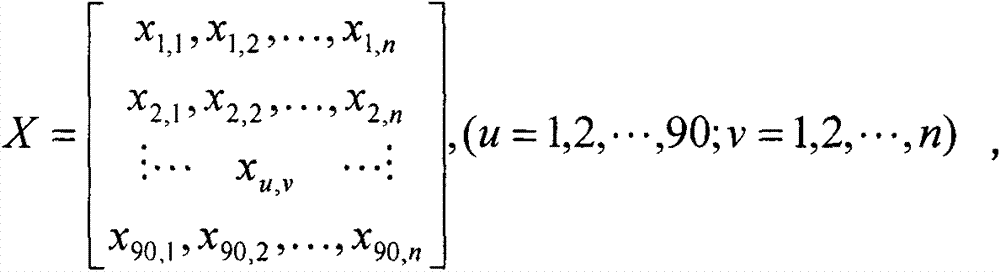FMRI dynamic brain function sub-network construction and parallel connection SVM weighted recognition method
An identification method and sub-network technology, which is applied in the field of fMRI dynamic brain function sub-network construction and parallel SVM weighted identification, can solve the problem of low recognition accuracy of classifiers, ignoring the non-stationary characteristics of the time dimension, and excessively high data dimensions of brain function networks. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
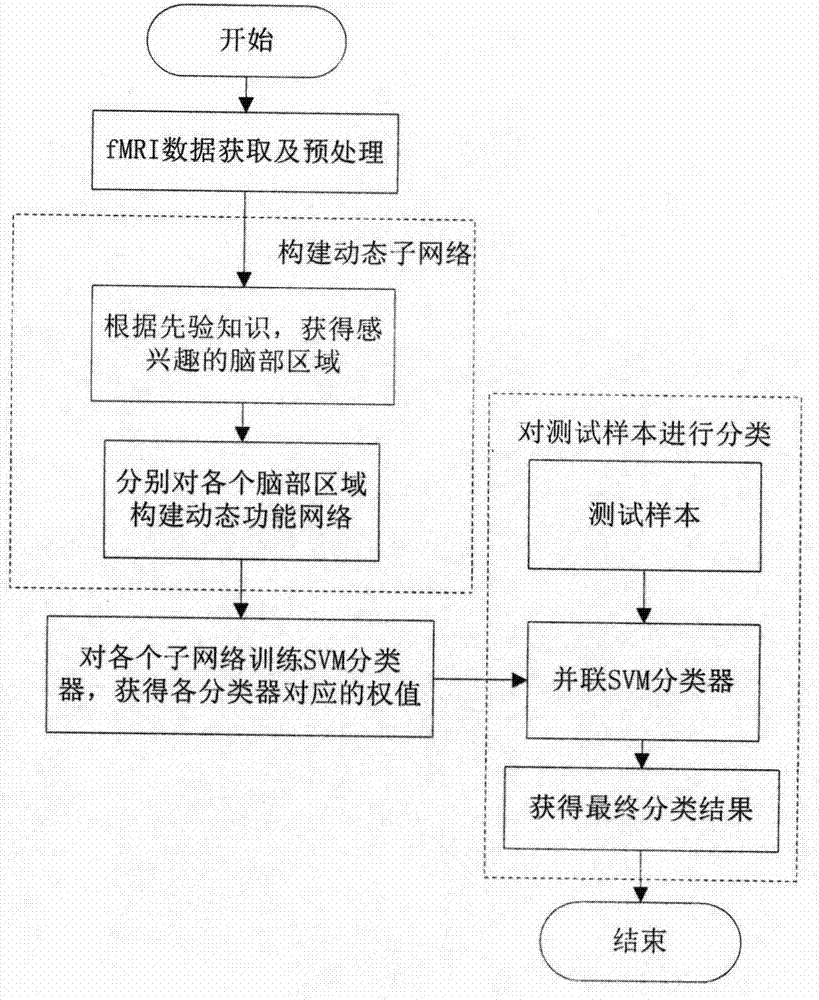
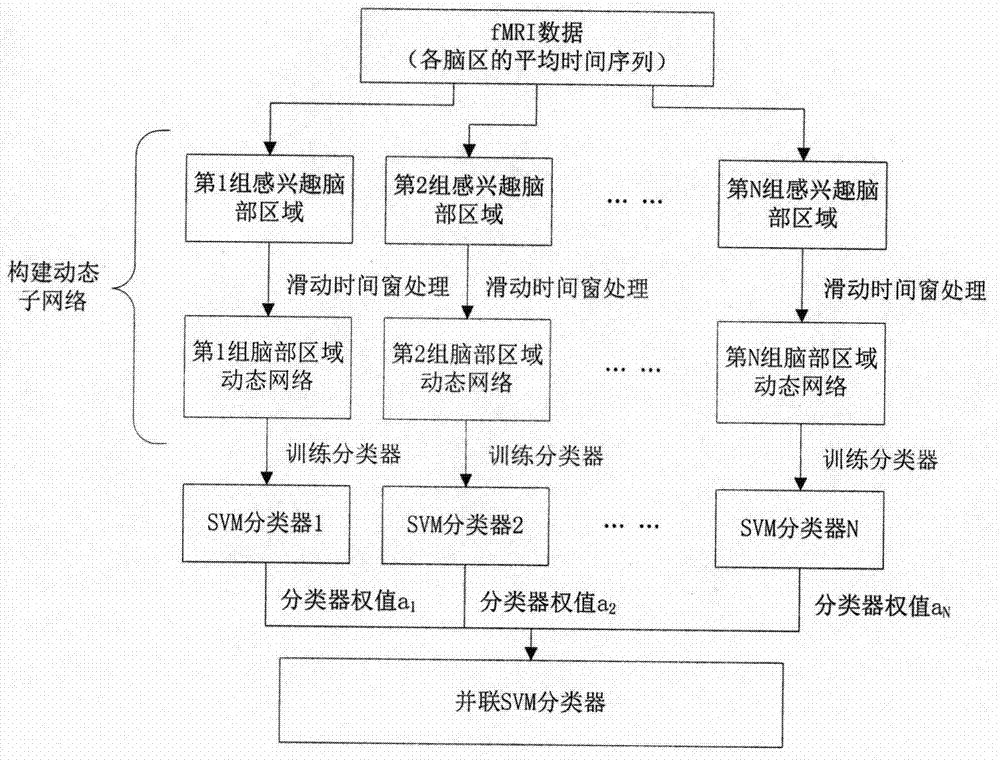
[0040] 1. Combine figure 1 The fMRI data acquisition and preprocessing part described in , obtains the fMRI data.
[0041] First, fMRI data of 56 experimental participants were acquired. When the resting state experiment data is acquired, the experimental participants are required to keep quiet during the resting state scanning process, not to fall asleep, not to spin their eyes, and to keep their eyes open. Then preprocess the obtained experimental data, the purpose of which is to remove the interference signal mixed in the data acquisition process, and standardize the experimental data to a unified time and space domain. Here, SPM8 software is used to preprocess the acquired fMRI data, including: temporal layer calibration, head motion correction, spatial normalization and spatial smoothing.
[0042] Then, the preprocessed fMRI data were compared with the AAL template, and the time series of all voxels in the 90 brain regions of each experimenter were averaged to obtain th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com