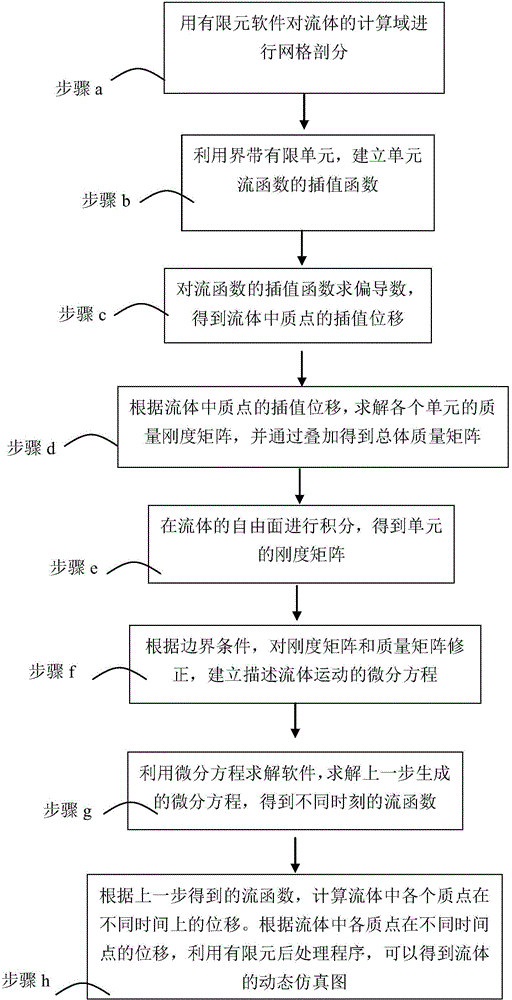
Fluid simulation method based on inter-belt finite element and Lagrange coordinate
A fluid simulation, finite element technology, used in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0054] Specific Embodiment 1: This embodiment is used to analyze the motion simulation problem of nonlinear incompressible fluid.
[0055] (a) Divide the computational domain Ω of the fluid into N e units, each unit is Ω i ;
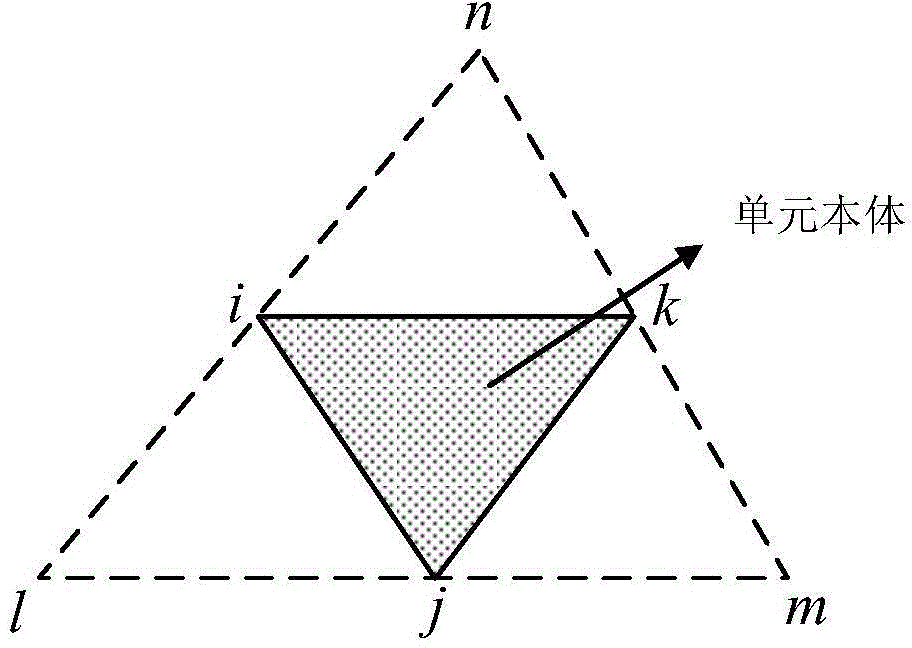
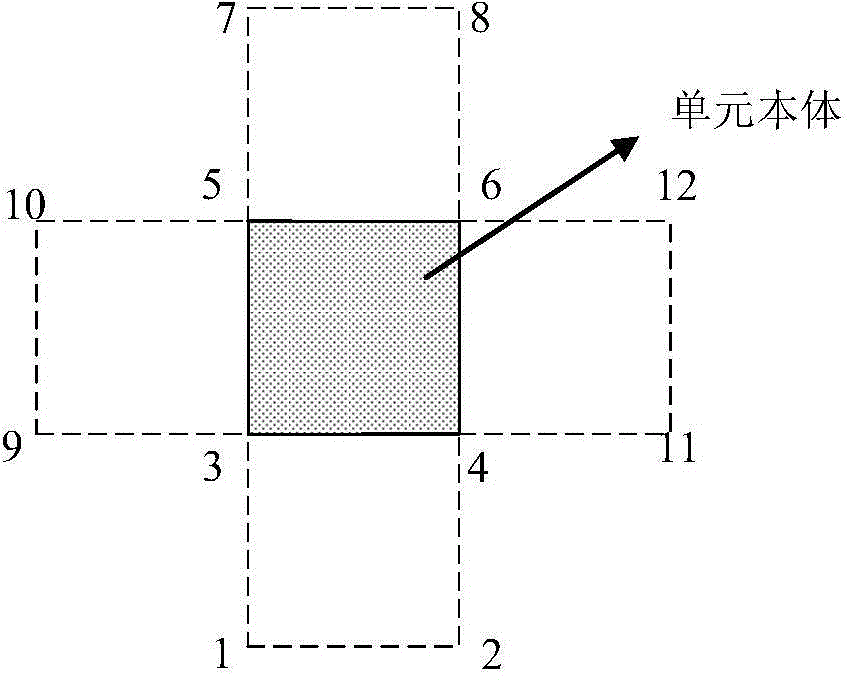
[0056] (b) in unit Ω i The interpolation field of the flow function ψ(x,y) is established on the above. in unit Ω i is the body, the unit Ω i The surrounding units are regarded as the boundary zone of the unit, and the nodes of these units are interpolated together to construct the unit Ω i The interpolation function above, the specific format of the interpolation function is:
[0057] ψ(x,y)=N T ψ i ,N T =p T (x,y)P -1
[0058] in
[0059] p T (x,y)=(1,x,y,x 2 ,xy,y 2 ,…)
[0060] P T =[p(x 1 ,y 1 ),p(x 2 ,y 2 ),…,p(x N ,y N )]
[0061] ψ T =(ψ(x 1 ,y 1 ),ψ(x 2 ,y 2 ),…,ψ(x N ,y N ))
[0062] N T is the shape function vector. (x j ,y j ) is the node coordinates of the boundary zone unit, a total of N, including the u...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0087] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is used for the simulation analysis of linear incompressible fluids. The difference from Embodiment 1 lies in step (e). At this time, the nonlinear stiffness matrix part is not considered, and a linear dynamic differential equation can be obtained. At this time, the differential equation solving software is used to solve the linear differential equation, and the flow function of each particle at different moments in the linear case can be obtained, and the rest of the steps are the same.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0088] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is used to analyze the vibration modes of incompressible fluids. The difference from Embodiments 1 and 2 lies in steps (e), (f), (g) and (h), which are not considered at this time. In the nonlinear stiffness matrix part, the eigenvalue problem is obtained:
[0089] K l ψ=ω 2 Mψ
[0090] where ω is the vibration frequency of the fluid. To solve the eigenvalue equation, existing software can be used, such as SIPESC software developed by Dalian University of Technology. According to the flow function mode ψ and the displacement expression given in step (c) in the first embodiment, the displacement of each particle in the fluid is obtained. Using the finite element post-processing program (such as SIPESC.POST, Jifex and other software developed by Dalian University of Technology), the vibration mode of the fluid can be obtained.
[0091] Simulation example: using the method of the present invention, the propagation of solitary waves in a c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com