High-voltage MOSFET current sampling circuit
A current sampling and MOS tube technology, applied in the direction of measuring current/voltage, measuring electrical variables, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor adaptability to different input voltages, power loss, etc., and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
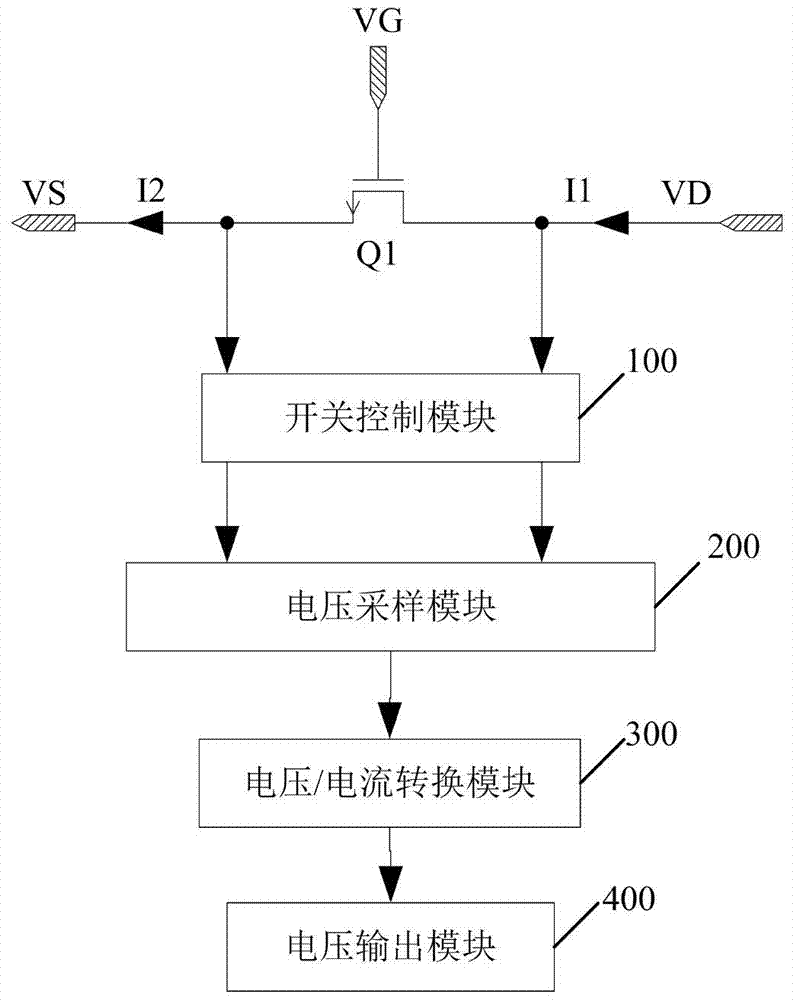
[0023] image 3 It is a block diagram of a current sampling circuit in an embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the current sampling circuit is directly electrically connected to the first terminal and the second terminal of the MOSFET switching device Q1, and the voltage difference between the first terminal and the second terminal of the MOSFET switching device Q1 is used to determine the voltage of the MOSFET switching device Q1. current value. Specifically, the current sampling circuit includes a switch control module 100, a voltage sampling module 200, a voltage / current conversion module 300, and a voltage output module 400, wherein:
[0024] The switch control module 100 is electrically connected to the first terminal and the second terminal of the MOSFET switching device Q1, and is turned on or off according to the first timing signal EN, and is used to control the sampling time point of the current sampling circuit, so as to satisfy the requirements...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Such as Figure 4 , 5 As shown, a current sampling circuit of a high-voltage power N-channel MOSFET switching device Q1 includes a switch control module 100a, a voltage sampling module 200a, a voltage / current conversion module 300a, and a voltage output module 400a, wherein:
[0031] The switch control module 100a includes a first high-voltage power PMOS transistor HVMP1, a second high-voltage power PMOS transistor HVMP2, and a third high-voltage power PMOS transistor HVMP3: the source of the first high-voltage power PMOS transistor HVMP1 and the source of the second high-voltage power PMOS transistor HVMP2 Both are electrically connected to the source of the N-channel MOSFET switching device Q1, the source of the third high-voltage power PMOS transistor HVMP3 is connected to the drain of the N-channel MOSFET switching device Q1, and the first, second and third high-voltage power PMOS The gates of the tubes (HVMP1, HVMP2, HVMP3) are all controlled by the first timing s...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Such as Image 6 As shown, a current sampling circuit of a high-voltage power N-channel MOSFET switching device Q1 includes a switch control module 100b, a voltage sampling module 200b, a voltage / current conversion module 300b, and a voltage output module 400b. from Image 6 It is easy to see that the difference between the third embodiment and the second embodiment is that the components of the switch control module 100b are replaced by replacing the P-channel MOS transistors used in the second embodiment with N-channel MOS transistors. details as follows:
[0064] The switch control module 100b includes a first high-voltage power NMOS transistor HVMN1, a second high-voltage power NMOS transistor HVMN2, and a third high-voltage power NMOS transistor HVMN3: the drain of the first high-voltage power NMOS transistor HVMN1 and the drain of the second high-voltage power NMOS transistor HVMN2 Both are electrically connected to the source of the N-channel MOSFET switching d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com