Non-volatile semiconductor storage device
A storage device, non-volatile technology, applied in semiconductor devices, information storage, read-only memory, etc., can solve the problem that data cannot be written
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
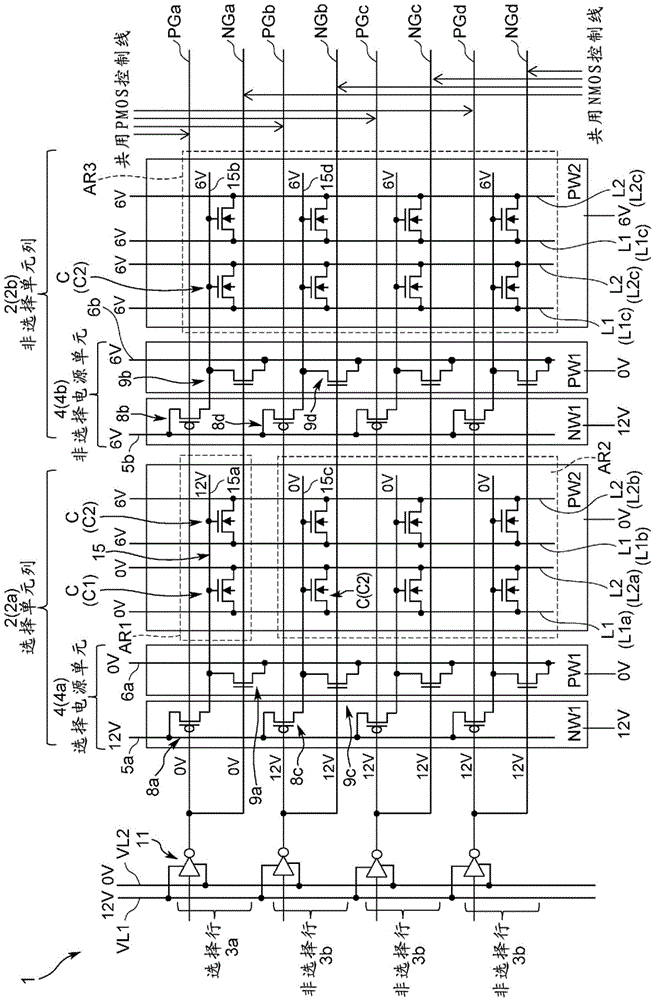
[0077] (1-1) Overall structure of nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
[0078] in with Figure 13 Corresponding parts are denoted by the same symbols figure 1 Here, 1 represents the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of the present invention, which has a structure in which a plurality of cell columns 2 of the same structure are arranged in a row direction (left-right direction). Here, the structures of the plurality of cell columns 2 are the same, so the following description will focus on the cell column 2 of the first column. At this time, an N-type slot NW1, a P-type slot PW1, and a P-type storage slot PW2 are sequentially arranged on the cell column 2, and a power supply unit 4 is formed on the N-type slot NW1 and the P-type slot PW1. A plurality of memory cells C are formed in a matrix on the memory groove PW2.
[0079] In the power supply unit 4, a first power supply line 5a extending in the column direction (vertical direction) is formed on the N-type groove...
no. 2 approach
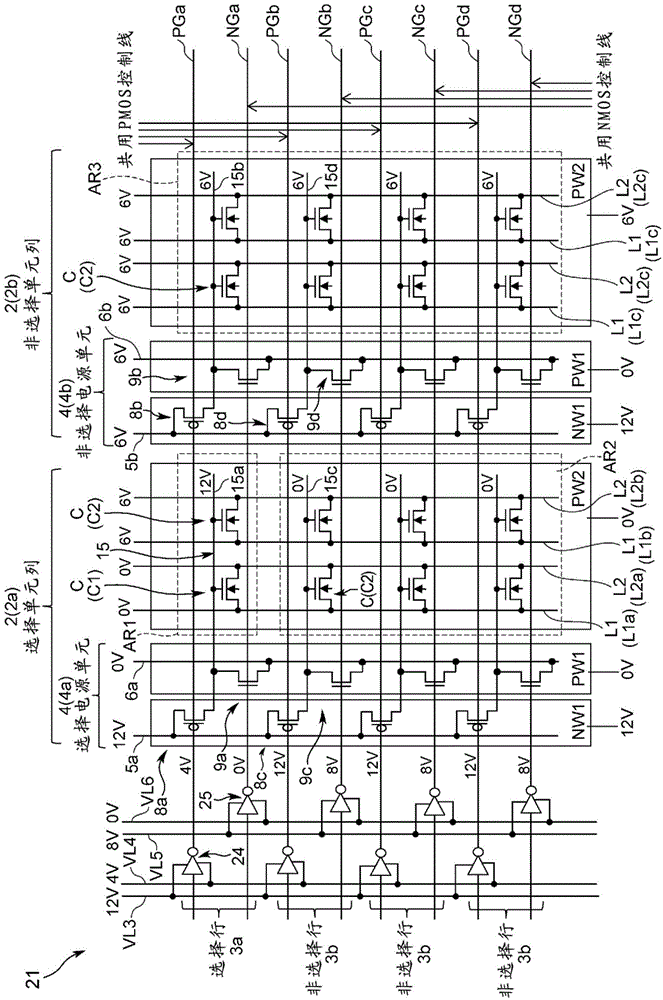
[0124] (2-1) Data writing operation
[0125] in the same figure 1 Corresponding parts are denoted by the same symbols figure 2 Among them, 21 represents the nonvolatile semiconductor storage device of the second embodiment. The difference between the second embodiment and the nonvolatile semiconductor storage device 1 of the first embodiment is that the nonvolatile semiconductor storage device 1 of the second embodiment Replacement in storage figure 1 The first MOS power line VL1 and the second MOS power line VL2 are provided with a first PMOS power line VL3, a second PMOS power line VL4, a first NMOS power line VL5, and a second NMOS power line VL6. Actually, the nonvolatile semiconductor storage device 21 has the following structure: the first PMOS power line VL3 and the second PMOS power line VL4 are extended in the column direction, parallel to the first PMOS power line VL3 and the second PMOS power line VL4 Likewise, the first NMOS power line VL5 and the second NMOS...
no. 3 approach
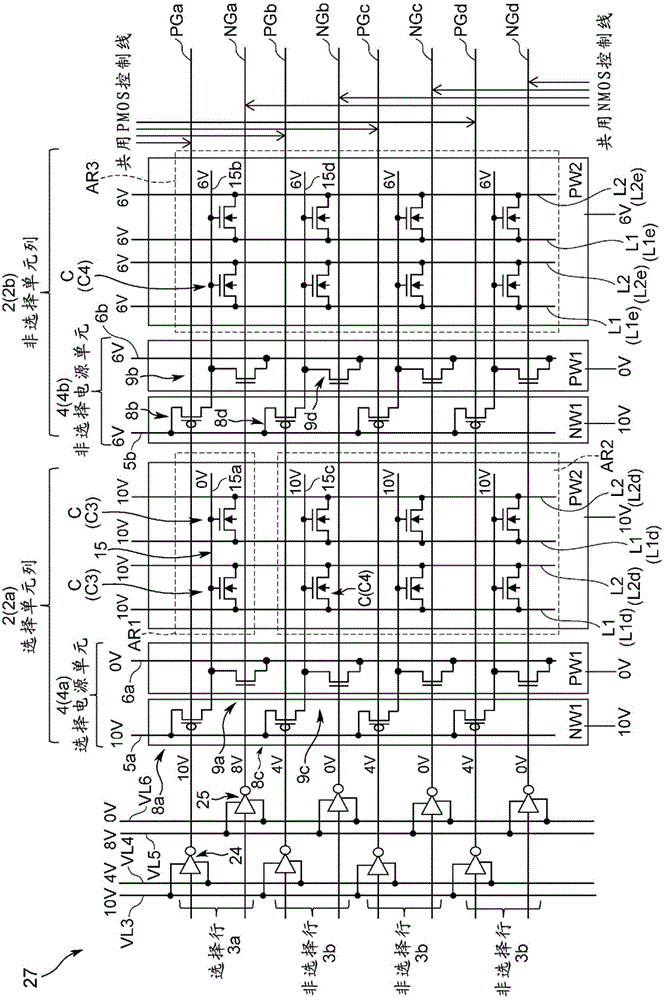
[0179] (3-1) Data writing operation
[0180] in with figure 2 Corresponding parts are denoted by the same symbols Figure 4 Among them, 31 denotes a nonvolatile semiconductor storage device according to the third embodiment. The difference between this nonvolatile semiconductor storage device 31 and the above-mentioned nonvolatile semiconductor storage device 21 according to the second embodiment is that not only PMOS switches 8a, 8c, ... (8b, 8d, ...) and NMOS switches 9a, 9c, ... (9b, 9d, ...), and also auxiliary NMOS switches 36a, 36c, ... (36b, 36d, ...) are provided on each power supply unit 34, and when data is written, in the non-selected cell column 32b, 0V is applied to each non-selected word line 15b, 15d, ... through the auxiliary NMOS switches 36b, 36d, ... Disable gate voltage.
[0181] Also, in the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device 31 according to the third embodiment, since it has such a structure, it is possible to turn on and off the PMOS switches 8a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com