Extracranial standing wave suppression method for high-intensity ultrasound transcranial focusing
A high-intensity, standing wave technology, used in ultrasonic therapy, treatment and other directions, can solve the problems of no research on the selection of conversion time interval, no research and discussion on the method of reducing standing waves, etc. Wave attenuation ability, effect of reducing the intensity of standing waves
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
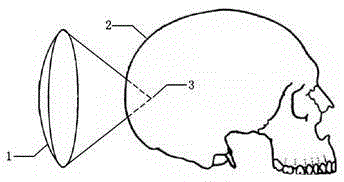
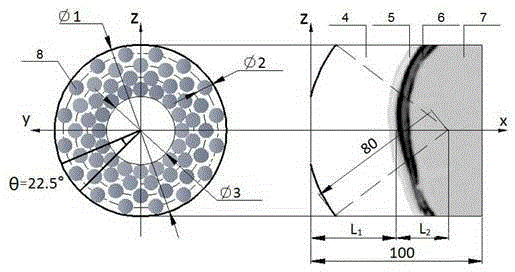
[0047] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the transcranial focusing space of the spherical coronal concave spherical phased transducer, figure 2 The example model is shown here, where the squamous part of the temporal bone is used as the bone acoustic window, and the transducer is irradiated with a spherical coronal concave spherical 64-element phased array transducer at a frequency of 0.6MHz as an example, as follows Step implementation.
[0048] S1: Use the random function in Matlab to generate a sequence of random 0 or π. In this example, the acoustic window model selects the temporal bone window, and the intracranial focus is located at the geometric focus of the transducer, that is, the focal point is set at a distance of 80mm from the transducer.
[0049] S2: According to the position of the intracranial target area and the zoom range of the phased transducer, the selected treatment target depth is =25mm, that is, the distance between the skull and the phased tra...
Embodiment 2
[0058] S1: Use the random function in Matlab to generate a random sequence of 0, π / 2 or π. In this example, the acoustic window model selects the temporal bone window, and the intracranial focus is located at the geometric focus of the transducer, that is, the focal point is set at a distance of 80mm from the transducer.
[0059] S2: According to the position of the intracranial target area and the zoom range of the phased transducer, the selected treatment target depth is =25mm, that is, the distance between the skull and the phased transducer is =55mm. Using formula (1) As an excitation signal, the generated random sequence is added to the element excitation function at regular time intervals, and formula (1) is rewritten as formula (2) . in The phase of 0, π / 2 or π is taken from the 0, π / 2 or π random phase sequence generated by the random function, formula (3) (n=1,2,3...) read once value, is the phase transition time interval.
[0060] S3: Select differen...
Embodiment 3
[0063] S1: Use the random function in Matlab to generate random sequences of 0, π / 2, π or 3π / 2. In this example, the acoustic window model selects the temporal bone window, and the intracranial focus is located at the geometric focus of the transducer, that is, the focal point is set at a distance of 80mm from the transducer.
[0064] S2: According to the position of the intracranial target area and the zoom range of the phased transducer, the selected treatment target depth is =25mm, that is, the distance between the skull and the phased transducer is =55mm. Using formula (1) As an excitation signal, the generated random sequence is added to the element excitation function at regular time intervals, and formula (1) is rewritten as formula (2) . in The phase of 0, π / 2, π or 3π / 2 is taken from the random phase sequence of 0, π / 2, π or 3π / 2 generated by the random function, formula (3) (n=1,2,3...) read once value, is the phase transition time interval.
[0065]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com