A method of slowing down the compaction of floating mud in muddy ports by using heterotrophic microorganisms
A silt and heterotrophic bacteria technology, applied in biological sludge treatment, polluted waterway/lake/pond/river treatment, etc. The effect of prolonging the maintenance dredging period, quick effect and slowing down the speed of compaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
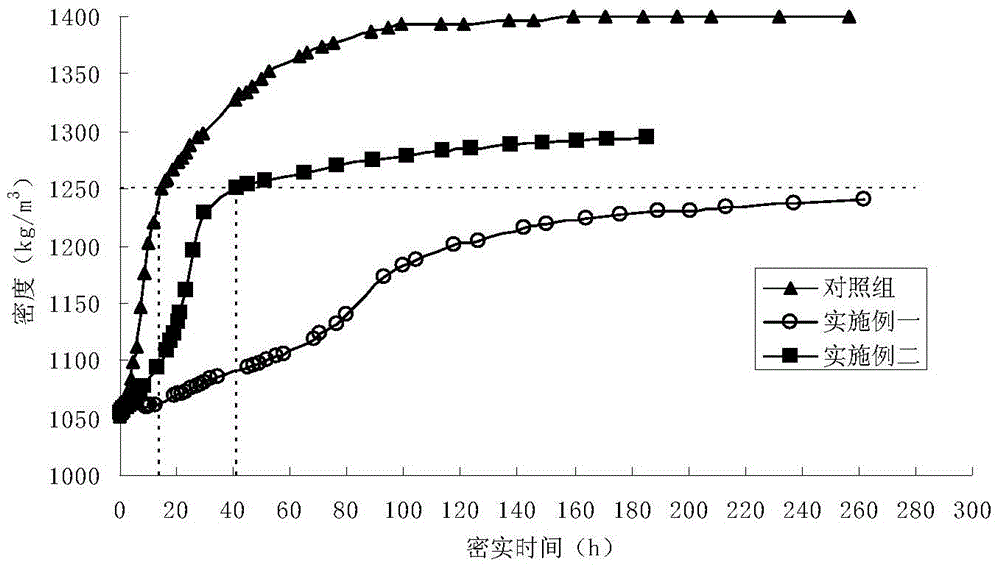
Embodiment 1
[0018] A method for slowing down the compaction of floating mud in muddy ports by using heterotrophic bacteria microorganisms, comprising the following steps:
[0019] 1) Screening heterotrophic bacteria that can produce extracellular polymers and can slow down the compaction of floating mud in muddy ports from the floating mud of muddy ports;
[0020] In this example, the floating mud taken from the muddy port was used as the material, and Burkholderia was screened from the floating mud samples based on the ability of the colonies to produce extracellular polymers and slow down the compaction of the floating mud as indicators.
[0021] 2) Enabling heterotrophic bacteria to produce extracellular polymers and interacting the extracellular polymers with the floating mud in the silty port to slow down the compaction speed of the floating mud in the silty port.
[0022] In this embodiment, the specific method of the above-mentioned step 2) is: culture the heterotrophic bacteria in...
Embodiment 2
[0024] A method for slowing down the compaction of floating mud in muddy ports by using heterotrophic bacteria microorganisms, comprising the following steps:
[0025] 1) Screening heterotrophic bacteria that can produce extracellular polymers and can slow down the compaction of floating mud in muddy ports from the floating mud of muddy ports;
[0026] In this example, the floating mud taken from the muddy port was used as the material, and Burkholderia was screened from the floating mud samples based on the ability of the colonies to produce extracellular polymers and slow down the compaction of the floating mud as indicators.
[0027] 2) Enabling heterotrophic bacteria to produce extracellular polymers and interacting the extracellular polymers with the floating mud in the silty port to slow down the compaction speed of the floating mud in the silty port.
[0028] In this embodiment, the specific method of the above step 2) is: inoculate the heterotrophic bacteria into the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com