Function and application of mitochondria-associated ribosomal GTPase 1 (MTG1) in the treatment of cardiac hypertrophy
A myocardial hypertrophy and ribosome technology, applied in the field of gene function and application, can solve the problems of lack of research, decreased expression of respiratory chain complex I and IV, decreased mitochondrial DNA translation level, etc., to protect heart function and inhibit myocardial hypertrophy , the effect of anti-cardiac fibrosis and myocardial hypertrophy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
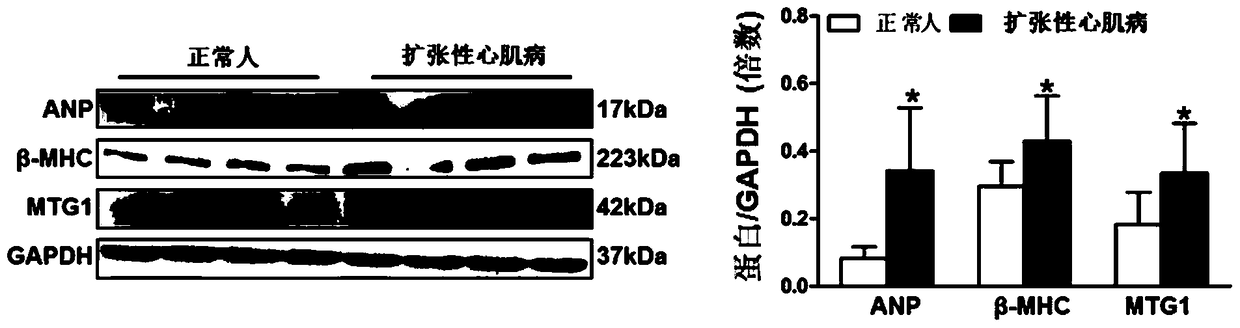
[0081] Example 1 Expression of MTG1 in the hearts of normal people and patients with cardiomyopathy
[0082] Select normal human hearts (individuals donated by non-cardiac causes of death) and dilated cardiomyopathy patients’ hearts (recipients replaced by patients undergoing heart transplantation), and perform SDS-PAGE-Western blot test (Western blot) on proteins extracted from the hearts, combined with Antibodies that specifically recognize MTG1 protein and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy markers ANP (Millipore, AB2232) and β-MHC (santa cruz, sc53090) were detected to measure the expression of MTG1 (santa cruz, sc160545), and GAPDH (Cell Signaling Technology, 2128) as an internal reference. Test results such as figure 1 As shown, the expression of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy markers ANP and β-MHC in the hearts of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy was significantly up-regulated, and the expression of MTG1 was significantly up-regulated ( figure 1 ).
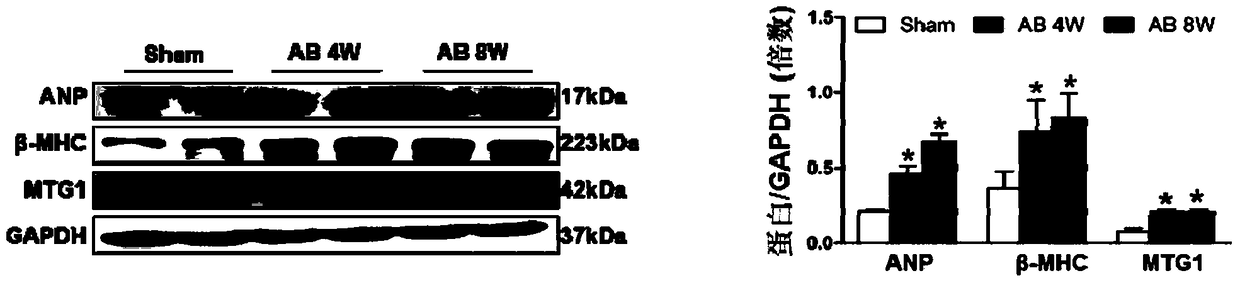
Embodiment 2
[0083] Example 2 Expression of MTG1 in the heart of wild-type mouse sham operation group and cardiac hypertrophy model group
[0084] 1. Aortic arch constriction (AB) was used to establish a mouse model of myocardial hypertrophy. The model operation process:
[0085] 1.1 Preoperative preparation
[0086] (1) Anesthesia: First weigh the mice, calculate the required amount of anesthetic (3% pentobarbital sodium) according to 90 mg / kg body weight, inject intraperitoneally, and record the injection time point. There is no obvious reaction between tail and toe pinching and the mouse is in good condition. This is the standard for successful anesthesia (generally there is no obvious reaction about 10 minutes after injection, and the mouse has a reaction to pinch toe about 50 minutes after anesthesia, and about 30 minutes after anesthesia is the best operation time).
[0087] (2) Preparation of the operation area: the skin of the left chest, left chest and armpit of the left forelimb...
Embodiment 3
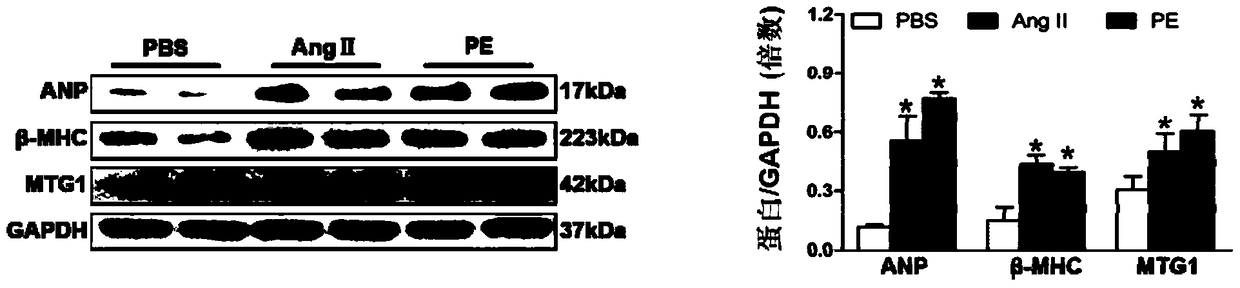
[0098] Example 3 Expression of MTG1 in cardiomyocytes stimulated by control group (PBS) or angiotensin II (Ang II) or phenylephrine (PE)
[0099] Isolate and culture newborn 1-day Sprague-Dawley neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, culture the primary cardiomyocytes for 48 hours and change the medium (see the following example 4 for the specific process of primary neonatal SD rat cardiomyocyte culture), add serum-free DMEM / F12 Starve the cardiomyocytes for 12 hours to synchronize the cells, give PBS, angiotensin II (Ang II, 1 μM) and phenylephrine (PE, 1 μM) stimulation for 48 hours respectively, and perform SDS-PAGE-immunoblotting test on proteins extracted from cardiomyocytes (Western blot), combined with antibodies that specifically recognize MTG1 protein and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy markers ANP and β-MHC to detect the expression of MTG1, GAPDH was used as an internal reference, and the detection results were as follows image 3 As shown, the expressions of ANP and β-MHC in cardio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com