A wall with automatic adjustment of heat transfer coefficient
A technology of heat transfer coefficient and automatic adjustment, applied in the direction of walls, building components, buildings, etc., can solve the problems of increasing heat, no automatic adjustment of heat transfer coefficient, etc., to achieve easy realization, broad market practical prospects, and saving air conditioning energy consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
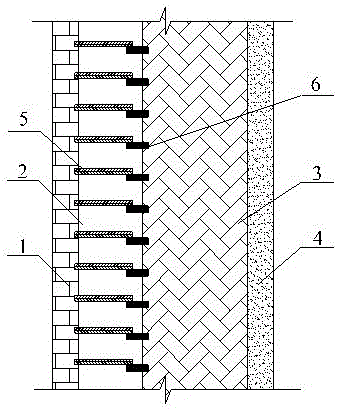
[0028] as attached figure 1 As shown, the wall body with automatic adjustment of heat transfer coefficient includes a surface layer 1, a thermal resistance layer 2, a load-bearing layer 3 and a surface layer 4, each layer is stacked in sequence, and a The heat variable resistance layer 2 is also provided with a surface layer 4 on the inner surface of the load-bearing layer 3 . The variable thermal resistance layer 2 includes several bimetallic sheets 5 and several thermally conductive substrates 6, each bimetallic sheet 5 and a corresponding thermally conductive substrate 6 constitute a conductive thermal bridge between the surface layer 1 and the load-bearing layer 3, along the wall A number of parallel thermal conduction bridges are established between the surface layer 1 and the load-bearing layer 3 in the height direction of the body. For each conduction heat bridge, one end of the heat-conducting matrix 6 is fixed on the surface of the load-bearing layer facing the surfa...
Embodiment 2
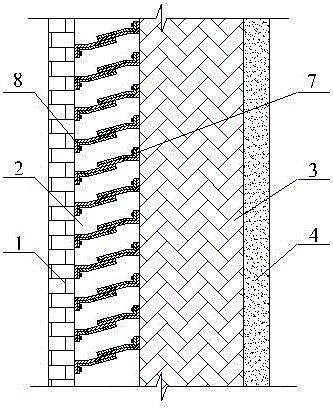
[0030] The main difference between Example 2 and Example 1 lies in the variable thermal resistance layer. In Example 2, the thermally conductive substrate in Example 1 is replaced by a bimetallic sheet. Other structural settings are the same, as shown in the attached figure 2 As shown, the variable thermal resistance layer 2 includes several bimetallic strips 7 and several bimetallic strips 8, and a corresponding group of bimetallic strips constitutes a conduction heat bridge between the surface layer 1 and the load-bearing layer 3, along the wall height direction Several groups of conduction heat bridges are established between the surface layer 1 and the load-bearing layer 3 . For each conduction heat bridge, one end of the bimetallic strip 7 is fixed on the surface of the load-bearing layer, one end of the bimetallic strip 8 is fixed on the surface of the surface layer 1, and the bimetallic strip 7 is fixed on the surface of the surface layer. The other end is freely lappe...
Embodiment 3
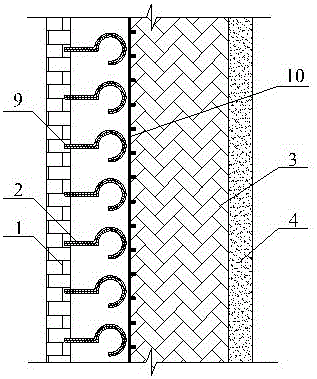
[0032] The main difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is that in embodiment 3, a round-headed bimetal sheet and a heat conduction plate are used in the variable thermal resistance layer, and other structural settings are the same, as shown in the attached image 3 As shown, the variable thermal resistance layer arranged between the surface layer 1 and the load-bearing layer 3 includes several round-headed bimetallic sheets 9 and a heat conducting plate 10, one end of the round-headed bimetallic sheet 9 is linear, and the other end Bent into a circle, the straight end of the round head bimetal 9 is fixed on the surface of the surface layer 1 facing the load-bearing layer, and the heat conducting plate 10 is arranged along the entire surface of the load-bearing layer facing the surface layer 1, and is fixed on the surface of the load-bearing layer. on the entire surface. In a normal state, the circular curved end of the round-headed bimetal 9 abuts against the surface...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com