A real-time service-oriented component carrier configuration switching method
A component carrier and real-time service technology, applied in the directions of allocation standards, transmission path sub-channel allocation, digital transmission systems, etc., can solve the problem that the spectrum aggregation technology does not consider the real-time service delay requirements and cannot meet the real-time service delay requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
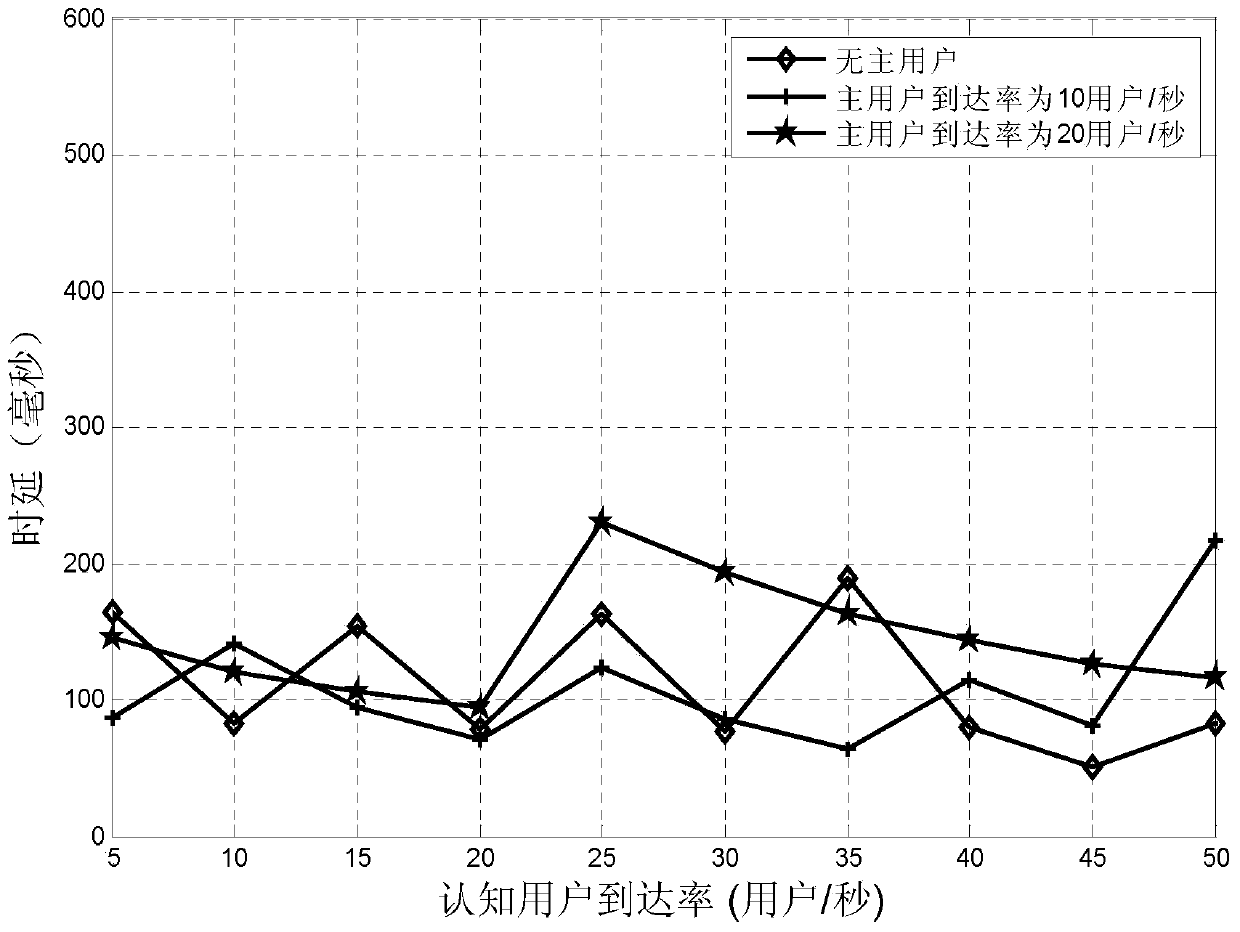
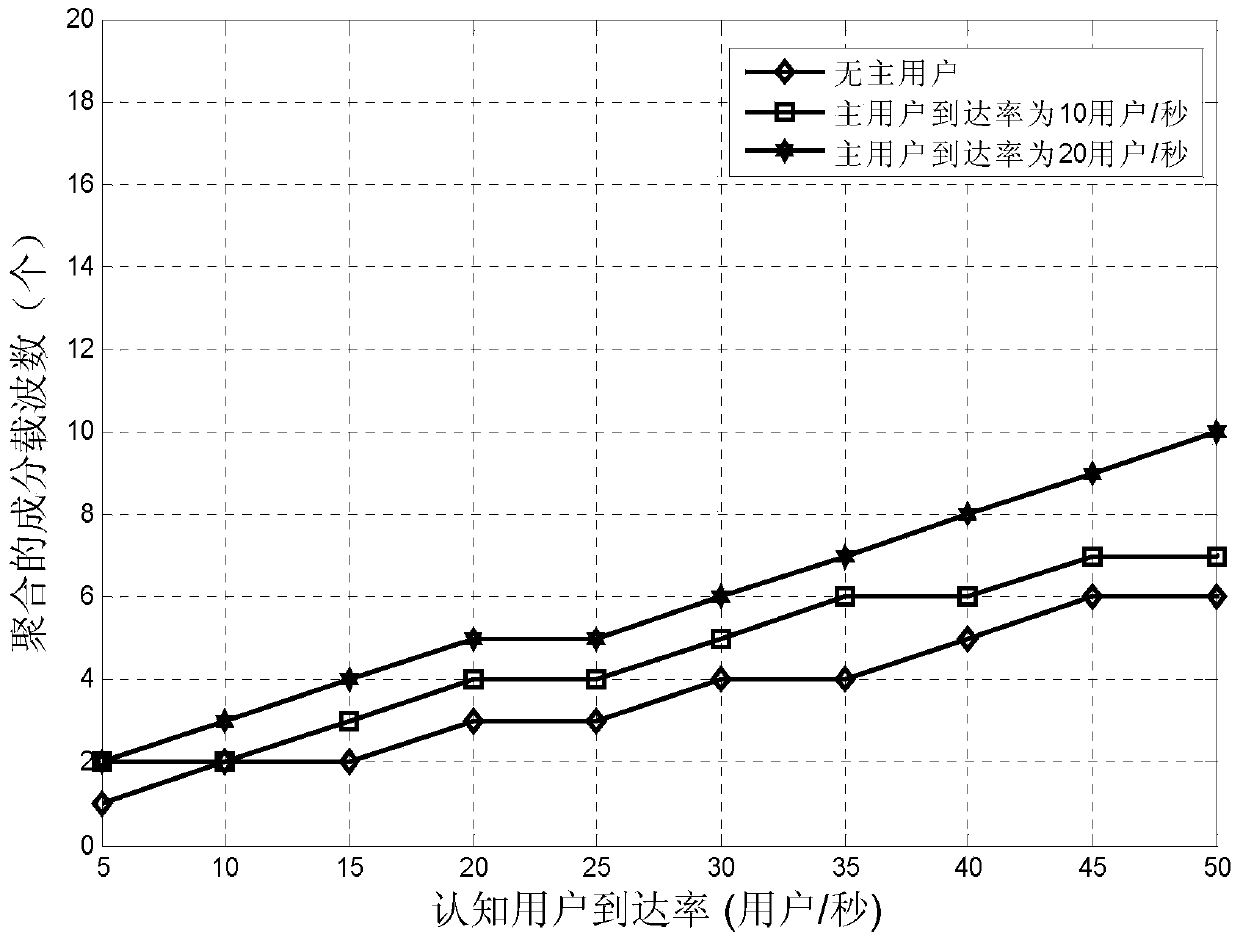
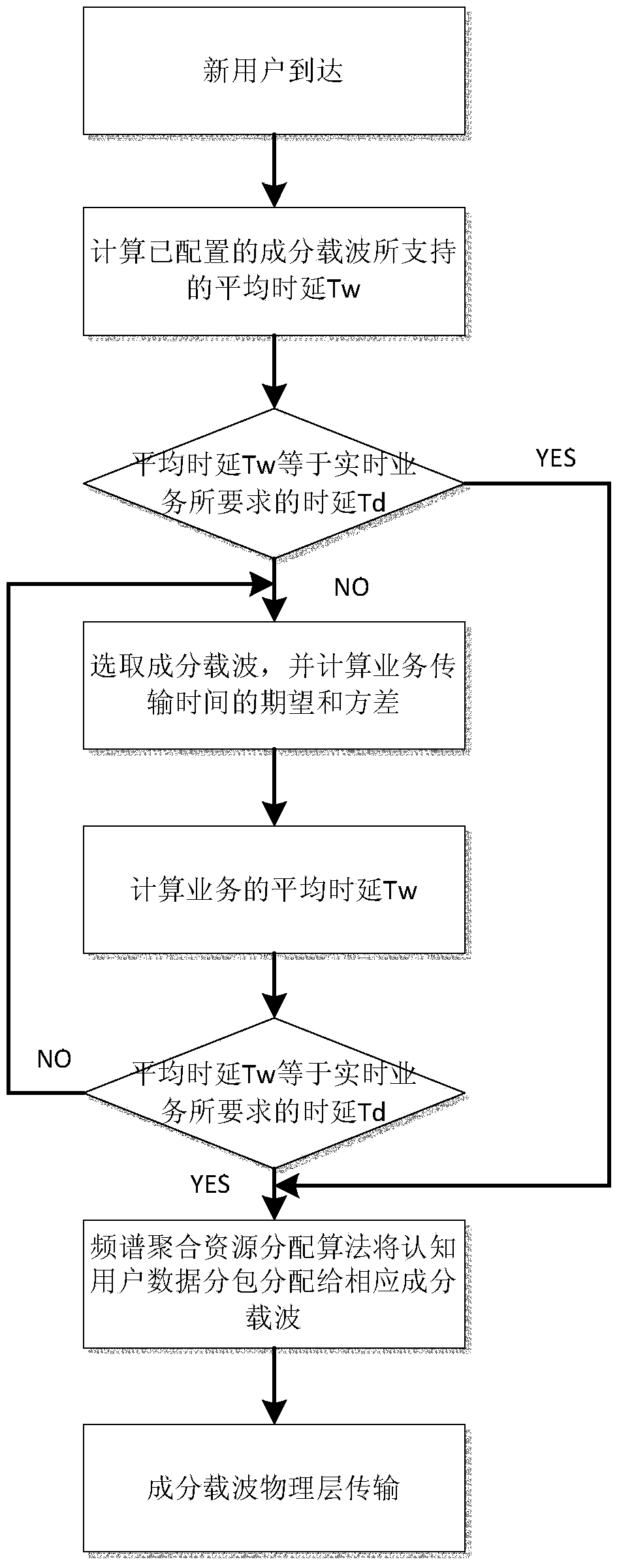
[0016] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 A real-time service-oriented component carrier configuration switching method in this embodiment is described, which is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0017] Step 1. Select N component carriers to be aggregated according to the cognitive user data, and obtain the cognitive user transmission time T;
[0018] Step 2. Calculate the mathematical expectation E(T) and variance D(T) of the cognitive user transmission time T according to the arrival rate and service rate of the primary user on the N component carriers to be aggregated;
[0019] Step 3: Calculate the service intensity ρ of the cognitive user according to the mathematical expectation of the cognitive user's transmission time T su , according to ρ su Calculate the average delay T of cognitive user aggregation w ;
[0020] Step 4. If the average time delay T of cognitive user aggregation w Equal to the average delay T exp...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0027] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in step 1, N component carriers to be aggregated are selected according to the cognitive user data, and the transmission time T of the cognitive user is obtained as follows:
[0028]
[0029] Among them, F is cognitive user data (unit bit), C is the throughput of all component carriers (unit bps), N is the number of component carriers aggregated during spectrum aggregation, and C i is the throughput of the i-th component carrier (in bps), T i,pu is the master user data transfer time. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that: in step two, calculate the mathematical expectation E(T) of the transmission time T of the cognitive user:
[0031]
[0032] Among them, λ i,pu is the arrival rate of the primary user on the i-th component carrier, μ i,pu is the service rate of the primary user on the i-th component carrier. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com