Line fault identification method using pole line fault voltage curve clusters to perform principal component clustering analysis
A fault voltage and line fault technology, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve the problems of DC blocking accident, long delay of the longitudinal differential protection outlet, and inability to detect the high resistance fault at the remote end of the UHVDC line, so as to effectively describe the problem. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
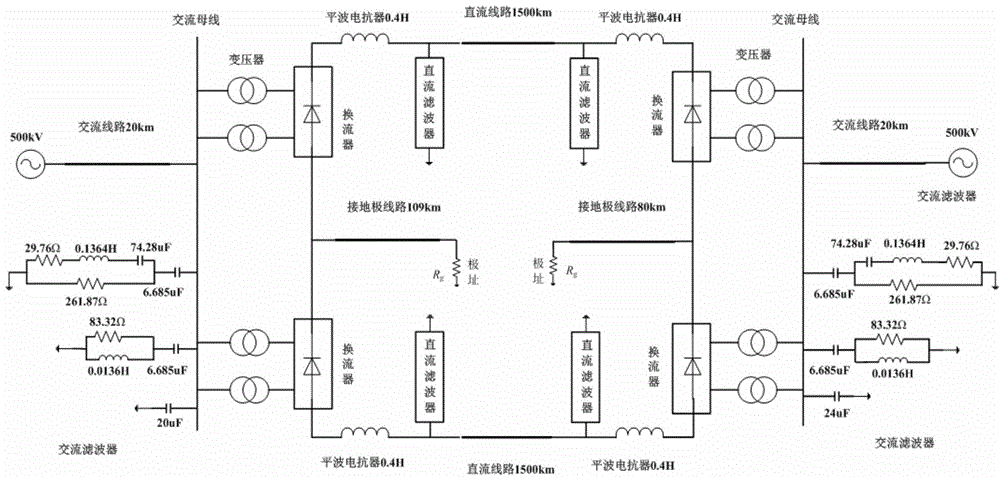
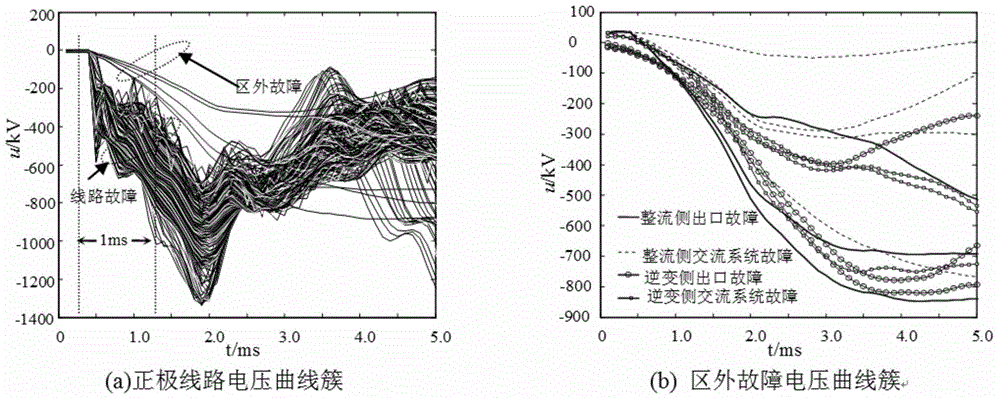
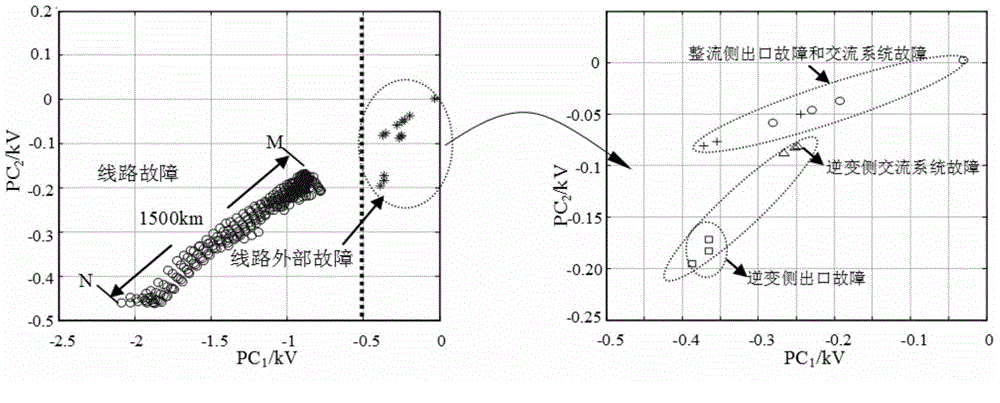
[0021] Embodiment 1: adopt figure 1 In the simulation system shown, according to the above steps (1) and (2), the clustering results of line faults and external faults in PCA space are obtained as follows: image 3 shown. Select 4 cluster centers as the cluster centers of line faults, namely (-1.7261,-0.3977), (-1.2570,-0.2770), (-0.9649,-0.2062), (-0.8875,-0.1960) and 1 external Fault cluster centers (-0.2556, -0.2761). And express the Euclidean distance between the test sample data and the four centers of line fault clustering as d 1 ~ d 4 , the Euclidean distance table between the test sample data and one center of the external fault cluster is d 5 .
[0022] (1) Calculate d according to steps (3) and (4) in the claims 1= 0.0345, d 2= 0.5063, d 3= 0.8064, d 4= 0.8837 and d 5= 1.4921;
[0023] (2) get d according to step (5) in the claims min = d 1 , so it is judged as a line failure.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2: The fault distance is 400km from the M terminal, and the transition resistance is 100Ω.
[0025] (1) Calculate d according to steps (3) to (4) in the claims 1= 0.8024, d 2= 0.3182, d 3= 0.0199, d 4= 0.0602 and d 5= 0.6931;
[0026] (2) get d according to step (5) in the claims min = d 3 , so it is judged as a line failure.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: The outlet of the rectifier side is faulty, and the transition resistance is 10Ω.
[0028] (1) Calculate d according to steps (3) to (4) in the claims 1= 1.4920,d 2= 1.0082,d 3= 0.7082,d 4= 0.6302 and d 5= 0.1888;
[0029] (2) get d according to step (5) in the claims min = d 5 , so it is judged as an out-of-area fault.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com