Determination method of adsorption performance of drilling fluid organic treatment agent
An organic treatment and drilling fluid technology, which is applied in the measurement of high-temperature adsorption performance of drilling fluid organic treatment agents, and the measurement field of the adsorption performance of drilling fluid organic treatment agents. Inaccurate and other problems, to achieve the effect of true and reliable test results and scientific measurement methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
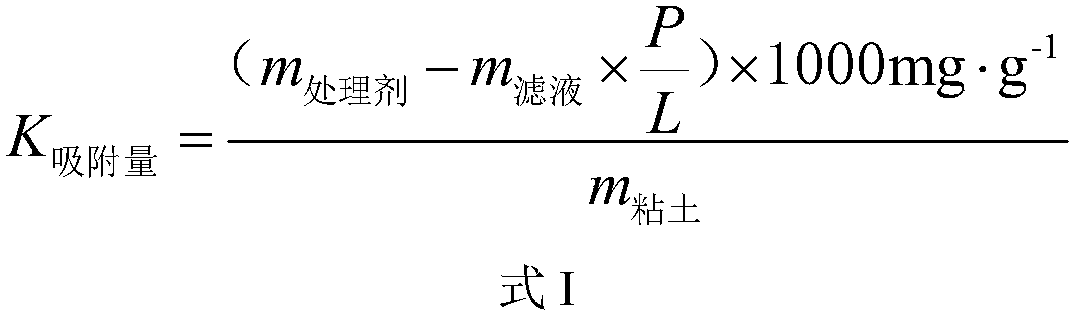
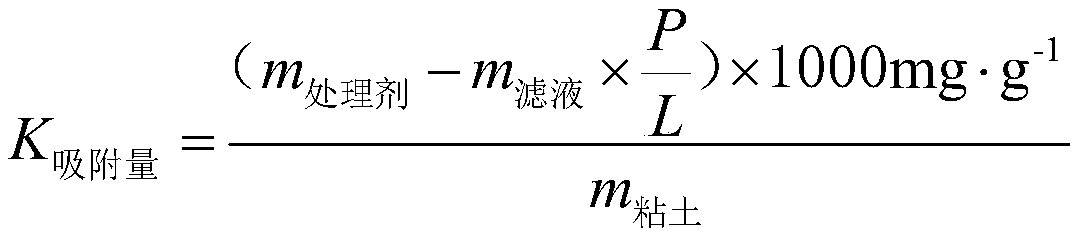
[0031] Determination of High Temperature (150°C) Adsorption Capacity of Viscosity Reducer Sulfonated Tannin in Drilling Fluid Containing 4.0% by Weight of Clay
[0032] The specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0033] 1) Fully mixing sulfonated tannins, clay and water in proportion to prepare a drilling fluid suspension with a sulfonated tannin concentration of 1.0% by weight, wherein the weight of clay accounts for 4.0% of the total weight of clay and water.
[0034] 2) Measure the apparent viscosity (AV) and dynamic shear force (YP) of the above-mentioned drilling fluid suspension, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0035] 3) Add the drilling fluid suspension to the high-temperature and high-pressure fluid loss instrument, raise the temperature to 150° C., and set the pressure to 3.5 MPa.
[0036] 4) After 1.0 hour, open the back pressure valve on the high-temperature and high-pressure filter loss meter, discard the filtrate obtained from the initial filtration...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Determination of High Temperature (150°C) Adsorption Capacity of Viscosity Reducer Tannin in Drilling Fluid Containing 4.0% by Weight of Clay
[0048] The experimental procedure is the same as that of Example 1, except that tannin is used instead of sulfonated tannin, and the measurement results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Determination of High Temperature (150°C) Adsorption Capacity of Viscosity Reducer Iron Chromium Lignosulfonate in Drilling Fluid Containing 4.0% by Weight of Clay
[0051] The experimental procedure is the same as that of Example 1, except that iron chromium lignosulfonate is used instead of sulfonated tannin, and the measurement results are shown in Table 1.
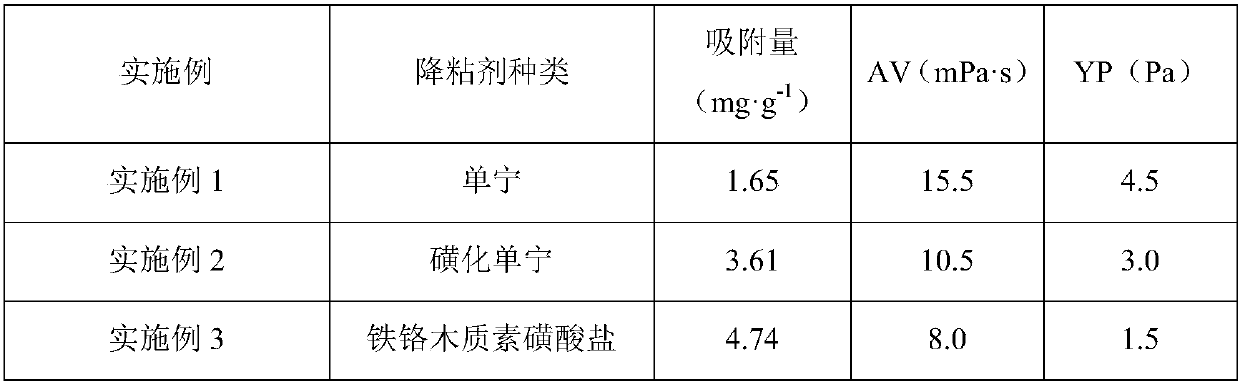
[0052] The measurement result of table 1 embodiment 1-3
[0053]
[0054] Note: AV and YP of the drilling fluid suspension are measured according to the determination method in "GB / T16783.1-2006 Oil and Gas Industry Drilling Fluid Field Test Part 1: Water-based Drilling Fluid".
[0055] According to the measurement results shown in Table 1, it can be seen that the greater the adsorption amount of the viscosity reducer on the clay, the smaller the AV and YP of the drilling fluid system, which means the better the viscosity reduction effect. It shows that the greater the adsorption amount of treatment agent mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com