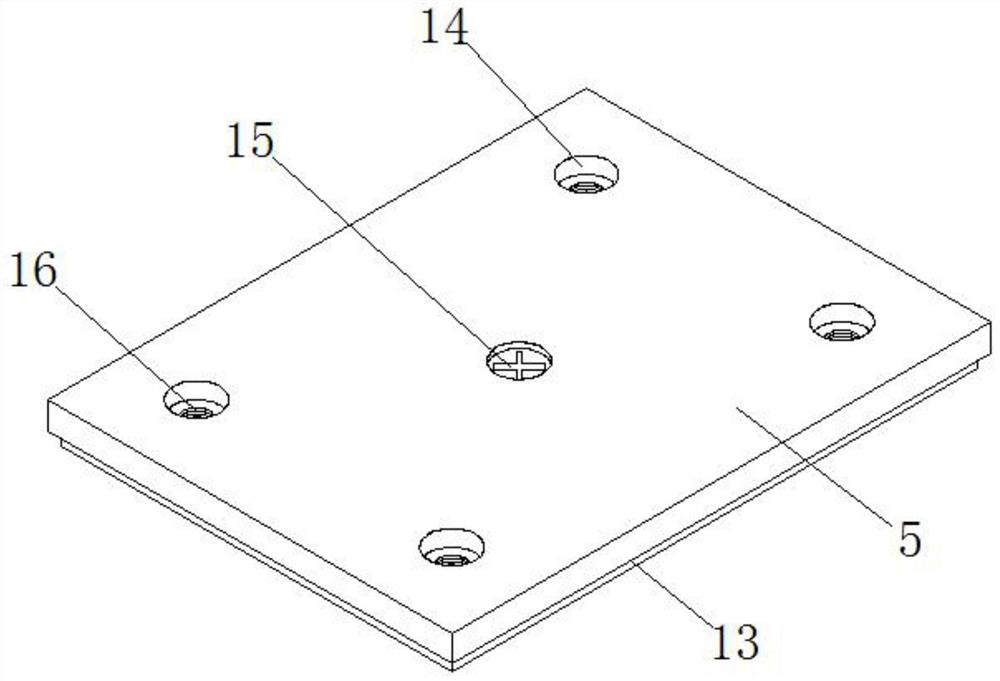
Multifunctional orthodontic appliance
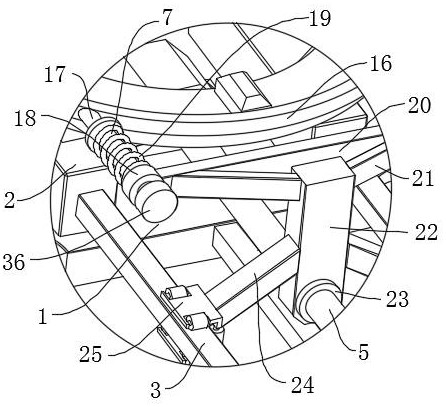
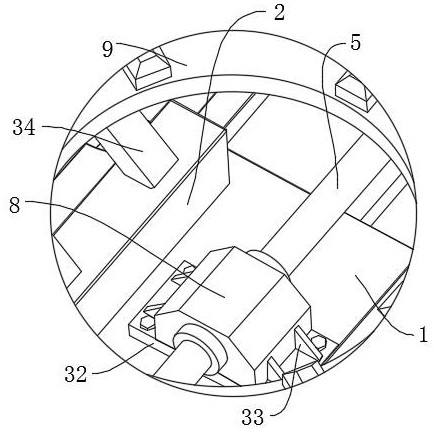
A multifunctional orthodontic appliance comprises a plurality of sets of fixing assemblies and arch wires connected with the fixing assemblies, two ends of each arch wire are connected with the corresponding fixing assembly, the fixing assemblies and the arch wires are arranged at intervals, and the two ends of each arch wire are fixedly connected with clamping blocks; each fixing assembly comprises a top cover, a bottom plate, a connecting pad, a limiting plate, a limiting piece, a connecting base, a connecting block, a first fastener, a second fastener, a clamping plate, a connecting rod anda first bolt. For each fixing assembly, the bottom end of the top cover is connected with the upper end face of the bottom plate, a limiting groove used for installing the limiting plate is formed inthe lower end face of the bottom plate, the connecting pad is fixedly installed on the lower end face of the limiting plate and fixedly connected with the bottom plate through a third bolt, the top cover is fixedly connected with the bottom plate through a second bolt, and a cavity is formed in the top cover. The multifunctional orthodontic appliance has the advantages of being reasonable in design and convenient to adjust.
Owner:QINGDAO STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL
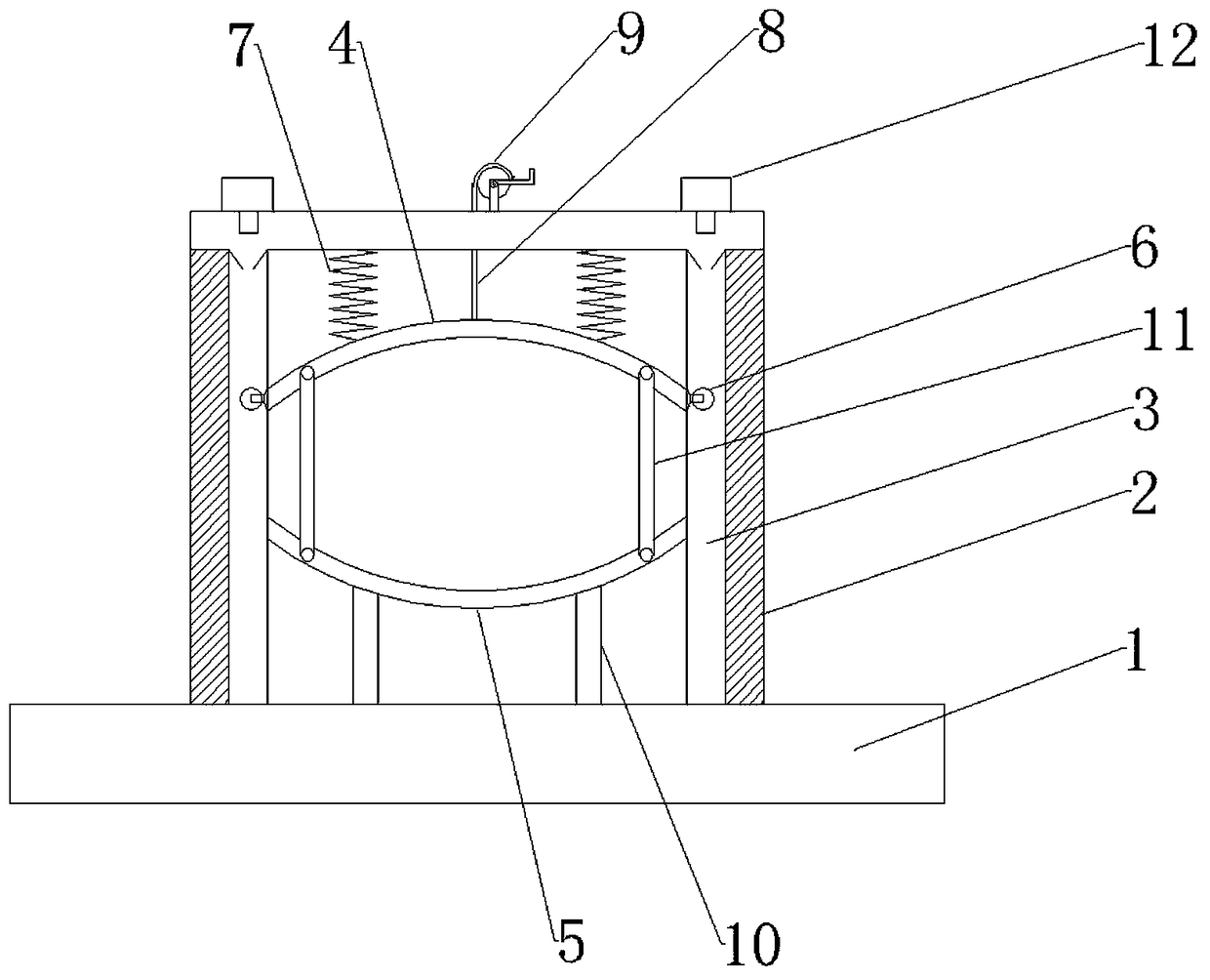
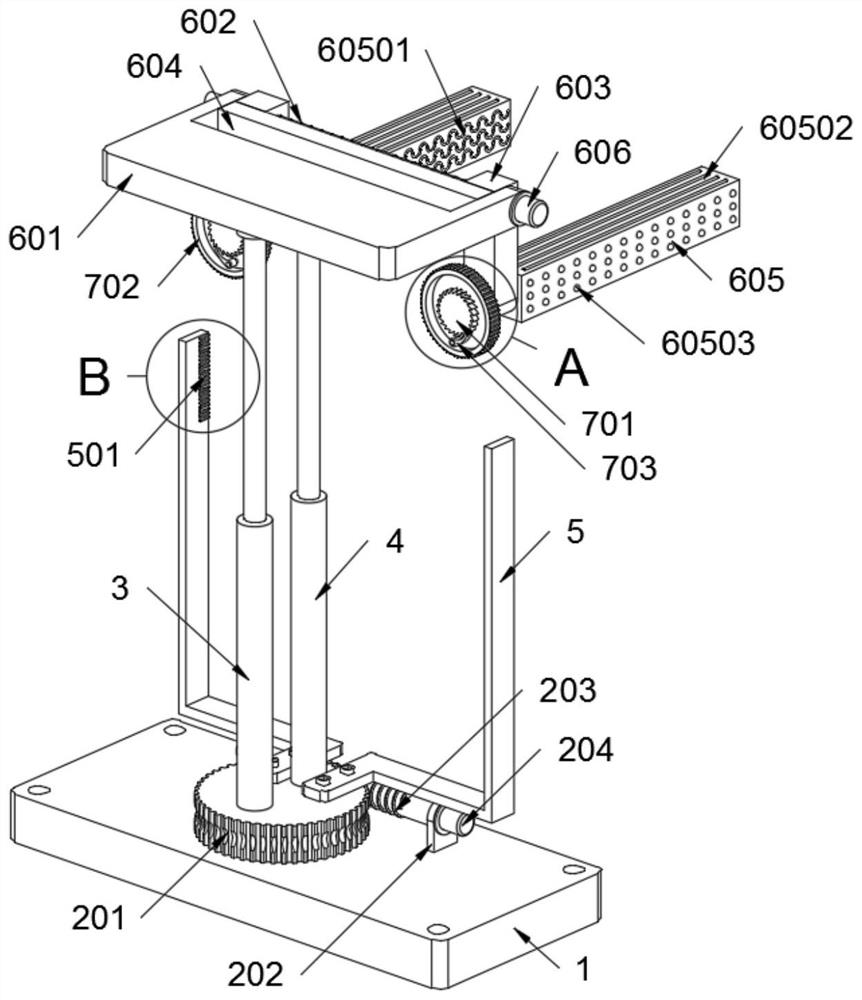
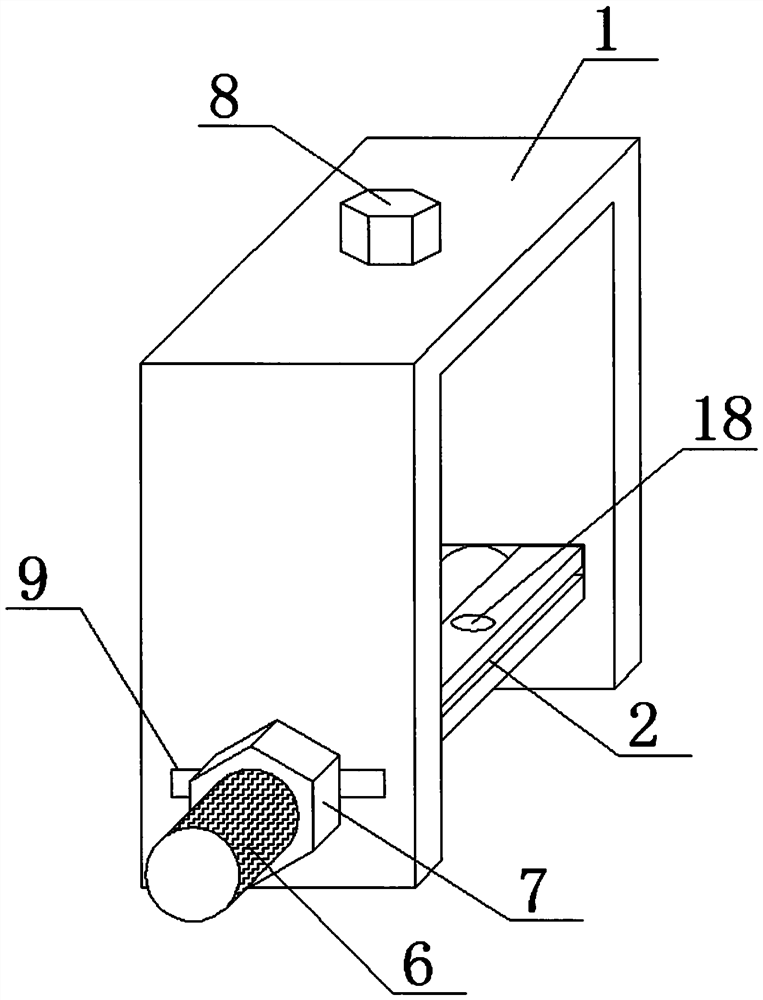
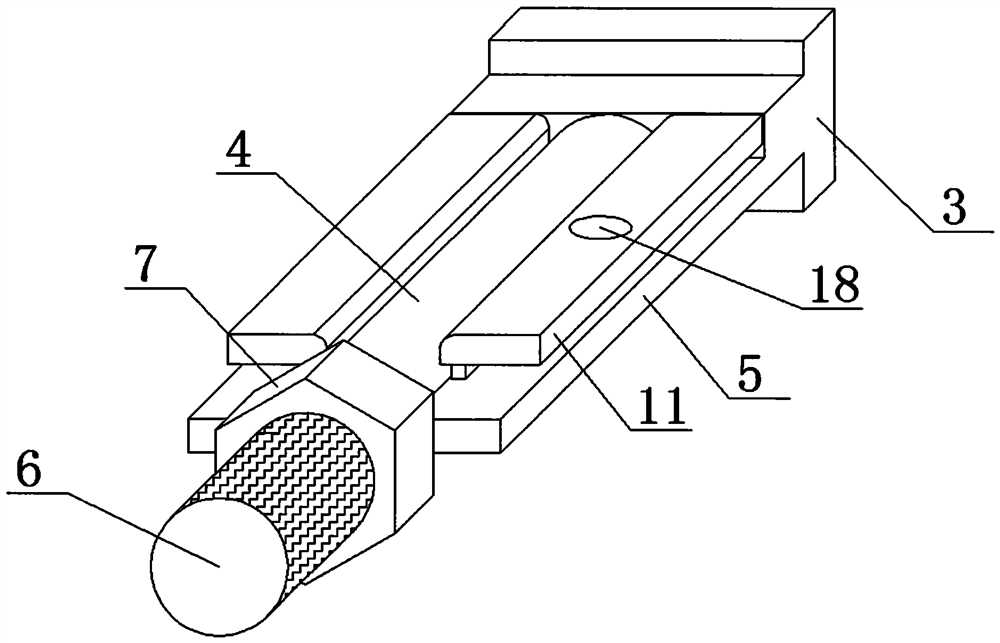
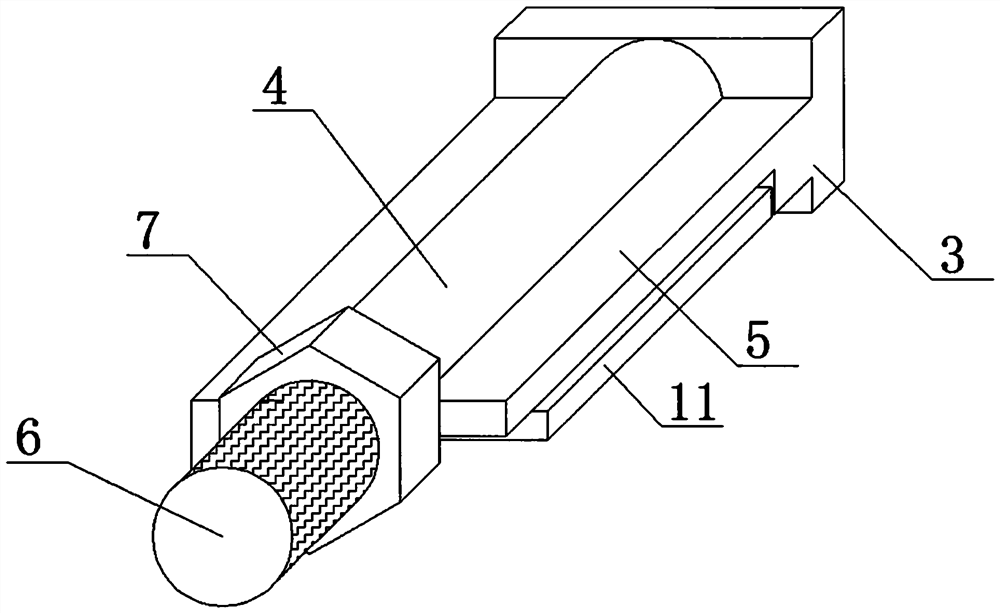
A pipe installation device
The invention discloses a pipeline installing device in the technical field of mechanical installation. The pipeline installing device comprises a base plate, wherein a gate-shaped frame body is fixed to the base plate, a groove is formed in the inner side of the frame body in the vertical direction, an upper clamping plate and a lower clamping plate are arranged on the inner side of the frame body and are arc-shaped, rollers are arranged at two ends of the upper clamping plate and are connected in the groove in a rolling mode, the upper clamping plate is connected to the top of the frame body through a spring, a traction rope is further connected to the upper clamping plate, a hand wheel is arranged at the top of the frame body, a traction roper penetrates through the top of the frame body and is wound around the hand wheel. The lower clamping plate is fixedly connected to the base plate, a supporting rod is connected between the lower clamping plate and the base, the upper clamping plate and the lower clamping plate are arranged in a mirror symmetry mode, a round cavity for containing a pipeline is formed between the upper clamping plate and the lower clamping plate, and a fastener for fixing the upper clamping plate and the lower clamping plate is further arranged between the upper clamping plate and the lower clamping plate. By adoption of the pipeline installing device, operation is convenient, the pipeline can be firmly fixed, the pipeline does not rotate or slide, and the stability of the pipeline is good.
Owner:贵州省遵义市永力机电安装有限公司
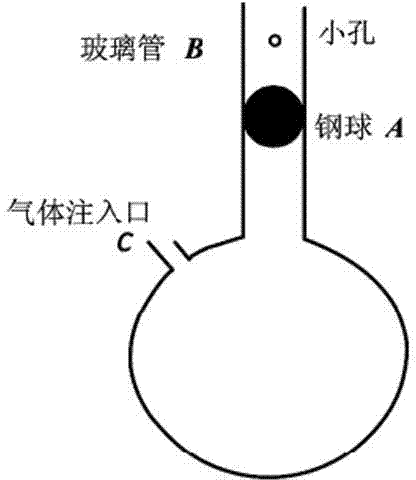
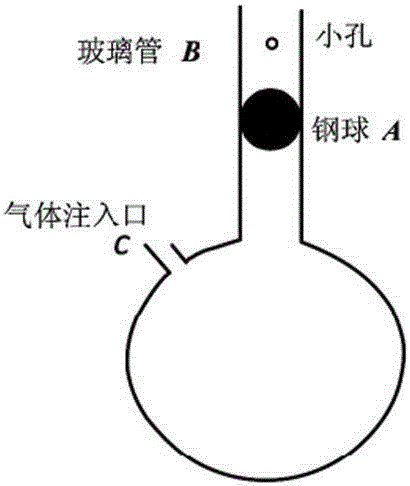
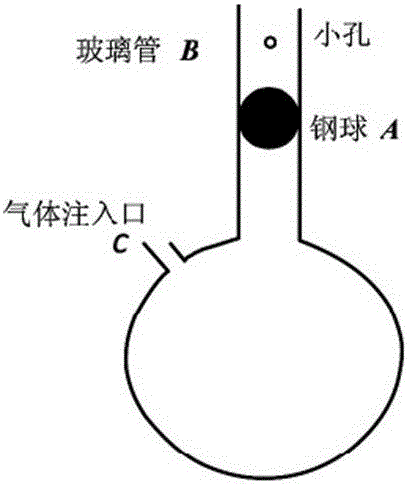
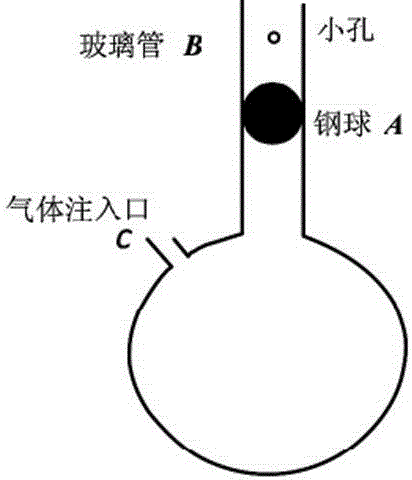
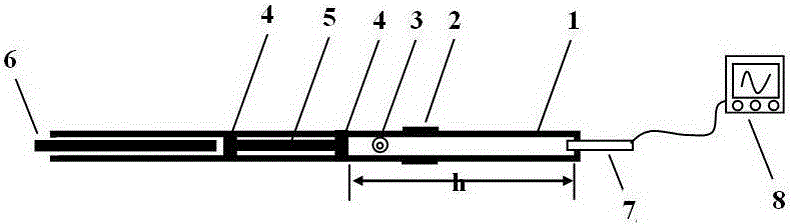
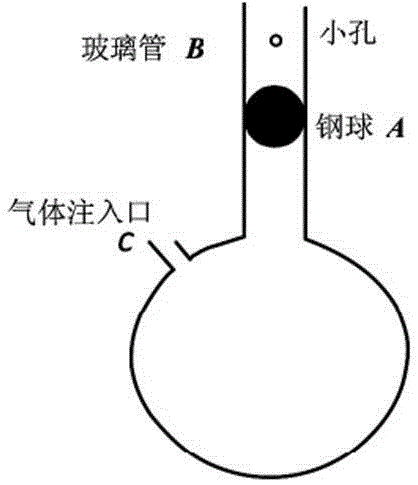
Method for measuring air specific heat ratio by vibration of piston in single-end sealed vertical cylinder
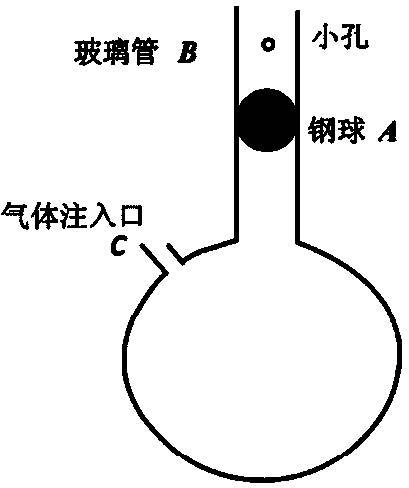
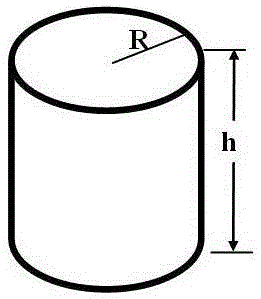
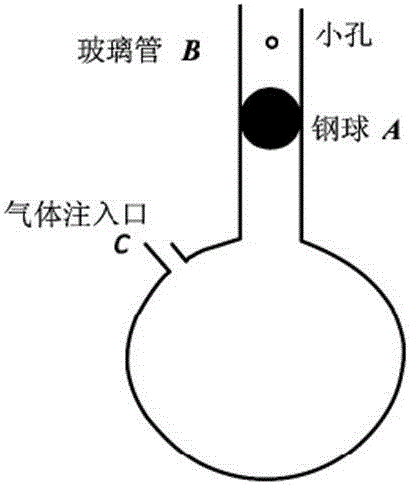
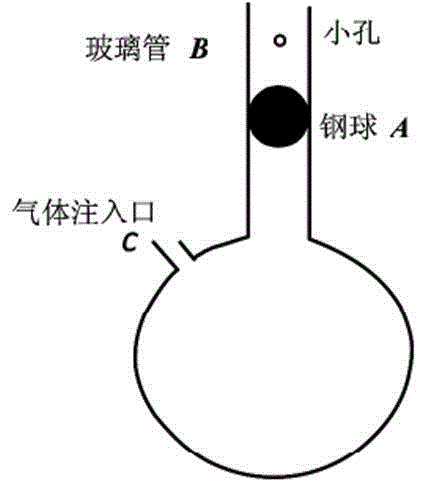
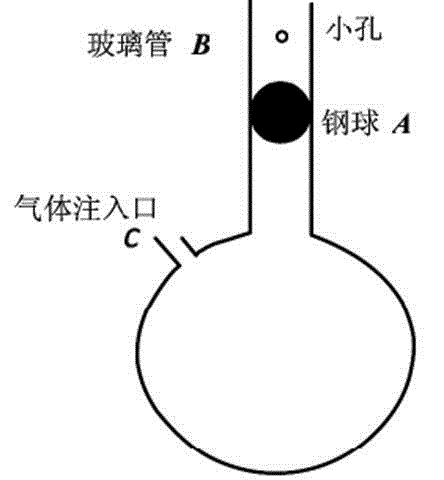
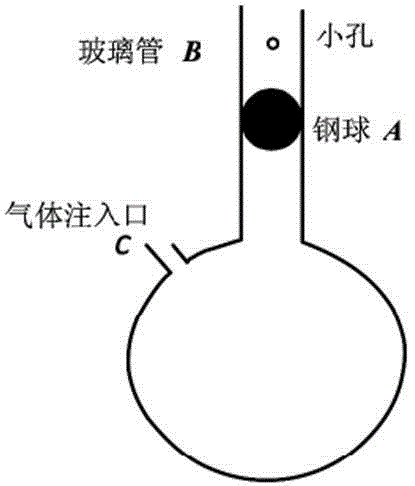
The invention discloses a method for measuring an air specific heat ratio by vibration of a piston in a single-end sealed vertical cylinder. A horizontal bubble is arranged at the upper end face of the outer side of a cylinder with internal diameter r, an air hole and a millimeter dividing ruler are arranged at the vertical side surface of the cylinder, the cylinder is vertically fixed on a bracket; a sealing piston is arranged inside the cylinder, a metal half-sphere is fixed at the lower end of the piston, the symcenter of the outer surface of the half-sphere is fixed with one end of a pull rod, the other end of the pull rod is fixed with a pull ring; an air hole is opened, the piston is pushed into any position inside the cylinder by virtue of the pull rod, then a sealing cap of the air hole is sealed, the pull ring at the tail end of the pull rod is pulled, and then immediately released, the piston can vibrate under an elastic function of sealed air; the air specific heat ratio gamma is equal to 4 pi mh / (r<2>T<2>P). The method has the beneficial effects that the air is in a sealed state, the sealed air has good elasticity; an experiment principle is relatively precise; the vibration is strict simple harmonic vibration; the phenomenon of rotation of the prior art can not be caused; no inflating device is needed, the structure is relatively simple and the cost is relatively low.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
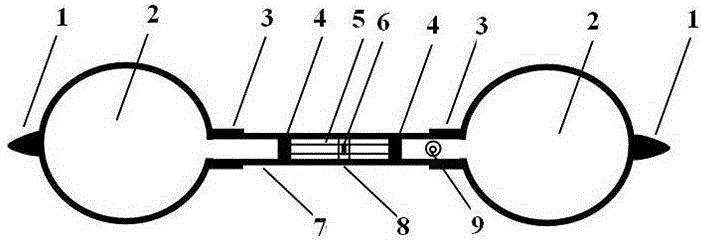
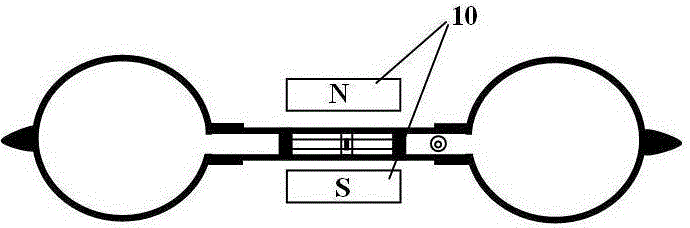
Method for measuring air ratio and heat capacity ratio by vibration of piston in single-end sealed cylinder
InactiveCN104237062AFlexibleIncrease elasticityMaterial analysisHarmonic vibrationPressure difference
The invention relates to a method for measuring an air ratio and a heat capacity ratio by vibration of a piston in a single-end sealed cylinder. The transparent cylinder with an internal radius of r comprises two sections; the bottom end of one section is sealed and a pressure sensor is arranged on the one section; a signal wire of the pressure sensor is connected to a digital oscilloscope to measure a vibration period of T; a millimeter graduation ruler and a spirit bubble are arranged on the outer surface of the cylinder in the length direction of the cylinder; the two-position sealed piston with a mass of m and a piston connecting rod are arranged inside the cylinder; the piston connecting rod can be attracted by a magnetic field; one magnet extends into the hollow round tube end of the cylinder and is in contact with the piston, the magnetic field attracts stainless steel of the piston connecting rod, then the piston connecting rod is pulled towards the open end of the cylinder, and when the magnetic field force is smaller than a force generated by air pressure difference, the two-position sealed piston is separated from the magnet and vibrates and a meter measures an atmospheric pressure value P of the air; the air ratio and the heat capacity ratio are calculated according to the formula gamma=4pimh / (r<2>T<2>P). The method has the benefits that the sealed air has excellent elasticity; the experiment principle is more rigorous; vibration in the method is strict simple harmonic vibration; the rotating phenomenon cannot be generated; a vibration starting method is simple and easy to operate; a structure is simpler and cost is lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
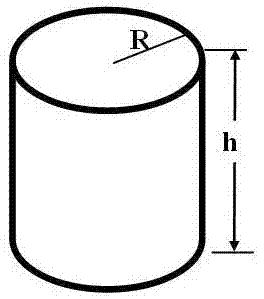
Method for measuring air specific heat ratio via vibration of drumhead object
The invention discloses a method for measuring an air specific heat ratio via vibration of a drumhead object. The method comprises the following steps: covering a layer of elastic rubber at the opened end of a cylinder to form a drumhead, one end of which is opened, and fixedly adhering a sphere or a semisphere or an axially symmetric solid at the center of the drumhead, wherein the inner diameter of the cylinder is R, the inner height of the cylinder is h, the mass of the sphere or the semisphere is m and air is sealed in the cylinder; pressing the axially symmetric solid and then releasing, wherein the axially symmetric solid vibrates by suffering the elastic force of the elastic rubber of the drumhead and the elastic function of the air; obtaining the air specific heat ratio gamma which is equal to [(2pi / T)2-k / m]*3m*h / (piR2P), wherein k is the elastic coefficient of the rubber drumhead, the circumference to diameter ratio pi is equal to 3.14159, T is the period of vibration and P is the pressure of the external air. The method disclosed by the invention has the benefits that favorable elasticity is provided as the air is sealed, the experiment principle is more rigorous, a strict simple harmonic vibration is carried out, no rotation occurs, an inflation device is not required, the structure is simpler and the cost is lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Drive mechanism for fused mass milling degree regulating device of milling extrusion pressing granulation machine group
The invention relates to a novel extruding granulation machine unit. In a device for regulating melt mixing degree of a mixing granulation machine unit, a material runner is arranged in a valve body; a rotatable valve core or a rotatable valve plate are arranged in the material runner and with the difference of a rotation angle, flow area of the valve core or the valve plate is different; the valve core or the valve plate are connected with a driving mechanism through a rotation shaft and the driving mechanism is connected with a reducer by a motor output shaft; the reducer is connected with the rotation shaft of the device for regulating the melt mixing degree. In the novel extruding granulation machine unit, the motor drives the reducer to drive the regulation device and the novel extruding granulation machine unit has a simple and compact structure, less parts; a diction function is brought into play by an angular displacement sensor fixed on the end of the shafts. As the motor can realize positive and reverse rotation, the angle can be changed at any time, which means the melt mixing degree can be changed with the advantages of timely and simple control. The reducer directly connected with the motor adopts a worm gear form to effectively realize self-locking and accurate location as well as avoid the rotation of the valve core caused by the material.
Owner:恒力石化股份有限公司
Method for measuring specific heat ratio of air by vibration of piston in cylinder
The invention relates to a method for measuring the specific heat ratio of air by the vibration of a piston in a cylinder. The method comprises the steps of connecting the two ends of a horizontally arranged transparent cylinder with gas containers respectively, forming an air hole which can be sealed in the outer side of each gas container, and arranging a horizontal bubble in the cylinder; unscrewing the gas containers respectively arranged at the two ends of the cylinder, plugging a piston body into the opening end of the cylinder, and overlapping the center of the piston body and the center of the cylinder; then, screwing the gas containers respectively arranged at the two ends of the cylinder, then screwing sealing caps respectively arranged at the outer sides of the gas containers at the two ends of the cylinder, turning on a power supply of a piece of electromagnet arranged at the outer side of the cylinder so as to move the piston body by the magnetic field, and cutting off the power supply to enable the piston body to vibrate under the elasticity of air. The specific heat ratio gamma of air is equal to 2mV / (r4T2P), wherein m is the mass of the piston body, r is the internal radius of the cylinder, V is the volume of the single-side sealed air, T is period of vibration, and P is atmospheric pressure value of the outside air. The method has the beneficial effects that the sealed air has good elasticity, the experiment principle is precise, a strict harmonic vibration is realized, the structure is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Special fixture for cylindrical bearing retainer
ActiveCN114851026AImproved gripping convenienceReduce frictionGrinding drivesGrinding machinesRetainerPhysics
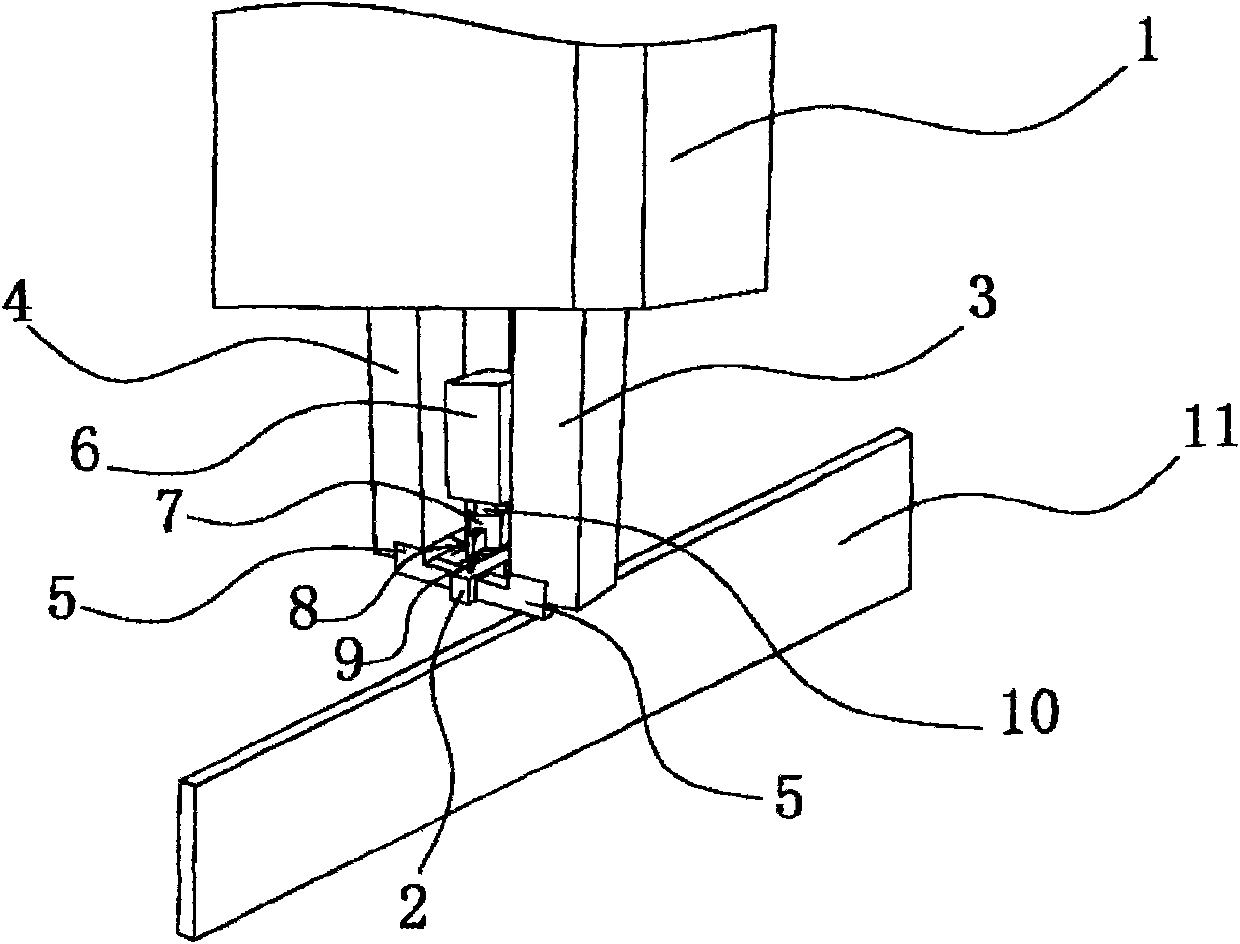
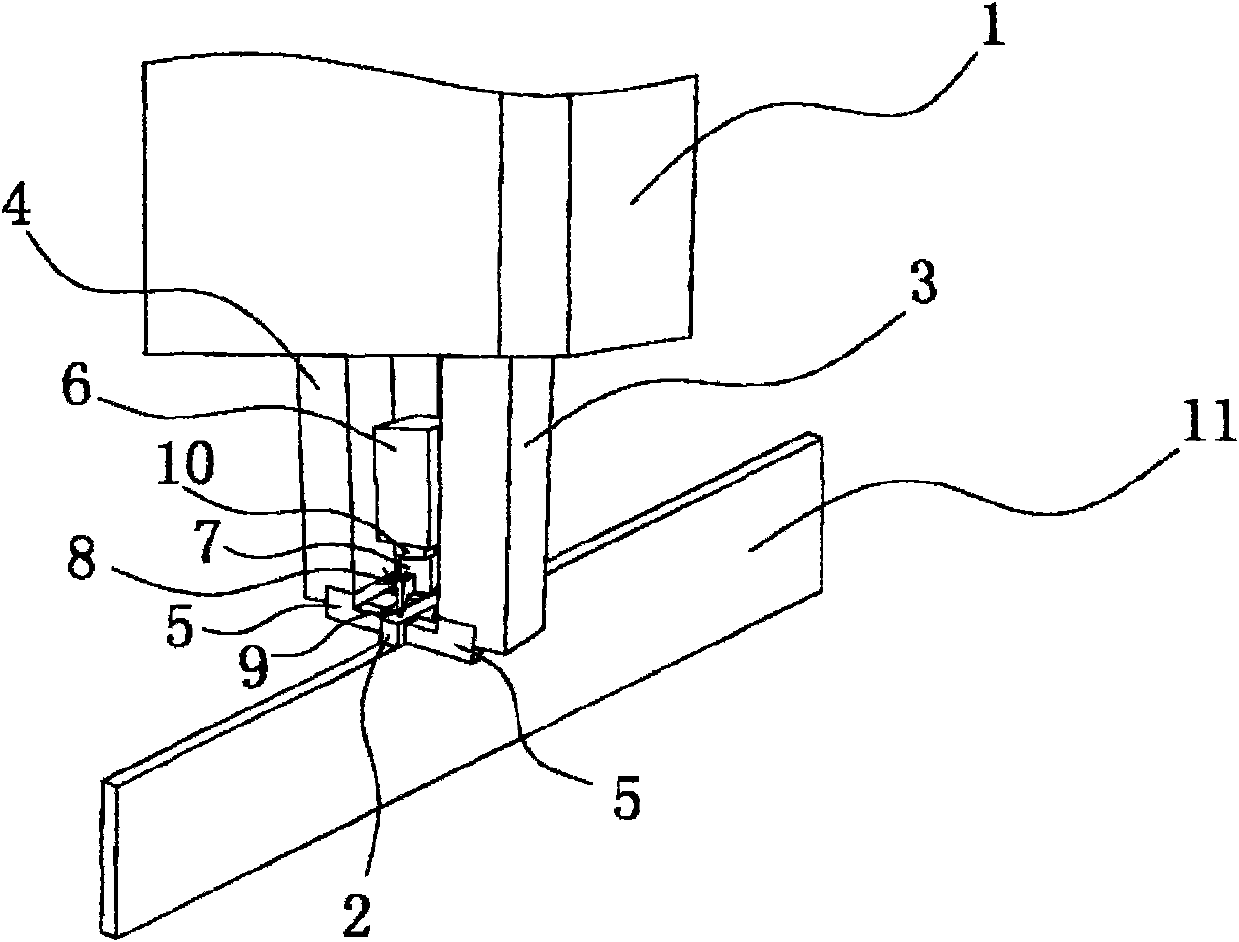
The invention relates to the field of bearing production, in particular to a special fixture for a cylindrical bearing retainer, which comprises a clamping seat, a pushing part is mounted in the middle of the upper end of the clamping seat, a clamping part is connected to the end part of the pushing part, an ejection part is mounted at the edge of the upper end of the clamping seat, and the axis of the ejection part and the axis of the clamping part are collinear. Mounting holes are formed in the corners of the upper end face of the clamping base in a penetrating mode, and the ejecting piece is connected with the pushing piece. According to the holder clamping device, the convenience degree of holder clamping can be improved, it can be guaranteed that more labor is saved during clamping, and the protection force on the holder during clamping and the clamping stability can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG GOLDEN EMPIRE PRECISION MACHINERY TECH CO LTD
Method for measuring air specific heat ratio through the adoption of vibration method
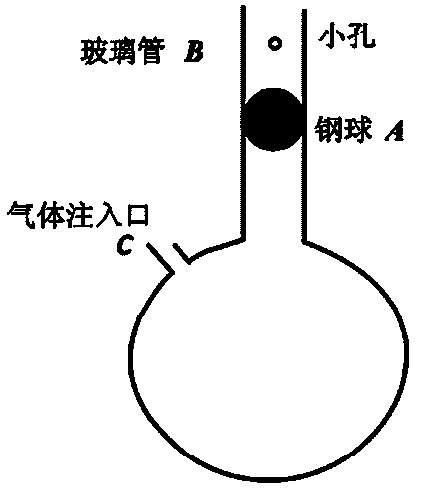
The invention provides a method for measuring air specific heat ratio through the adoption of the vibration method, relates to measurement of physical constant and overcomes problems existing in the conventional technology. The technical scheme adopted by the method is as follows: a cylinder with a sealed upper end and an opened lower end is provided, wherein a spirit bubble is arranged in the plane surface on the outer side of the upper end surface; one or more air holes are formed in the upper part on the side surface of the cylinder and can be sealed through sealing nuts; the cylinder is vertically fixed on a support; a spring is connected between the plane surface at the upper end on the inner side of the cylinder and a piston; the upper end of a suspension line is fixed to the center of the lower end face of the piston; a heavy object is tied to the lower end of the suspension line; when the air holes are open, the vibration period T1 of the heavy object equals to 2Pi(m / k)<0.5>; when all the air holes are sealed, the vibration period of the heavy object is T and the air specific heat ratio gamma equals to 4Pimh(T1<2> minus T<2>) / (r<2>PT<2>T1<2>), wherein Pi is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, m is the quality sum of the piston and the heavy object, k is the elastic coefficient of the spring, P is the pressure of the sealed air and r is the inner diameter of the cylinder. The method has the benefits that the sealed air is elastic, the experiment principle is stricter, strict simple harmonic vibration is realized, rotation is avoided and the device is simpler in structure and lower in cost.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A Method of Measuring Air Specific Heat Capacity Ratio by Vibration Method
The invention provides a method for measuring air specific heat ratio through the adoption of the vibration method, relates to measurement of physical constant and overcomes problems existing in the conventional technology. The technical scheme adopted by the method is as follows: a cylinder with a sealed upper end and an opened lower end is provided, wherein a spirit bubble is arranged in the plane surface on the outer side of the upper end surface; one or more air holes are formed in the upper part on the side surface of the cylinder and can be sealed through sealing nuts; the cylinder is vertically fixed on a support; a spring is connected between the plane surface at the upper end on the inner side of the cylinder and a piston; the upper end of a suspension line is fixed to the center of the lower end face of the piston; a heavy object is tied to the lower end of the suspension line; when the air holes are open, the vibration period T1 of the heavy object equals to 2Pi(m / k)<0.5>; when all the air holes are sealed, the vibration period of the heavy object is T and the air specific heat ratio gamma equals to 4Pimh(T1<2> minus T<2>) / (r<2>PT<2>T1<2>), wherein Pi is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, m is the quality sum of the piston and the heavy object, k is the elastic coefficient of the spring, P is the pressure of the sealed air and r is the inner diameter of the cylinder. The method has the benefits that the sealed air is elastic, the experiment principle is stricter, strict simple harmonic vibration is realized, rotation is avoided and the device is simpler in structure and lower in cost.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Self-switching gripper arm structure using handling robot in narrow environment
The invention provides a self-switching fixture arm structure for a handling robot used in a narrow environment, including a base; a rotation adjustment structure is installed on the base, and an electric telescopic rod, a telescopic rod and an adjustment arm are installed on the rotation adjustment structure; the electric telescopic rod A clamping structure is installed on the head end of the telescopic rod, and two driving structures are installed on the clamping structure; the adjustment arm includes a gear row, and the two adjustment arms are symmetrically fixedly connected to the gear, and each adjustment arm is welded with a gear row ;When the electric telescopic rod shrinks and drives the driving structure to move downward, the gear sleeve and the gear row mesh, and at this time the clamping arm is in a rotating state; the two driving structures are set in mirror images, and when the gear sleeve and the gear row on the driving structure After the meshing is completed, the adjustment arm rotates at an angle of 90 degrees. In the narrow environment of the present invention, the self-switching fixture arm structure of the handling robot is used to realize the problem of self-switching of various fixture arms without using a motor drive, and realizes the accuracy of adjusting the arm switching.
Owner:河南工学院
Method of Measuring Air Specific Heat Capacity Ratio by Piston Vibration in Cylinder
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
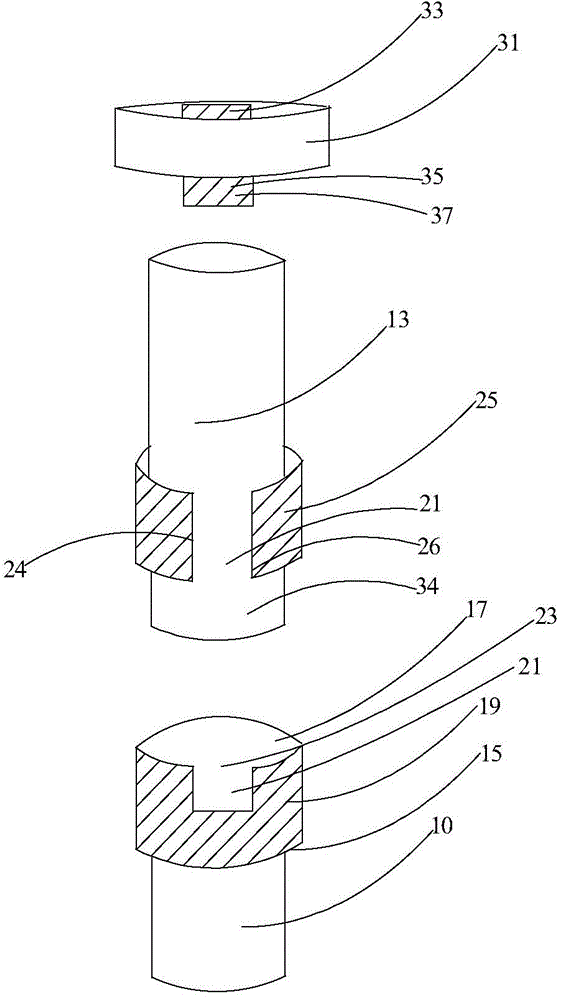
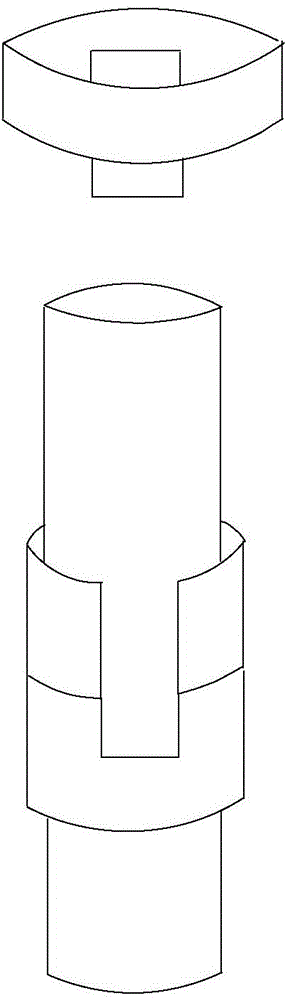
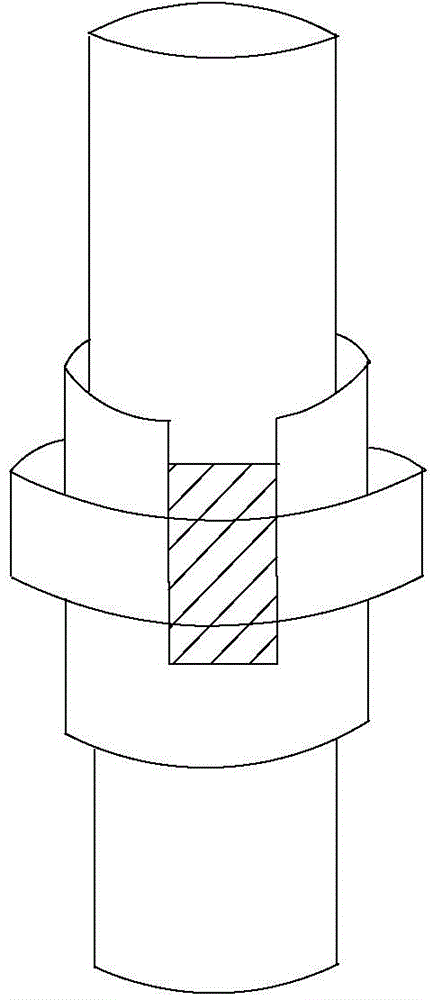
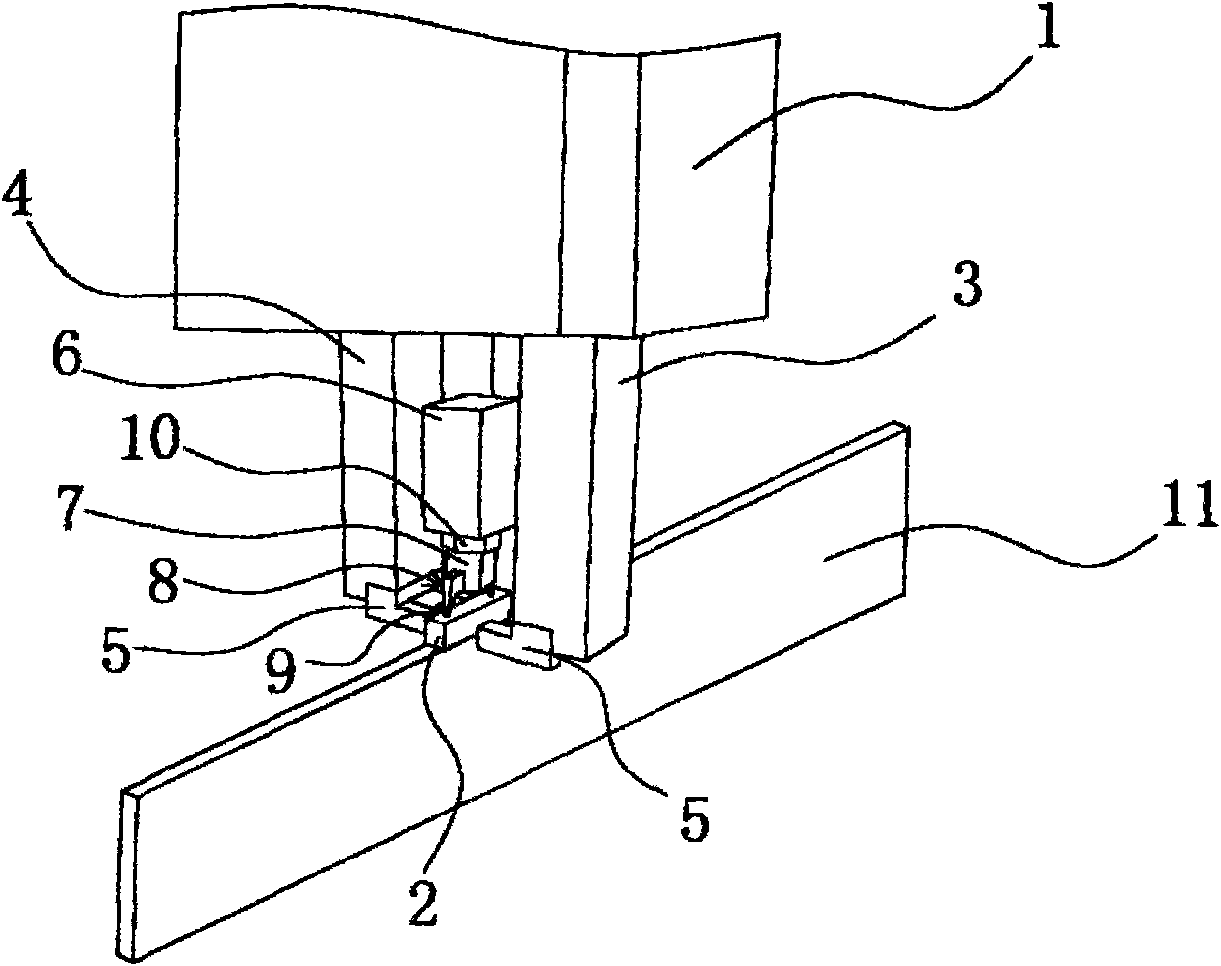
Oil pipe
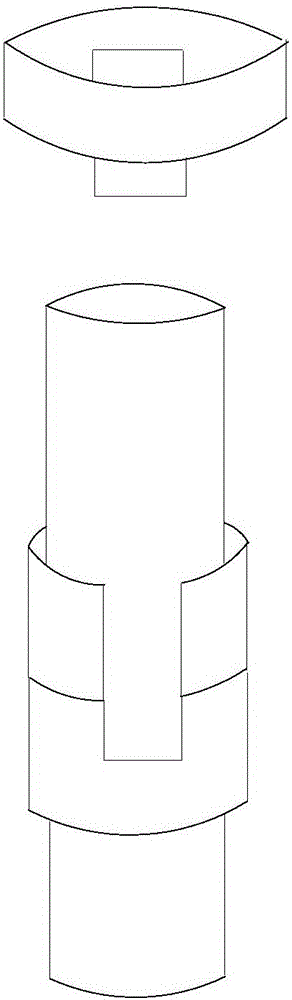
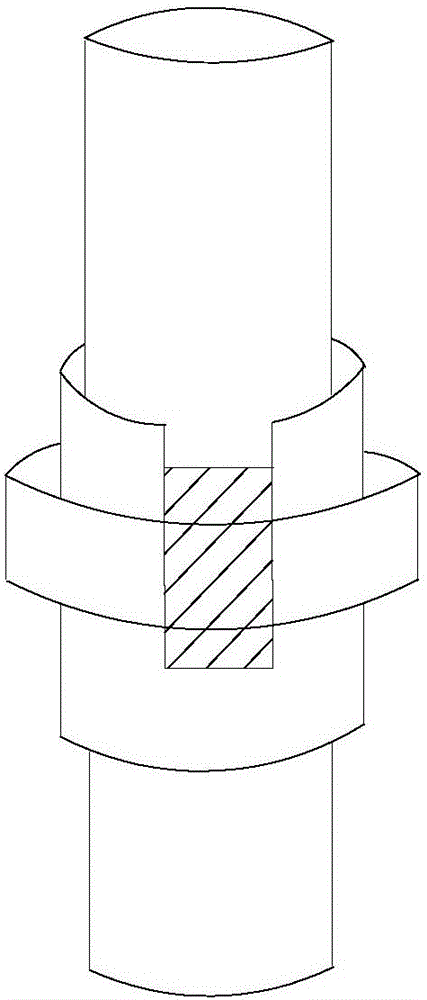
ActiveCN104632092ANo turning phenomenonPrevent rotationDrilling rodsDrilling casingsPetroleum engineering
The invention provides an oil pipe. The oil pipe comprises a first oil pipe, a second oil pipe, a connector, a first groove, a projection and an anti-rotation body, wherein the first oil pipe and the second oil pipe longitudinally extend, the connector is provided with a first end and a second end which are opposite, the first end is used for being connected with the first oil pipe, the first groove recessed from the end face of the second end to the first end is formed on the side wall of the connector, the projection protrudes out of the side wall of the second oil pipe and is provided with a first operating surface and a second operating surface which are opposite in the circumference of the second oil pipe, a notch is formed by the first operating surface, the second operating surface and the side wall of the second oil pipe adjacent to the first operating surface and the second operating surface; the anti-rotation body can be received in the first groove and the notch. By the oil pipe, the purpose for preventing rotation of the oil pipe at the joint is achieved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Steel pipe clamp of drainage discharge pipe
InactiveCN108061197ANovel structureHigh tensile strengthPipe supportsTear resistanceMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a steel pipe clamp of a drainage discharge pipe. A pipe clamp main body is formed by an upper half-annular pipe clamp body and a lower half-annular pipe clamp body, the upper half-annular pipe clamp body and the lower half-annular pipe clamp body having left and right turning-out connecting plates and connecting bolt holes. Two sides of a pipe clamp are connected by bolts and are in a closed annular shape. The connecting plate is a round ring without a landing edge. Positioning holes are uniformly distributed on the pipe clamp main body. One end of the pipe clamp main body is provided with a pinch plate. The size of the pinch plate is consistent with the size of the positioning hole. A flexible rubber plate of the pipe clamp main body is adhered on the upper part ofan arc surface of the connected round ring. A clamping limiting plate is arranged on the flexible rubber plate. The clamping limiting plate is arranged on a single-board pull rod with synchronous teeth. The steel pipe clamp can synchronously contract with a drainage pipe, and has relatively high tensile strength (tear resistance), and connection is reliable. The flexible rubber plate can make thenovel steel pipe clamp would not rotate in a whole loading and unloading working process. The steel pipe clamp can improve working efficiency, and is convenient in operation, low in investment cost,and tightness degree of the pipe clamp can freely adjusted, and fixation effect is good.
Owner:青岛鼎和精铸有限公司
Method of Measuring Air Specific Heat Capacity Ratio by Piston Vibration in Single-End Sealed Cylinder
The method of measuring air specific heat capacity ratio by piston vibration in a single-end sealed cylinder. A transparent cylinder with an inner radius of r is divided into two sections, one section is sealed at the bottom and a pressure sensor is arranged. The signal line of the pressure sensor is connected to a digital oscilloscope. To measure the period T of vibration, the outer surface of the cylinder has a millimeter scale and a horizontal bubble along the length of the cylinder; inside the cylinder, there are two sealed pistons with a mass of m and a piston connecting rod. The piston connecting rod is Can be attracted by a magnetic field; put a magnet into the hollow tube end of the cylinder, touch the piston, the magnetic field attracts the stainless steel of the piston connecting rod, and then pull the piston connecting rod to the open end of the cylinder, when the magnetic field force is less than the air pressure difference The power generated, the two sealed pistons will break away from the magnet and vibrate, and the meter will measure the atmospheric pressure value P of the air; the specific heat capacity ratio of the air is given by the formula γ=4πmh / (r 2 T 2 P) calculation. The beneficial effects are: the sealed air has good elasticity; the experimental principle is more rigorous; it is a strict simple harmonic vibration; no rotation phenomenon occurs; the method for initiating vibration is simple and easy;
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Lifting driving device for wire installation pay-off device
InactiveCN111392494ANo porosityNo turning phenomenonFilament handlingApparatus for laying cablesRotational axisPull force
The invention discloses a lifting driving device for a wire installation pay-off device. The lifting driving device comprises a bottom fixing baseplate. The lifting driving device couples with a support for the wire installation pay-off device, a power transmission line in a hoisting wheel can neutralize the friction force required by rotation when the end of the power transmission line is pulled,the wire can be subjected to rotation pulling under the premise of low pulling force, and the self-adaptability is improved. The phenomenon of the loosened wire cannot occur, the lifting driving device can control the maximum resistance of rotation, and the phenomenon that the hoisting wheel rotates since the hoisting wheel does not have pulling force is avoided. The lifting driving device is provided with a reverse-thread-structure rotation-type vertical height limit mechanism and can move synchronously with the support for the wire installation pay-off device so as to achieve coupling, in addition, the lifting driving device is provided with a rotation shaft fixing-type part connection mechanism and can achieve a fixing limit function on the rotation shaft and achieve a mounting fixingfunction on the part.
Owner:张昕伟
Stainless steel plate spring clamp
InactiveCN112709771AReduce deformation speedReduce wear rateLeaf springsStructural engineeringSS - Stainless steel
Owner:湖北宇力汽车悬架弹簧股份有限公司
Method of Measuring Air Specific Heat Capacity Ratio by Vibration of Drum Surface Object
The invention discloses a method for measuring an air specific heat ratio via vibration of a drumhead object. The method comprises the following steps: covering a layer of elastic rubber at the opened end of a cylinder to form a drumhead, one end of which is opened, and fixedly adhering a sphere or a semisphere or an axially symmetric solid at the center of the drumhead, wherein the inner diameter of the cylinder is R, the inner height of the cylinder is h, the mass of the sphere or the semisphere is m and air is sealed in the cylinder; pressing the axially symmetric solid and then releasing, wherein the axially symmetric solid vibrates by suffering the elastic force of the elastic rubber of the drumhead and the elastic function of the air; obtaining the air specific heat ratio gamma which is equal to [(2pi / T)2-k / m]*3m*h / (piR2P), wherein k is the elastic coefficient of the rubber drumhead, the circumference to diameter ratio pi is equal to 3.14159, T is the period of vibration and P is the pressure of the external air. The method disclosed by the invention has the benefits that favorable elasticity is provided as the air is sealed, the experiment principle is more rigorous, a strict simple harmonic vibration is carried out, no rotation occurs, an inflation device is not required, the structure is simpler and the cost is lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method of Measuring Air Specific Heat Capacity Ratio by Vibration of Piston in Cylinder with Both Ends Sealed
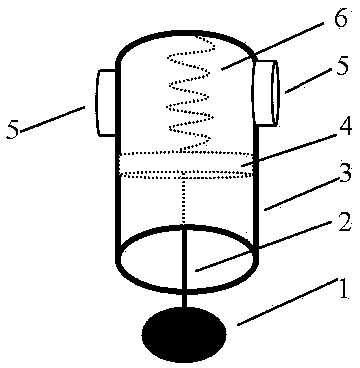
The method of measuring the specific heat ratio of air by piston vibration in a cylinder with both ends sealed. A transparent cylinder with both ends can be sealed. There are two cylinder center circles at the center of the outside of the cylinder, and a horizontal bubble on the outside to make the horizontal bubble Fix the cylinder horizontally on a bracket facing upwards; unscrew the sealing caps at both ends of the cylinder, and insert the piston body from one end of the cylinder. The piston body has a stainless steel connecting rod so that the center of the piston body coincides with the center of the cylinder. Then tighten the sealing caps at both ends, move the piston body for a certain distance through the electromagnet, and then turn off the power of the electromagnet, the piston body will vibrate under the elasticity of the sealed air, and the air specific heat ratio γ is γ=2πmL / (r 2 T 2 P), where pi = 3.14159; m is the mass of the piston body, L is the length of the air sealed on one side, r is the inner radius of the cylinder, T is the vibration period, and P is the external pressure. The beneficial effects are: the sealed air has good elasticity; the experimental principle is more rigorous; it is a strict simple harmonic vibration; the piston body does not appear to rotate; no pumping device is needed, the structure is simpler, and the cost is lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for Measuring Air Specific Heat Capacity Ratio by Piston Vibration in Single-End Sealed Vertical Cylinder
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Positioning device for tool bit holder of diamond tool bit welding rack
InactiveCN102079028BHigh strengthSuitable for high temperature heating environmentWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesTool bitEngineering
The invention provides a positioning device for a tool bit holder of a diamond tool bit welding rack, which belongs to the technical field of machinery and solves the problems of low tool bit welding efficiency and low quality of the conventional positioning device for the tool bit holder of the diamond tool bit welding rack. The positioning device for the tool bit holder of the diamond tool bit welding rack is arranged on a lifting mechanism of the tool bit holder of the diamond tool bit welding rack and used for positioning a tool bit, and comprises a front holding seat and a rear holding seat, wherein the front and rear holding seats are arranged opposite; the upper ends of the front and rear holding seats are provided with a protruded positioning block respectively; the upper ends of the front and rear holding seats are connected to the lifting mechanism; the two positioning blocks of the front and rear holding seats can clamp the two lateral surfaces of the tool bit; an extrusion seat fixedly connected to the lifting mechanism is arranged between the front and rear holding seats; a positioning structure with two sharp corners is arranged at the bottom end of the extrusion seat; and the two sharp corners can position the upper surface of the tool bit. The positioning device for the tool bit holder of the diamond tool bit welding rack has the advantages of high welding efficiency, high quality and long service life.
Owner:项大清
Vacuum cinerary casket
InactiveCN114259378AAvoid wrinkles, fromAvoid direct breakageEngine sealsUrnsEngineeringMaximum pressure
The vacuum type cinerary casket comprises a shell with a bottom and an air exhaust nozzle with a one-way valve, the shell and the air exhaust nozzle are integrally formed in a stamping mode, two outwards-sunken device tables are arranged at the symmetrical positions of the side wall of the shell, and an annular folded plate is fixedly arranged on the inner wall of the upper end of the shell; a soft airtight ring is arranged at the bottom of the annular folded plate between the annular folded plate and the shell in a contact mode, an air pressure cover is arranged on the inner wall of the upper end of the shell, and downward bent rings are fixedly arranged on the edges of the inner wall and the outer wall of the air pressure cover and connected between the annular folded plate and the shell through threads in a threaded mode. Threads used for keeping internal and external balance when the bending ring moves downwards are arranged on the contact faces of the annular folding plate, the shell and the bending ring. According to the vacuum cinerary casket, the problems that an upper end sealing device is directly pressed on a sealing ring under the maximum pressure before an existing vacuum cinerary casket is vacuumized, so that the sealing ring is overloaded, the sealing effect is poor, even the sealing ring is directly broken, and sealing fails are solved.
Owner:李晓红
Impact-resistant tensile power protection pipe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111987662AReduce frictionEasy insertion and removalElectrical apparatusEngineeringStructural engineering
The invention provides an impact-resistant tensile power protection pipe and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of power protection pipes. The power protection pipe comprises an outer sheath pipe, an inner sheath pipe and an inner smooth pipe which are sequentially arranged from outside to inside, the inner smooth pipe is used for fixing a power cable, abrasion-resistant protrusions are distributed between the inner sheath pipe and the inner smooth pipe in an annular array mode, inserting parts are distributed on the periphery of the inner smooth pipe in an annular array mode, and clamping parts matched with the inserting parts are distributed on the inner periphery of the outer sheath tube in an annular array mode. Friction force between the inner sheath pipeand the inner smooth pipe is increased, the phenomenon that the inner smooth pipe rotates when the power cable is installed is avoided, meanwhile, the inserting parts are clamped in the clamping parts, and the stability, impact resistance and tensile strength of the power cable in the mounting process are guaranteed.
Owner:NINGGUO MINGFU CABLE CO LTD
Automatic household fan assembling equipment
InactiveCN112936131AImprove stabilityStable clamping workWork holdersStructural engineeringElectric cooling fan
The invention relates to automatic household fan assembling equipment which comprises a bottom plate, a moving device, a clamping device, a positioning device and a jacking device. The moving device is installed at the left end of the bottom plate, the clamping device and the positioning device are installed on the moving device, and the jacking device is installed at the right end of the bottom plate. According to the automatic household fan assembling equipment, the following problems existing when an existing electric fan base plate and an electric fan base supporting rod are assembled can be solved, firstly, when the traditional electric fan base plate and the electric fan base supporting rod are assembled, an electric fan base needs to be manually clamped and positioned through tools, then a tool is used for rotating an electric fan threaded rod into the electric fan base supporting rod, and the manual assembly efficiency is low; and secondly, when an existing electric fan is assembled, the electric fan base plate and the electric fan base supporting rod cannot be stably clamped, consequently the electric fan base supporting rod and the electric fan base plate rotate when being assembled, and the assembling efficiency of the electric fan is influenced.
Owner:伍晓明
Conveying method for main drive of shield machine in narrow and small space
The invention relates to the technical field of shield construction device structures, in particular to a conveying method for a main drive of a shield machine in a narrow and small space. Guide railsare laid in a tunnel; a support platform is arranged on the guide rails; the main drive is hoisted and conveyed to the support platform and is fixed onto the support platform; and the support platform is dragged to move along the guide rails until the main drive is moved to the truck loading position outside the tunnel. The conveying method has the advantages that the main drive is convenient toinstall, the operation is convenient, the safety is high, materials are easily available, the cost is low, and the difficulty and the working hour of hoisting and conveying are respectively lowered and shortened, and the conveying method has very great promotion value.
Owner:中交(广州)建设有限公司
a kind of tubing
ActiveCN104632092BNo turning phenomenonPrevent rotationDrilling rodsDrilling casingsPetroleum engineering
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Numerical control precise four-stage rolling mill for ore screen machining
PendingCN114042751AReduce speedRotation does not affectMetal rolling arrangementsNumerical controlRatchet
The invention relates to the technical field of ore screen machining, in particular to a numerical control precise four-stage rolling mill for ore screen machining, which comprises a track, a wire releasing frame and an electric control cabinet, the wire releasing frame, a first-stage rolling mill, a second-stage rolling mill, a third-stage rolling mill and a fourth-stage rolling mill are sequentially mounted at the upper end of the track from left to right, and a rotating shaft is mounted at the upper end of the wire releasing frame through a bearing seat. A plurality of round rods are fixed to the outer wall of the rotating shaft, overspeed prevention assemblies are installed at the outer ends of the round rods correspondingly, a rotating disc is fixed to the top end of the rotating shaft, a ratchet ring is fixed to the outer wall of the rotating disc, a fixed shaft is fixed to the upper end of the rotating disc, a circular ring block is further fixed to the upper surface of the wire releasing frame, and a plurality of pawls are hinged to the inner wall of the periphery of the circular ring block. The back faces of the pawls abut against leaf springs. The raw material metal wire can stably enter the rolling mill, and normal wire discharging is ensured; and the rotating disc can only rotate in one direction, and the rotation phenomenon is avoided.
Owner:安徽屹翔滤材有限公司
Winding drum conveying and cutting production line
The invention provides a winding drum conveying and cutting production line which comprises a cutting machine, a main guide rail, a conveyor belt, an auxiliary conveying belt, a housing, a fixed rod,a bracket, a first guide rail, a second guide rail, a first auxiliary conveying belt, a second auxiliary conveying belt, a first belt wheel, a second belt wheel, a guide belt wheel, a third guide railand a fourth guide rail. The cutting machine comprises a machine shell and a cutting knife, and the axial direction of a cutting knife shaft is the X-axis direction; the main guide rail comprises a first main guide rail body, a second main guide rail body and an isolation plate, a rotating shaft is arranged over the isolation plate, and a guide plate is fixedly installed on the rotating shaft inthe radial direction; and the conveying belt is fixedly provided with a push plate, and the push plate penetrates from the position below the main guide rail to the position above the main guide railthrough an interval between two arc-shaped guide rails which are symmetrically arranged in parallel. Manual feeding only needs to be conducted on the auxiliary conveying belts, the efficiency is improved, and automatic production is achieved.
Owner:旭耀新材料(淮安)科技有限公司
Method for measuring air specific heat ratio by piston vibration in single-ended sealed horizontal cylinder
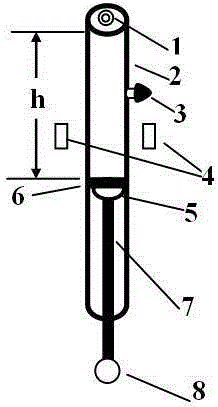
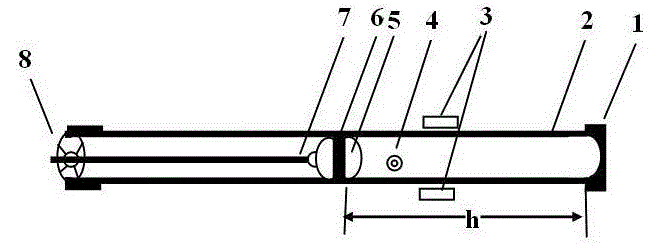
A method for measuring air specific heat ratio by piston vibration in a single-ended sealed horizontal cylinder is disclosed. One end of a transparent cylinder is sealed, and the other end of the transparent cylinder is sleeved with a mesh cap. The mesh cap has a central circular hole. a millimeter calibrated scale and a horizontal bubble are arranged on the outer surface of the cylinder. A piston is arranged inside the cylinder, and two sides of the piston are respectively fixed with a hemisphere. The center of the outer surface of each hemisphere outside the piston is connected with one end of a pull rod, and the other end of the pull rod is inserted into the central circular hole of the mesh cap. A sealing cap of the cylinder is opened, and the pull rod is pushed to push the piston into some position inside the cylinder. Then, the sealing cap is tightly screwed to seal one end of the cylinder, the cylinder is horizontally fixed on a horizontal support frame, and the pull rod is pulled outwards. When the pull rod is released, the piston is vibrated under elastic action of sealed air. Air specific heat ratio gamma is 4 Pi mh / (r<2>T<2>P). The invention has beneficial effects as follows: sealed air has good elasticity; experiment principle is more rigorous; the method is a strict simple harmonic vibration; present technical rotary movement will not happen; an inflation unit is not required; the structure is simpler; and costs are lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method of Measuring Air Specific Heat Capacity Ratio by Piston Vibration in One-End Sealed Cylinder
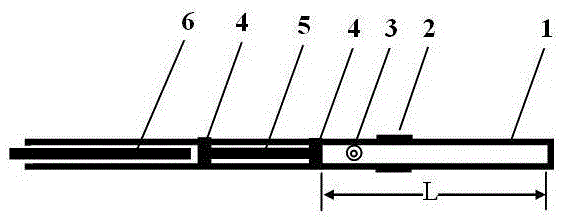
The method of measuring air specific heat ratio by piston vibration in a sealed cylinder at one end. A transparent cylinder with an inner radius r is placed horizontally and divided into two sections. One section is a hollow cylinder with a bottom seal, and the other section is a hollow circular tube. Threaded sealing connection; the outer surface of the cylinder has a millimeter scale and a horizontal bubble along the length direction; the piston body is composed of two pistons and a stainless steel connecting rod; after the threaded connection of the cylinder is unscrewed, the hollow circle of the cylinder The pipe end is inserted into the piston body, and then the cylinder is sealed by threads, and a magnet is inserted into the hollow pipe end of the cylinder. The magnetic field attracts the stainless steel connecting rod and pulls the piston body to move. The piston body will break away from the magnet, and the piston body will vibrate. ; Air specific heat capacity ratio γ is γ=4πmL / (r 2 T 2 P), where m is the mass of the piston body, L is the length of the sealed air at the equilibrium position, r is the inner radius of the cylinder, T is the vibration period, and P is the atmospheric pressure value of the outside air. The beneficial effect is that the sealed air has good elasticity; the experimental principle is more rigorous; it is a strict simple harmonic vibration; the vibration starting method is simple and easy; the structure is simpler and the cost is lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com