Ultra-low frequency pendulum tuned mass damper and its realization method
A technology for tuning mass damping and implementation methods, which can be applied to building components, earthquake resistance, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to apply pendulum TMD, difficulty in quantitative adjustment, and large installation space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
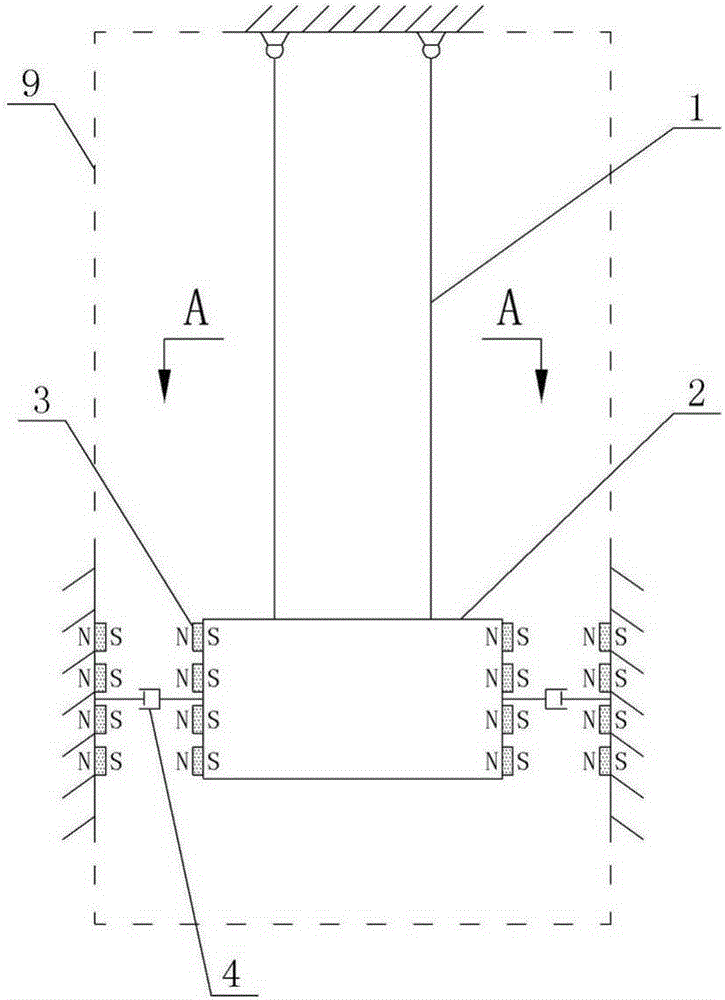
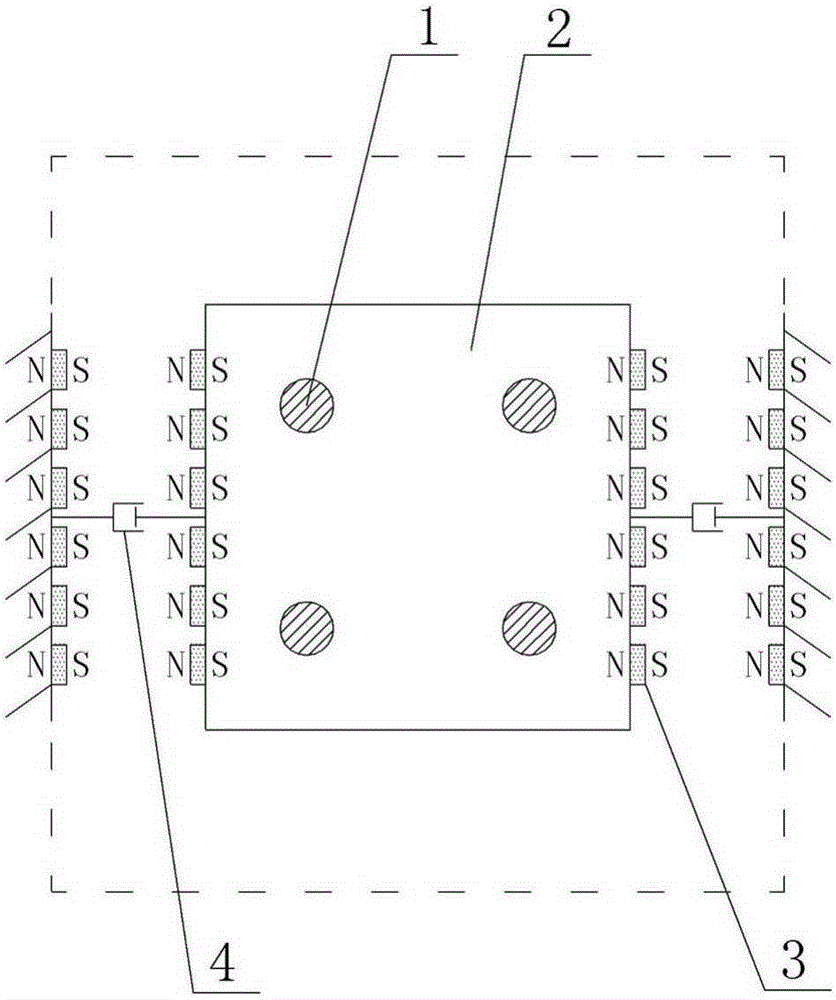
[0050] Embodiment one: see figure 1 , an ultra-low frequency pendulum tuned mass damper, comprising a pendulum chamber 9 arranged in a structure, a sling 1 connected to the structure at the top of the pendulum chamber 9, a quality block 2 suspended at the lower end of the sling 1, and The viscous damper 4 and the negative stiffness adjustment device between the mass block 2 and the structure, the number of the viscous damper 4 and the negative stiffness adjustment device are two and are on both sides corresponding to the mass block 2 Arranged symmetrically, the negative stiffness adjustment device includes n pieces of permanent magnets 3 arranged on one side of the mass block 2 with a polarity of N pole / S pole, and n pieces of poles arranged on the corresponding structure of the side The permanent magnet 3 is S pole / N pole, and the permanent magnets 3 on both sides of the mass block 2 are cylindrical permanent magnets.
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a realization method of the ultra-low frequency pendulum-type tuned mass damper described in Embodiment 1.
[0052] At first the working principle of the present invention is set forth:
[0053] (1) by Figure 1-Figure 3 As shown, when the structure is stationary, the negative stiffness adjustment devices on the left and right sides of the mass block of the tuned mass damper balance each other, and the mass block is in a balanced state;
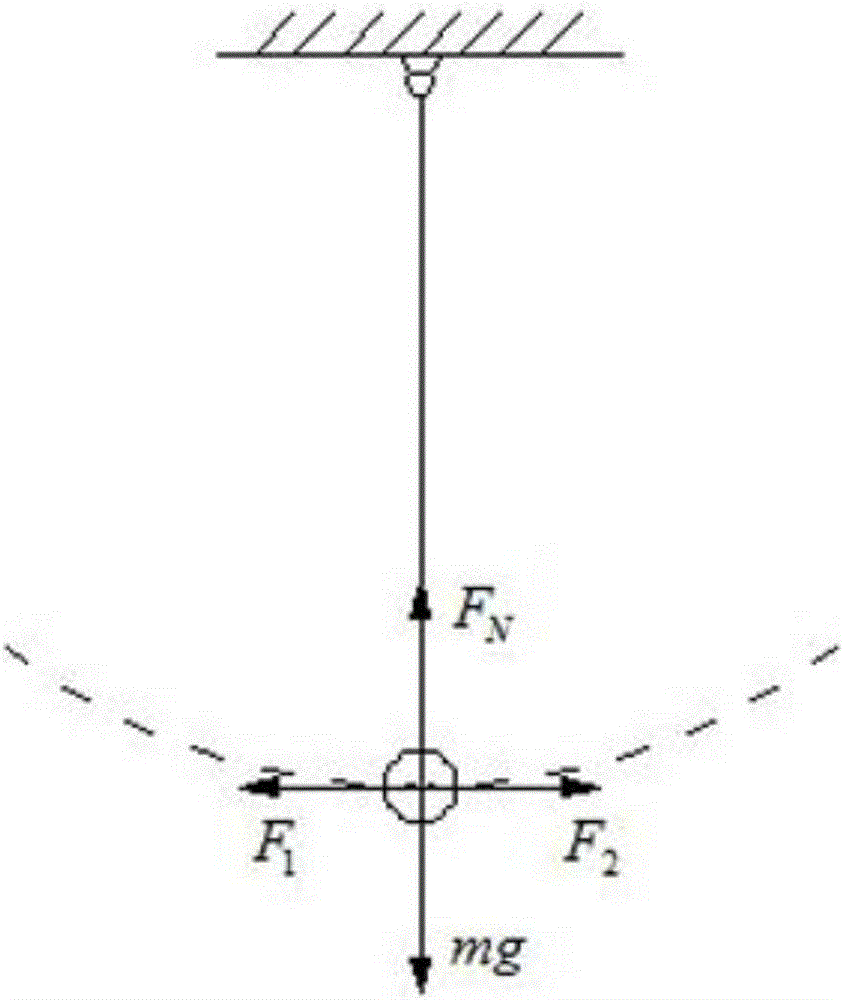
[0054] (2) When the structure vibrates, the pendulum of the tuned mass damper also swings accordingly, as Figure 4 As shown, when the pendulum swings to the left at an angle θ (θ1 ≥F 2 , the differential equation of motion mlθ″+p(θ)=0, p(θ) is the restoring force dependent on the swing angle θ:
[0055] p(θ)=mgsinθ-(F 1 cosθ-F 2 cosθ)
[0056] Because the angle θ is very small (within 5 degrees), approximately taking sinθ≈θ and cosθ≈1, we can get:
[0057] p(θ)≈mgθ-(F 1 -F 2 )①
[0058] in
...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Embodiment Three: Taking the wind-induced vibration damping design of Taiwan 101 Building as an example, the structure and design method of the present invention are adopted: the specific parameters of the pendulum-type tuned mass damper designed for wind-induced vibration damping of Taiwan 101 Building in China: mass m TMD is 660 tons, frequency f TMD 0.147Hz, pendulum length l i =11.5m, TMD design amplitude A=0.80m.
[0108] Pick Determine the pendulum length target adjustment value l=8.7m, and use the frequency adjustment method provided by this patent to optimize the final result: the distance d when the permanent magnet is in a balanced position 0 =0.79m, model N38 is required, 128 groups of circular permanent magnets with a size of D150×10mm (256 groups on both sides of the mass block, a total of 512 permanent magnets, the total mass is about 678kg, and the required cost is about 200,000). At this time, the calculation corresponds to Meets the design goal of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com