An improved pathway-based genome-wide association analysis algorithm
An association analysis and genome-wide technology, applied in the field of pathway-based genome-wide association analysis algorithms, can solve problems such as SNP linkage disequilibrium, reduced accuracy of association analysis, SNP or genes cannot explain genetic variation, etc., to achieve SNP linkage, The effect of removing interaction effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
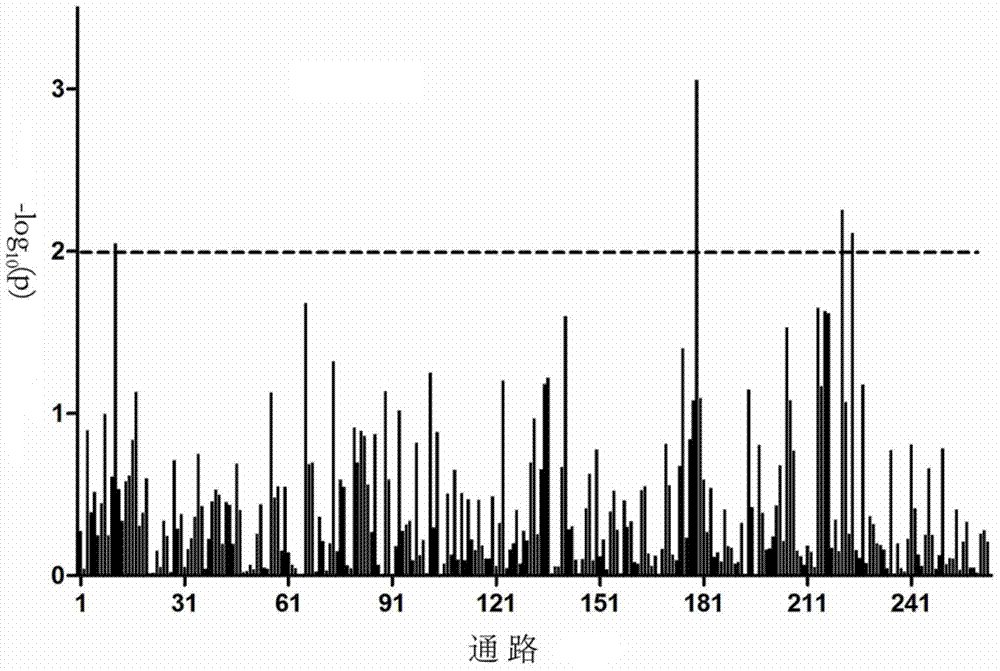
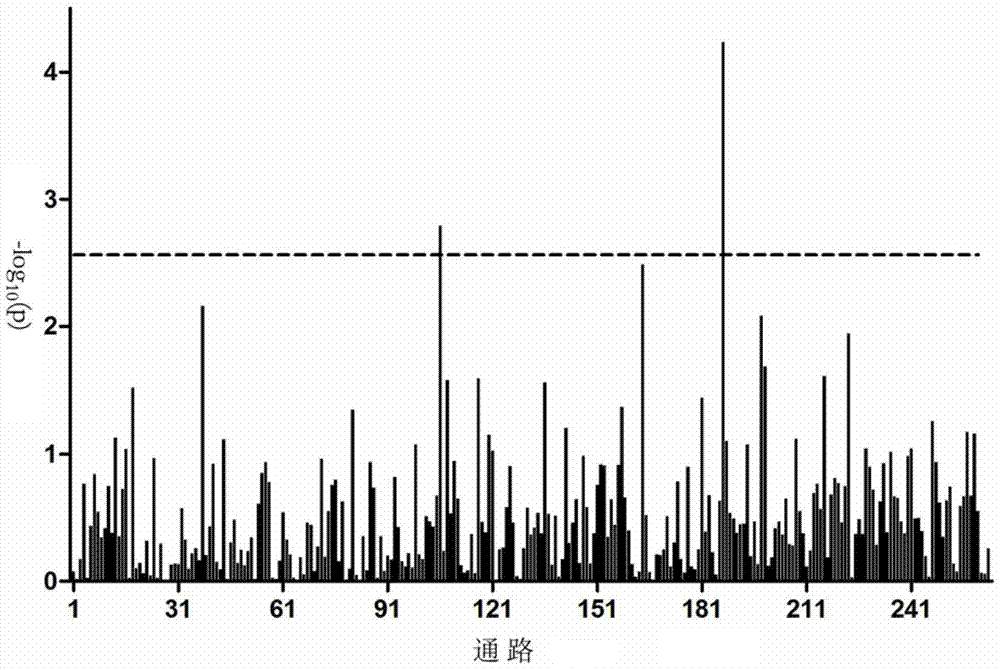
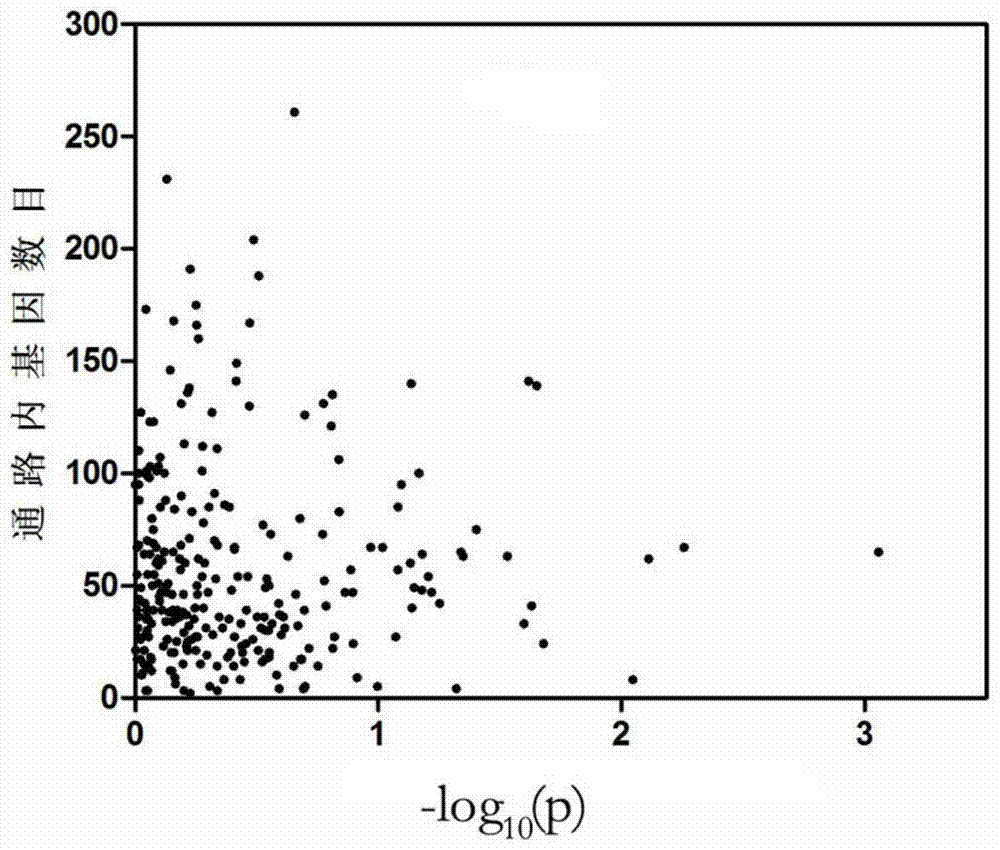
[0062]We use the idea of principal component analysis to improve the existing pathway-based genome-wide association analysis algorithm, and use a new formula to construct gene statistics. The improved algorithm takes the SNP interaction effect into the pathway-based GWAS analysis, which can effectively reduce the impact of SNP linkage on the results.
[0063] The present invention will be specifically introduced below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0064] We selected 807 beef cattle in the Ulagai area of Inner Mongolia as a reference group, and collected the phenotypic data of the two traits of live weight and eye muscle area before slaughter. The calculation results of the data of the two traits are shown in Table 1.
[0065] Table 1 Basic information of the phenotype data of two meat quality traits
[0066] Phenotype
average value
standard deviation
standard error
maximum value
minimum value
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com