Efficient heat dissipation substrate for optoelectronic devices
A technology for optoelectronic devices and heat-dissipating substrates, which is used in electrical solid-state devices, electrical components, and semiconductor devices. Thermal conductivity, the effect of improving the overall heat dissipation capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
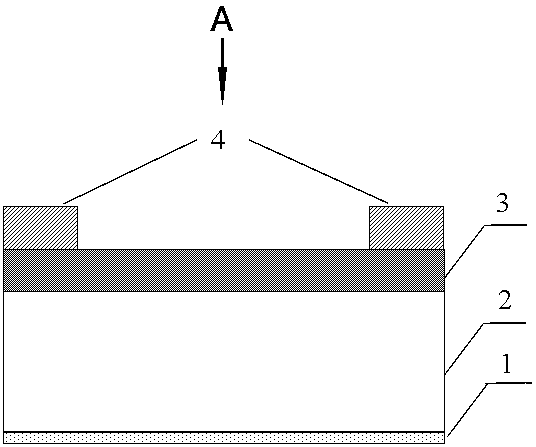
[0024] In this example, see figure 1 , a high-efficiency heat dissipation substrate for optoelectronic devices, heat dissipation is carried out from its conductive layer 4, and a composite heat dissipation substrate is formed by stacking a heat-conducting insulating layer 3, a metal substrate 2 and a carbon-based material coating 1 in sequence, wherein the heat-conducting insulating layer 3 The surface on the other side of the carbon-based material coating 1 is closely combined with the conductive layer 4 of the optoelectronic device, and the exposed surface on the other side of the carbon-based material coating 1 forms the external heat dissipation surface of the composite heat dissipation substrate, which passes the heat generated by the optoelectronic device during operation through the conductive layer 4, Then it is led out through the heat-conducting insulating layer 3, the metal substrate 2 and the carbon-based material coating 1 in order to dissipate heat.
[0025] In t...
Embodiment 2
[0028] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
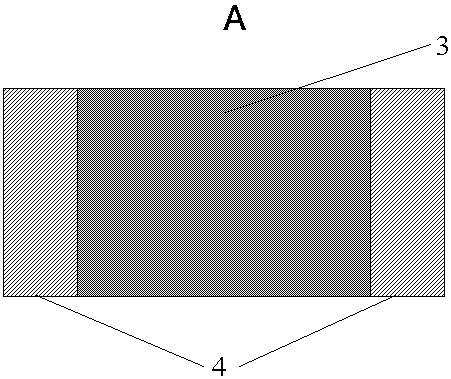
[0029] In this example, see figure 2 and image 3 A high-efficiency heat dissipation substrate for optoelectronic devices includes a metal substrate 2, a carbon-based material coating 1 located on the lower surface of the metal substrate, a thermally conductive insulating layer 3 located on the upper surface of the metal substrate, and a conductive layer 4 located on the upper surface of the thermally conductive insulating layer. The metal substrate 2 is made of copper and has a thickness of 1.5 mm. The graphene / carbon nanotube composite coating on the lower surface of the metal substrate 2 has a thickness of 1 nm. A thermally conductive insulating layer 3 is covered on the surface of the metal substrate 2, and the material of the thermally conductive insulating layer 3 is AlN doped with element zirconium, with a thickness of 5um and a thermal conductivity of 20 W / (m·K). There is a conducti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com