Thermal Transistor
A heat pipe and volume technology, used in heat transfer modification, heat exchange equipment, indirect heat exchangers, etc., can solve the problem of difficult connection of heat pipes with multiple heat sources, and achieve the effect of simple structure, simplified manufacturing process and low manufacturing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
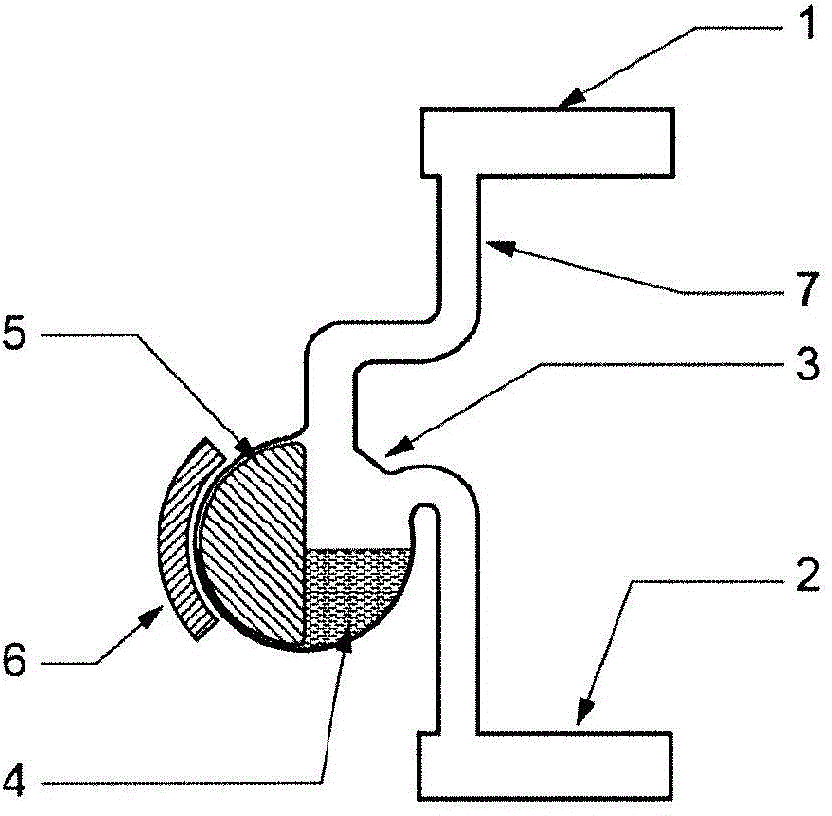
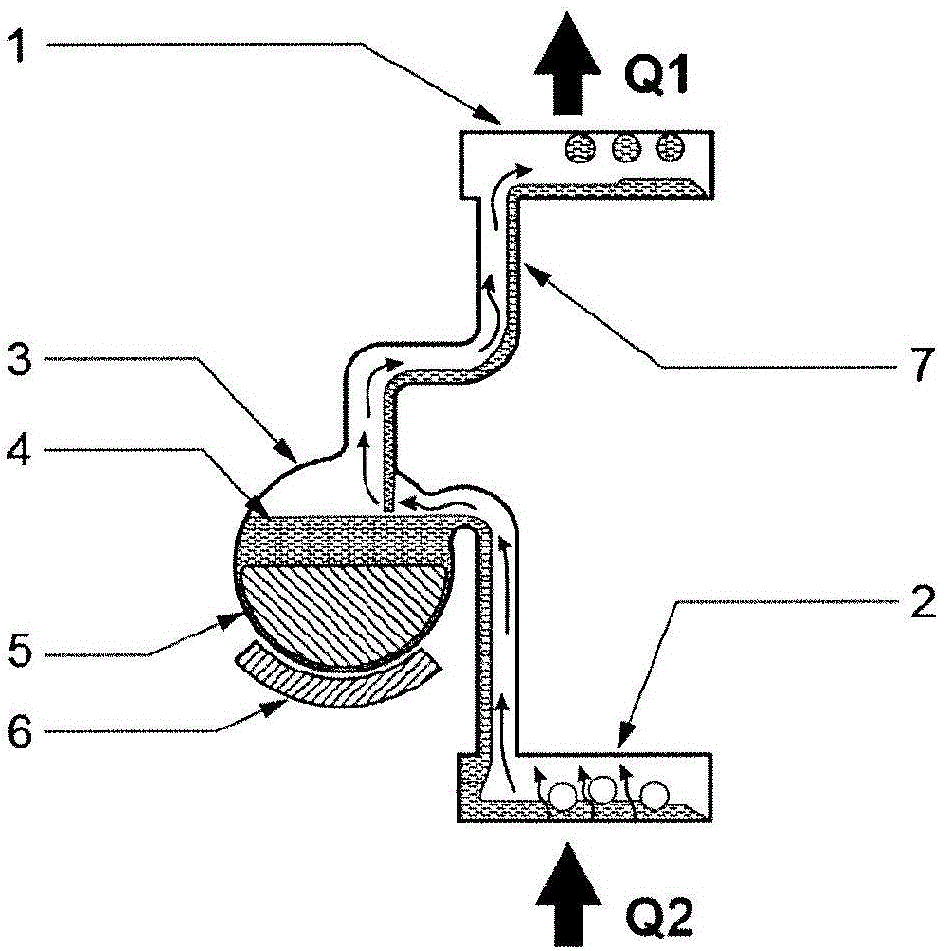
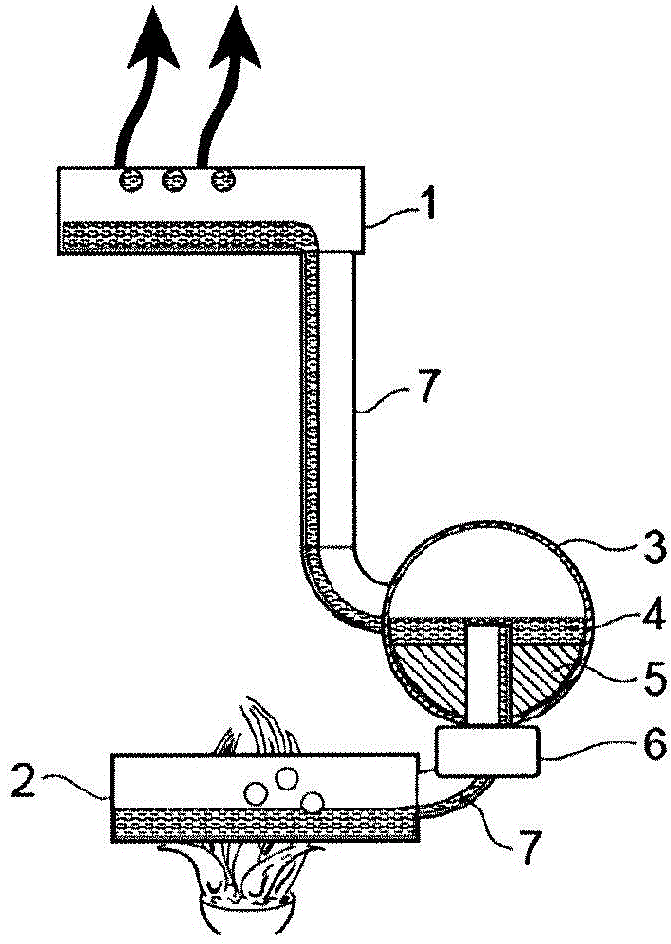
[0082] The heat pipe will now be described in more detail by giving a non-limiting example, with reference to Figure 1a , 1b , where 1 denotes a condenser, 2 denotes an evaporator, 3 denotes a replacement container, 4 denotes a working fluid, 5 denotes a floating body with a magnet, 6 denotes a magnet, and 7 denotes a tube for transporting a gas-phase working fluid and a liquid-phase working fluid. Q1 and Q2 represent the energy transferred from the condenser and the energy transferred to the evaporator, respectively. The condenser 1 is located in the upper part and is represented as a vessel in which the steam is condensed. The evaporator 2 is located in the lower part where heat is applied to the surface area causing evaporation of the working fluid. The third part is the displacement container 3, in which the working fluid 4 is stored when the heat pipe is in the off mode. In more detail, the working fluid 4 is stored in the lower part of the displacement container, indi...
Embodiment 2
[0085] The heat pipe will now be described in more detail by giving a non-limiting example, with reference to Figure 5 . External heat pipes are thermally connected to the heat pipes, in particular to the evaporation regions e1-e6 of the heat pipes. The condenser sections of the external heat pipes h1-h6 are in thermal contact with the evaporation zones e1-e6, respectively. The external heat pipes are in thermal contact with different chemical heat pumps that work in a two-step process, including heat storage and heat release. Chemical heat pumps are set up to store heat from any heat source. Examples of heat sources include, but are not limited to, the sun, gas heaters, oil burners, electric heaters, coal fired stoves, and wood stoves. During the exothermic process, heat can be transferred to the heat pipe via the external heat pipe and further to the desired destination. When the chemical heat pump stores energy through the heat source, the heat transfer is switched off...
Embodiment 3
[0087] The heat pipe will now be described in more detail by giving a non-limiting example, with reference to Figure 6 . Each of the two chemical heat pumps works in a two-step process and each includes a reactor section, and two heat pipes are arranged to transfer heat from the two chemical heat pumps to the water heater. A heat pipe is according to the invention and can be adjusted and switched on and off. Heat can also be transferred to one of the reactors from an external heat source, see Figure 6 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com