Wireless sensor routing method based on routing table node energy
A wireless sensor and node energy technology, applied in the field of data transmission, can solve the problems of only considering the next hop, frequent changes in the routing table, unfavorable routing table management, etc., to improve the life cycle, save sensor energy, and choose reasonable routes Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
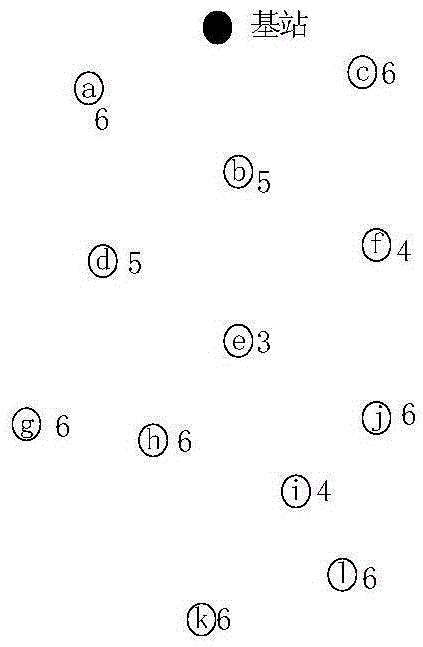
[0065] A wireless sensor network routing method based on node energy of a routing table, establishing a route to a base station, comprising the following steps:
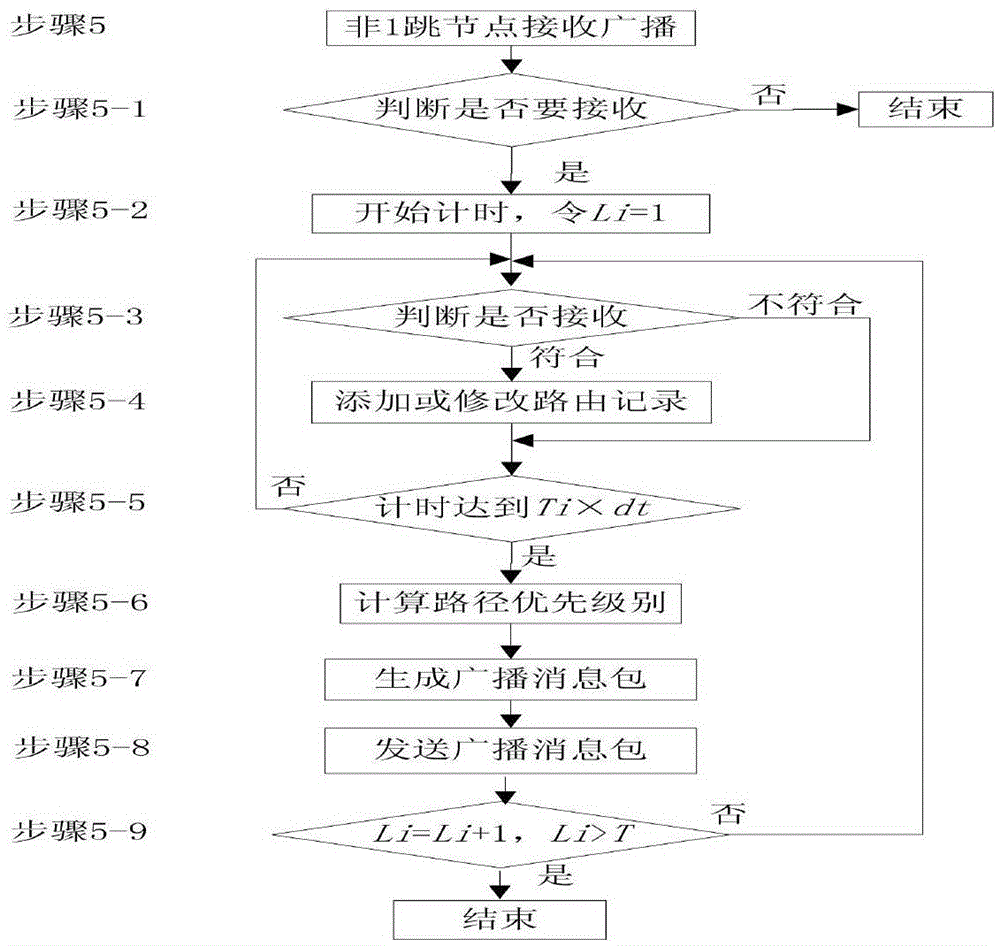
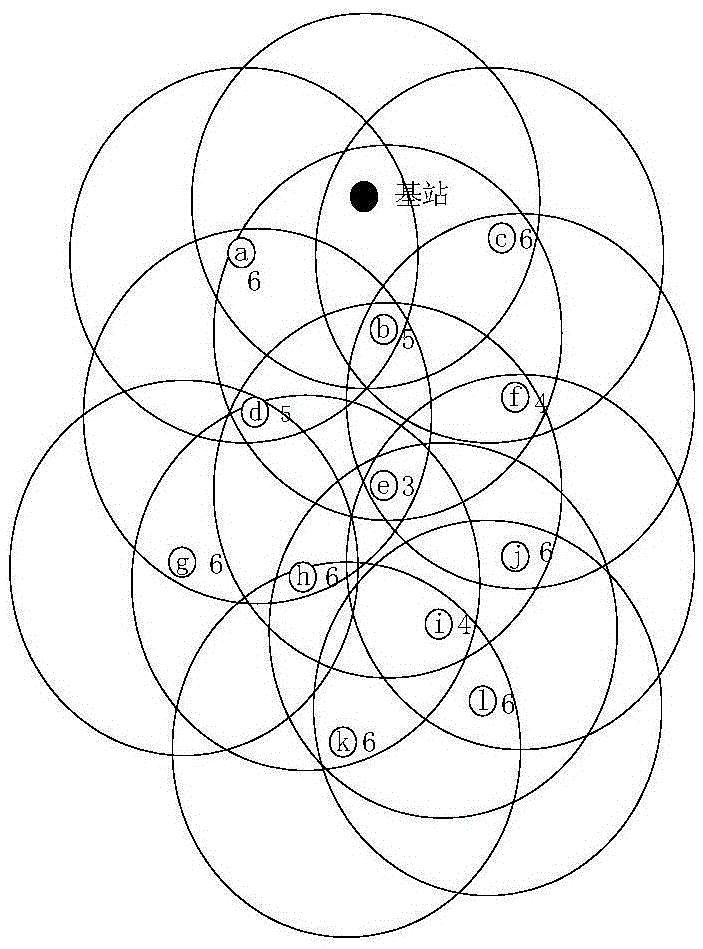
[0066] Step 1: Set the maximum number of times T that the node forwards the broadcast message, T≥2, the first T-1 times of the maximum number of times the node forwards the broadcast message, the node adopts the cross-broadcast method to propagate, and the T-th time adopts the transfer broadcast method to forward the broadcast packet forward ; Set the forwarding delay time dt; the forwarding delay time dt is determined by the time when the node receives the broadcast message forwarded by the surrounding nodes, including processing signal collision time;
[0067] Step 2: The base station sends a broadcast message to the network: the structure of the broadcast message is shown...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com