Method for controlling corner cracks of boron micro-alloy steel continuous-casting billet
A boron microalloying and corner cracking technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of antegrade affecting production, reducing the qualified rate of casting billets, etc., to save labor costs, reduce crack sensitivity, and avoid corner cleaning.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
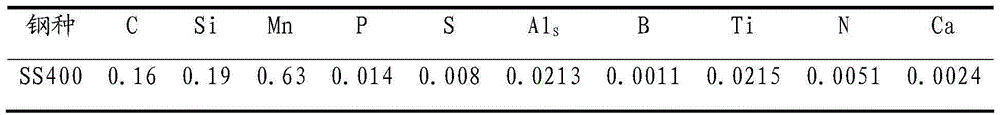
[0017] This example is to use the present invention to control the corner crack defect of SS400 boron-containing steel. Refining process: (1) After adjusting the molten steel composition and temperature, feed aluminum wire, [S] weight percentage in molten steel = 0.008%, [Mn] / [S] = 81.25, [N] weight percentage = 0.0051%, [Als] weight percentage = 0.0263%; (2) Feed aluminum wire and finish weak argon blowing for four minutes, then add ferrotitanium to molten steel, [Ti] weight percentage = 0.0215, three minutes later Feed boron iron, [B] weight percentage=0.0011%, finally carry out calcium treatment, [Ca] / [Als]=0.11. The composition of the final molten steel is shown in Table 1.
[0018] Table 1 Steel Chemical Composition (weight percent, %)
[0019]
[0020] Continuous casting process: (1) Slab specifications: width 1800mm, thickness 250mm, casting speed controlled at 1.2m / min; (2) water volume at the wide and narrow sides of the crystallizer at 4400L / min and 420L / min; cr...
Embodiment 2
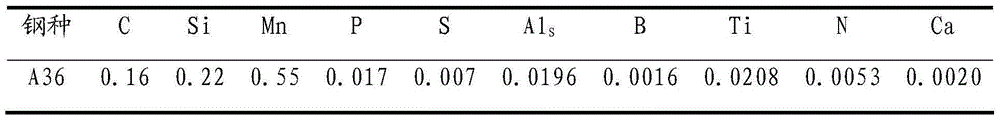
[0023] This example is to use the present invention to control the corner crack defect of A36 boron-containing steel. Refining process: (1) After the liquid steel composition and temperature are adjusted, aluminum wire is fed, [S] weight percentage in the steel liquid = 0.007%, [Mn] / [S] = 78, [N] weight percentage = 0.0053%, [Als] weight percentage = 0.0196%; (2) Feed aluminum wire and finish weak argon blowing for four minutes, then add ferro-titanium to molten steel, [Ti] weight percentage = 0.0208%, three minutes Feed boron into the molten steel afterward, the weight percentage of [B]=0.0016%, finally carry out calcium treatment to the molten steel, [Ca] / [Als]=0.102. The composition of the final molten steel is shown in Table 2.
[0024] Table 2 steel chemical composition (weight percent, %)
[0025]
[0026] Continuous casting process: (1) Slab specifications: width 1800mm, thickness 250mm, casting speed controlled at 1.1m / min; (2) water volume at the wide and narrow ...
Embodiment 3
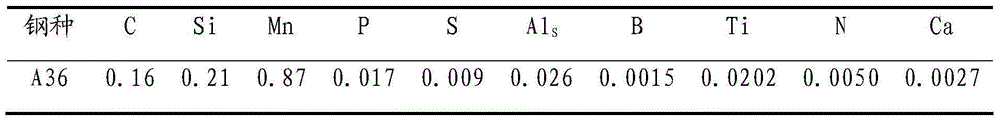
[0029] This example is using the present invention to control S275JR boron-containing steel corner crack defects. Refining process: (1) After the molten steel composition and temperature are adjusted, aluminum wire is fed, [S] weight percentage in molten steel = 0.009%, [Mn] / [S] = 96.67, [N] weight percentage = 0.0050%, [Als] weight percentage = 0.026%; (3) After feeding the aluminum wire and completing weak argon blowing for four minutes, add ferrotitanium to the molten steel, [Ti] weight percentage = 0.0202%, three minutes Feed boron into molten steel afterward, [B] weight percentage=0.0015%, finally carry out calcium treatment to molten steel, [Ca] / [Als]=0.104. The composition of the final molten steel is shown in Table 3.
[0030] Table 3 steel chemical composition (weight percent, %)
[0031]
[0032] Continuous casting process: (1) Billet specifications: width 2100mm, thickness 250mm, casting speed controlled at 0.9m / min; (2) water volume at the wide and narrow side...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com