Apparatus and method for measuring parameters of transient plasmas in high-speed impact
An ultra-high-speed impact and plasma technology, applied in the aerospace field, can solve the problems of difficult to accurately design microwave and laser transmission paths, difficult to meet the plasma parameter measurement, low plasma energy, etc., to achieve perfect shielding design, good time The effect of distinguishing characteristics and accurate measurement results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be further described now in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
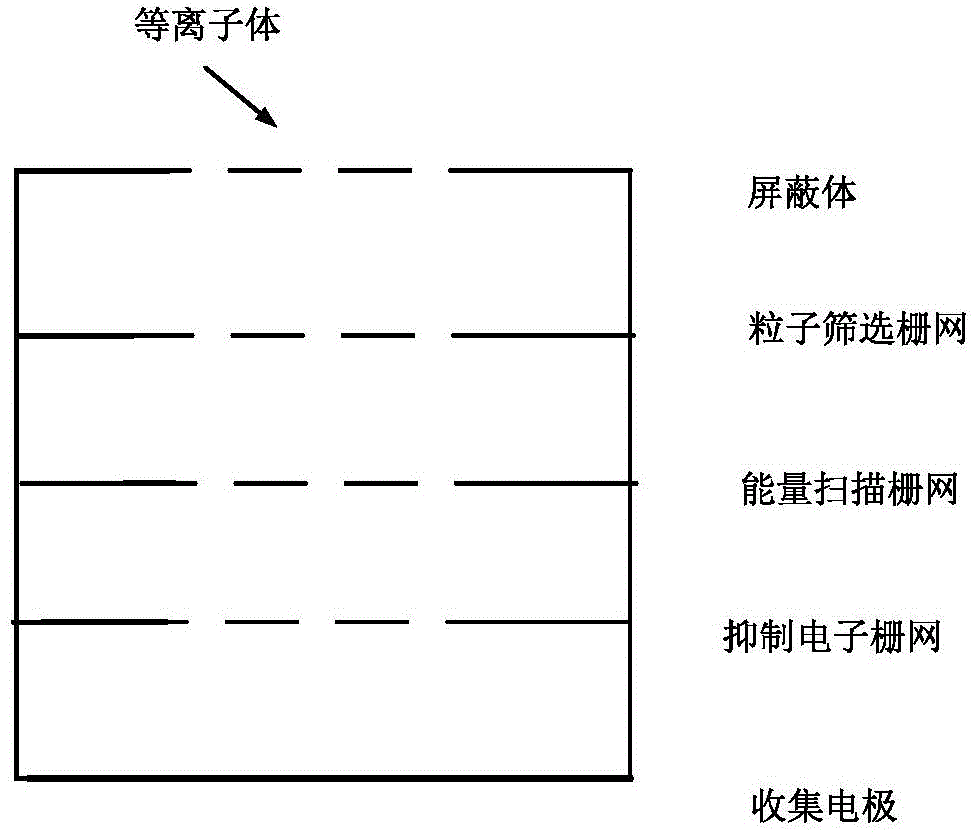
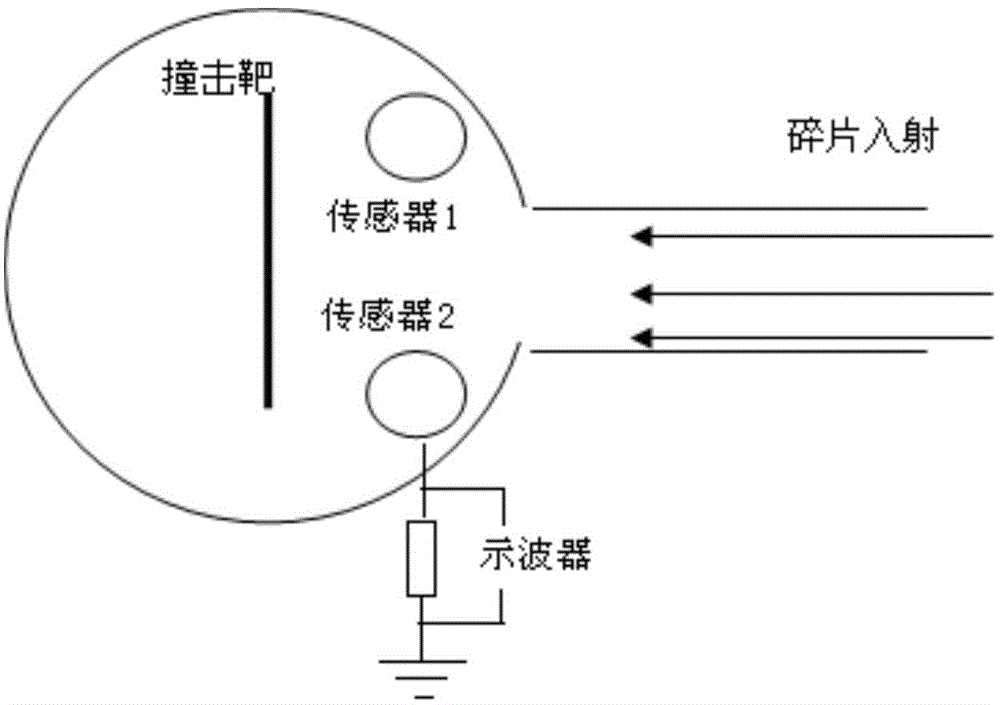
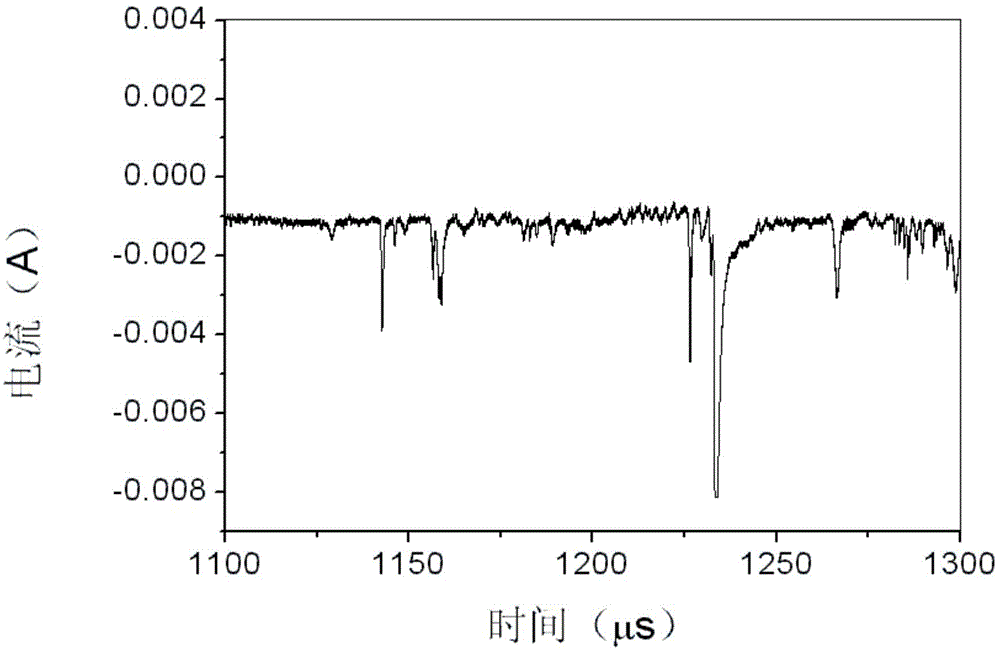
[0041] The device of the present invention for measuring transient plasma parameters in space debris ultra-high-speed impacts includes a multilayer grid sensor, a power supply and an oscilloscope; wherein, the power supply provides electrical energy for the multilayer grid sensor and the oscilloscope, and the The multi-layer grid sensor uses the charged grid to analyze the plasma energy formed by the impact of space debris, thereby obtaining parameters including plasma density, energy, and diffusion speed; the obtained results are displayed on the oscilloscope.
[0042] exist figure 1 The structure of the multi-layer grid sensor is further described in . As shown in the figure, the sensor includes in order from top to bottom: a shield, a particle screening grid, an energy scanning grid, an electron suppression grid, and a collecting electrode; the shield is used to shield the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com