Soft-in soft-out self-iterative soft equalization underwater acoustic communication method based on receiving hydrophone array
A hydrophone array and underwater acoustic communication technology, which is applied to the shaping network, baseband system, and baseband system components in the transmitter/receiver, and can solve problems such as limited performance and poor reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
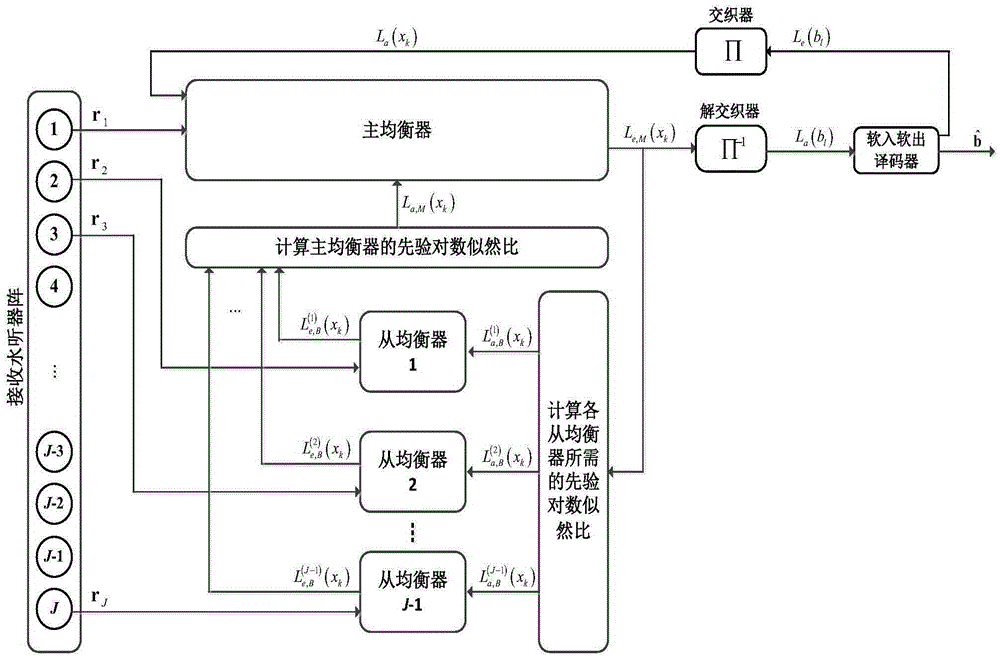
[0045] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Description of this embodiment, the soft-in and soft-out iterative soft-balanced underwater acoustic communication method based on the receiving hydrophone array includes the following steps:
[0046] Step 1. The communication transmitter adopts binary QC-LDPC encoding to channel encode the binary information bit stream b, b=[b 1 ,b 2 ,...,b l ,...b L ], L is the length of the binary information bit stream, where b l ∈{0,1}, l=1,...,L; perform interleaving and symbol mapping on the coded information bit stream, and obtain the symbol stream x=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x k ,...x K ], K is the length of the symbol stream, k∈[1,K]; x k Can be any phase modulation symbol (as BPSK or QPSK etc.), the present invention is example with BPSK modulation; With x=[x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x K ] modulated onto the designated carrier and sent out;
[0047] Step 2, the transmission signal of step 1 reaches the receiving end of each hydrophone in...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: The branch equalizer includes two parts: channel estimation and channel equalization. The channel equalization algorithm in the branch equalizer described in step 2 of this embodiment adopts a decision feedback equalization algorithm, a linear equalization algorithm or a decision feedback equalization algorithm. Combination algorithm with linear equalization algorithm.
[0050] Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: The channel estimation part of the branch equalizer described in step 2 in this embodiment adopts the classical adaptive RLS algorithm.
[0052] Other steps are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com