Winding type permanent magnet coupling transmission device
A permanent magnetic coupling and transmission technology, which is applied in the direction of electromechanical transmission, synchronous clutch/brake, asynchronous induction clutch/brake, etc., can solve the problems of increased volume, small output power, complex structure, etc., and achieve simple maintenance, The effect of simple structure and small volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
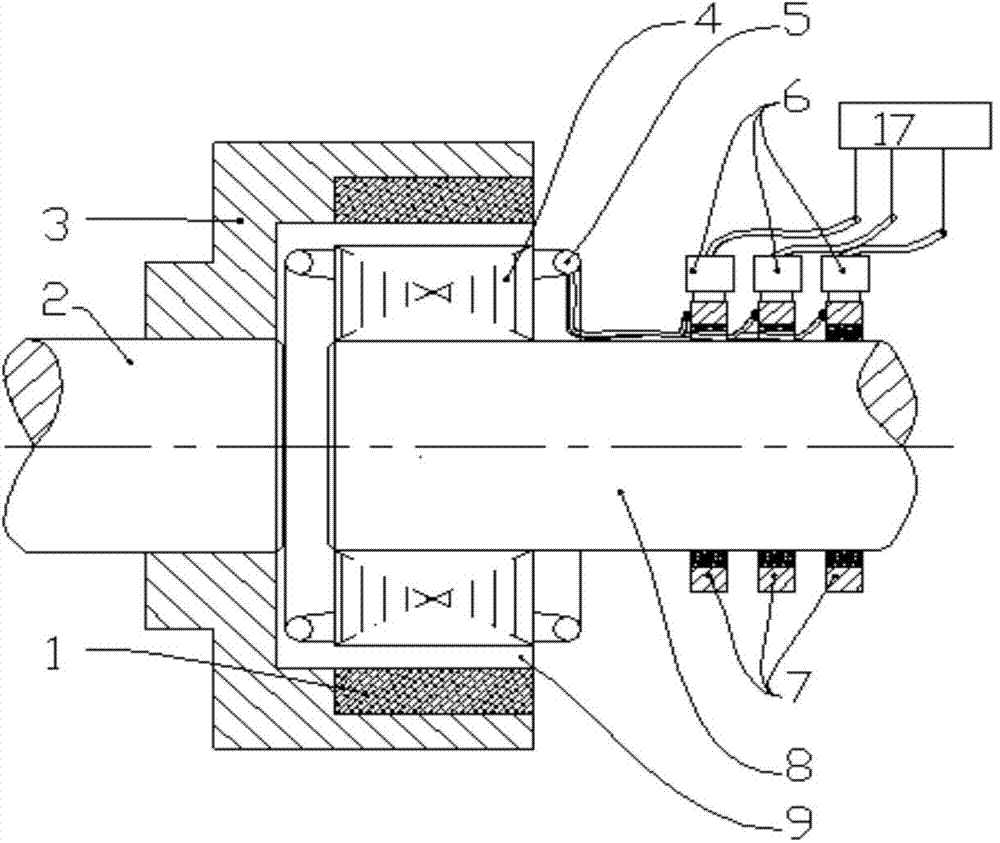
[0050] Such as Figure 1-6 As shown, a winding type permanent magnet coupling transmission device of this embodiment includes a permanent magnet rotor, and a winding rotor coaxial with the permanent magnet rotor and capable of relative rotation between the two; wherein the permanent magnet There is an air gap 9 between the rotor and the winding rotor; the winding rotor is connected with a control structure 17 that can adjust the current of the winding rotor; we know that the torque transmitted by the permanent magnet coupling transmission depends on In addition to the size of the air gap magnetic density (provided by the permanent magnet rotor), it also depends on the size of the conductor rotor current. If the size of the conductor rotor current can be controlled, the output torque can be achieved without a mechanical actuator;
[0051] In this embodiment, the control structure 17 can control the current or voltage of the winding rotor, changing the idea of using a mechanic...
Embodiment 2
[0069] As a convertible implementation mode, the differences between this embodiment and embodiment 1 are:
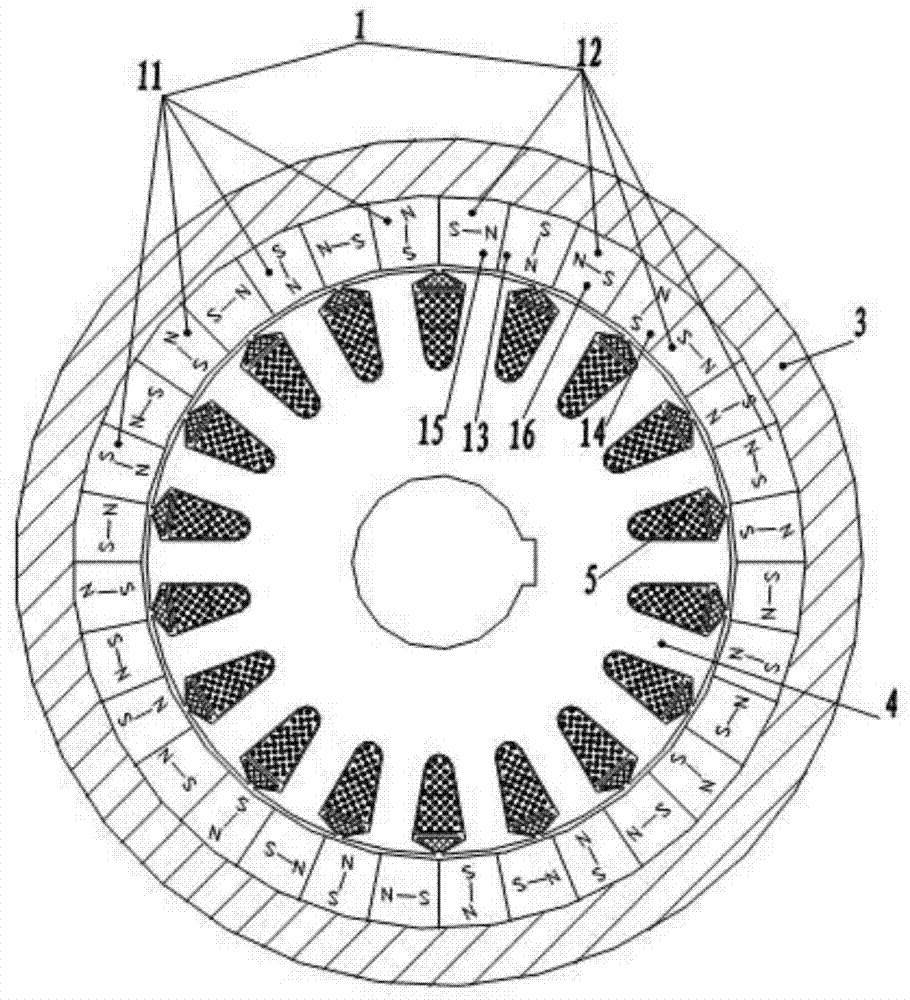
[0070] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the permanent magnet array in this embodiment also includes a third permanent magnet array 20 embedded between the first permanent magnet array 11 and the second permanent magnet array 12; wherein , the respective magnetic field directions of the first permanent magnet array 11, the second permanent magnet array 12, and the third permanent magnet array 20 respectively form a first angle, a second angle, and a first angle that are not obtuse angles with corresponding radii. Three included angles, the angle difference between the first included angle, the second included angle and the third included angle is 45 degrees respectively.
[0071] Specifically, the third permanent magnet array 20 includes a fifth unit magnet block 21, a sixth unit magnet block 22, a seventh unit magnet block 23, and an eighth unit magnet block 24 arranged at...
Embodiment 3
[0076] As a convertible implementation mode, the differences between this embodiment and embodiment 1 are:
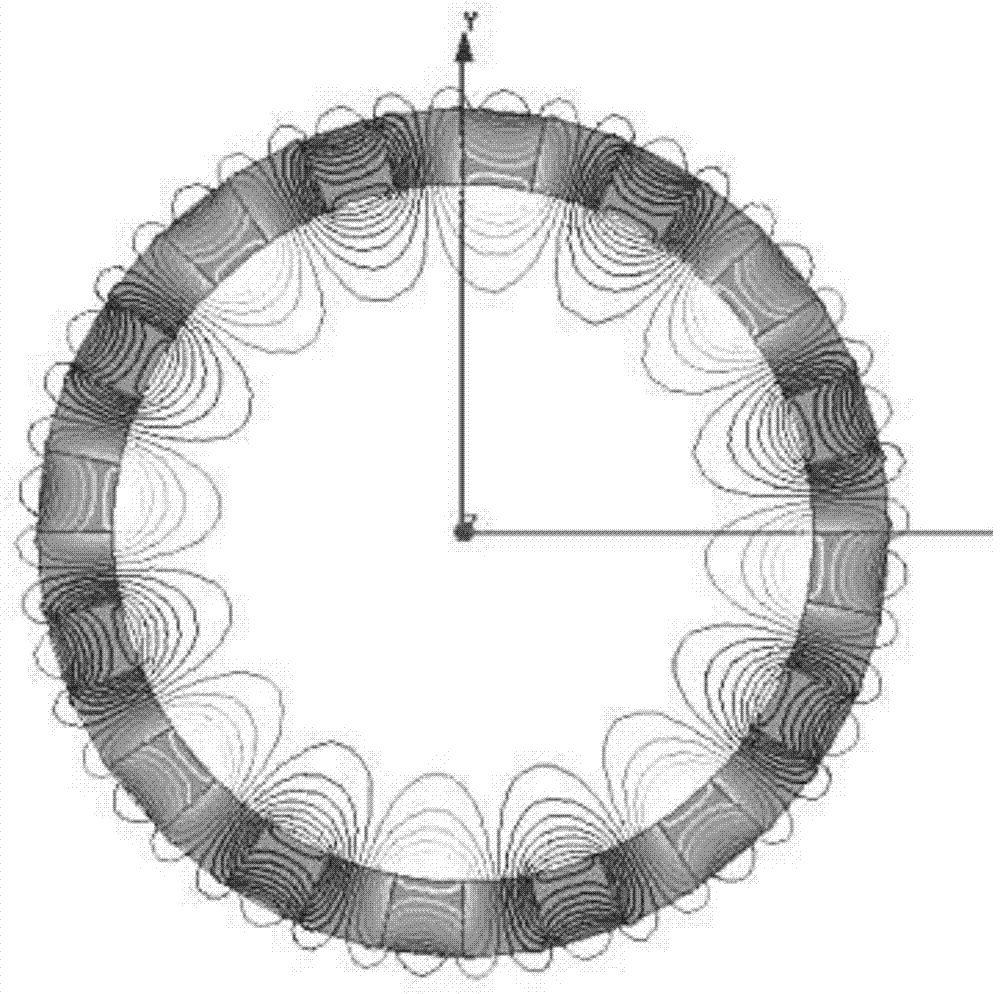
[0077] In this embodiment, the specific structure between the permanent magnet arrays is as Figure 8 As shown; the permanent magnet 1 with the above structure can obtain a single-plane magnetic field, and obtain a nearly sinusoidal air-gap magnetic field.
[0078] Further, in this embodiment, the iron core 4 is a wound iron core, and a plurality of slots for winding the coil are formed on the wound iron core. The number of the grooves is set to be 3n (n=1, 2, 3...). In this embodiment, preferably n is set to 8, that is, the number of the grooves is set to 24, and the specific structure is as follows Figure 9 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com