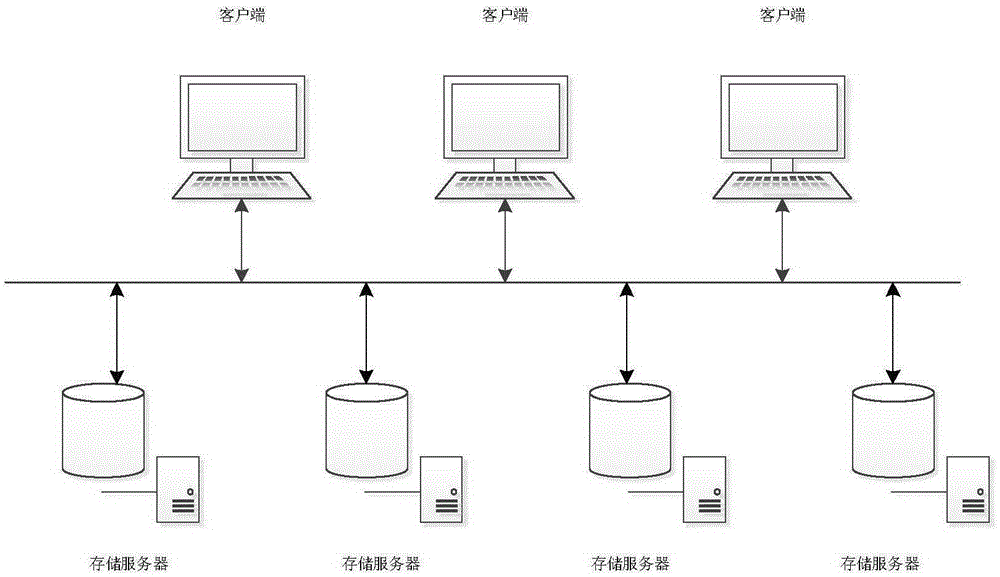
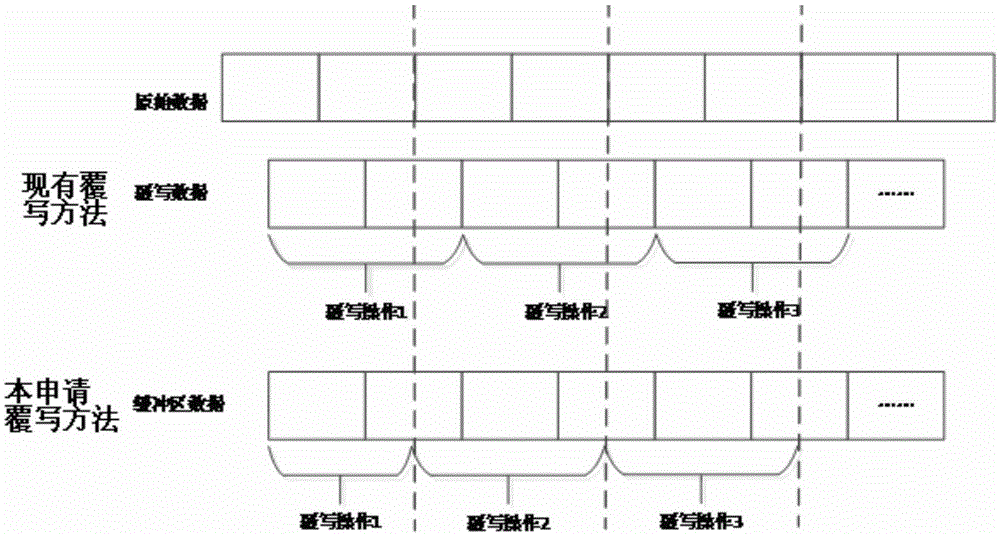
Distributed storage system-oriented erasure coding write buffer method with stream detection technology
A technology of distributed storage and buffering method, which is applied in the field of erasure code write buffering for distributed storage system with streaming detection technology, which can solve problems such as excessive read operations, reduce read operations, improve command response speed and write The effect of operating bandwidth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
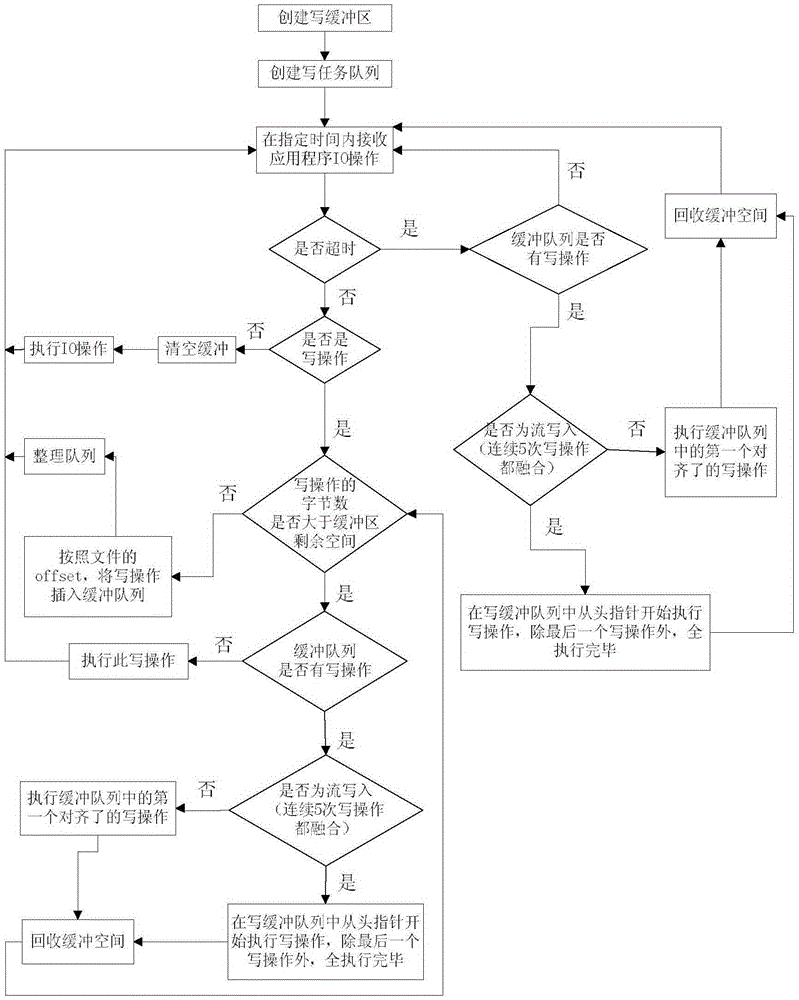
[0048] 101. Allocate memory with a size of B bytes on the client side as a buffer layer for IO write operations. B is usually set to 1M, the maximum not exceeding 1G;
[0049] 102. Establish an IO write operation queue, and all buffered IO write operations form a queue in a linked list structure. The queue head pointer points to the first incoming IO write operation, and the queue tail pointer points to the last incoming IO write operation. The queue is initially empty.
[0050] 103. Receive an application IO operation within a specified time, that is, receive an IO operation from a user program;
[0051] "Receiving application IO operations within a specified time" means that the client waits to receive the IO operation commands issued by the user operation application. If the IO operation is not received after the preset time, it will be processed as timeout.
[0052] 104. Determine whether the operation has timed out;
[0053] 105. In the case of no timeout, judge wheth...
Embodiment 2
[0056] 201. Allocate memory with a size of B bytes on the client as a buffer layer for IO write operations. B is usually set to 1M, the maximum not exceeding 1G;
[0057] 202. Establish an IO write operation queue, and all buffered IO write operations form a queue in a linked list structure. The queue head pointer points to the first incoming IO write operation, and the queue tail pointer points to the last incoming IO write operation. The queue is initially empty.
[0058] 203. Receive an IO operation from a user program;
[0059] 204. Determine whether the operation has timed out;
[0060] 205. In the case of no timeout, determine whether the IO operation is a write operation;
[0061] 206. If it is a write operation, determine whether the data volume (for example 128KB) of the write operation is greater than the remaining space of the buffer layer;
[0062] 207. If it is larger than the remaining space (for example, 256KB), determine whether there are other write opera...
Embodiment 3
[0065] 301. Allocate memory with a size of B bytes on the client as a buffer layer for IO write operations. B is usually set to 1M, the maximum not exceeding 1G;
[0066] 302. Establish an IO write operation queue, and all buffered IO write operations form a queue in a linked list structure. The queue head pointer points to the first incoming IO write operation, and the queue tail pointer points to the last incoming IO write operation. The queue is initially empty.
[0067] 303. Receive an IO operation from a user program;
[0068] 304. Determine whether the operation has timed out;
[0069] 305. In the case of no timeout, judge whether the IO operation is a write operation;
[0070] 306. If it is a write operation, determine whether the data volume (for example 128KB) of the write operation is greater than the remaining space of the buffer layer;
[0071] 307. If it is less than the remaining space (for example, 64KB), insert the write operation into the buffer queue acc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com