Method and system for diagnosing fault of clutch control failure
A technology for clutch control and fault diagnosis, applied in transmission control, components with teeth, belts/chains/gears, etc., can solve problems such as inability to determine or accurately determine whether one or two solenoid valves are faulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
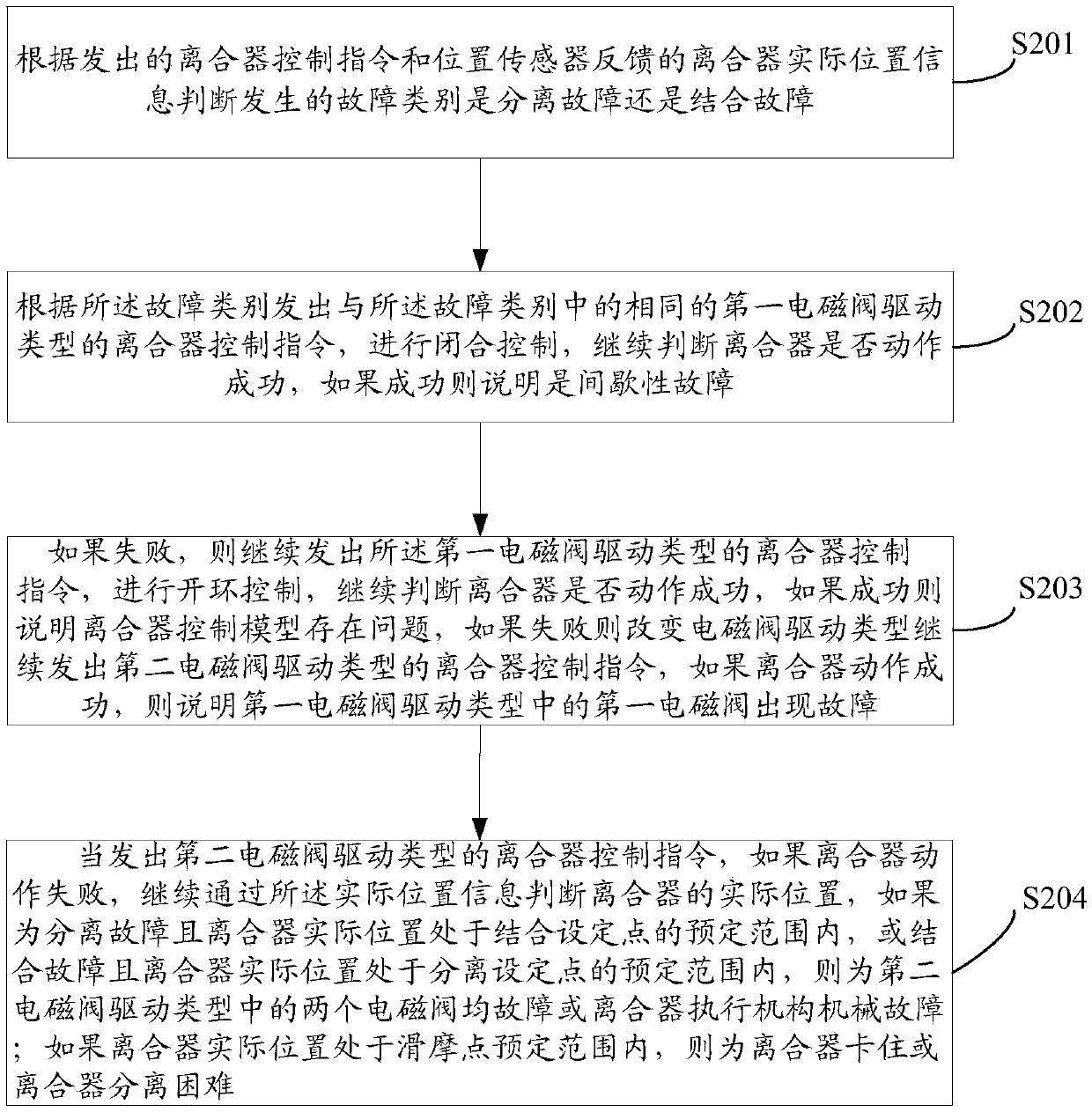
[0061] see figure 1 , which is a flow chart of Embodiment 1 of the fault diagnosis method for clutch control failure provided by the present invention.
[0062] This embodiment provides a fault diagnosis method for clutch control failure, including the following steps:
[0063] S101: According to the issued clutch control command and the actual position information of the clutch fed back by the position sensor, it is judged whether the type of fault occurred is a separation fault or a coupling fault;
[0064] Firstly, when controlling the action of the clutch, an action control command will be sent to the clutch, for example, it can be a separation and closing control command driven by a slow split valve. However, the clutch may break down and the control command is not executed. In this way, the actual position information of the clutch fed back by the position sensor can be used to judge whether the clutch is broken down. Moreover, the type of fault in the clutch can be ju...
Embodiment 2
[0074] see figure 2 , which is a flow chart of Embodiment 2 of the fault diagnosis method for clutch control failure provided by the present invention.
[0075] The difference between method embodiment two and method embodiment one is that the following steps are added:
[0076] S204: When the clutch control command of the second electromagnetic valve driving type is issued, if the clutch action fails, continue to judge the actual position of the clutch through the actual position information, if it is a separation failure and the actual position of the clutch is within the predetermined range of the engagement set point , or combined failure and the actual position of the clutch is within the predetermined range of the disengagement set point, then both solenoid valves in the second solenoid valve drive type are faulty or the clutch actuator is mechanically faulty; if the actual clutch position is at the predetermined slip point If it is within the range, the clutch is stuc...
Embodiment 3
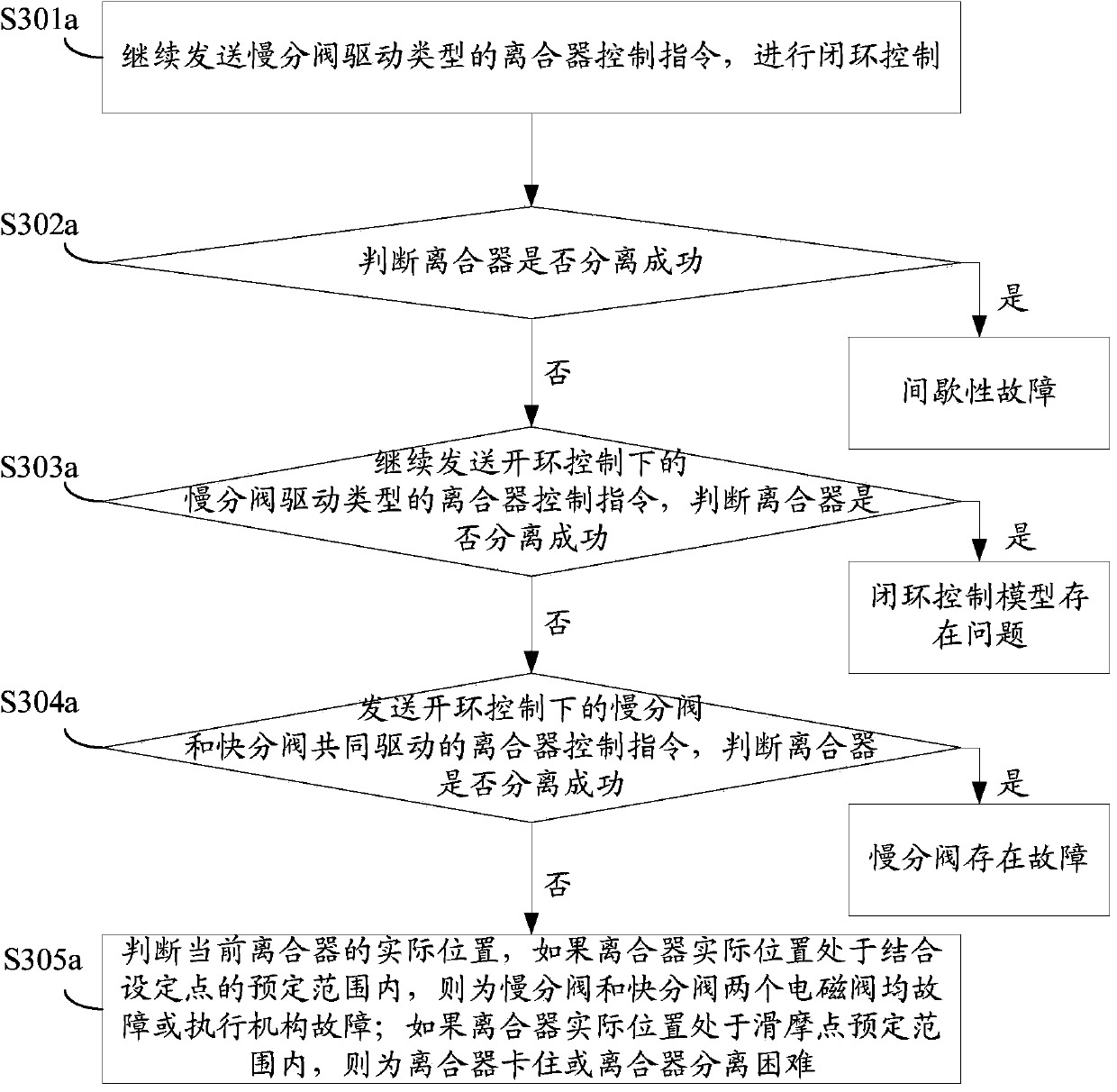
[0088] see Figure 3a , which is a flow chart of Embodiment 3 of the fault diagnosis method for clutch control failure provided by the present invention.
[0089] In this embodiment, the independent drive of the slow branch valve is taken as an example for introduction.
[0090] S301a: continue to send the clutch control command of the slow valve drive type to perform closed-loop control;
[0091] S302a: Judging whether the clutch disengagement is successful, if successful, it means an intermittent fault; if it fails, execute S303a;
[0092] S303a: continue to send the clutch control command of the slow opening valve drive type under open-loop control, and judge whether the clutch is separated successfully. If successful, it means that there is a problem with the closed-loop control model; if it fails, execute S304a;
[0093] S304a: Send a clutch control command jointly driven by the slow opening valve and the fast opening valve under open-loop control, and judge whether the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com