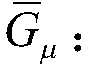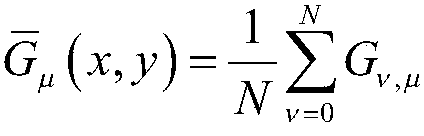A computerized automatic grading method for degeneration of intervertebral disc images
A degenerative and automatic grading technology, applied in the field of clinical medicine, can solve the problems that doctors are prone to errors in grading degenerative changes, and there is no quantitative grading standard.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] As shown in the figure, the degeneration computer automatic grading method of a kind of intervertebral disc image provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0051] S1: Obtain an image of the intervertebral disc, and obtain a sample image through image preprocessing;
[0052] S2: Extract the intervertebral disc position from the intervertebral disc image to obtain an oval intervertebral disc area;
[0053] S3: Calculating the gray ratio of the nucleus pulposus and the annulus fibrosus in the oval intervertebral disc region;
[0054] S4: Grading the degeneration of the intervertebral disc image according to the gray ratio.
[0055] The oval intervertebral disc area is formed in the following steps:
[0056] S21: Obtain the rectangular area of each intervertebral disc through a positioning algorithm;
[0057] S22: Process the intervertebral disc image with a Gabor filter to obtain filter images of different frequencies;
[0058] S23: Calculate...
Embodiment 2
[0081] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is only:
[0082] figure 2 In (2a) segmented intervertebral disc region based on positioning results; (2b) intervertebral disc boundary determined by Gabor features; (2c) edge point detection; (2d) ellipse fitting; image 3 (3a) Negative values in the Gabor coefficient graph are set to zero; (3b) G(n); (3c) spine extraction results; Figure 4 (4a) intervertebral disc characteristics; (4b) G h (n) Curve; (4c) Intervertebral disc boundary determined by Gabor features; (4d) Comparison of positioning results before and after algorithm improvement; Figure 8 (8a) Level 2; (8b) Level 3; (8c) Level 4; (8d) Level 5;
[0083] The Gabor wavelet transform used in this embodiment is a windowed Fourier transform; in the spatial domain, the impulse response of the two-dimensional Gabor filter is the result obtained by multiplying the complex exponential oscillatory function by the Gaussian envelope function:
[0084]
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com