Cathode active material, method of preparing the cathode material, cathode, and lithium secondary battery including the same
A positive electrode active material and secondary particle technology, applied in secondary batteries, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as low mixing density, stability problems, and low capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
[0141] Preparation Example 1: Preparation of Positive Active Material
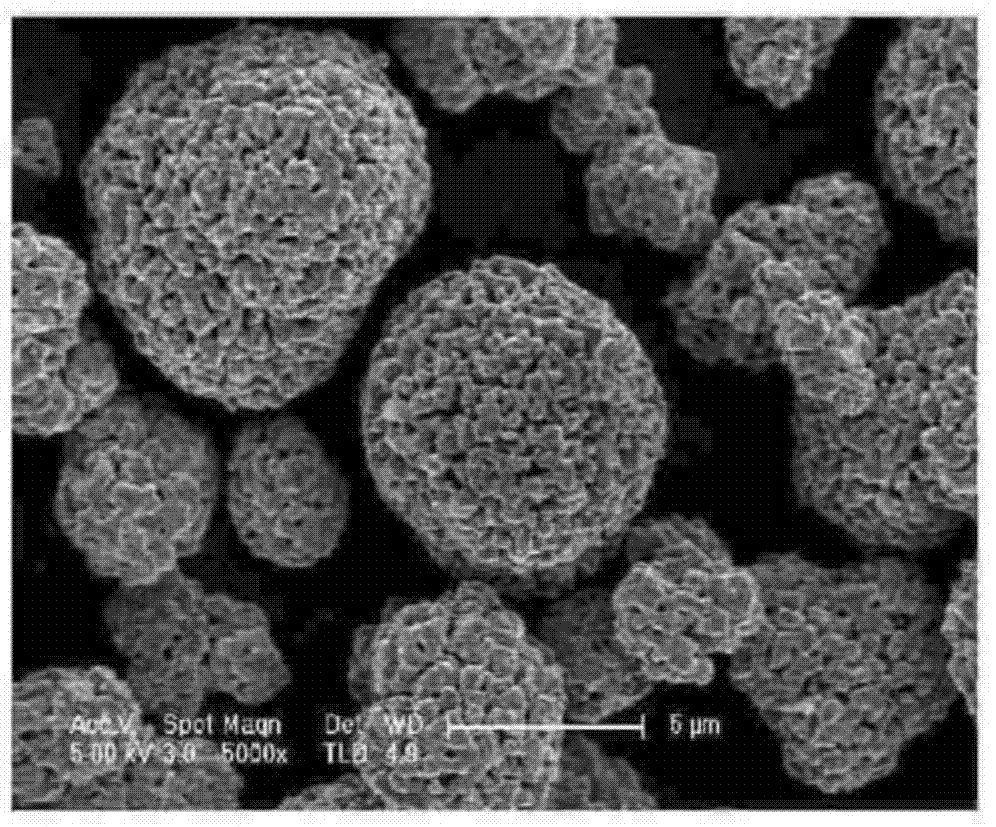
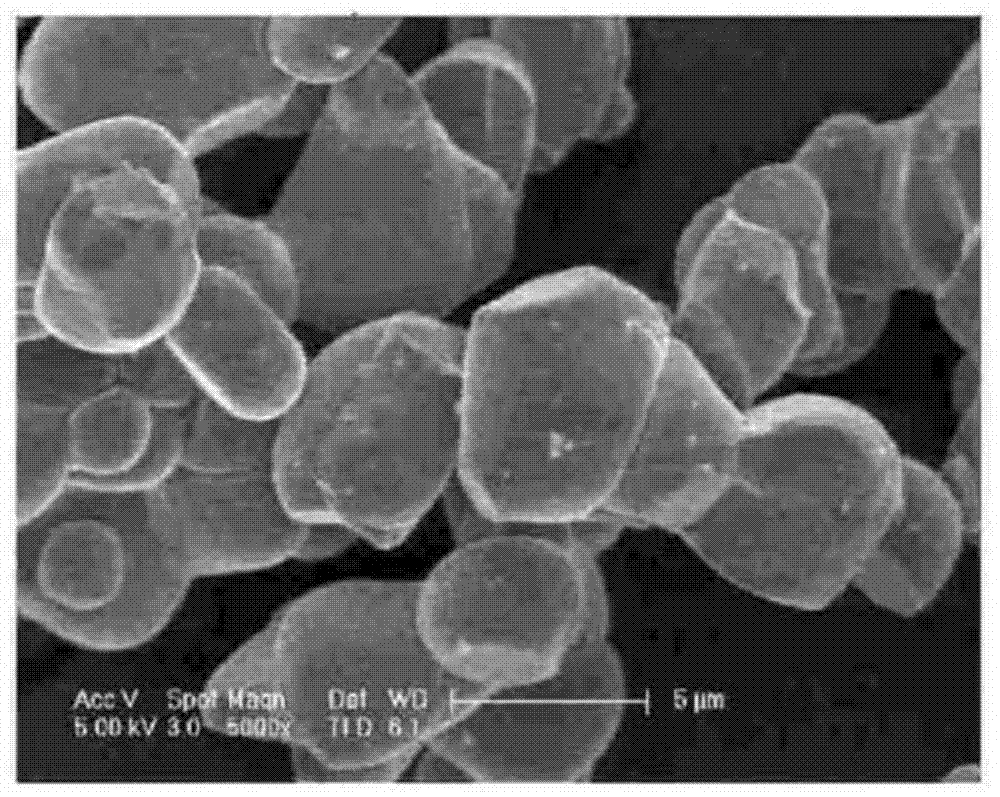
[0142] NiSO as nickel precursor 4 , CoSO as cobalt precursor 4 and MnSO as manganese precursor 4 Mixed together in water at a molar ratio of 0.5:0.2:0.3 to prepare an aqueous NiCoMn(NCM) hydroxide precursor solution. While stirring the aqueous solution, an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was slowly added thereto. The reaction mixture was then stirred for 5 hours, and NCM hydroxide (Ni 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 (OH) 2 )precipitation. The resultant was filtered and then washed to obtain a precipitate. The precipitate was dried at a temperature of 80° C. in an air atmosphere to obtain Ni formed of small particles having an average particle diameter of 6 μm 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 (OH) 2 powder.
[0143] will Ni 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 (OH) 2 The powder was heat-treated at a temperature of 600° C. for 1 hour in an air atmosphere to remove moisture. Then, a nickel transition metal oxide formed in a shape that e...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0148] Preparation Example 2: Preparation of Positive Active Material
[0149] The positive active material was prepared in the same manner as in Preparation Example 1, except that the mixture was stirred for 9.5 hours to obtain Ni 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 (OH) 2 , obtaining Ni formed from large particles with an average particle size of 15 μm 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 (OH) 2 Powder instead of Ni formed of small particles with an average particle size of 6 μm 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 (OH) 2 , and the secondary particles of the positive electrode active material are large particles having an average particle diameter of 15 μm instead of small particles having an average particle diameter of 6 μm.
preparation Embodiment 3
[0150] Preparation Example 3: Preparation of Positive Active Material
[0151] The positive electrode active materials of Preparation Examples 1 and 2 were mixed in a weight ratio of 20:80. Then, positive electrode active material Li formed by primary particles having an average particle diameter of 4 μm and secondary particles including small particles having an average particle diameter of 6 μm and large particles having an average particle diameter of 15 μm was obtained. 1.05 [Ni 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 ]O 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com