Heavy manned walking robot steering-by-wire system road feeling simulation method
A technology of steer-by-wire and road sense simulation, which is applied in control/regulation systems, vehicle position/route/height control, instruments, etc. It can solve problems such as lack of road sense, achieve rapid response and improve anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
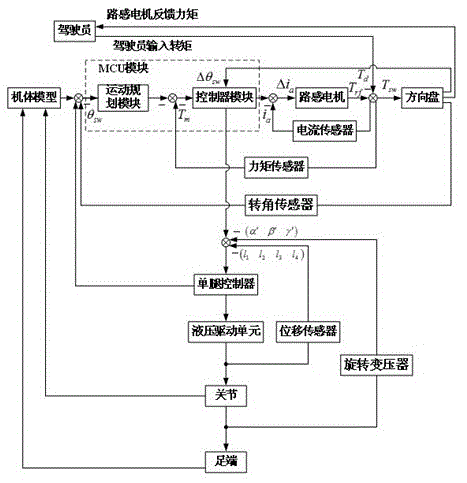
[0021] Specific implementation mode 1: refer to the attached figure 1 Describe this embodiment in detail, the road feeling simulation method of the linear steering system of a heavy-duty manned legged robot described in this embodiment first needs to determine the basic composition of the steering-by-wire system. The steering-by-wire system includes a steering wheel module, a motion control module and Steering execution module, the steering wheel module is composed of steering wheel, steering shaft, torque sensor, angle sensor, road sense motor, reducer and motor current sensor; the motion control unit module is composed of motion planning unit and motion controller; The steering execution module is composed of a single-leg controller, three free hydraulic drive legs, a rotary transformer, a pressure sensor and a displacement sensor.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0022] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is based on the structure of the steering-by-wire system of the heavy-duty manned legged robot described in specific embodiment 1, and further explains the role of each module in the road feeling simulation link. In this embodiment, The output angle of the steering wheel is proportional to the steering radius of the body. The steering wheel used in the present invention has a unilateral forward / reverse rotation range, and the value of the steering radius of the robot determines the mode of the body’s steering. When the steering radius tends to When the turning radius is close to infinity, the robot enters the in-situ steering mode, and when the turning radius approaches infinity, the robot tends to the straight-line walking mode. In order to ensure the accuracy of manipulation and the convenience of calculation, the robot is not required to perform steering movement within the range of one-sided forward / reverse rotation of the steer...
specific Embodiment approach 3
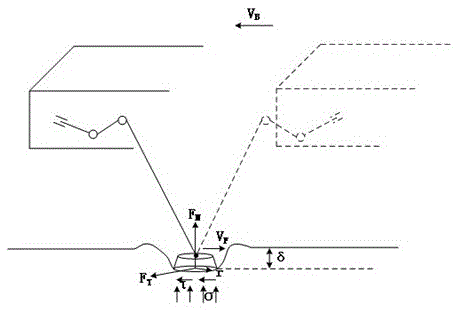
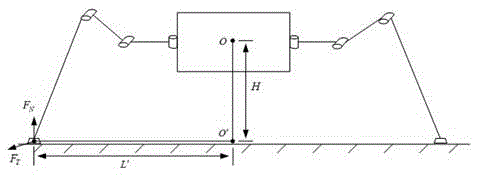
[0023] Specific embodiment 3: This embodiment is based on the structure of the steering-by-wire system of a heavy-duty manned legged robot described in specific embodiment 1, and further explains the role of each module in the road feeling simulation link. In this embodiment, The output rotation angle of the steering wheel is sent to the motion control unit module, and its internal motion planning unit includes three parts: on the one hand, the coordinates of the landing point of the support phase and the foot end of the swing phase are solved through the established kinematic equations during the robot's steering motion. track, and send the foot information to the single-leg controller; on the other hand, through the established robot dynamics model, the corresponding relationship between the analytical value of the foot-ground contact force and the actual torque of each joint is deduced, and then the single-leg The controller solves the actual torque of each joint through the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com