A gene controlling the erect development of rice leaves and its application
A gene and rice technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of unclear cellular and molecular mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Acquisition of a gene CYC U4;1 controlling the erect development of rice leaves:
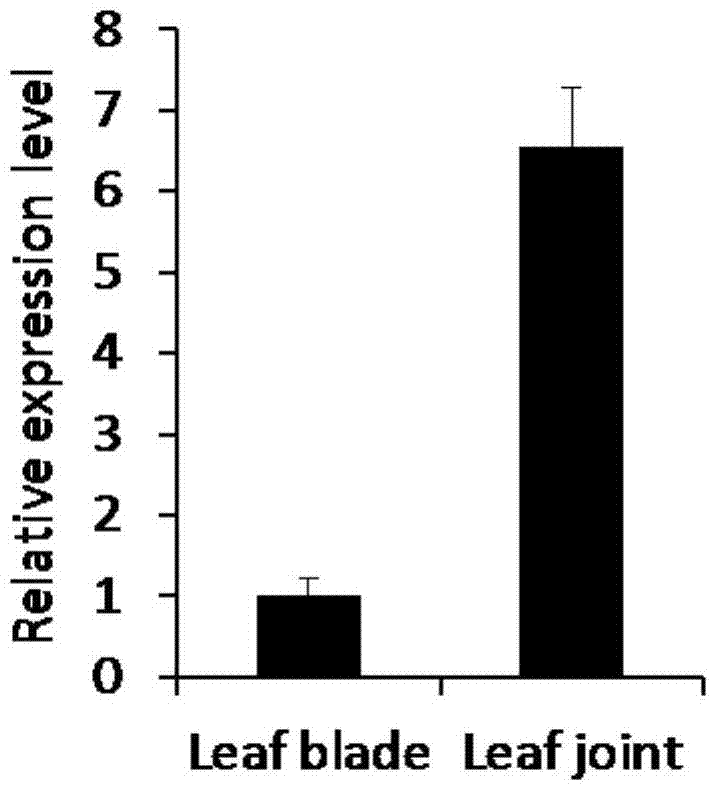
[0032] The inventor constructed a gene-specific expression chip for rice leaves and leaf pillows, and selected the gene CYC U4 specifically expressed in the leaf pillows from the differentially expressed genes of the chip through the method of reverse genetics; 1. Using real-time qRT- PCR verified the specificity of CYC U4;1 expression in the occipital. details as follows:
[0033] A gene CYC U4; 1, which controls the erect development of rice leaves, is obtained by the following method:
[0034] The total volume of the reaction system is 50μl, the template is Nipponbare CDNA 1ul (about 50ng), 10×KOD enzyme reaction buffer 5μl, 25mM MgCL 2 2μl, 5mM dNTP 5μl, 5uM primer 5μl (by step-by-step PCR, use primers CYCU4-U and CYCU4-L-1 for the first time, use primers CYCU4-U and CYCU4-L-2 for the second time, each primer 2.5μl), 1μl KOD enzyme, add ddH 2 O (sterile deionized water) to 50 μl....
Embodiment 2
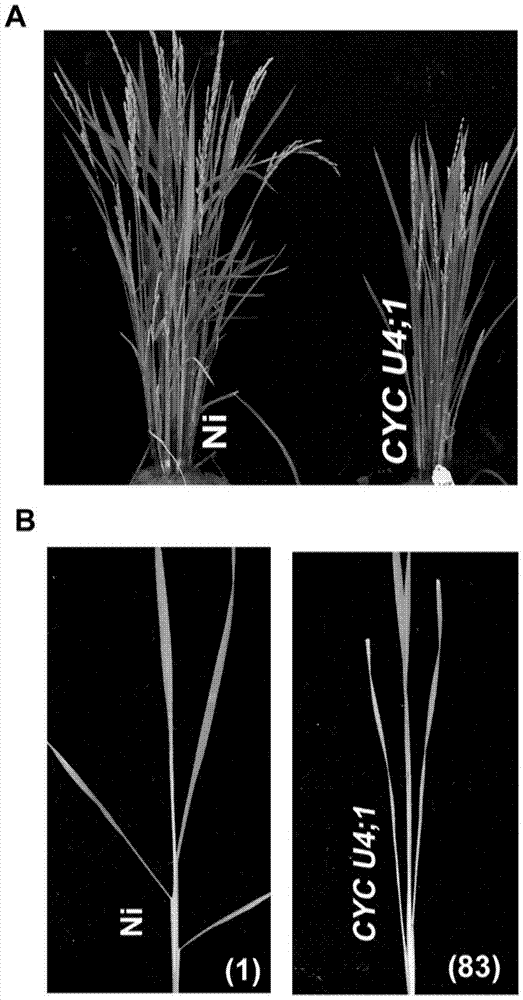
[0044] The application of CYC U4; 1 gene in controlling the uprightness of rice leaves is as follows:
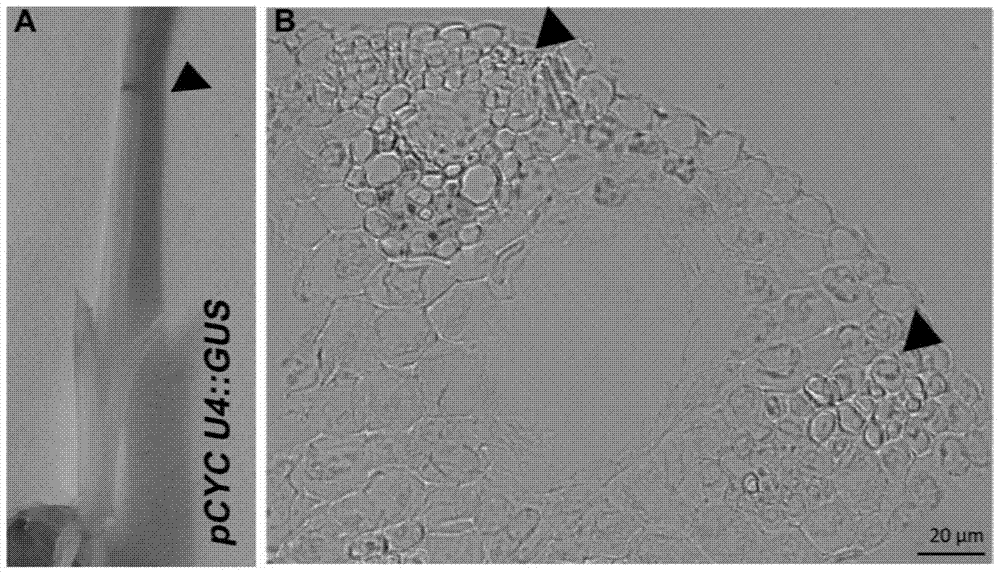
[0045] 1) Construction of plant expression vector pCYCU4; 1-GUS
[0046] Amplify the CYC U4; 1 promoter region, and use the HindIII / BamH1 restriction site to clone the fragment into pCAMBIA1300GN GUS (Ren Z H, Gao J P, Li L G, et al. A rice quantitative traitlocus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter[J ]. Nature genetics, 2005, 37(10): 1141-1146.) on the carrier.
[0047] The CYC U4; 1 promoter region is obtained by the following method:
[0048] The total volume of the reaction system is 50 μl, the template is Nipponbare Genomic DNA 1ul (about 50ng), 1×KOD enzyme reaction buffer 5μl, 25mM MgCL 2 2μl, 5mM dNTP 5μl, 5uM primer 5μl (primers pCYCU4-U and pCYCU4-L respectively 2.5μl), 1μl KOD enzyme, add ddH 2 O (sterile deionized water) to 50 μl. The reaction program was: denaturation at 94°C for 5min, 30s at 94°C, 1min at 55°C, 35cycles at 68°C for 2min, and ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com