Road network traffic flow analytical method based on RFID technology
An analysis method and traffic flow technology, applied in the field of dynamic OD matrix acquisition, can solve problems such as inability to obtain OD matrix, large manpower and material resources, and complex algorithms, and achieve the effects of strong operability, convenient modification, and strong scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The present invention will be further described in conjunction with embodiment and accompanying drawing now.
[0023] The embodiment is only the preferred implementation of the present invention, it should be pointed out that for those of ordinary skill in the art, without departing from the principle of the present invention, some improvements and equivalent replacements can also be made, these are the claims of the present invention The technical solutions after improvement and equivalent replacement all fall into the protection scope of the present invention.
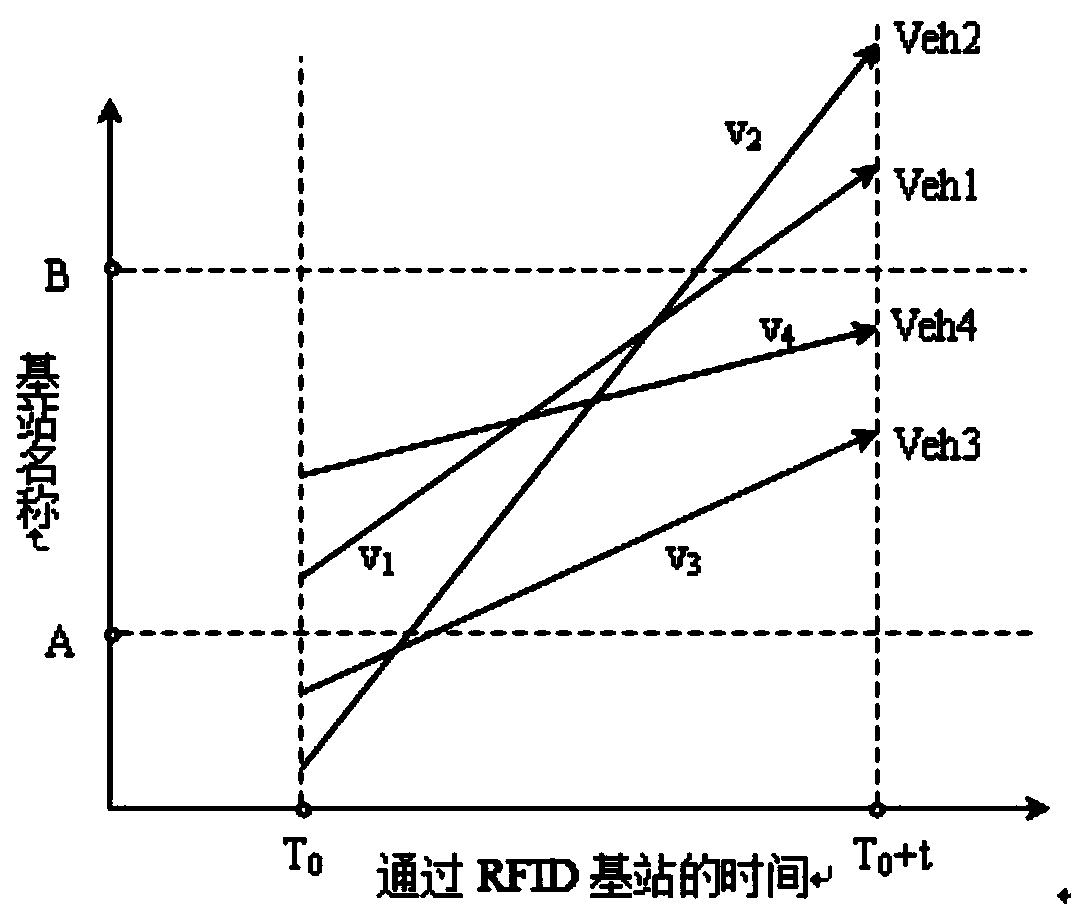
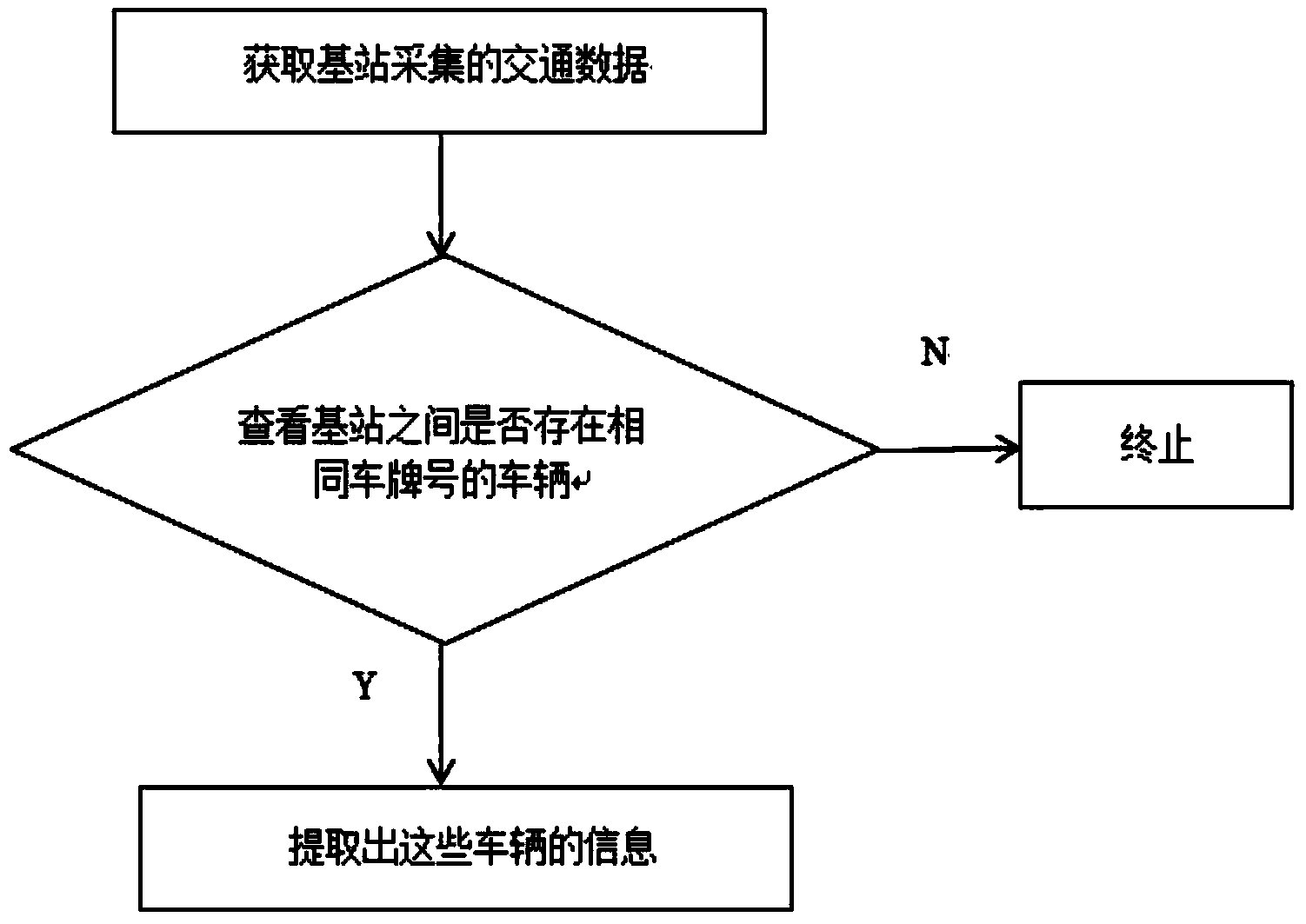
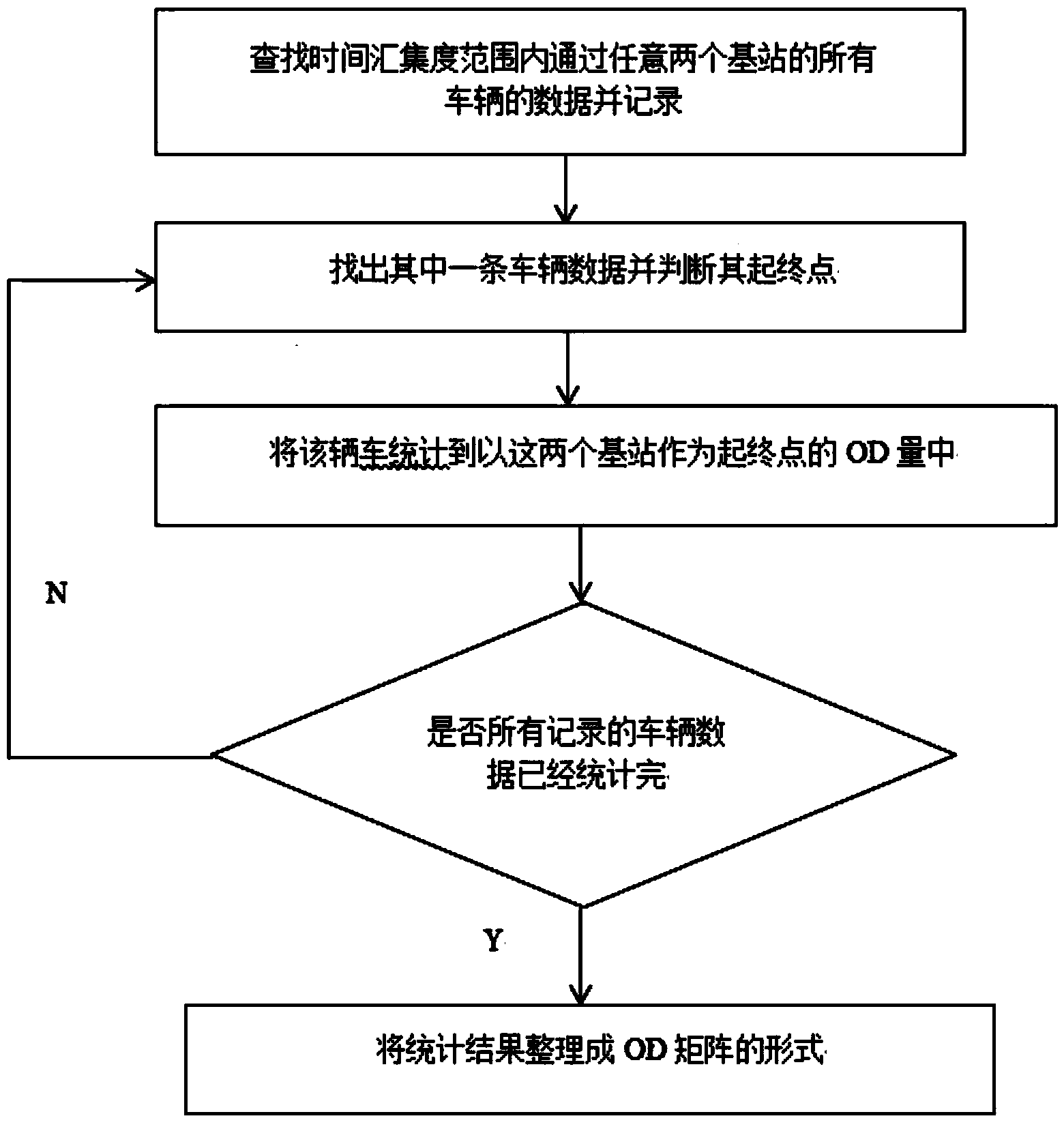
[0024] The purpose of the RFID technology-based road network traffic information flow analysis method of the present invention is to obtain a dynamic OD matrix by processing the vehicle information collected by the RFID base station, and then analyze the road network traffic flow. The method is mainly divided into three steps: firstly, obtain the information of vehicles with the same license plate number in di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com