Method for building array by adding mirror image structure to check-based RAID and read-write system
A construction method and technology of mirror structure, applied in the direction of response error generation, input/output to record carrier, redundant data error detection in operation, etc., can solve the problems of decreased space utilization, low I/O performance, Poor space utilization and other issues, to alleviate the problem of write amplification, improve write performance, and improve performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
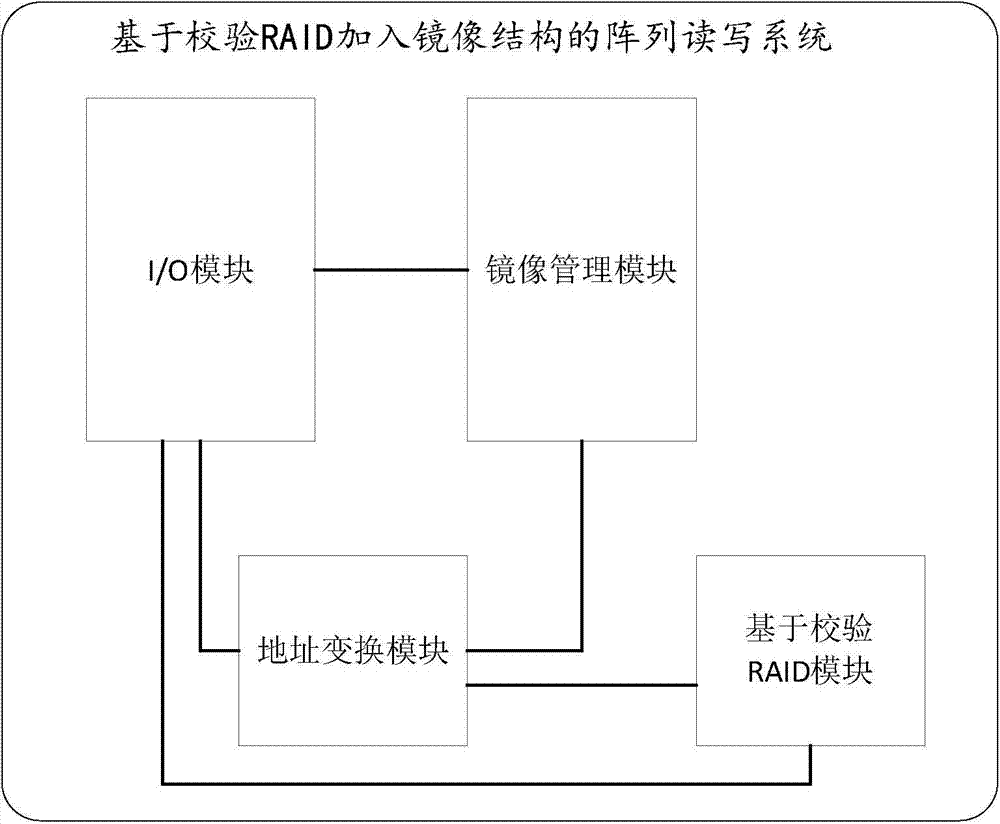
[0046] The system provided by embodiment 1 includes an I / O module, a mirror image management module, an address translation module and a RAID module based on verification;
[0047] Described I / O module accepts upper layer read and write request; Mirror image management module judges the image data segment of the original data segment that search address points to according to the address information in the read and write request, returns mirror image data segment address; Address conversion module logical address according to Segment address layout and data layout based on verification RAID are mapped to physical addresses on the disk. If it is a write request, it is also necessary to calculate the physical address of the verification block corresponding to the original data and mirror data; the I / O module decomposes the read and write requests, and the following Send to the disk corresponding to the physical address; based on the verification RAID module, it is used to execute...
Embodiment 2
[0053] In embodiment 2, the array construction method based on verifying RAID and adding mirror structure is applied to the array read-write system of the present invention, including four steps of address layout, data layout, data access and data reconstruction, as follows:
[0054] (1) Address layout:
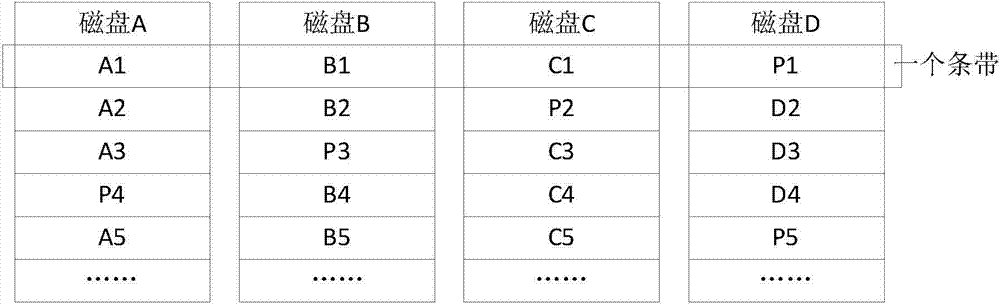
[0055] (1.1) Set the number of stripes in the segment according to the number of disks M, and the number of stripes in the segment is an integer multiple of M;
[0056] (1.2) determine the segment number K according to the number of data blocks in the disk and the number of stripes in the segment, the number of segments K=the number of data blocks in the disk / segment number of stripes;
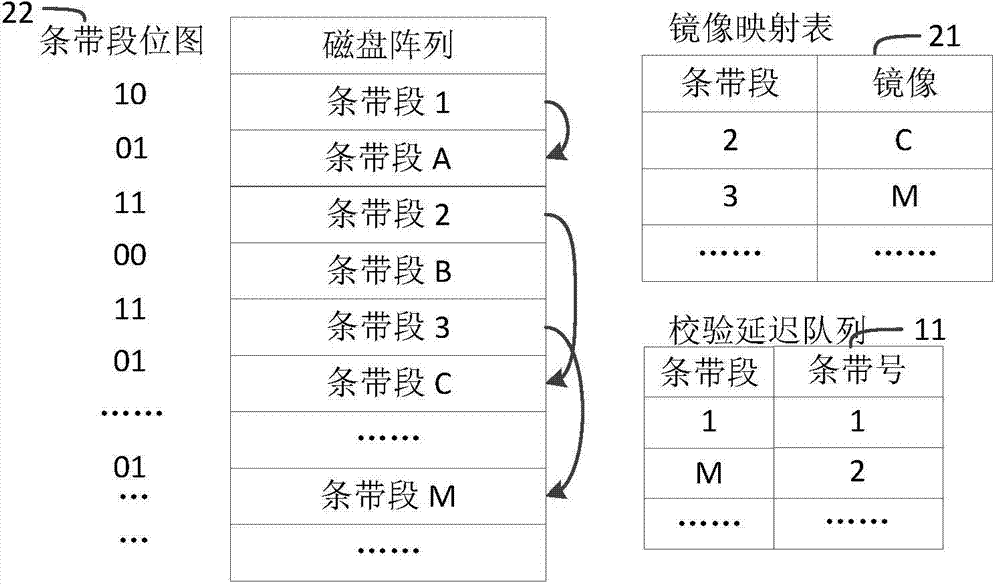
[0057] (1.3) Get N=K / 2; Interleave the segments whose segment numbers are 1 to N with the segments whose segment numbers are N+1 to K: store the segment whose number is N+1 after the segment whose number is 1, and then store For the segment numbered 2, the segment numbered N+2 will be stored...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com