Under-actuated biped walking robot based on flexible drivers
A walking robot and flexible drive technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as insufficiently compact structure, unnatural gait, and high energy consumption, and achieve the effects of convenient and fast disassembly, reduction of instantaneous torque, and anthropomorphic actions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
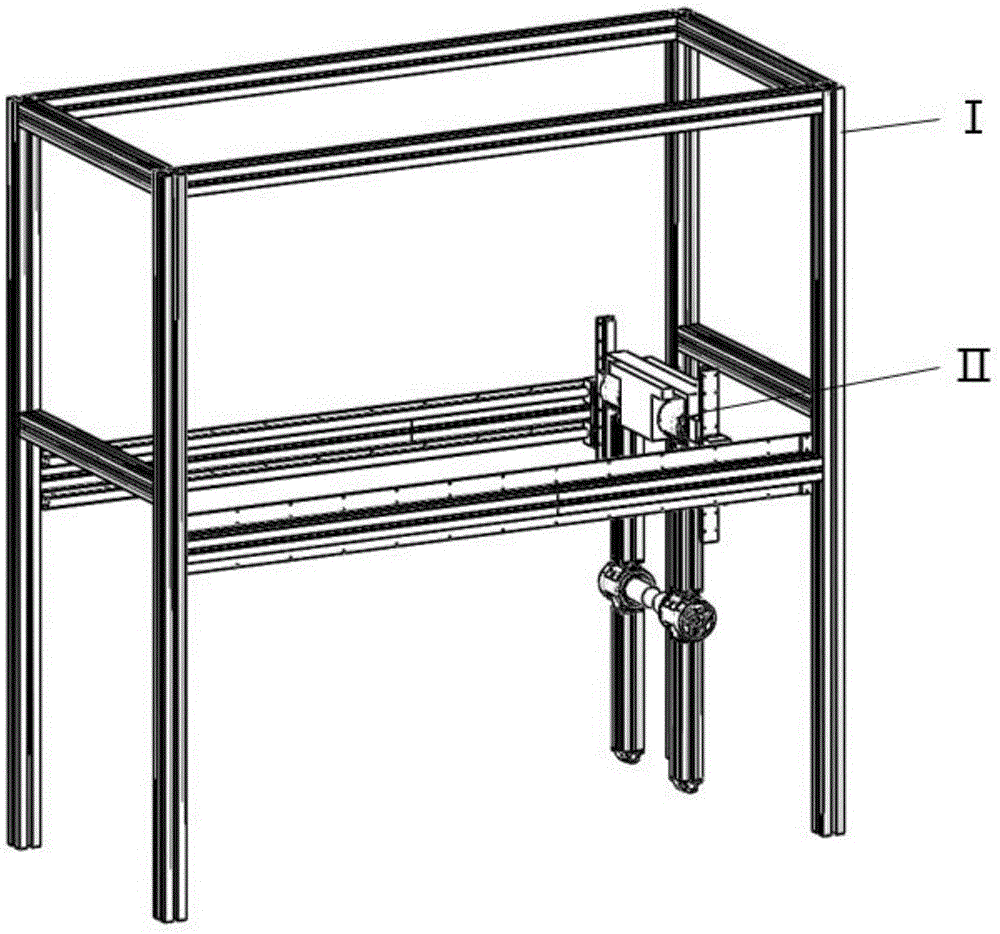
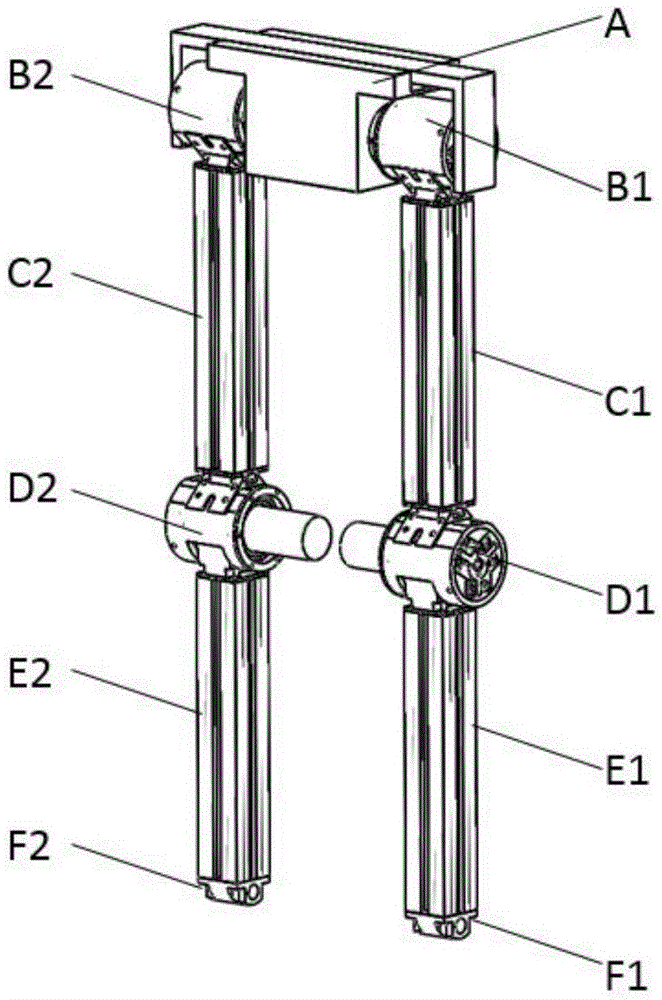
[0032] In terms of overall structural design, the present invention provides an underactuated biped walking robot based on a flexible driver, such as figure 2 As shown in , the robot has four degrees of freedom, including the joint module with only the pitch degree of freedom and the underactuated foot assembly. Each module is connected in a series-parallel manner, and the order is as follows: foot assembly F1—calf link E1—knee joint D1—thigh link C1—hip joint B1—crotch A—hip joint B2—thigh link C2—knee Joint D2—calf link E2—foot assembly F2. The rotation axes of each pitching degree of freedom are parallel to each other, and the robot is in an inverted U shape when standing. Such as figure 1 The figure shows that in the operating environment built by the robot, the robot as a whole can perform plane movement in the sagittal plane.
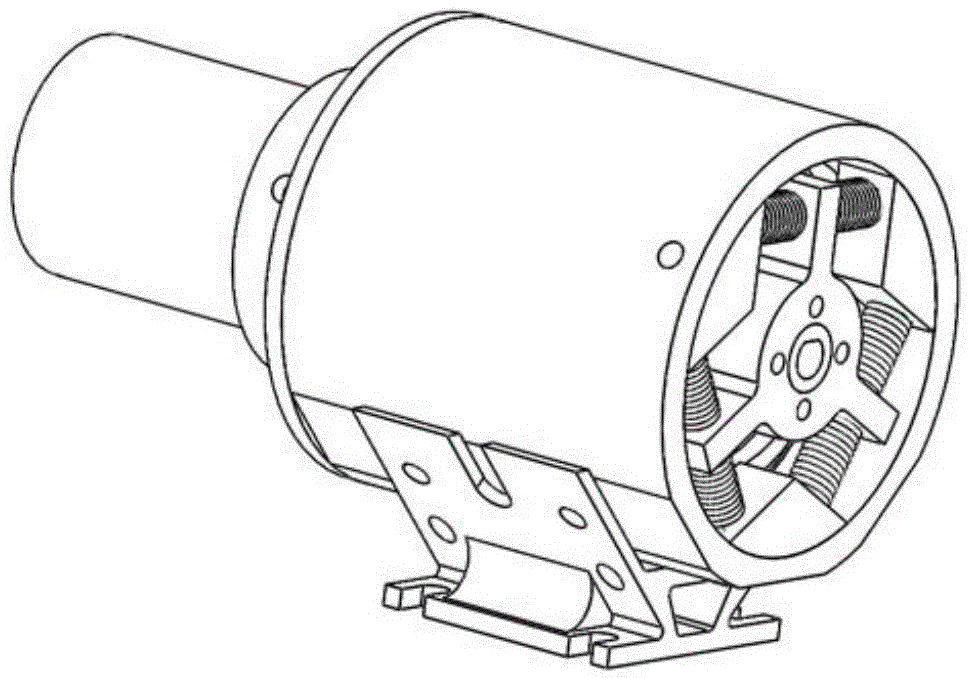
[0033] Such as image 3 Shown is the flexible actuator-based hip joint module of this biped walking robot. The pitch rotation degree of fre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com