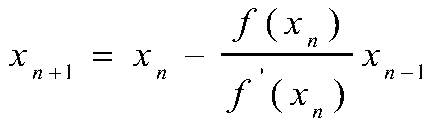Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Natural gait" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
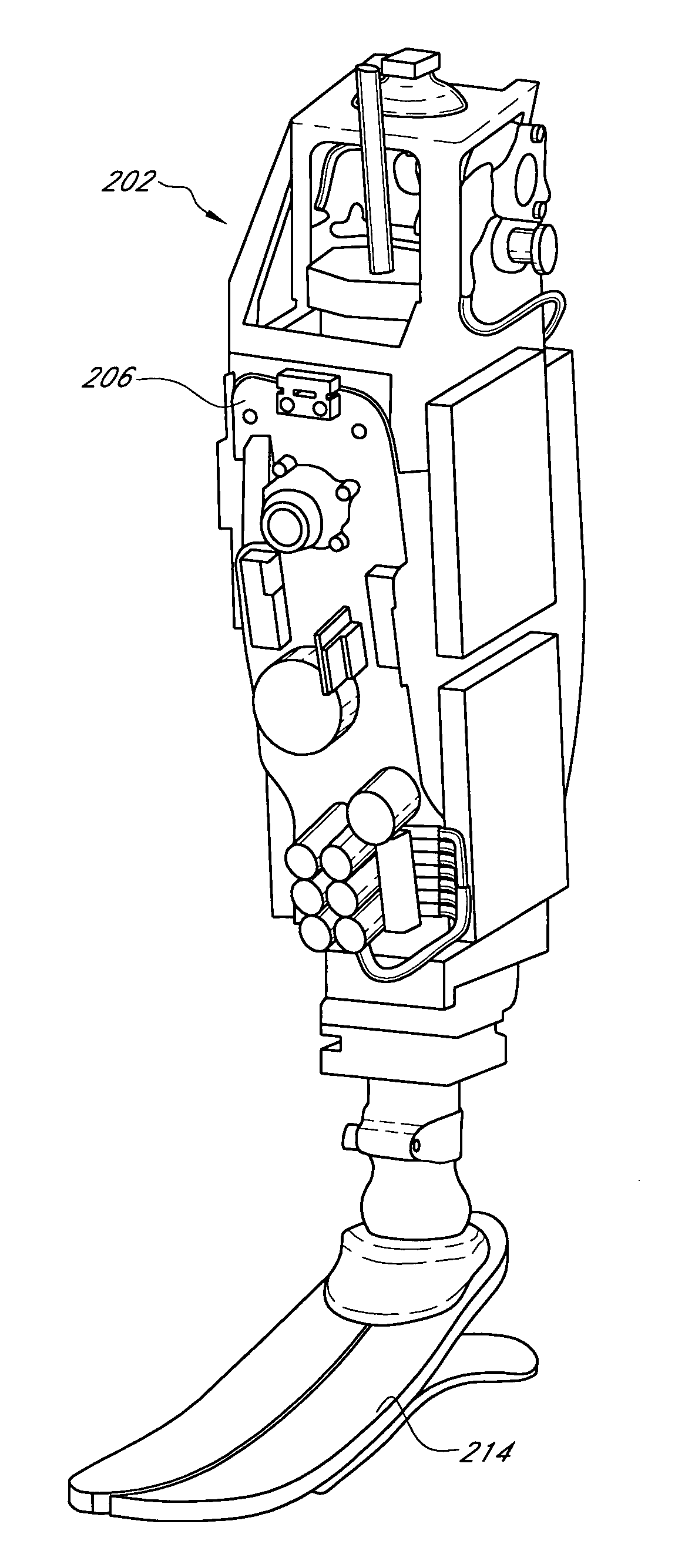
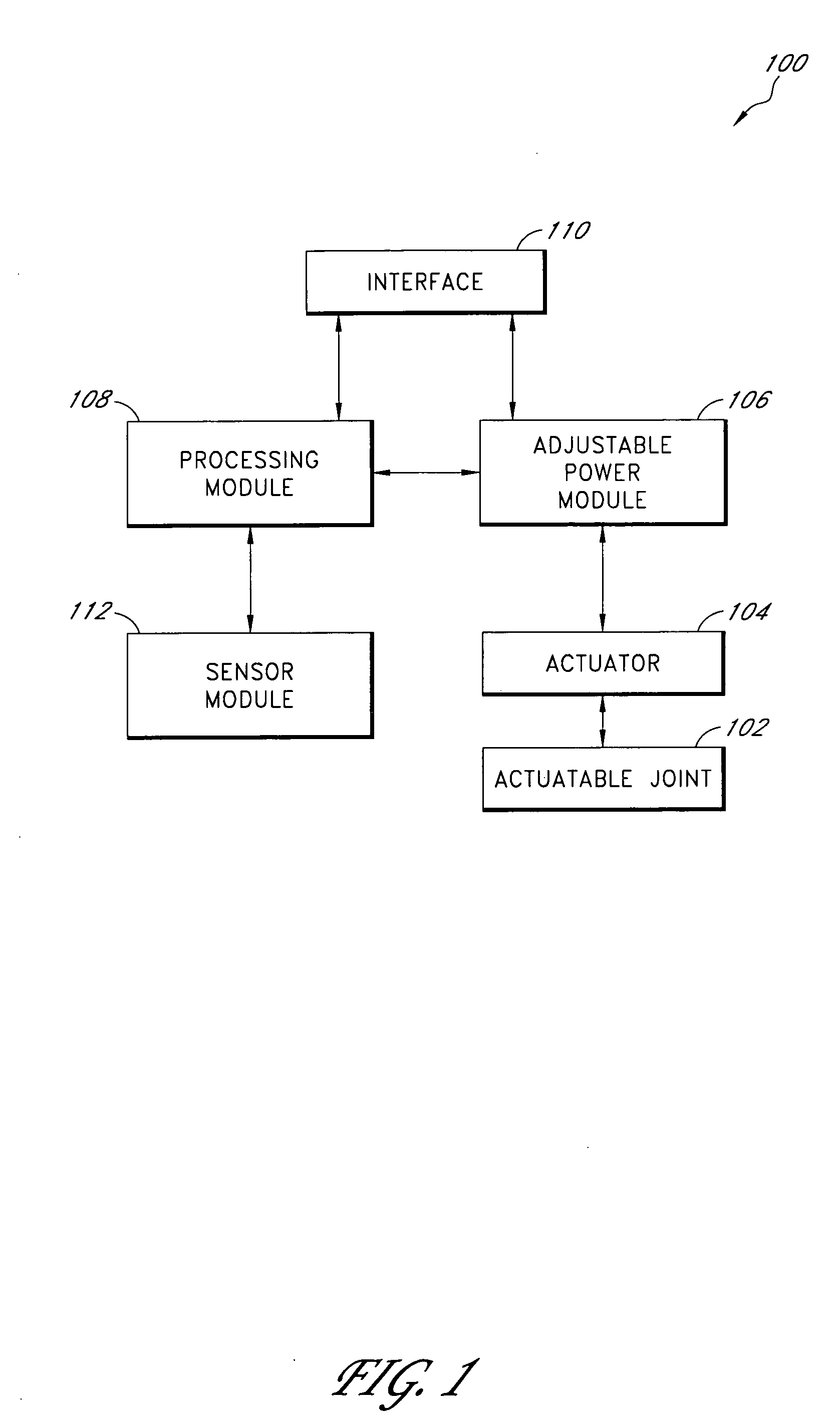
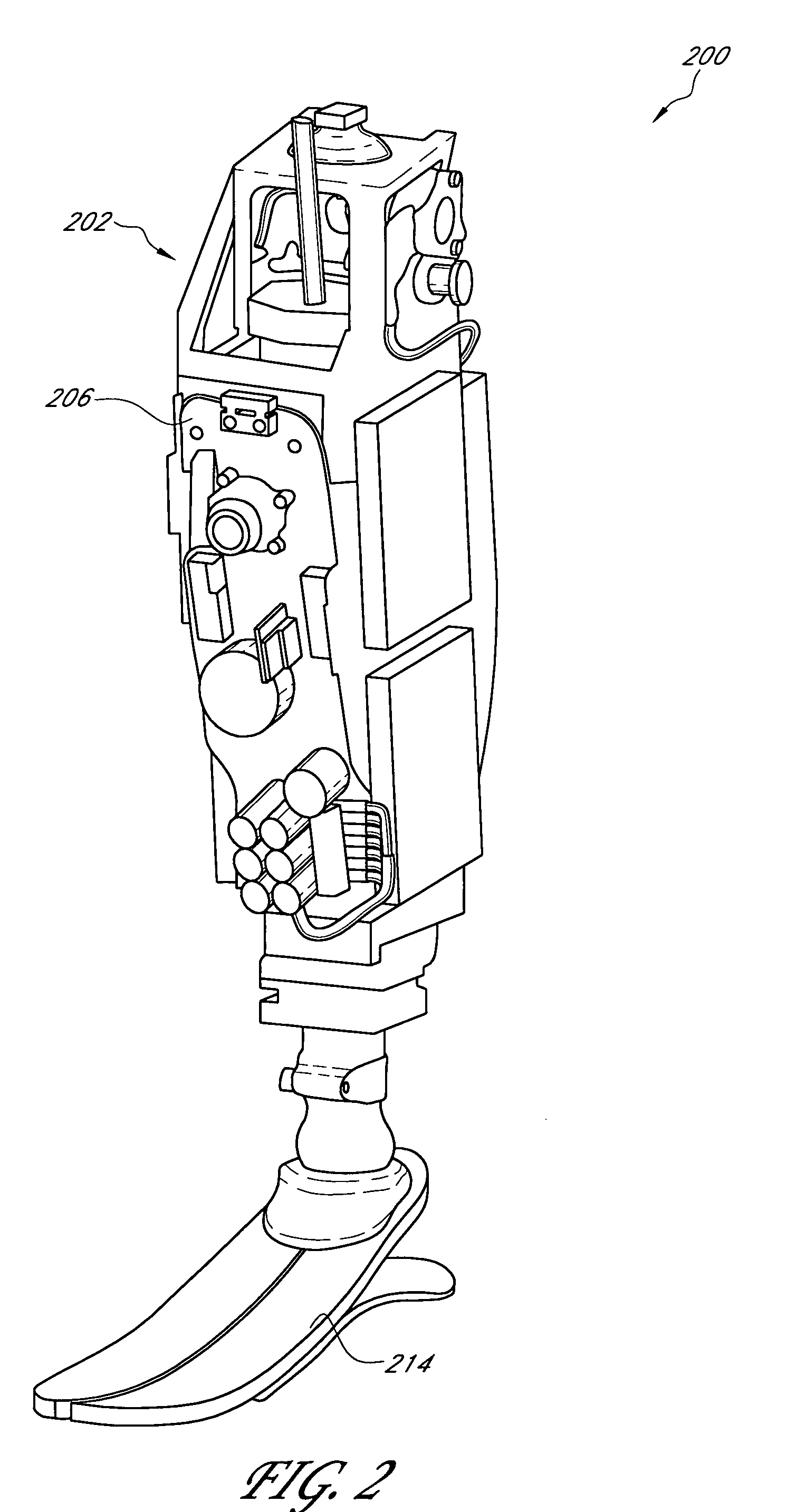
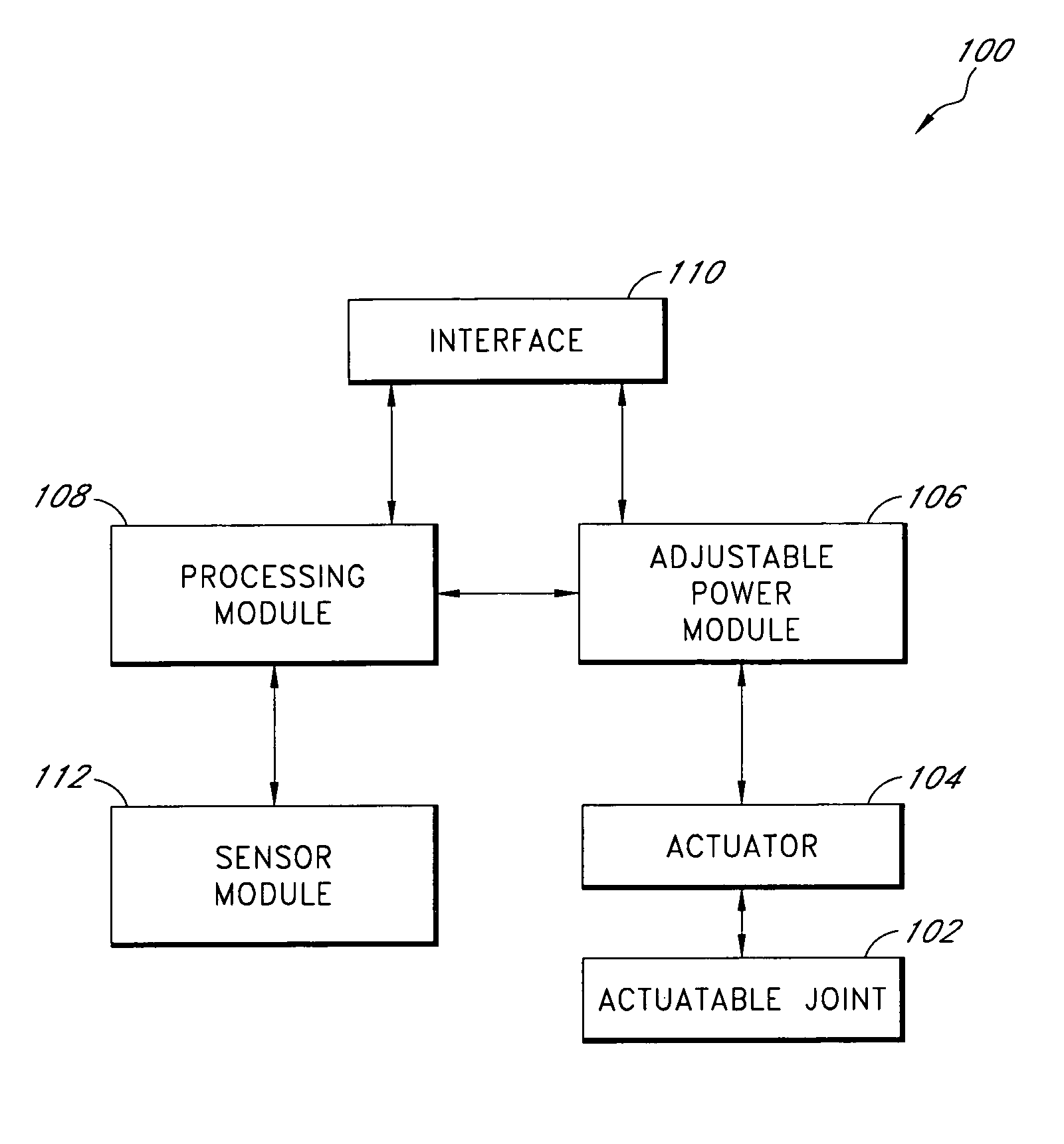
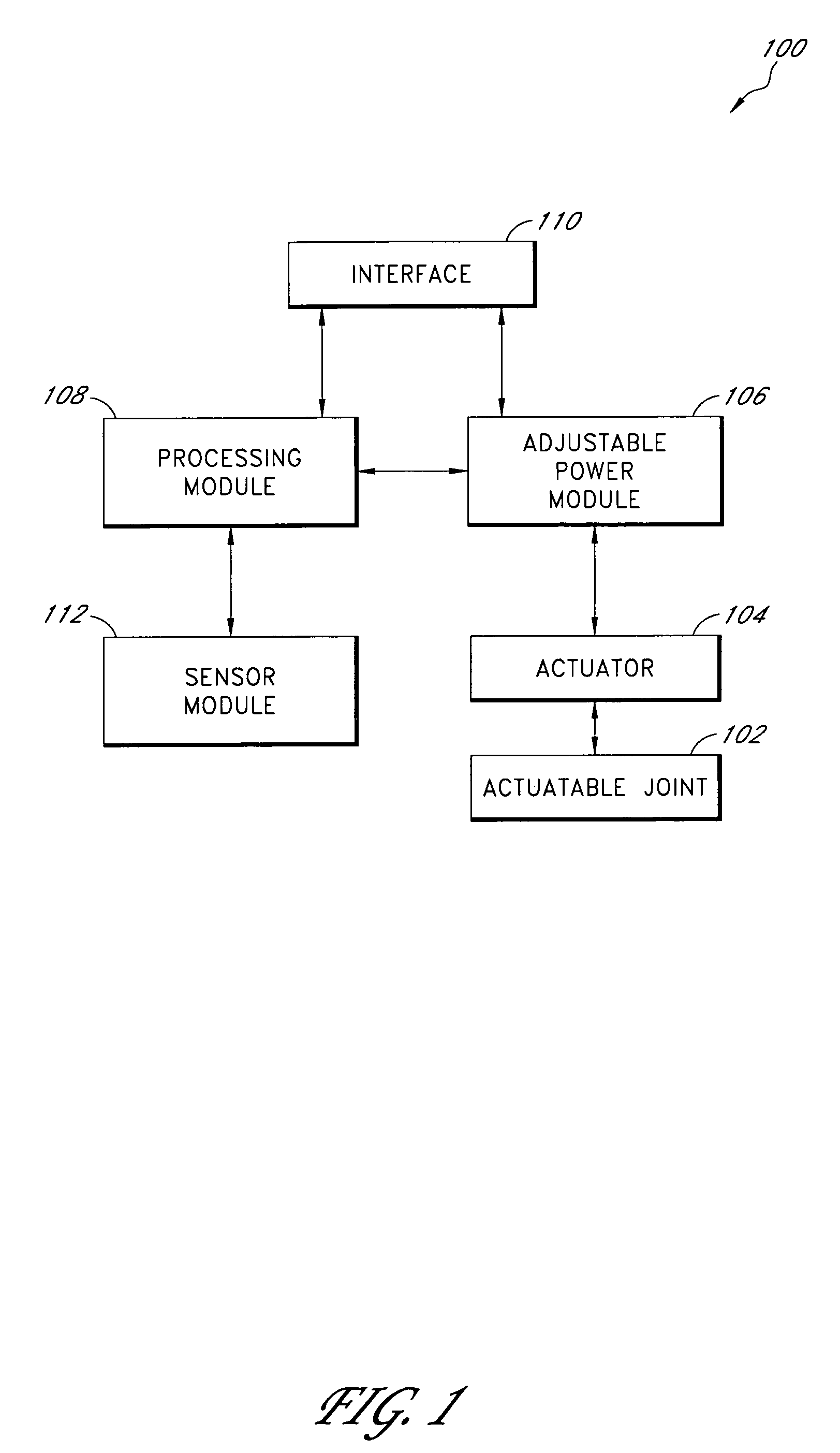
Prosthetic and orthotic systems usable for rehabilitation
ActiveUS20060173552A1Smooth rotationReduce energy consumptionSurgeryChiropractic devicesDevice prostheticMuscle power
Disclosed are adjustable powered rehabilitation devices and methods for using the same to rehabilitate and / or train a user. The rehabilitation devices preferably have a plurality of selectable power settings that correspond to one or more rehabilitation-oriented actions or functions of the rehabilitation devices. For example, the power of the rehabilitation device may be selected based on a need, ability, muscle-power and / or physiological characteristics of the user. For instance, a rehabilitation device may be operated at a relatively low power setting to allow a patient to use his or her own muscle power when moving with the rehabilitation device. The rehabilitation device may also include an adjustable sensitivity level that corresponds to a user difficulty in triggering a particular rehabilitation-oriented action. The powered rehabilitation device may also temporarily be used to train a user in interacting with a passive or more conventional prosthetic device.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Prosthetic and orthotic systems usable for rehabilitation
ActiveUS8048007B2Smooth rotationReduce energy consumptionSurgeryChiropractic devicesProsthesisDevice prosthetic
Disclosed are adjustable powered rehabilitation devices and methods for using the same to rehabilitate and / or train a user. The rehabilitation devices preferably have a plurality of selectable power settings that correspond to one or more rehabilitation-oriented actions or functions of the rehabilitation devices. For example, the power of the rehabilitation device may be selected based on a need, ability, muscle-power and / or physiological characteristics of the user. For instance, a rehabilitation device may be operated at a relatively low power setting to allow a patient to use his or her own muscle power when moving with the rehabilitation device. The rehabilitation device may also include an adjustable sensitivity level that corresponds to a user difficulty in triggering a particular rehabilitation-oriented action. The powered rehabilitation device may also temporarily be used to train a user in interacting with a passive or more conventional prosthetic device.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Control method of gait rehabilitation training robot
InactiveCN103536424AIncrease active participationExercise does not affectChiropractic devicesSacroiliac jointAngular velocity
The invention discloses a control method of a gait rehabilitation training robot. The control method is applied in an online gait planning technique, moving parameters of a patient's healthy limb in each walking cycle are detected, functional relationship of healthy limb hip joint angular displacement and time, functional relationship of hip joint angular velocity and time, functional relationship of knee joint angular displacement and time and functional relationship of knee joint angular velocity and time are acquired, and a gait model is produced and serves as an evaluation standard of patient's unhealthy limb movement; on the basis, angular displacement, angular velocity and force feedback information are used to perceive moving states of a unhealthy limb, the movement states are compared with that of the healthy gait model, situation whether the gait of the unhealthy limb is normal or not is analyzed, if so, the robot is controlled to move with the patient's unhealthy limb; if not, the robot is controlled to provide assistance to assist the unhealthy gait to be consistent with normal gait, intended movement compensation of the unhealthy limb is implemented, and human-machine cooperative rehabilitation training can be completed.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
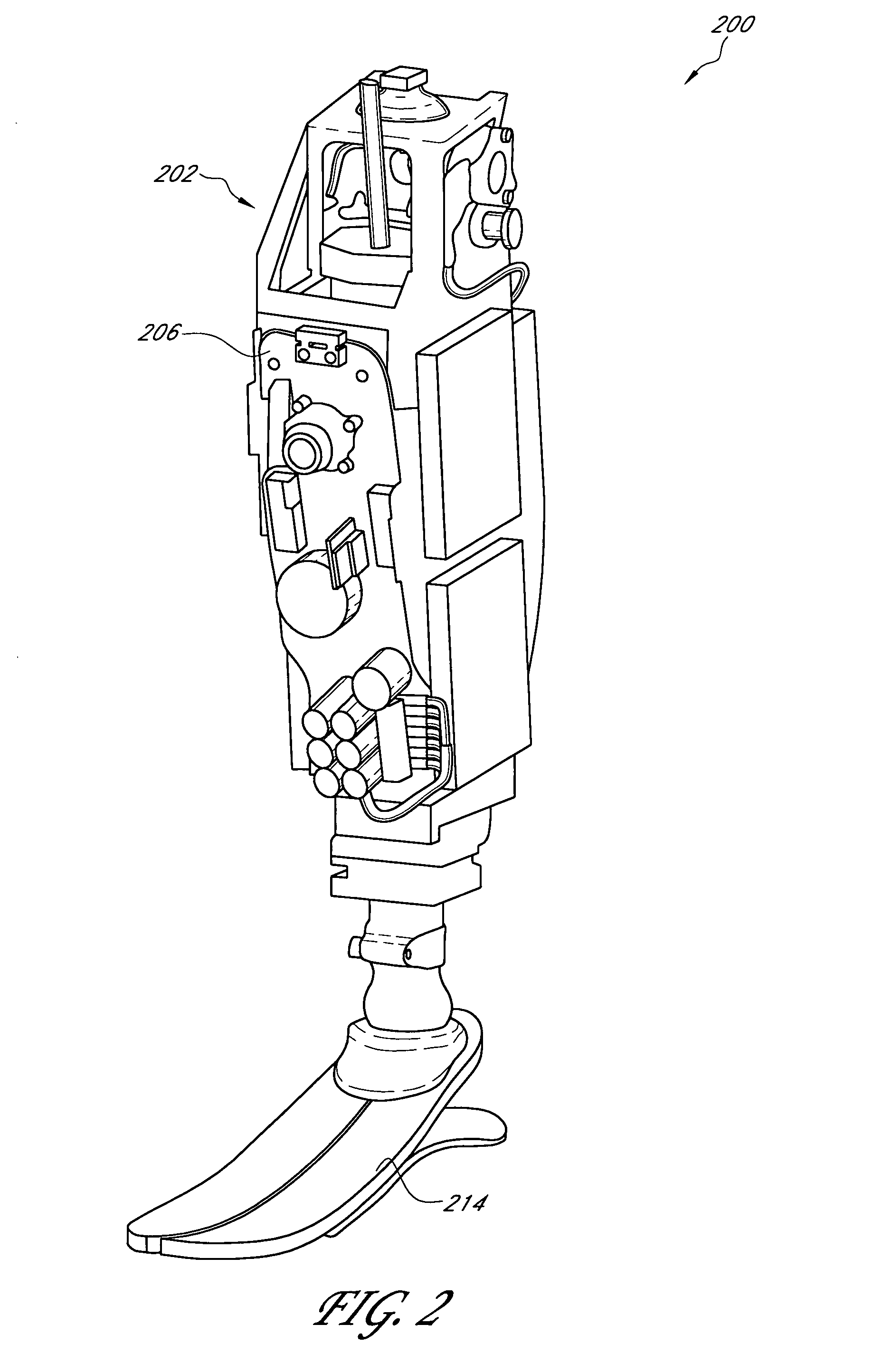
Electronically controlled prosthetic knee
InactiveUSRE42903E1Negligible changeNegligible pressureSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetorheological fluidControl theory
The present invention relates to a variable-torque magnetorheologically actuated prosthetic knee which utilizes a plurality of interspersed and alternating rotors and stators to shear magnetorheological fluid in gaps formed therebetween. Advantageously, by operating in the “shear mode” there is substantially no or negligible fluid pressure buildup or change. Moreover, the multiple MR fluid gaps or flux interfaces desirably allow for the production of a large torque at low speed—eliminating the need for a transmission—and also for a wide dynamic torque range. One embodiment of the invention allows the rotors and / or stators to close the gaps therebetween to create a frictional torque component, thereby forming a “hybrid” braking system which provides a total torque or damping which is a combination of viscous torque and frictional torque.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
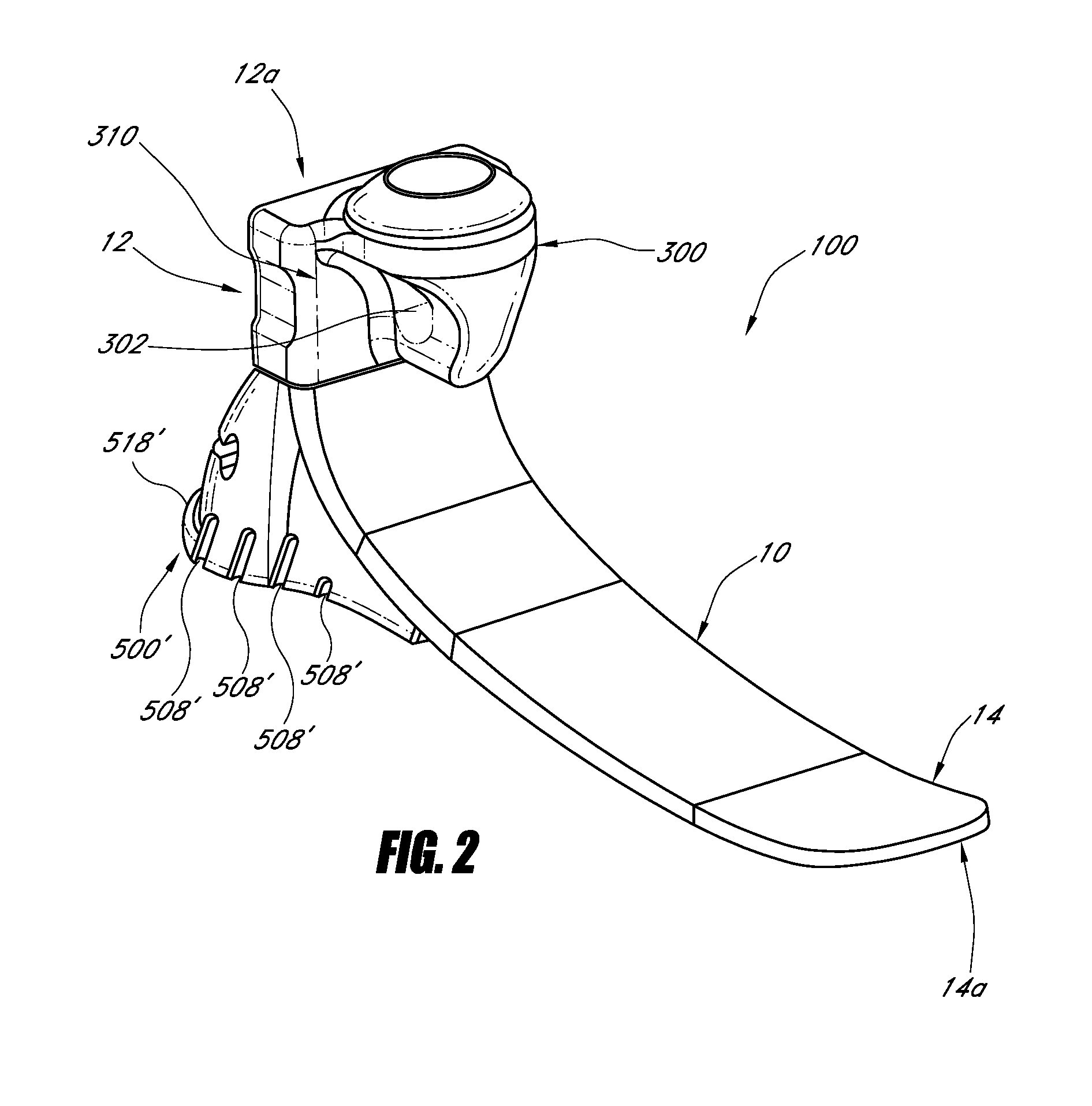
Prosthetic foot with resilient heel
ActiveUS8961618B2Improve balanceImprove stabilityAnkle jointsToe jointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHeel strike
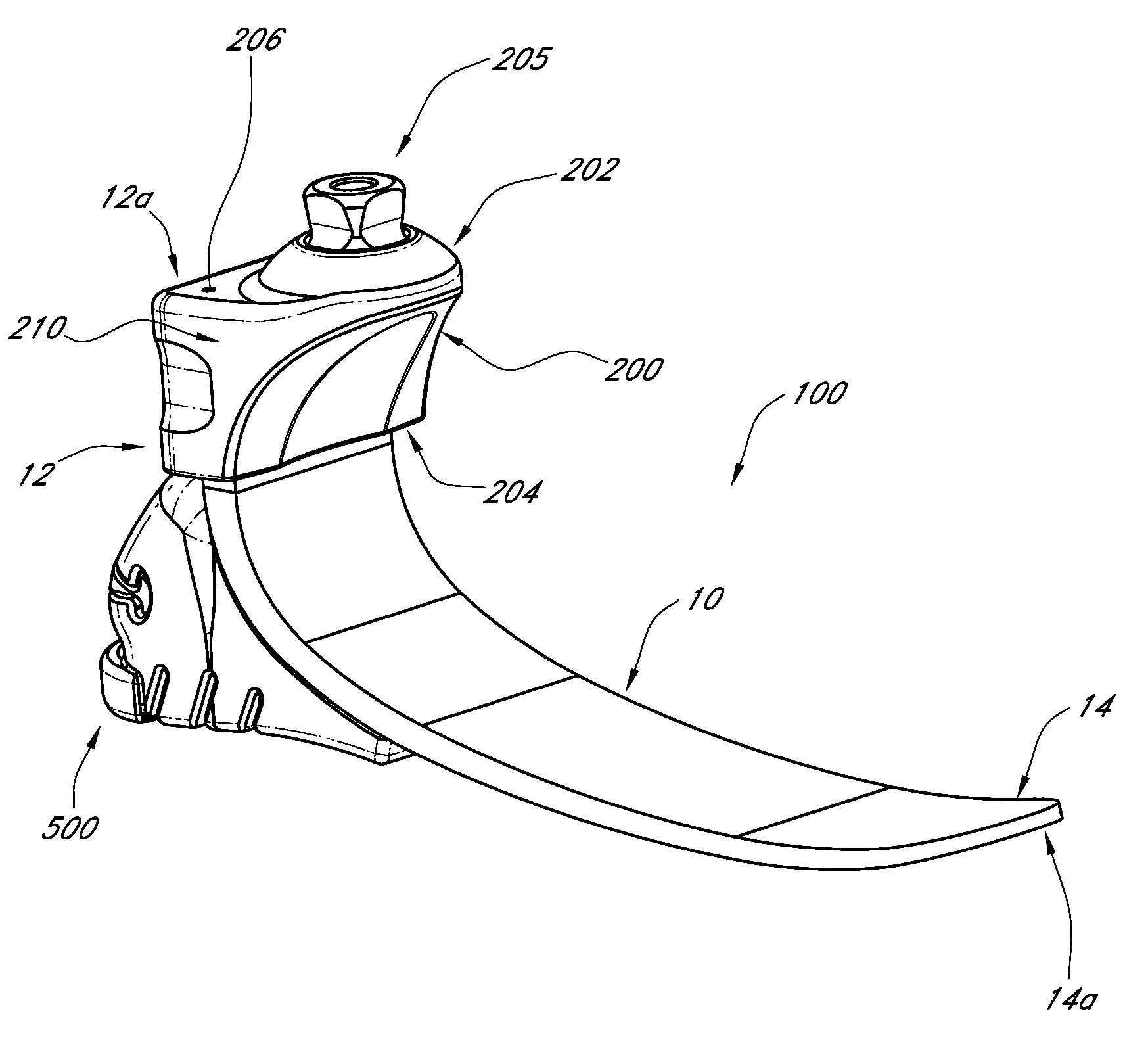
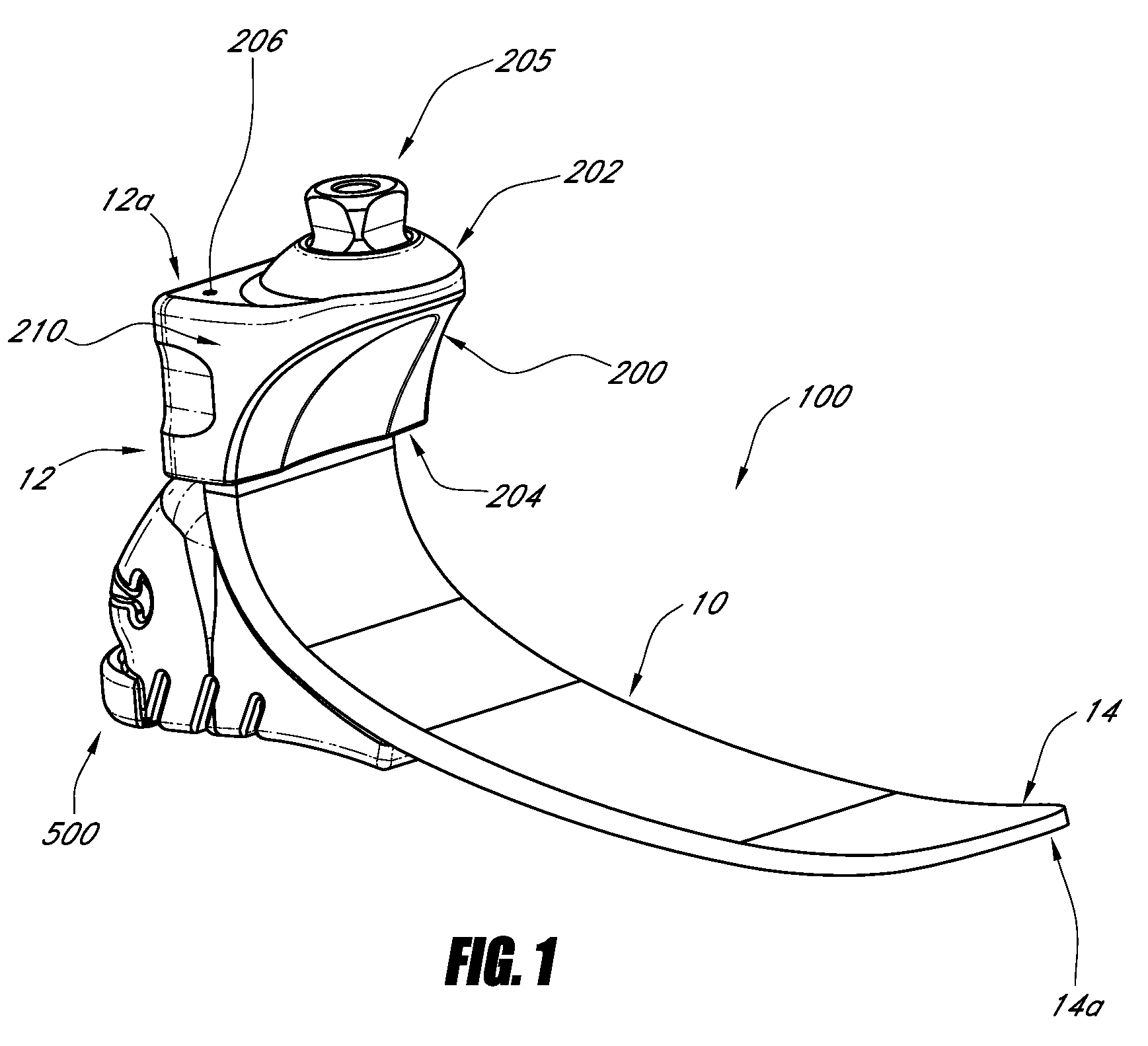
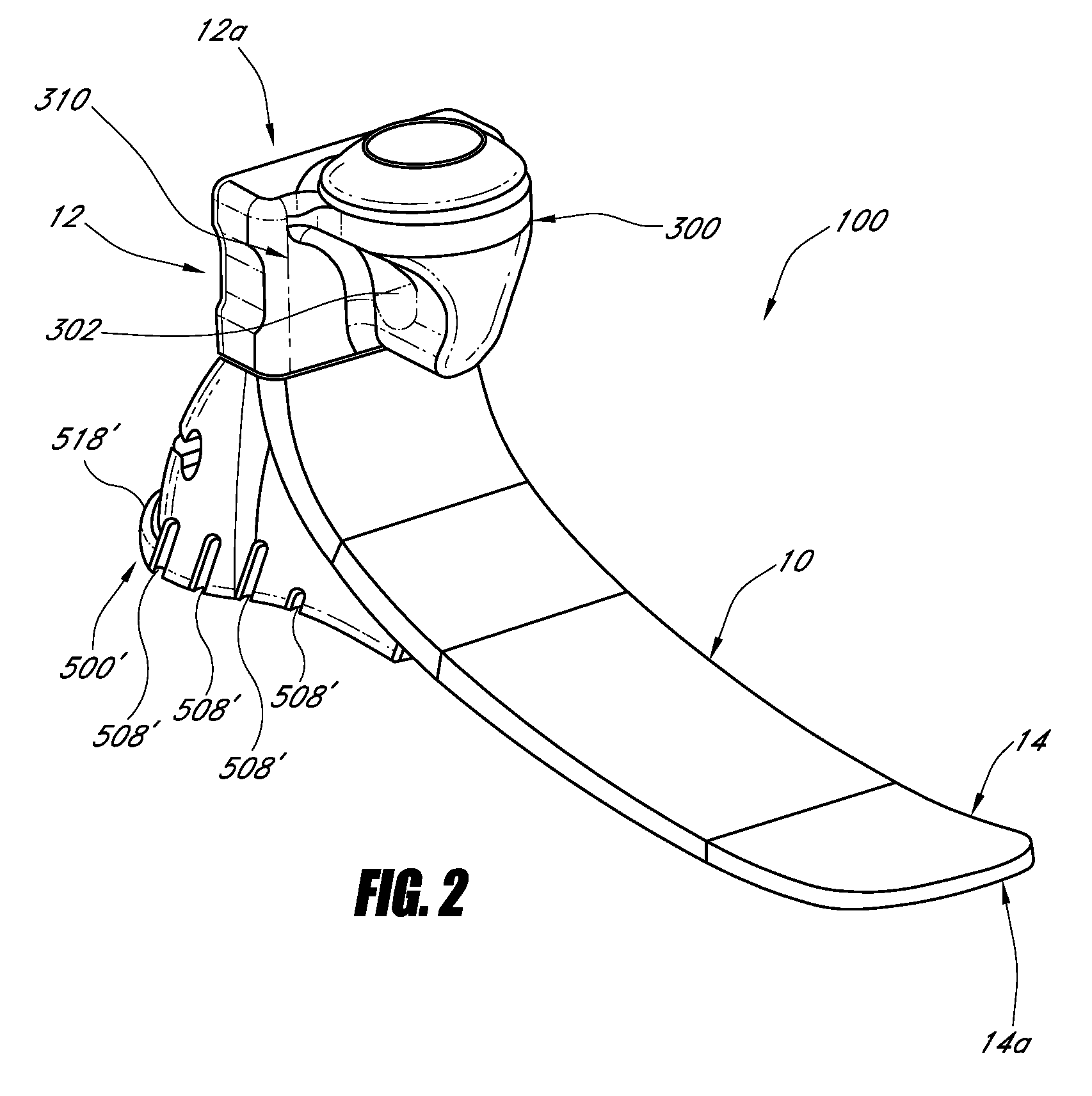
A prosthetic foot can include a resilient heel member that can be removably coupled to the bottom of a plate-like foot member of the prosthetic foot. The heel member can be made of a resilient material, such as foam. The heel member can have a shape that corresponds to a foot cover and allows the prosthetic foot to fit within a foot cover. A lip may be provided to engage with a corresponding portion of the foot cover to secure the heel member within the foot cover. A rib can be located on the bottom of the heel member to create horizontal or vertical displacement of the foot at heel strike. A recess can be created in the heel member to removably receive an insert, which can alter the stiffness of the heel member.
Owner:OSSUR HF
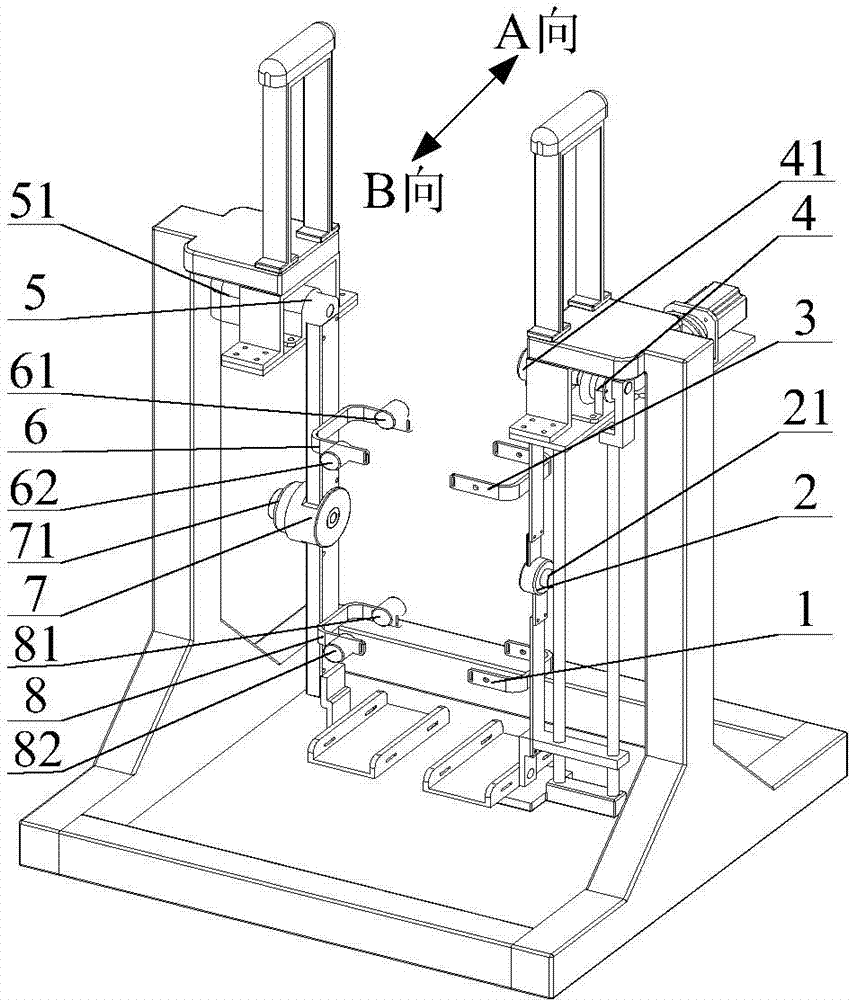
Assistive ambulatory device
InactiveUS8573612B1Reduce weightConvenient heightWalking aidsChildren furnitureAmbulatoryWeight-bearing
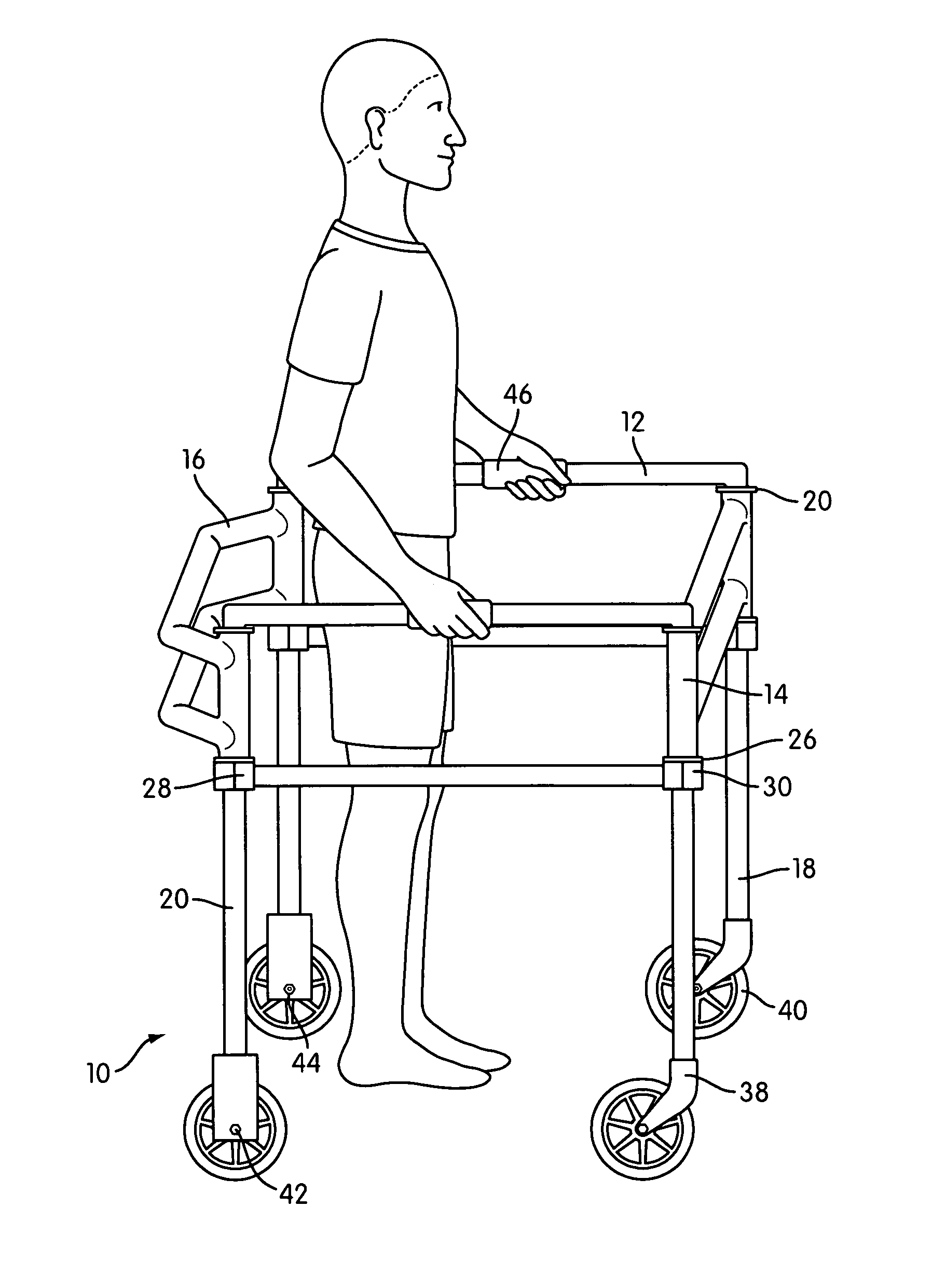
A method of producing a natural gait by a patient using an ambulatory device having a patient positioned in the middle of the ambulatory device to allow for an upright trunk, minimizing abnormal lower extremities kinematics and weight bearing on arms. By having hinged corners with an adjustable friction the device allows reciprocal arm swing when unlocked. The use of four wheels permits a continuous stepping motion that does not disrupt normal gait kinematics. Having an adjustable height allows the ambulatory device to have an optimal height for placement of patient hands that minimizes weight bearing on arms.
Owner:CLARKSON UNIVERSITY
Prosthetic foot with resilient heel
ActiveUS20130173023A1Increase stabilityIncrease stiffnessAnkle jointsToe jointsVertical displacementPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A prosthetic foot can include a resilient heel member that can be removably coupled to the bottom of a plate-like foot member of the prosthetic foot. The heel member can be made of a resilient material, such as foam. The heel member can have a shape that corresponds to a foot cover and allows the prosthetic foot to fit within a foot cover. A lip may be provided to engage with a corresponding portion of the foot cover to secure the heel member within the foot cover. A rib can be located on the bottom of the heel member to create horizontal or vertical displacement of the foot at heel strike. A recess can be created in the heel member to removably receive an insert, which can alter the stiffness of the heel member.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Reoccurring method for lower limb joint motion based on wearable walk-help exoskeleton
ActiveCN108888473AReduce the original errorStrong targetingChiropractic devicesDatum referenceEngineering
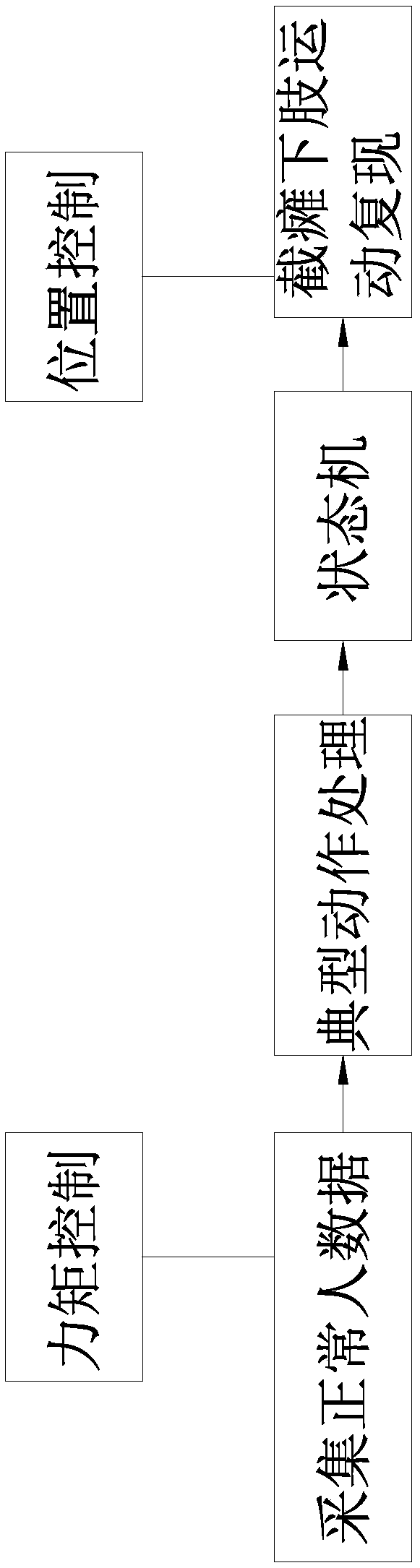
The invention relates to a reoccurring method for lower limb joint motion based on a wearable walk-help exoskeleton, and belongs to the field of exoskeleton joint motion control. The method includes the detailed steps that torque compensation is performed; the exoskeleton is in a torque control mode; information collection is performed; all joint motion data of a healthy person in all typical actions is collected through a driver of the exoskeleton and processed, and then joint motion data reference of all the typical actions is obtained; the control mode is switched; an exoskeleton position control method based on a state machine is designed; a trail is output; a paralyzed patient wears the walk-help exoskeleton, the exoskeleton actively drives the patient to move according to the referred joint trail, and meanwhile reoccurring of lower limb joint motion of the patient in different states is realized through state switching of the state machine. By the utilization of the reoccurring method, gaits are more natural and comfortable, and the process of motion reoccurring is simple. The naturality and comfort of joint motion of the wearable walk-help exoskeleton are poor, and adaptability to joint motion of the patient is good.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Bionic foot capable of improving gait naturality and stability of biped robot
ActiveCN105292297AIncrease the elastic deformation rangeReduce adverse outcomesVehiclesEngineeringGait
The invention discloses a bionic foot capable of improving the gait naturality and stability of a biped robot. The bionic foot comprises a bionic foot body and a bionic ankle. The bionic foot body comprises bionic arches, extension springs, a compression spring, a viscoelastic material layer and rubber non-slip mats. Part of impact borne by the bionic foot can be consumed by the viscoelastic material layer, and the rest of the impact is absorbed by the elastic deformation of the bionic arches, the extension springs and the compression spring. Due to the fact that the rubber non-slip mats are adopted, the non-slip performance of the bionic foot can be improved. The bionic ankle comprises a first ankle joint connecting piece, a first ankle joint platform, a second ankle joint connecting piece and a second ankle joint platform. The bionic ankle can do inward turnover and outward turnover movement through the rotation of the first ankle joint platform around a third pin shaft, and can do back bending and toe bending movement through the rotation of the second ankle joint platform around a fourth pin shaft. By means of the bionic foot, the harmful effect caused by the impact can be effectively reduced, meanwhile, the walking mode of human beings can be imitated, and the gait of the robot can be more natural.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
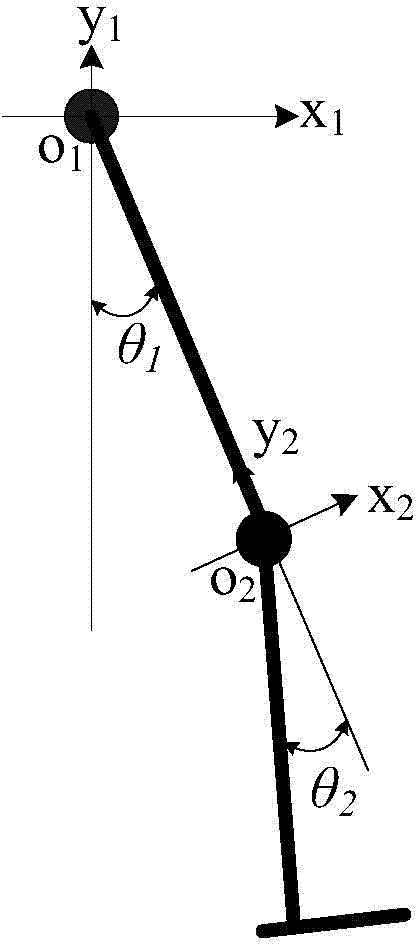
Telescopic-leg energy-saving 2D under-actuated traveling device and control method thereof
The invention relates to a telescopic-leg energy-saving 2D under-actuated traveling device. The telescopic-leg energy-saving 2D under-actuated traveling device comprises leg parts, a hip part, a drive device, a data acquisition device and a main control device, wherein the hip part comprises a left hip part and a right hip part, which are bilaterally symmetric to each other, the drive device comprises batteries and T-type double-end coaxial motors, the batteries are arranged inside the left hip part and the right hip part and used for powering the traveling device, the left hip part and the right hip part are connected with the leg parts through crankshaft rocking bars, each crankshaft rocking bar comprises an N-type crankshaft and a leg part rotating rocking bar, the T-type double-end coaxial motors are arranged inside the left hip part and the right hip part, stators of the T-type double-end coaxial motors are fixed in the left hip part and the right hip part, rotors of the T-type double-end coaxial motors penetrate through the outer sides of the left hip part and the right hip part to be connected with the crankshaft rocking bars, the other ends of the rotors penetrate through the inner sides of the left hip part and the right hip part to be connected with the crankshaft rocking bars in the left hip part and the right hip part so as to provide power to the traveling device. The traveling device is convenient to control and simple in structure.
Owner:上海卓益得机器人有限公司
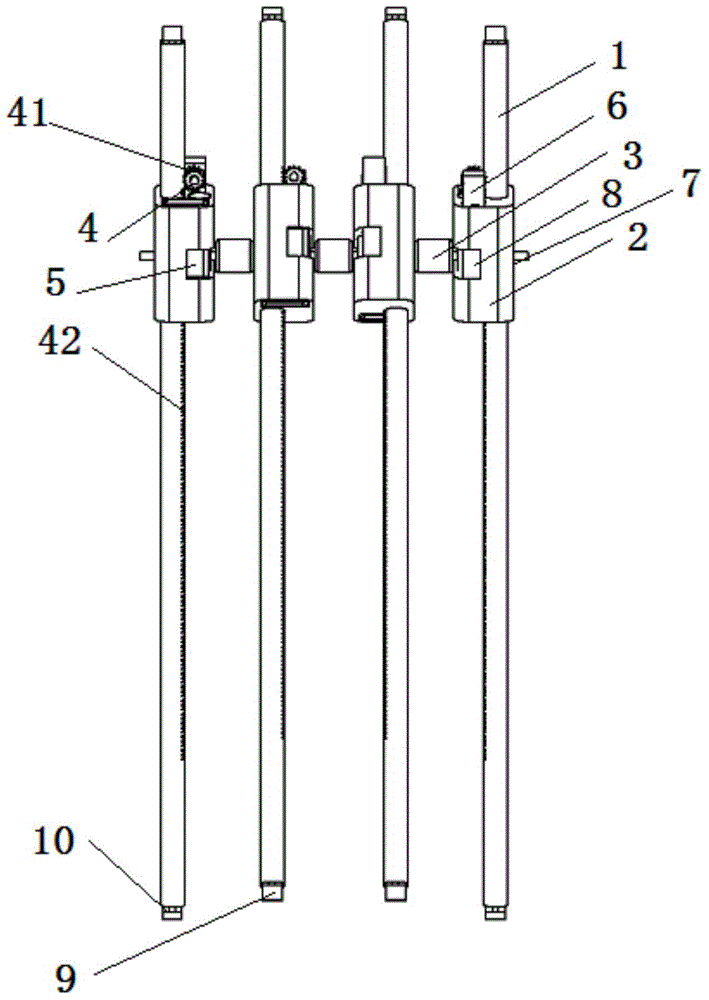
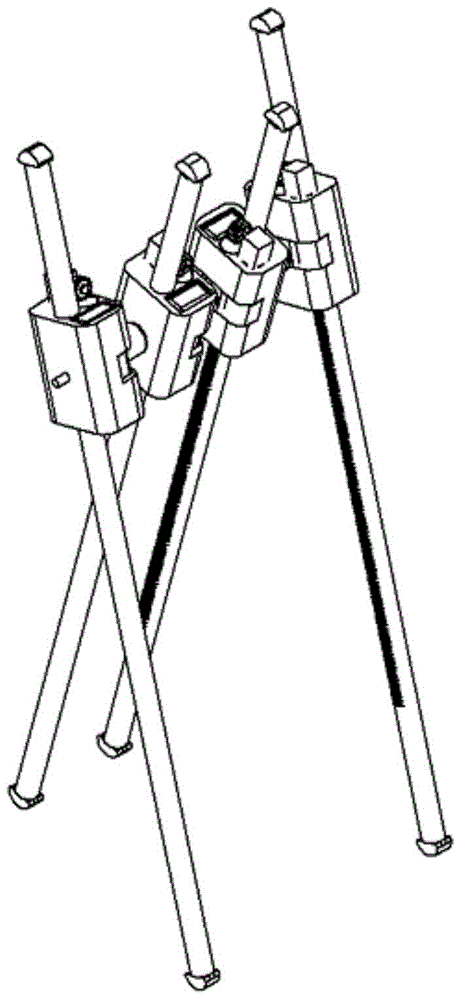
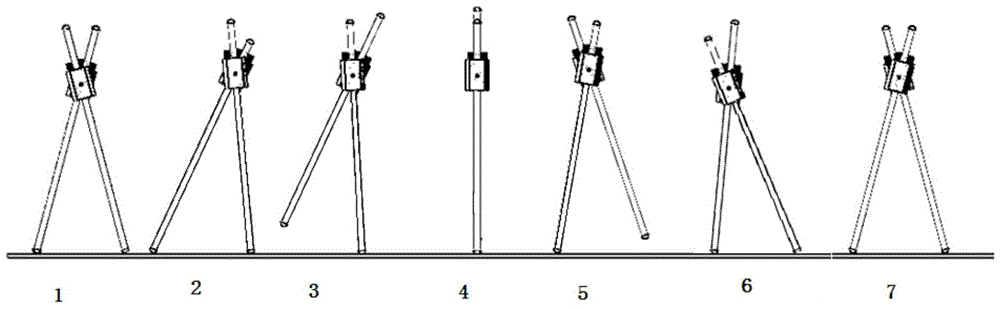
All-landform walking device and control method thereof
The invention discloses an all-landform walking device and a control method thereof. The all-landform walking device comprises at least four sets of walking mechanism units which are connected in sequence. Each walking mechanism unit comprises a straight leg used for walking and a hip used for driving the straight leg to move up and down and swing. The hips are connected through couplers. According to the all-landform walking device and the control method thereof, through the passive walking device with the straight legs capable of being driven to move up and down and swing, the dynamic characteristics of being high in self-stability during passive walking, natural in gait, efficient and capable of saving energy are achieved; meanwhile, the all-landform walking device has the advantages of being simple in structure and convenient to operate; the all-landform walking device has broad application prospects in the rehabilitation medical field and the toy field and even has high potential military application value.
Owner:中原动力智能机器人有限公司
Variable stiffness flexible actuator
InactiveCN108714913AImprove energy efficiencyLarge stiffness control rangeJointsVariable stiffnessEngineering
The invention discloses a variable stiffness flexible actuator. The variable stiffness flexible actuator comprises a power transmission mechanism, a stiffness adjusting mechanism and a stiffness output mechanism; the power transmission mechanism comprises a gear transmission mechanism and two motors, the two motors are arranged in parallel connection, and the gear transmission mechanism inputs power; the stiffness adjusting mechanism comprises two four-rod mechanisms, each four-rod mechanism comprises a first connecting rod, a second connecting rod, a third connecting rod and a plate spring, and a sliding block is arranged on the plate spring; the stiffness output mechanism comprises a stiffness output shaft, a pair of stiffness output rods, a shell and a support, and through two motors, the balance position of output of the stiffness output mechanism and the position of the sliding block on the plate spring are controlled, and therefore stiffness of the variable stiffness flexible actuator is adjusted; through dual-plate-spring dual four-rod mechanisms, the stiffness control range of the actuator is larger, the structure is compact, the size is small, and control is easy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Realization method for running of hexapod robot
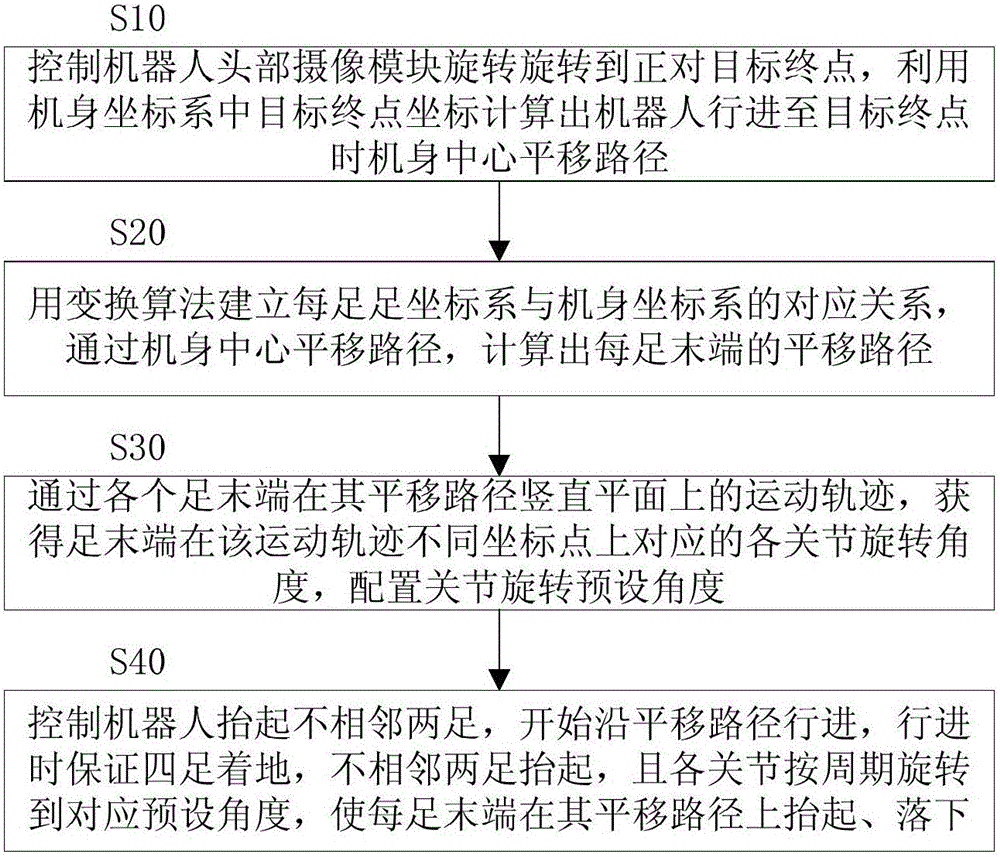
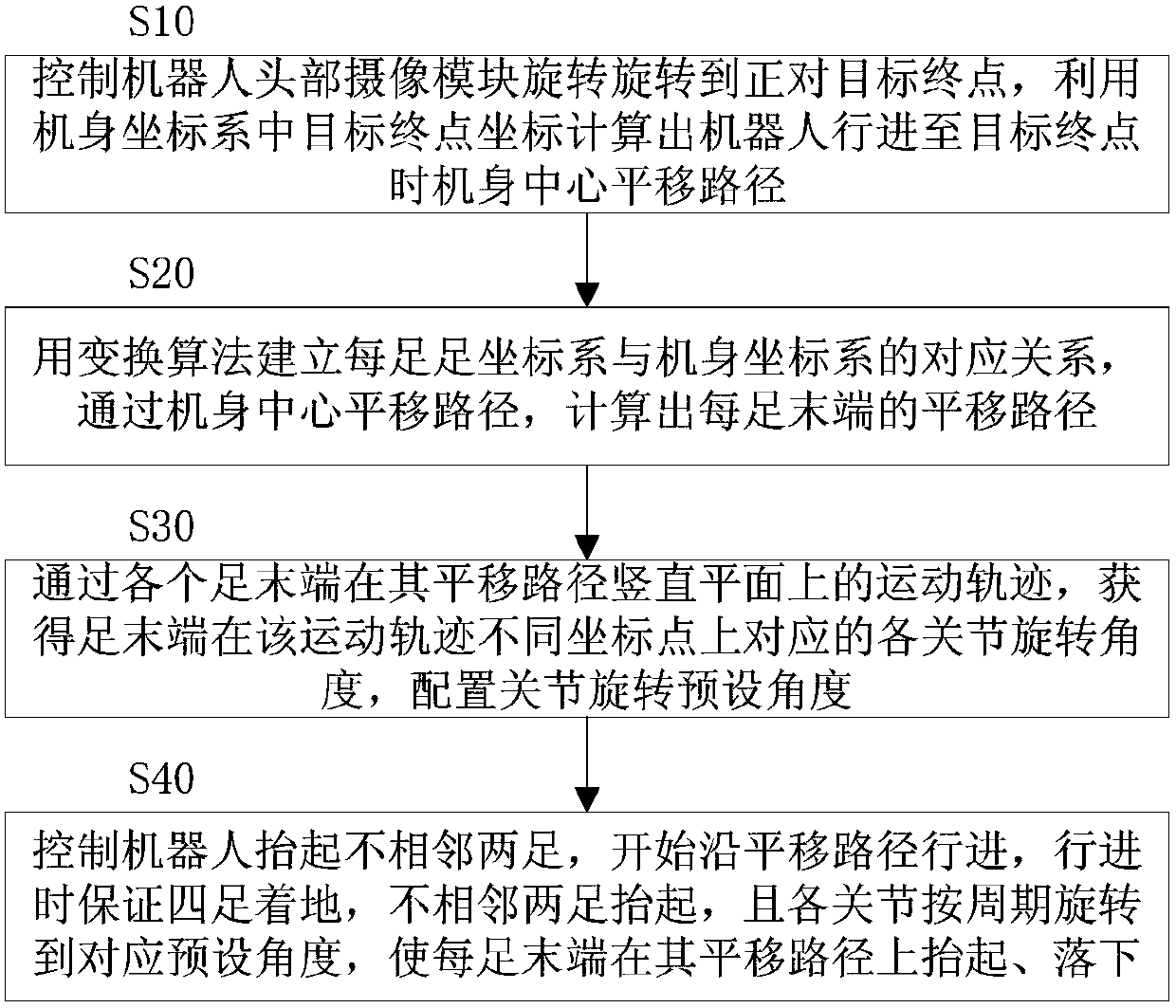
ActiveCN105773618AAvoid leaningAvoid setbacksProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesVertical planeAngular degrees
The invention discloses a realization method for running of a hexapod robot. The realization method comprises the following steps: a camera module is controlled to rotate to be aligned with a target end point, and a translation path of the body centre of the robot is calculated by virtue of the coordinates of the target end point; a corresponding relationship between a foot coordinate system of each foot and a body coordinate system is established by virtue of a transform algorithm, and a translation path of the tail end of each foot is calculated; through a movement track of the tail end of each foot on the vertical plane of the translation path of the tail end of the foot, a corresponding rotation angle of each joint of the tail end of the foot on different coordinate points of the movement track is obtained, and a preset rotation angle of the joint is configured; and the robot is controlled to lift up two non-adjacent feet, run along the translation path of the tail end of each foot at the beginning, and always keep four feet touching the ground during running, wherein the two non-adjacent feet are lifted up, each joint of each foot is periodically rotated to the corresponding preset angle, and the tail end of each foot is lifted up and down on the translation path thereof. The hexapod robot disclosed by the invention is smooth and stable in gait, the head is rotated only and the body is fixed during steering, and the front surface of the robot is kept always straight forward, without angle distortion.
Owner:QINU BEIJING TECH CO LTD
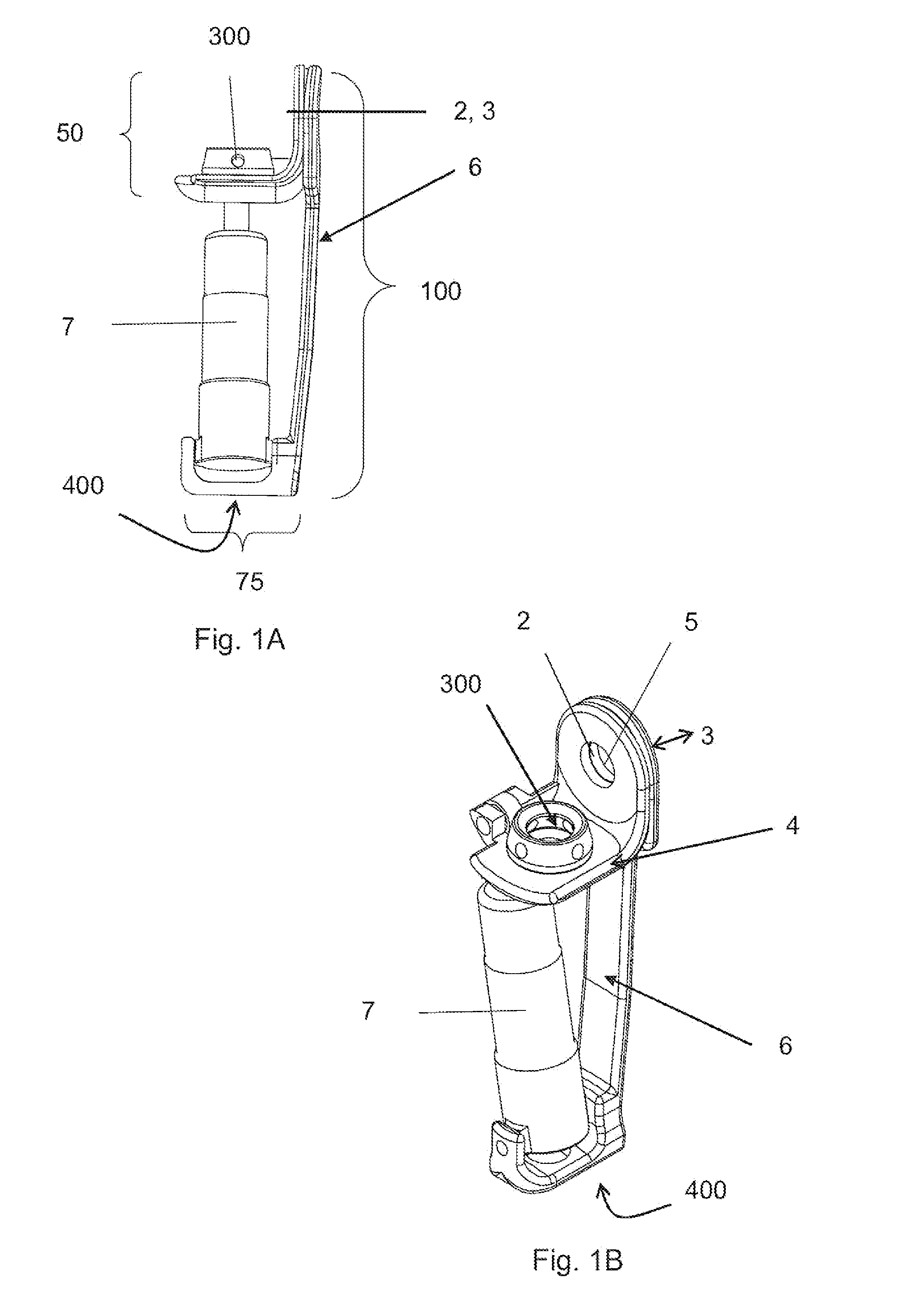
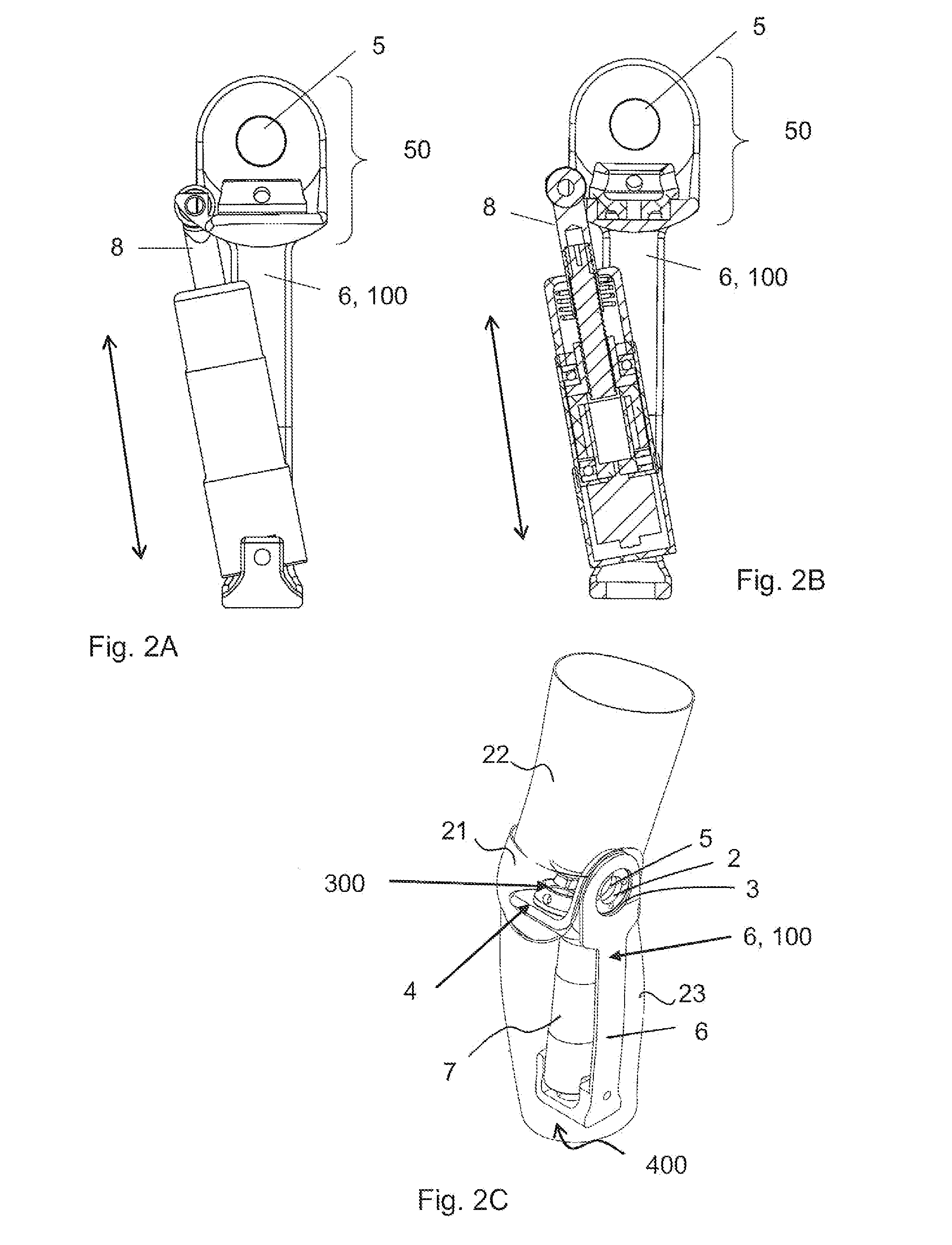
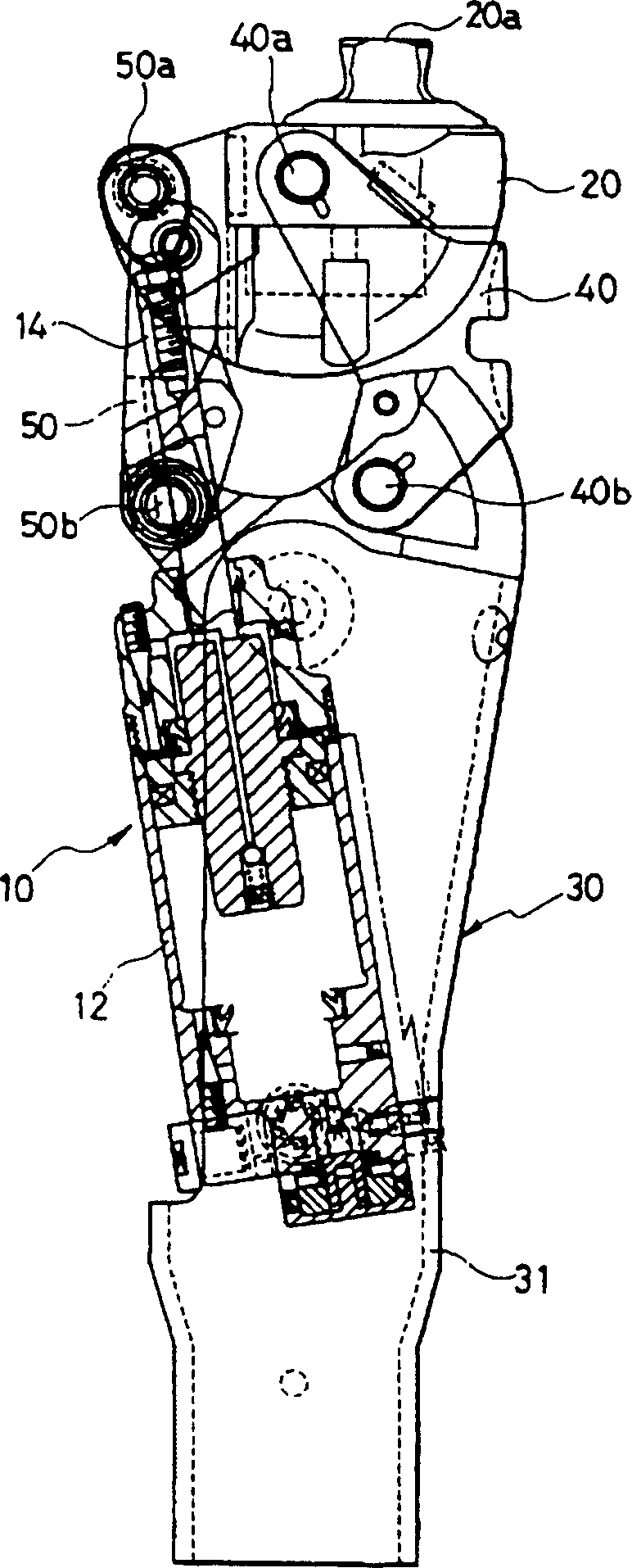
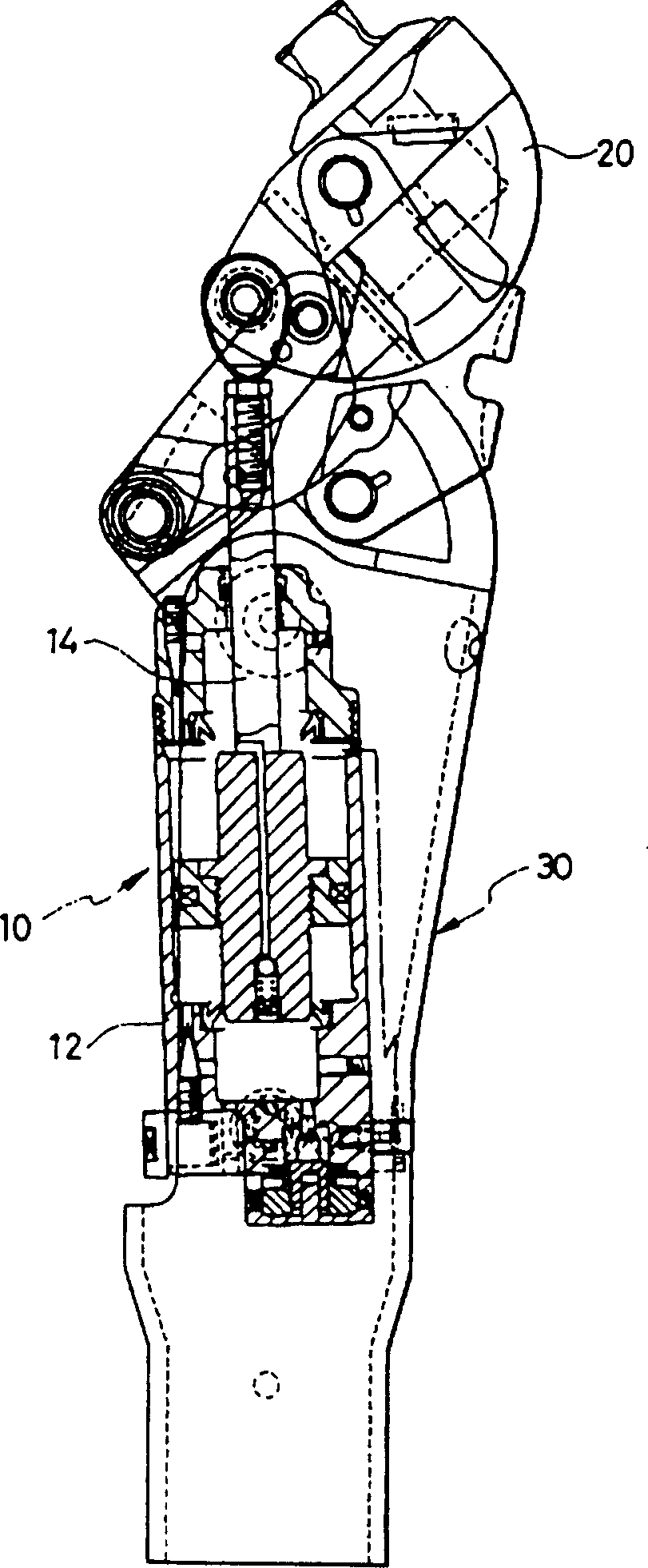
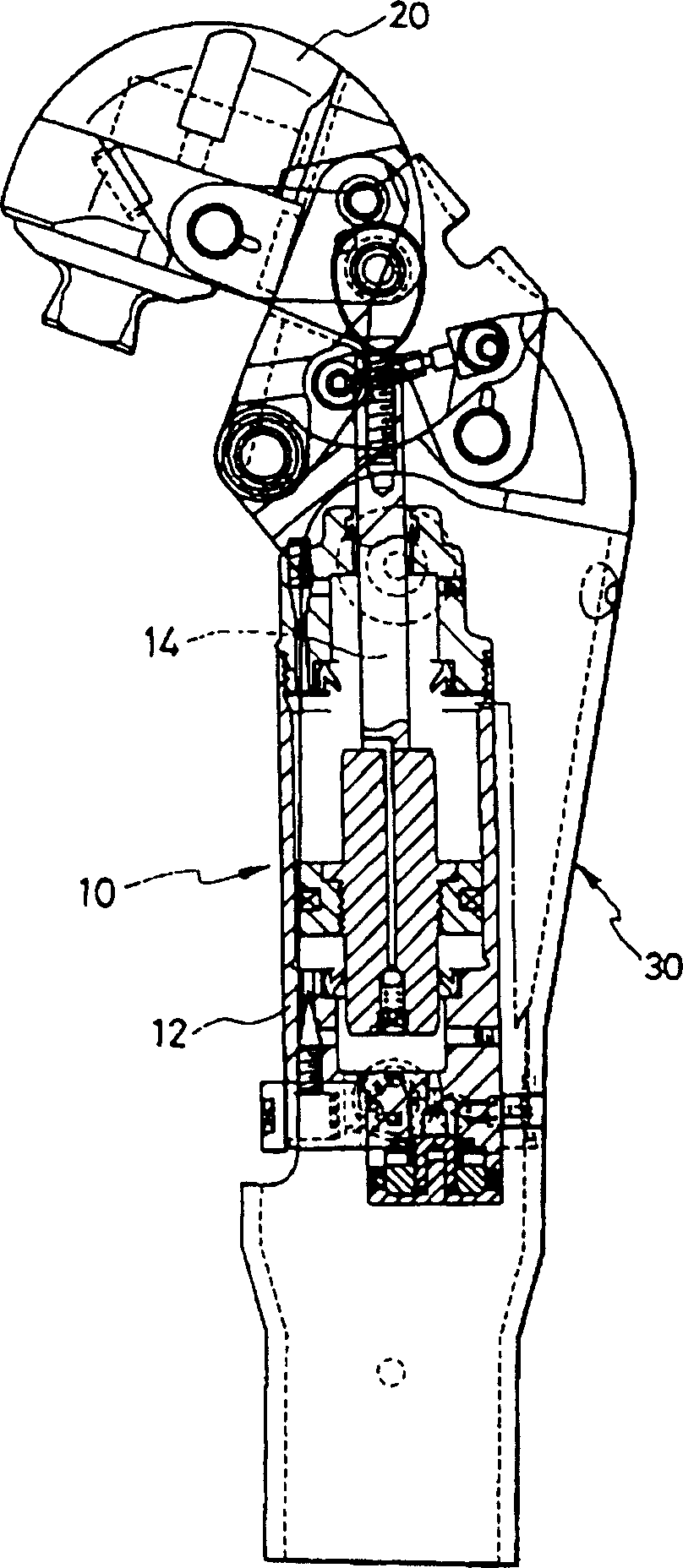
Knee joint prosthesis
The present invention relates to a knee joint for use in a lower limb prosthesis. The knee joint comprise an upper portion for connecting a custom socket and a proximal attachment, and a support comprising connecting means in its lower part for connecting a prosthetic limb. The support has at least one attachment arm on the medial or the lateral side of the knee joint prosthesis. An actuator is connected between a proximal attachment and the support and is adapted to pivot the upper portion relatively to the support. The actuator comprises a motor directly operatively connected to an axial displaceable shaft capable of changing angular velocity of the knee joint. An external control device can be used to control the knee joint.
Owner:FILLAUER EURO AB +1
Carbon fiber double-side elastic all-terrain artificial feet plate
The invention relates to a carbon-fiber and double-jumping artificial foot plate with full grounding. The artificial foot plate comprises a connection structure and is characterized in that the foot plate also comprises dual lower plates, an upper plate, a U-shaped front keel and a U-shaped rear keel, wherein, the upper plate and the dual lower plates are fixedly connected with each other by the U-shaped front keel and the U-shaped rear keel, the openings of which are all backward. The artificial foot plate is used during the transition from a load-bearing period to an off-ground period for a heel as well as from a load-bearing period to an off-ground period for a forefoot and the U-shaped front keel and the U-shaped rear keel can respectively release the stored energy to help the artificial foot to complete the movement of stepping. The artificial foot plate is characterized by high strength, light weight, good flexibility, comfort in walking, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Control method for artificial limb knee and ankle joints
The invention discloses a control method for artificial limb knee and ankle joints and relates to artificial limb knee joints. The control method includes the steps that firstly, the positions, on which Hall sensors are to be installed, on an artificial limb knee joint are determined through a test, the three Hall sensors are installed, a controller is installed in a groove in the rear cover of the artificial limb knee joint, and different gaits are judged and identified by the controller according to signal variation of the three Hall sensors; secondly, according to identification of the gaits in the first step, the controller judges different gaits according to the signal variation of the Hall sensors and controls a knee joint motor and an ankle joint motor to move up and down according to different gaits, different damping is generated according to different gaits and different step speeds, and therefore control of the gaits is achieved and coordination of the knee and the ankle is achieved. The defects that intelligent artificial limbs are not coordinate in gait and are prone to damage and energy consumption of wearers is large in the prior art are overcome.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Driving rear-mounted lower extremity exoskeleton robot
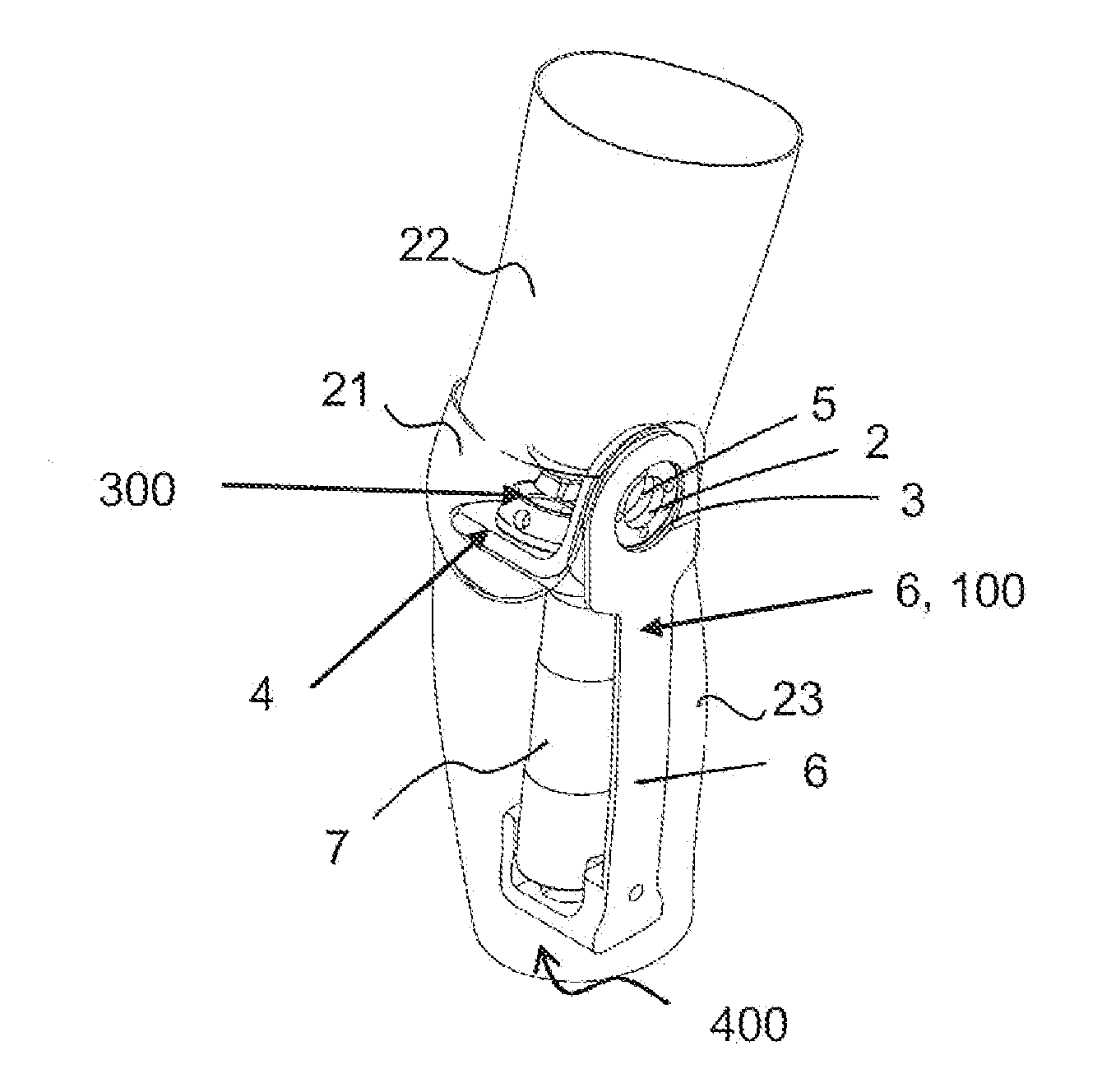
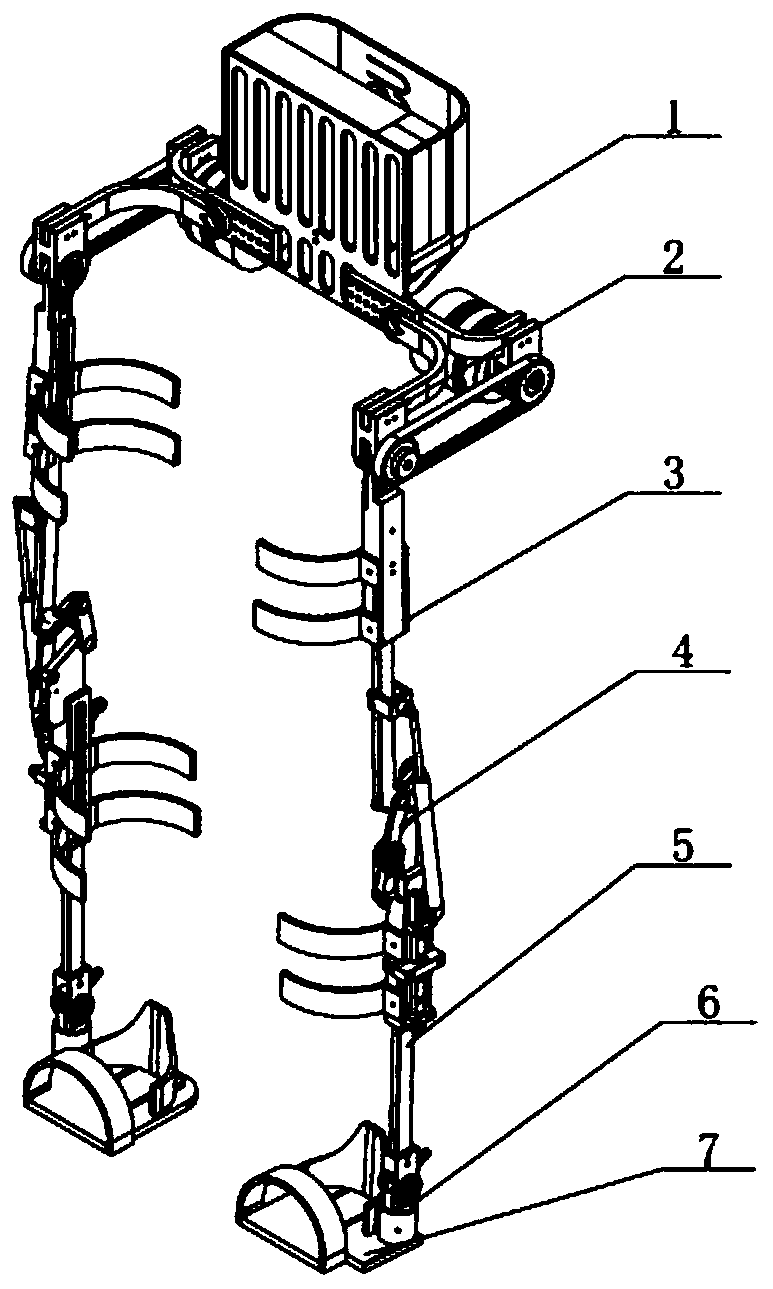
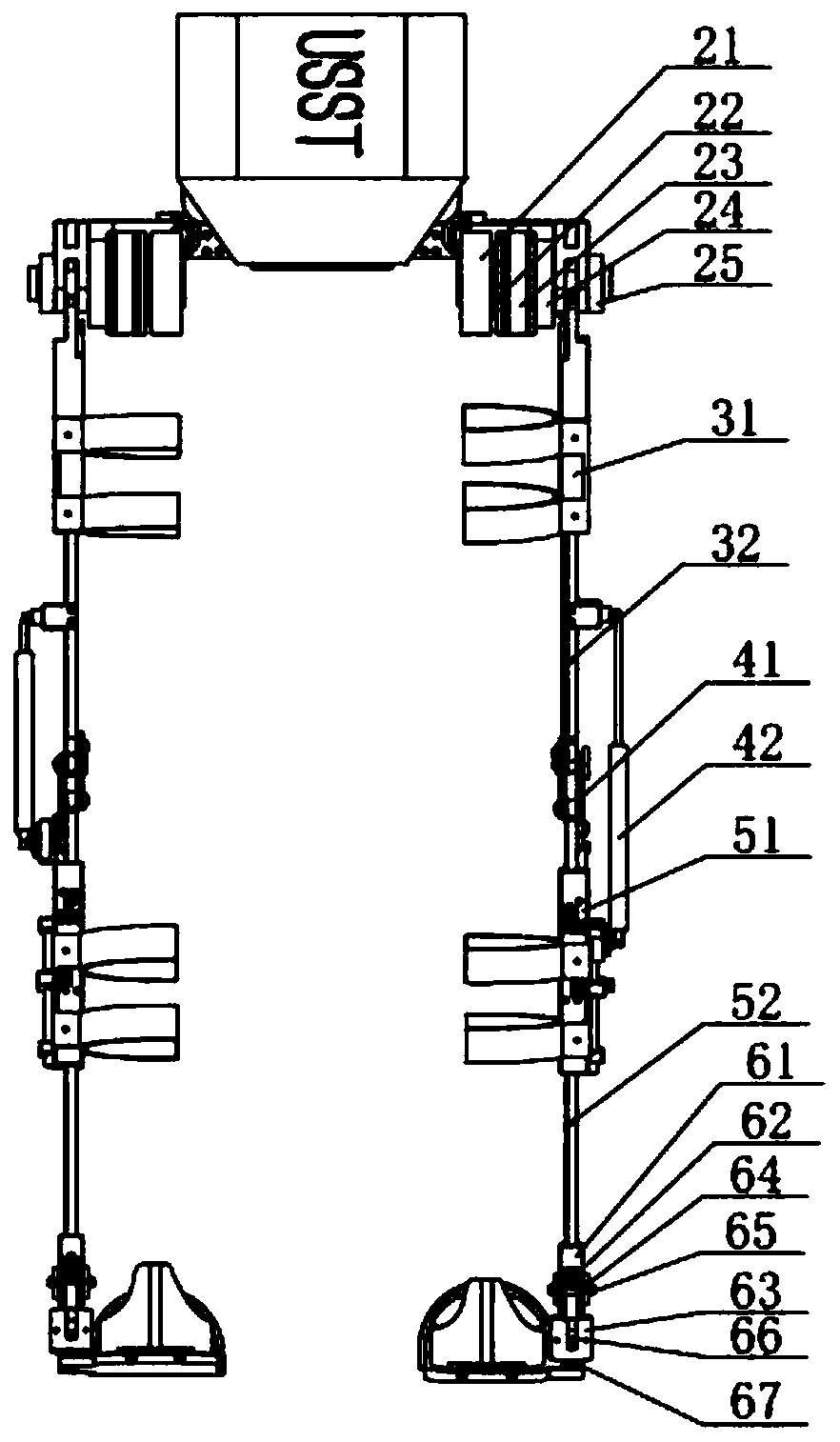
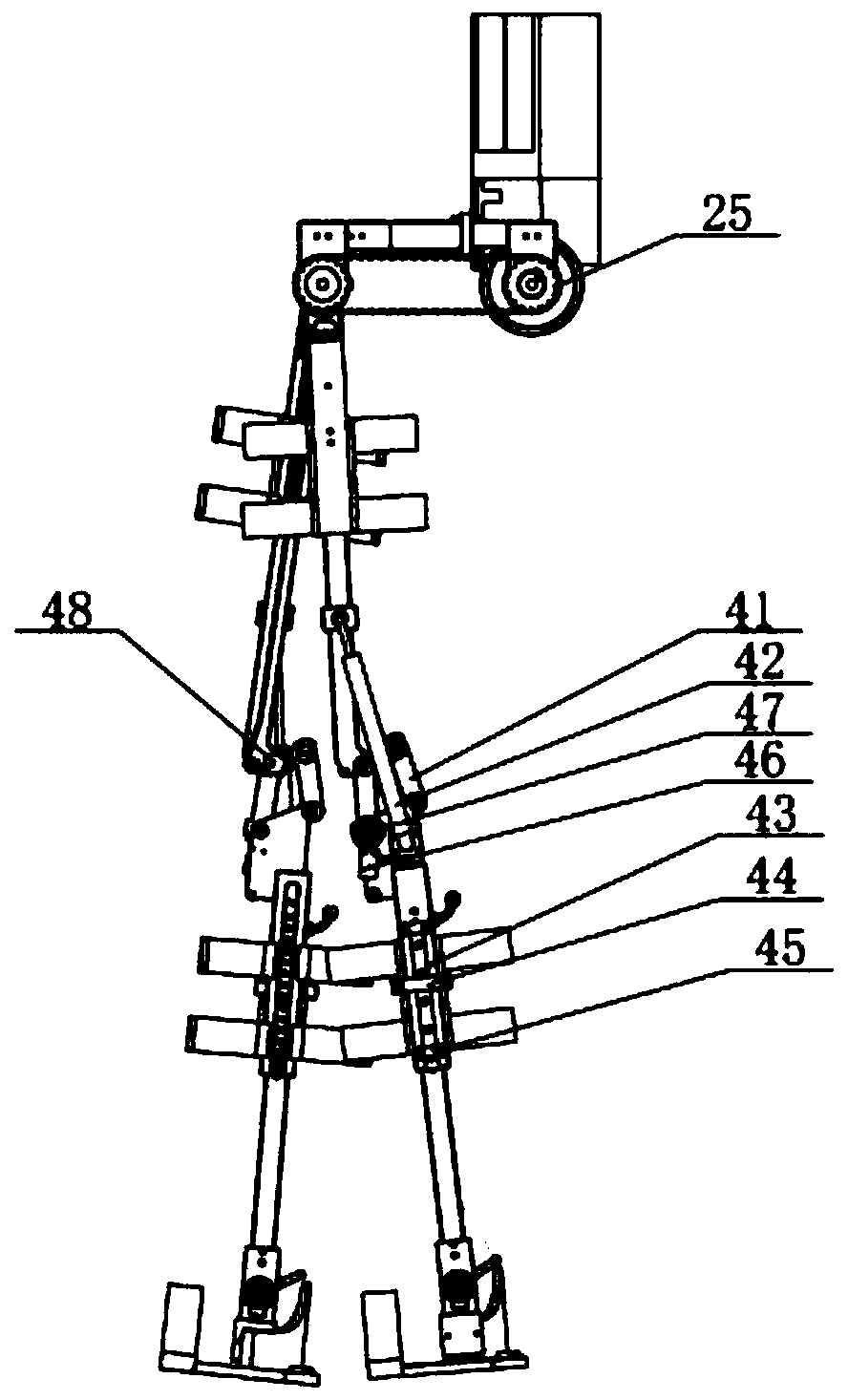
InactiveCN110063877AImprove transmission efficiencySmall sizeChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighHuman body
The invention provides a novel driving rear-mounted lower extremity exoskeleton robot. The robot comprises a back assembly (1), two hip joint assemblies (2), two thigh rod pieces (3), two knee joint assemblies (4), two calf rod pieces (5), two ankle joint assemblies (6) and two foot assemblies (7), wherein the hip joint assemblies (2), the two thigh rod pieces (3), the two knee joint assemblies (4), the two calf rod pieces (5), the two ankle joint assemblies (6) and the two foot assemblies (7) are sequentially connected to the two sides of the back assembly from top to bottom in sequence. Therobot is high in structural function adaptability, and the external dimension and size are flexible and meet the human body bionic design. According to the robot, a power source is completely placed at the back, power is transmitted to the hip joints through a synchronous belt, a transmission mechanism is simple, transmission is accurate, the transmission efficiency is high, the size of the two sides is effectively reduced, and the robot occupies a small space and is more portable.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Carbon fiber energy-storing pseudarthrosis artificial limb simulating functions of intertarsal joint
The invention relates to a carbon fiber energy-storing pseudarthrosis artificial limb simulating functions of an intertarsal joint. The artificial limb comprises an S-shaped upper plate, a lower plate and a connecting structure and is characterized by also comprising a heel shrapnel and a trapezoidal groove structure, wherein the upper end of the trapezoidal groove structure is horizontal and is fixedly connected with the connecting structure; the lower end of the trapezoidal groove structure is inclined for 30 degrees and is fixedly connected with the heel shrapnel; the small groove opening of the trapezoidal groove structure is backward; the big groove opening of the trapezoidal groove structure is forward; and the S-shaped upper plate passes through the groove openings and is connected with the connecting structure. An upper bent part of the S-shaped upper plate is combined with the trapezoidal groove structure, so the transmission force and the jogging function of the intertarsal joint are tactfully simulated; and a lower bent part of the S-shaped upper plate and a toe part of a lower plate are combined into a unique structure, so the dorsiflexion of a metatarsophalangeal joint can be simulated. An opening of the heel shrapnel is downward and the lower part of the heel shrapnel is connected with the lower plate. The artificial limb has the characteristics of high strength, light weight, high elasticity, stability in standing, graceful travelling tread and the like.
Owner:DALIAN XINGKE CARBON FIBER
Air cylinder device for artificial limb
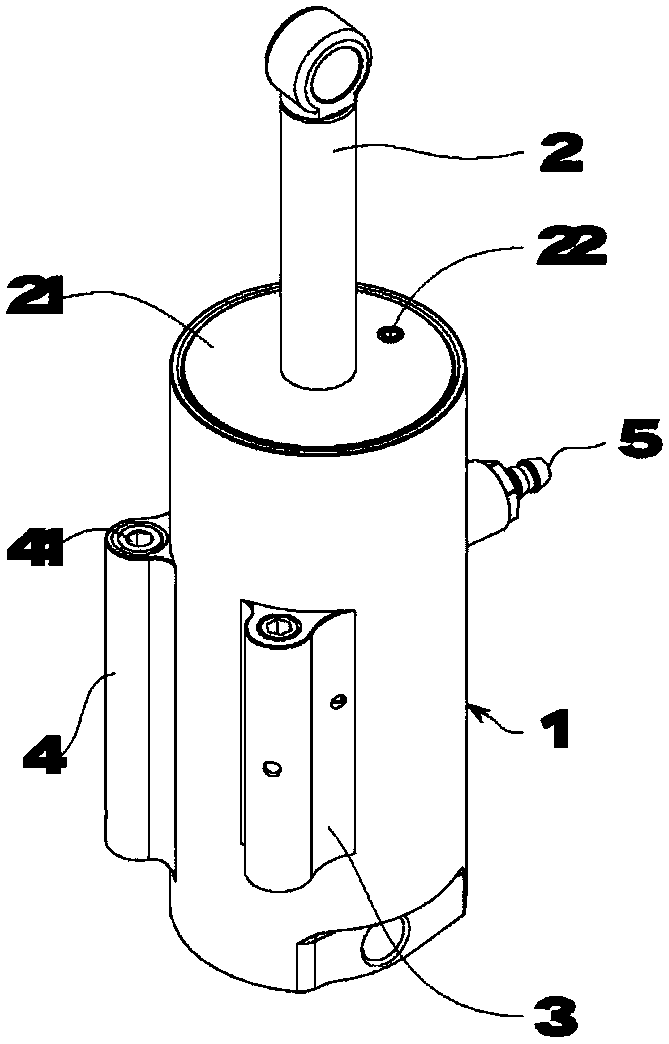
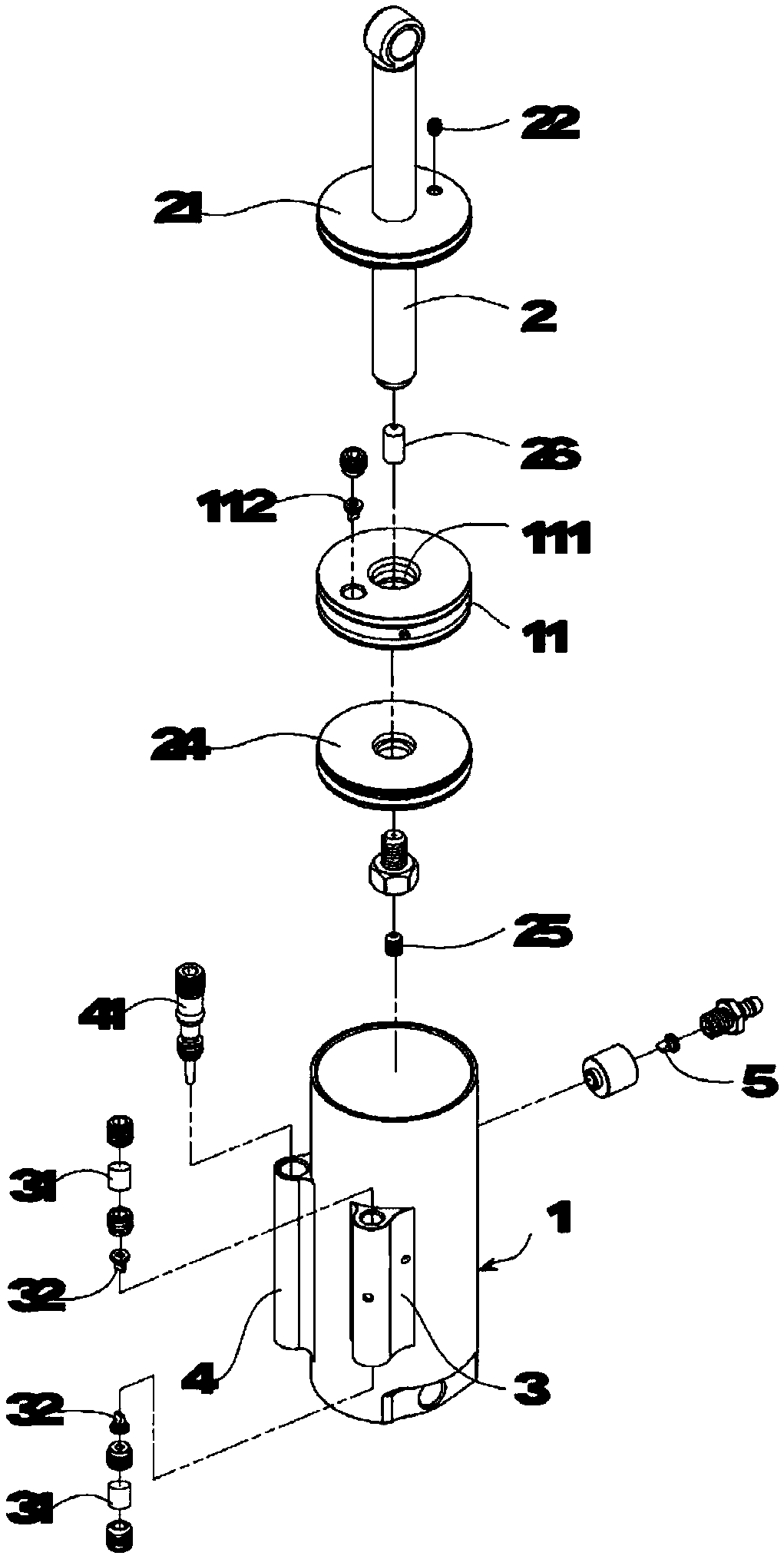
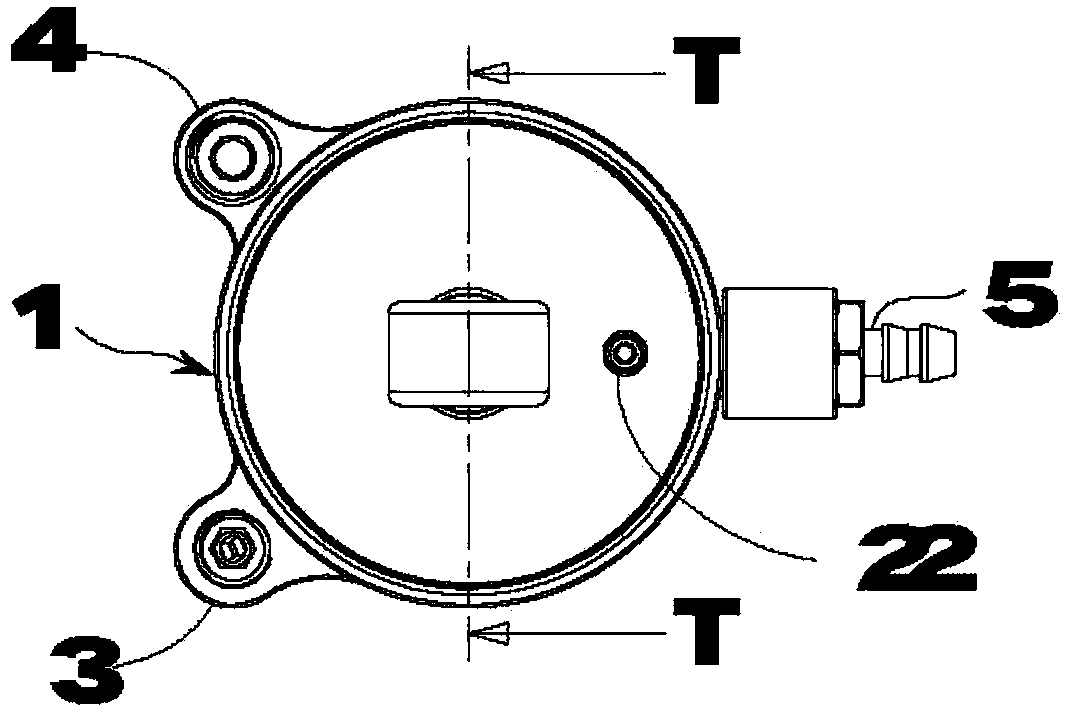
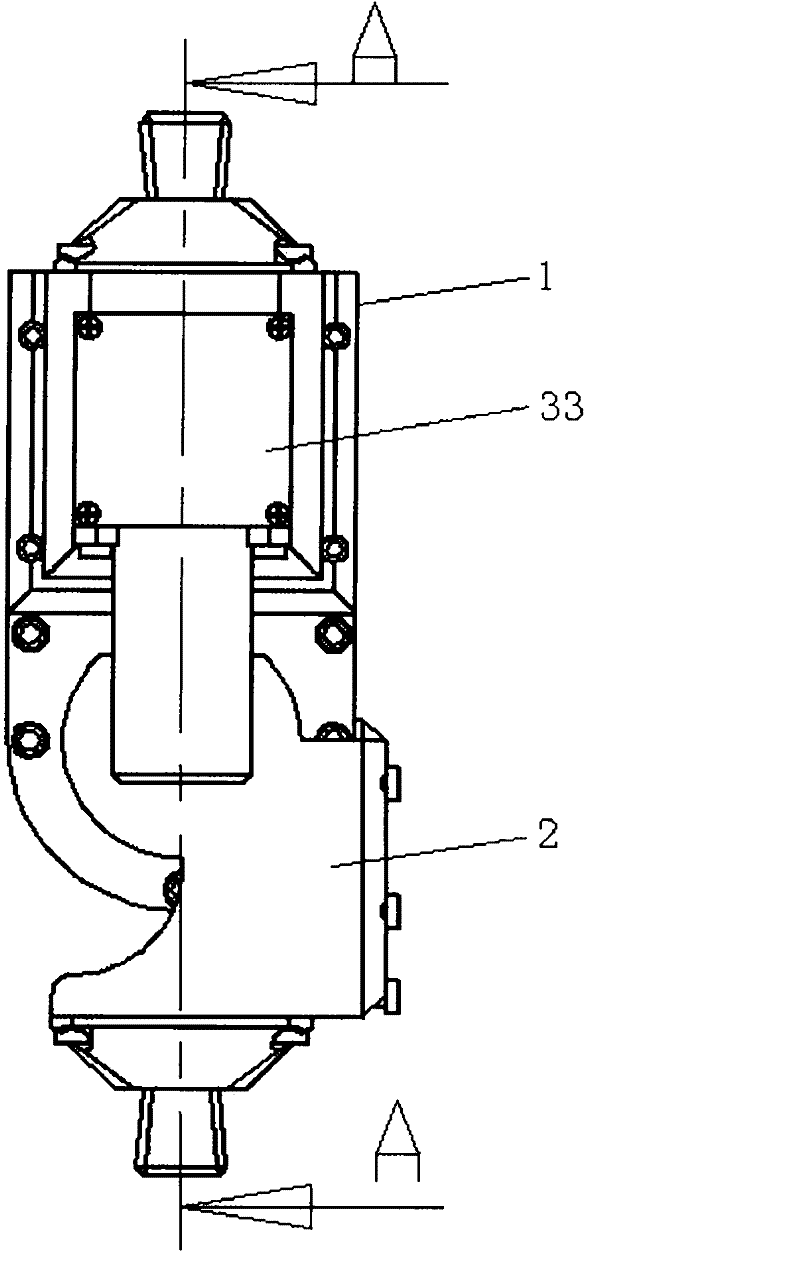
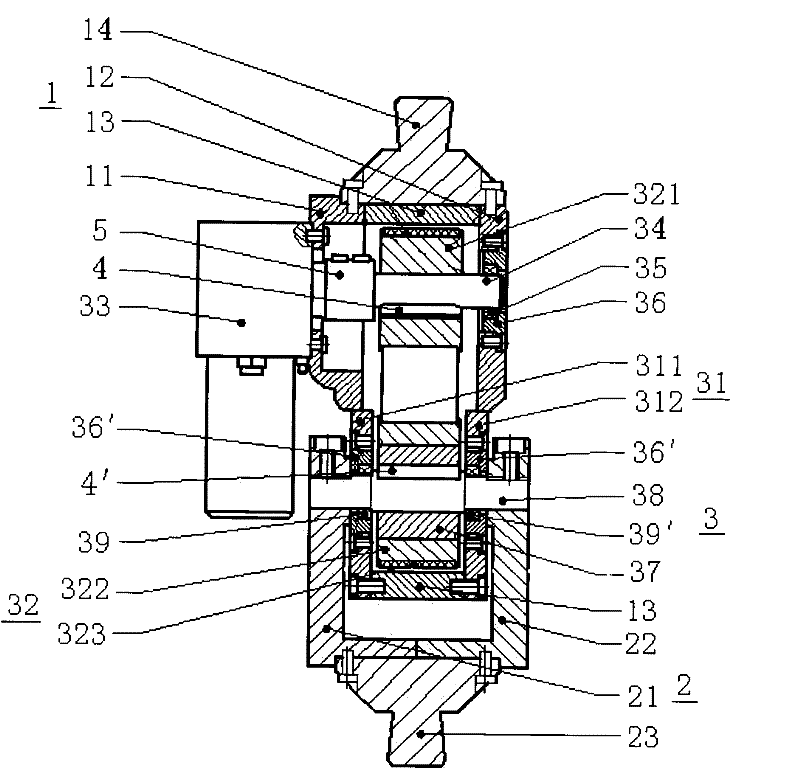
InactiveCN1178631CNatural gaitStable structureSpringsFluid-pressure actuatorsEngineeringControl theory
There is provided an air-cylinder apparatus for use in a prosthetic limb capable of effectively adjusting the pressure characteristics over a wide range of walking speed. A second chamber (82) defined by a piston (113) is increased in pressure by air confined therein in accordance with the bending motion of the knee. Air is restricted from flowing out of the second chamber (82) by a constant throttle valve 140. In addition, the second chamber (82) is divided into plural chambers (821, 822) in accordance with increase in bending angle of the knee and air is restricted from flowing out of the newly divided chambers by throttle valves corresponding thereto. The division of the second chamber 82 is achieved by mutual engagement between a projection (1140b) on the piston side and a recess (112&) on the bottom part of a cylinder body.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
A quasi-passive biped walking robot system with hip vibrator
The invention relates to a quasi-passive biped walking robot system with a hip vibrator, and aims at solving the problems that an existing active robot is unnatural in gait and high in energy consumption, coronal plane motion of an existing three-dimensional passive robot is unstable, and the reliability degree of a system is poor. The quasi-passive biped walking robot system comprises a hip assembly, two leg assemblies and two foot assemblies, and each leg assembly is arranged between the hip assembly and the corresponding foot assembly. The quasi-passive biped walking robot system further comprises the hip vibrator, and the hip vibrator comprises a speed reducer, a support, a bevel gear pair, a coupling and a gear shaft. The hip assembly comprises a barrel, a gear rack, a guide rail and two annular connecting pieces. Each foot assembly is mainly composed of a foot plate. Each leg assembly comprises a hip and leg connecting piece, a straight leg and a leg and foot connecting piece, and the upper ends of the straight legs are connected with the hip and leg connecting pieces. Stable three-dimension walking of the quasi-passive robot on a slope is achieved, and meanwhile the advantages of being natural in gait and low in power consumption are achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Low-energy artificial limb
The invention relates to the technical field of medical care devices, in particular to a low-energy artificial limb comprising a calf artificial limb, an ankle joint and a prosthetic foot plate. The ankle joint comprises two brackets arranged on the top surface on the rear part of the prosthetic foot plate, the two brackets are connected on one side of a swinging device through a rotating shaft respectively, the bottom of the swinging device is connected to the top of the prosthetic foot plate by a spring, and the swinging device is internally provided with a charging conversion device. The charging conversion device converts kinetic energy generated during spring stretching into electric energy and stores the energy in a battery pack. The electric energy stored in the battery pack is usedfor driving the stretching of the spring when the prosthetic foot plate is raised. The low-energy artificial limb can solve the problem in the prior art that the existing artificial limb is poor in comfort, inconvenient to wear and high in energy consumption during work, and a user cannot walk conveniently by wearing the artificial limb.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
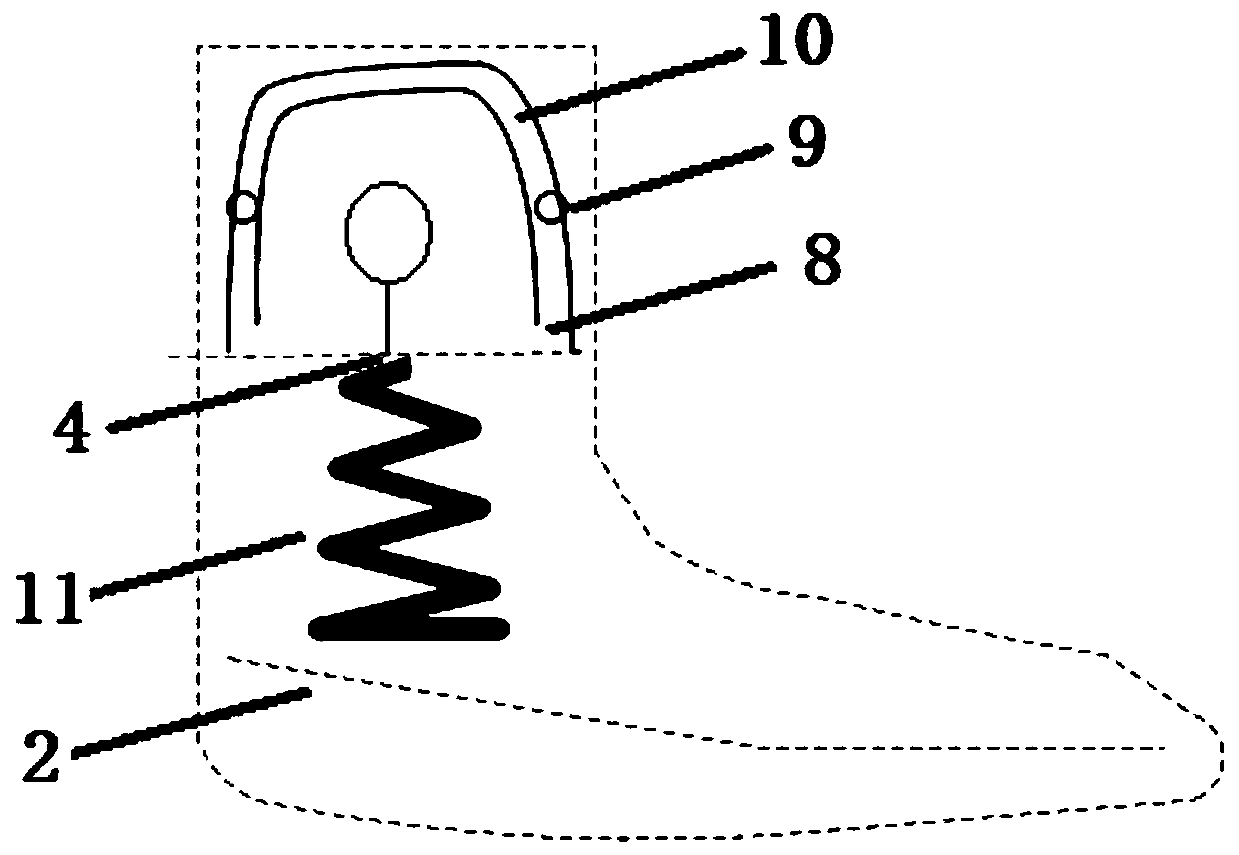
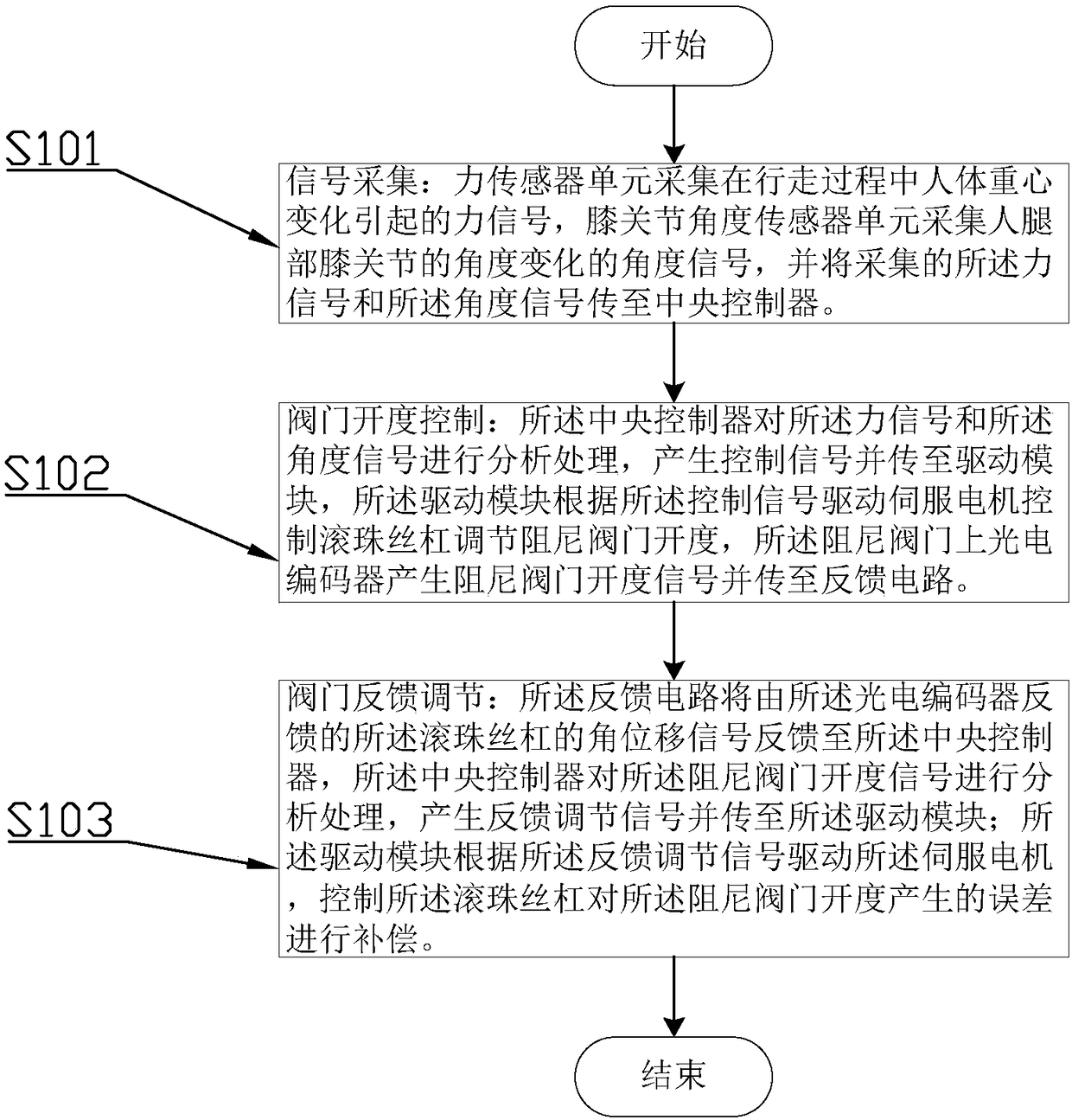
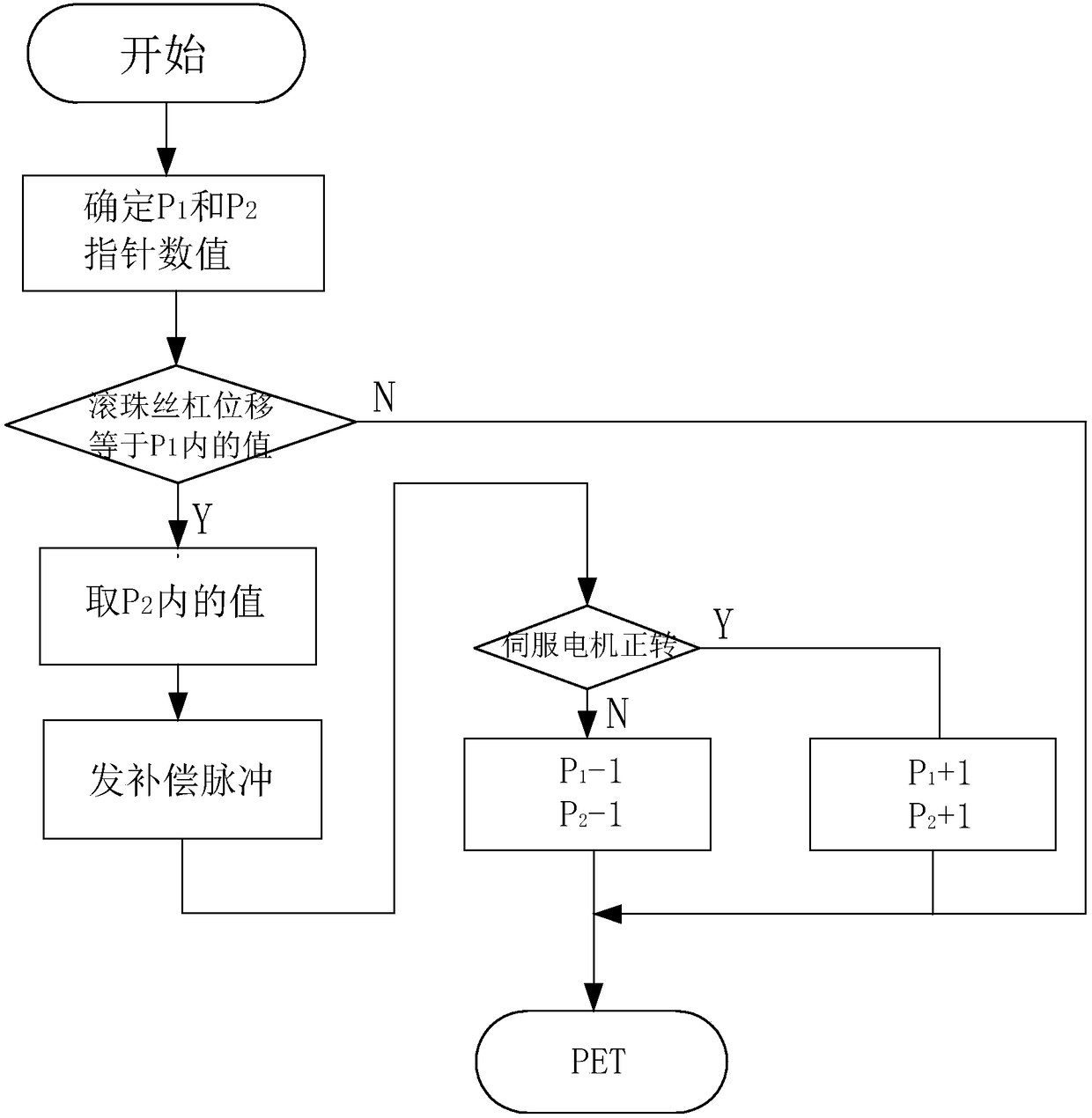
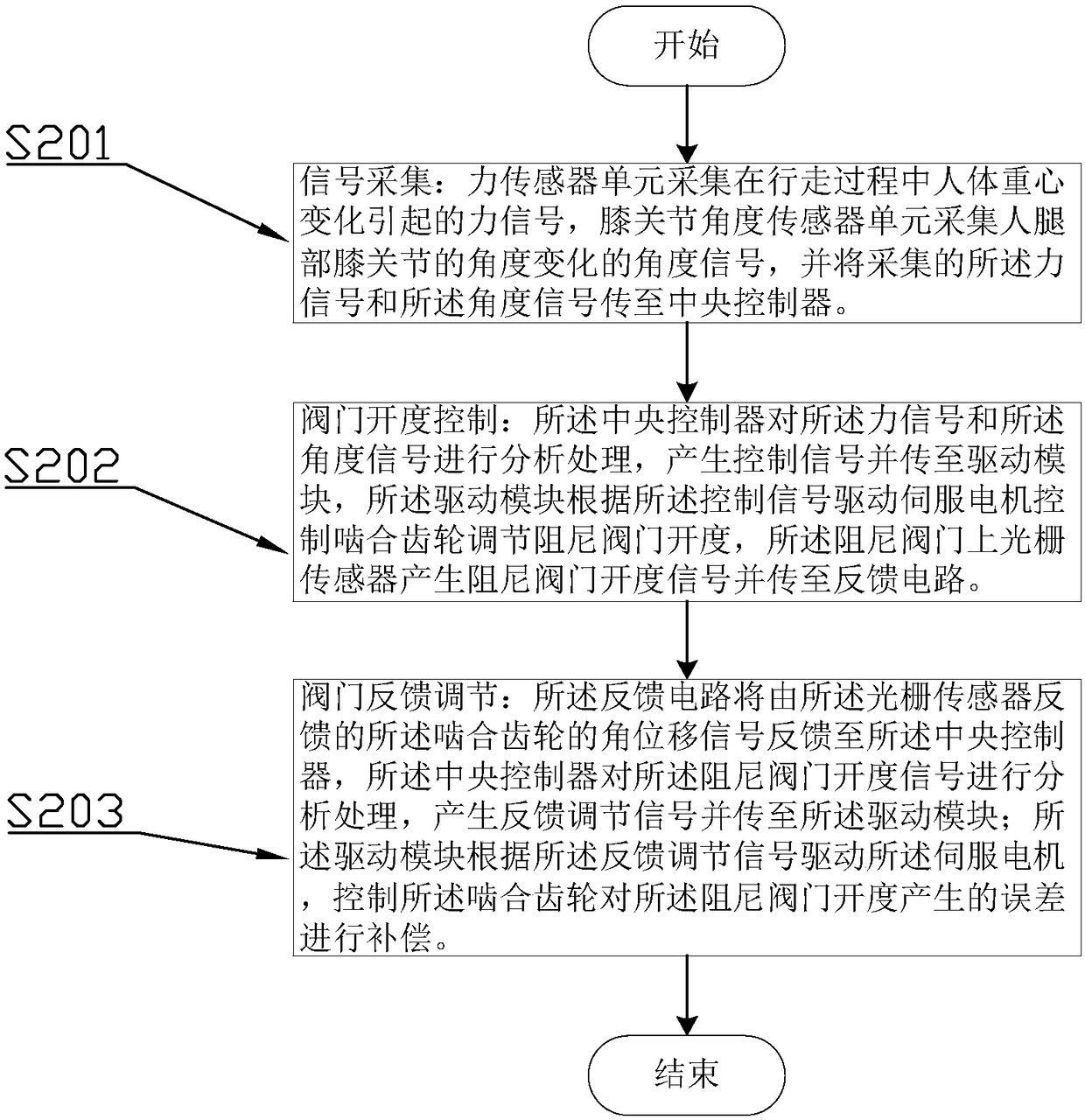
Compensation device for hydraulic damping valve opening degree of rehabilitation assisting robot and method thereof
InactiveCN108210243ANatural gaitCompensate in real timeChiropractic devicesWalking aidsElectric machineryFeedback circuits
The invention discloses a compensation device for the hydraulic damping valve opening degree of a rehabilitation assisting robot and a method thereof, and relates to the technical field of robot controlling. According to the method, an opening degree signal of a valve is transmitted to a central controller by a feedback circuit for analysis processing, a feedback regulation signal is transmitted to a driving module, and a servo motor is driven by the driving module according to the feedback regulation signal to control a regulation mechanism to compensate the error generated by the damping valve opening degree; real-time, accurate and sensitive regulation on the hydraulic damping valve controlled by the servo motor can be better conducted, so that the driving force and speed of a hydraulicdriving system meet the demands of human gaits, and the human gaits are more natural.
Owner:深圳市罗伯医疗机器人研究所
All-terrain walking device and control method thereof
The invention discloses an all-landform walking device and a control method thereof. The all-landform walking device comprises at least four sets of walking mechanism units which are connected in sequence. Each walking mechanism unit comprises a straight leg used for walking and a hip used for driving the straight leg to move up and down and swing. The hips are connected through couplers. According to the all-landform walking device and the control method thereof, through the passive walking device with the straight legs capable of being driven to move up and down and swing, the dynamic characteristics of being high in self-stability during passive walking, natural in gait, efficient and capable of saving energy are achieved; meanwhile, the all-landform walking device has the advantages of being simple in structure and convenient to operate; the all-landform walking device has broad application prospects in the rehabilitation medical field and the toy field and even has high potential military application value.
Owner:中原动力智能机器人有限公司
A bionic foot that improves the naturalness and stability of the gait of a biped robot
ActiveCN105292297BIncrease the elastic deformation rangeReduce adverse outcomesVehiclesEngineeringGait
The invention discloses a bionic foot capable of improving the gait naturality and stability of a biped robot. The bionic foot comprises a bionic foot body and a bionic ankle. The bionic foot body comprises bionic arches, extension springs, a compression spring, a viscoelastic material layer and rubber non-slip mats. Part of impact borne by the bionic foot can be consumed by the viscoelastic material layer, and the rest of the impact is absorbed by the elastic deformation of the bionic arches, the extension springs and the compression spring. Due to the fact that the rubber non-slip mats are adopted, the non-slip performance of the bionic foot can be improved. The bionic ankle comprises a first ankle joint connecting piece, a first ankle joint platform, a second ankle joint connecting piece and a second ankle joint platform. The bionic ankle can do inward turnover and outward turnover movement through the rotation of the first ankle joint platform around a third pin shaft, and can do back bending and toe bending movement through the rotation of the second ankle joint platform around a fourth pin shaft. By means of the bionic foot, the harmful effect caused by the impact can be effectively reduced, meanwhile, the walking mode of human beings can be imitated, and the gait of the robot can be more natural.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Oil pressure ankle joint
The invention provides an oil pressure ankle joint. The oil pressure ankle joint comprises an ankle hydraulic cylinder, wherein the ankle hydraulic cylinder comprises an oil supplementing chamber, a first pressure adjusting chamber PF, a second pressure adjusting chamber DF, and accommodating space communicating with each chamber, the accommodating space allows for pivoting of an oil pressure shaft core in match with a locating piece, set screws are matched at two sides of the oil pressure shaft core for screwing, and the ankle hydraulic cylinder is pivoted in a pivoting base and can carry out rotation swing movement relative to the pivoting base; an extending part is arranged in the middle of the oil pressure shaft core, an oil baffle block is arranged below the oil pressure shaft core, so that a front chamber and a rear chamber which communicate with each other and allow fluid to flow inside are formed through the separation by the oil pressure shaft core, meanwhile, the first pressure adjusting chamber PF and the second pressure adjusting chamber DF can be used for correspondingly adjusting the pressure of fluid in the front chamber and the rear chamber, so that the impact force born by a user during walking is effectively alleviated, the walking posture is natural and easy, in addition, the oil supplementing chamber can automatically supplement fluid by utilizing the differences of oil pressure, and thus the maintenance times of the user can be reduced.
Owner:KEN DALL ENTERPRISE
A Realization Method of Hexapod Robot Walking
ActiveCN105773618BAvoid leaningAvoid setbacksProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesVertical planeCamera module
The invention discloses a realization method for running of a hexapod robot. The realization method comprises the following steps: a camera module is controlled to rotate to be aligned with a target end point, and a translation path of the body centre of the robot is calculated by virtue of the coordinates of the target end point; a corresponding relationship between a foot coordinate system of each foot and a body coordinate system is established by virtue of a transform algorithm, and a translation path of the tail end of each foot is calculated; through a movement track of the tail end of each foot on the vertical plane of the translation path of the tail end of the foot, a corresponding rotation angle of each joint of the tail end of the foot on different coordinate points of the movement track is obtained, and a preset rotation angle of the joint is configured; and the robot is controlled to lift up two non-adjacent feet, run along the translation path of the tail end of each foot at the beginning, and always keep four feet touching the ground during running, wherein the two non-adjacent feet are lifted up, each joint of each foot is periodically rotated to the corresponding preset angle, and the tail end of each foot is lifted up and down on the translation path thereof. The hexapod robot disclosed by the invention is smooth and stable in gait, the head is rotated only and the body is fixed during steering, and the front surface of the robot is kept always straight forward, without angle distortion.
Owner:QINU BEIJING TECH CO LTD
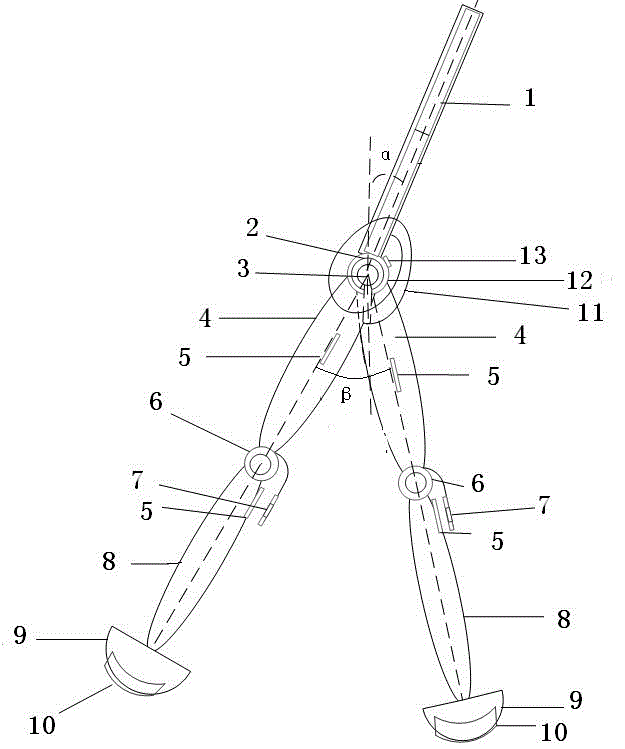
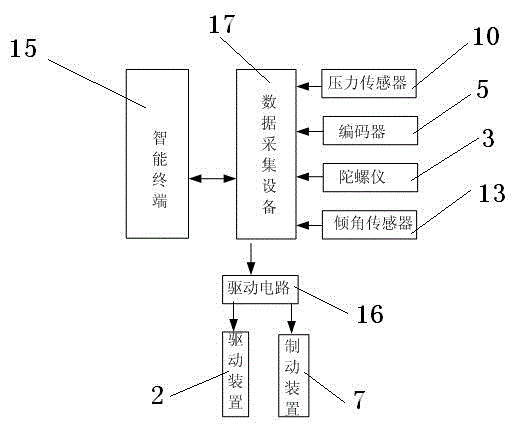
A low-power consumption walking device and control method based on an intelligent terminal
ActiveCN103481965BReasonable humanoid formAvoid collisionVehicle position/course/altitude controlVehiclesGyroscopeData acquisition
The invention discloses a low-power dissipation running gear and a control method based on an intelligent terminal. The low-power dissipation running gear comprises a pair of leg portions, a driving device, a braking device, and an upper body. Tilt angle sensors are arranged at the upper ends of hip joints, encoders are respectively arranged on inner sides of upper legs and lower legs, gyroscopes are respectively arranged on the left side and the right side of the hip joints and are fixed on a first revolving shaft connecting the leg portion and the hip joints, pressure sensors are respectively arranged on the bottom of two feet, the upper body comprises a support frame and an intelligent terminal, a driving circuit and a data acquisition device which are arranged on the supporting frame, the lower end of the supporting frame is connected with the hip joints through a second revolving shaft, the data acquisition device is respectively connected with the intelligent terminal, the driving circuit, the tilt angle sensors, four encoders, two gyroscopes and two pressure sensors, and the driving circuit is connected with the driving device and the braking device respectively. The low-power dissipation running gear and the control method based on the intelligent terminal have more reasonable human simulating shape, and are equipped with low energy consumption and natural steps of a driven walking device.
Owner:中原动力智能机器人有限公司
Vacuum attracting and pressure regulation pneumatic cylinder
ActiveCN108071733AReduce air pressureSuction tightSpringsLiquid based dampersEngineeringPressure balance
The invention discloses a vacuum attracting and pressure regulation pneumatic cylinder. The vacuum attracting and pressure regulation pneumatic cylinder includes a pneumatic cylinder. The pneumatic cylinder is internally provided with a fixing isolation plate. A piston piece is arranged in the fixing isolation plate in a sliding mode. The center of the piston piece is provided with an air sealingpiston. The tail end of the piston piece is provided with a second air sealing piston. In this way, the interior of the pneumatic cylinder is composed of three air chambers and the air chambers are connected with a sleeving tube. When displacement of the piston piece occurs, the piston piece is matched with the flow of the air flow to be in and out of the pneumatic cylinder, so that the sizes of the air chambers can be adjusted corresponding spaces. Changing of sizes of the air chambers is used to vacuummize the sleeving tube, so that a stump and a prosthesis can suck with each other closely.Weight sense of the prosthesis during walking is greatly reduced, and in this way, matched with a user and in walking action, pressure balance of each air chamber is achieved and natural stability isachieved. A channel inside the piston piece is further provided with a floating piston and an airflow reduction screw. The airflow in the third air chamber can be adjusted to be reduced and dischargedsuitably. In this way, besides the fact that the user can obtain power to walk quickly, and the using safety can be retained.
Owner:KEN DALL ENTERPRISE
Dynamic knee joint with combined active movement and passive movement
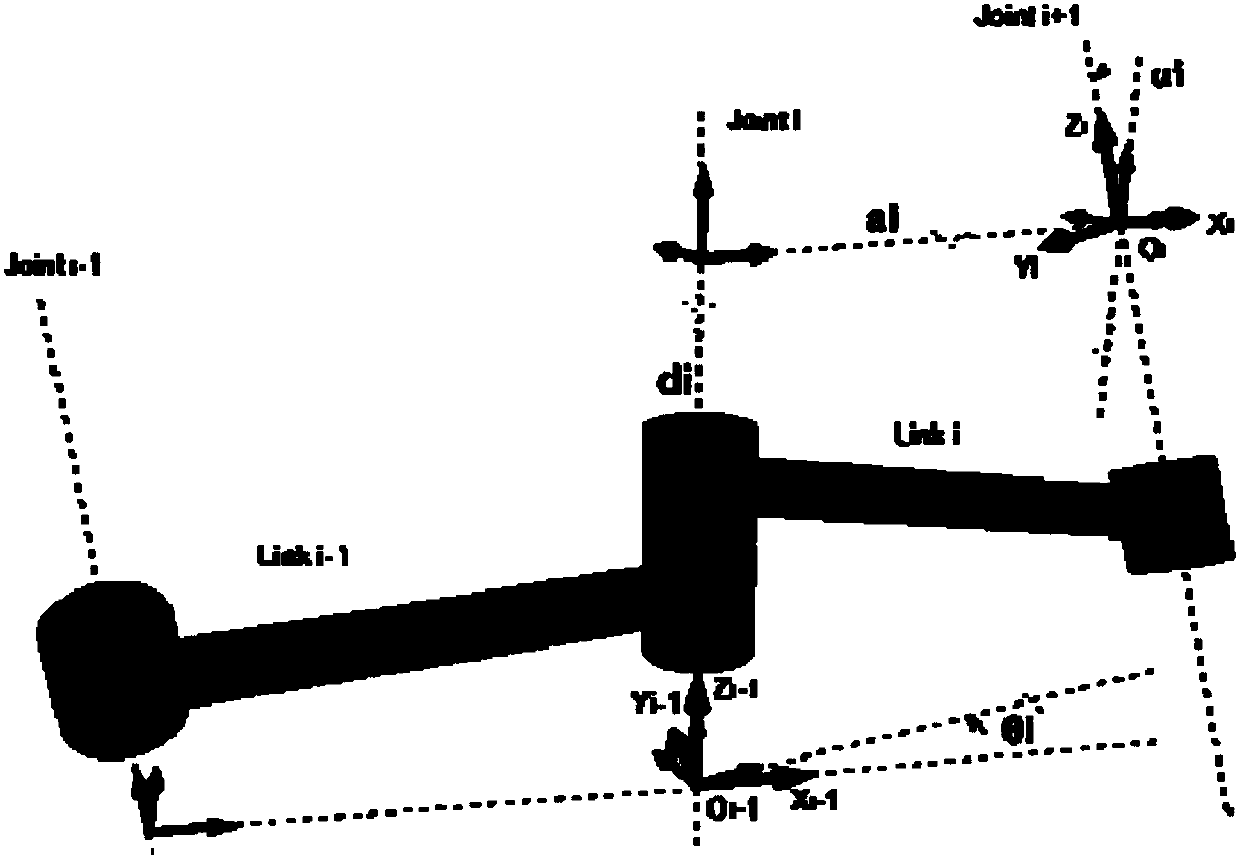
The invention relates to a dynamic knee joint with combined active movement and passive movement. The dynamic knee joint is characterized by comprising a thigh connecting rack, a shank connecting rack and a knee joint moving mechanism, wherein the knee joint moving mechanism comprises a knee joint connecting rack, a synchronous pulley connecting mechanism and a motor; the motor is fixedly connected with the thigh connecting rack and an output end of the motor is connected with one end of a driving shaft through a coupling; the other end of the driving shaft is fixedly connected with the thighconnecting rack through a driving shaft bearing; a knee joint shaft is fixedly supported on the knee joint connecting rack through a knee joint bearing; the two ends of the knee joint shaft are fixedly connected with the shank connecting rack; the knee joint shaft is fixedly connected with an inner ring of a one-way clutch through a knee joint shaft connecting key; and an outer ring of the one-way clutch is connected with the driving shaft through the synchronous pulley connecting mechanism. The dynamic knee joint is widely applied to the research of a flexible dynamic joint of an artificial limb and can serve the disabled.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Multi-shaft hydraulic knee joint
The invention provides a multi-shaft hydraulic knee joint, and belongs to the field of bionic devices. The multi-shaft hydraulic knee joint comprises a connector, a connecting body, a first connectingrod, a second connecting rod and a brake assembly, wherein one end of the connector is provided with a protruding end, one end of the connecting body is a connecting end, the other end of the connecting body is a connecting part for connecting a shank prosthesis, one end of the first connecting rod is connected with the protruding end by means of a rotating shaft structure, the other end of the first connecting rod is connected with the connecting end of the connecting body through a rotating shaft structure, one end of the second connecting rod is rotationally connected with the connector through a rotating shaft structure, the other end of the second connecting rod is connected with the connecting body by means of a rotating shaft structure, the brake assembly is arranged between the first connecting rod and the second connecting rod, one end of the brake assembly is rotatably connected with the protruding end through a rotating shaft structure, and the other end of the brake assembly is rotatably connected with the second connecting rod through a rotating shaft structure. The provided multi-shaft hydraulic knee joint is reasonable in structural design, small in occupied space and long in service life; and the multi-axis hydraulic knee joint also has the characteristics of high motion stability and high safety.
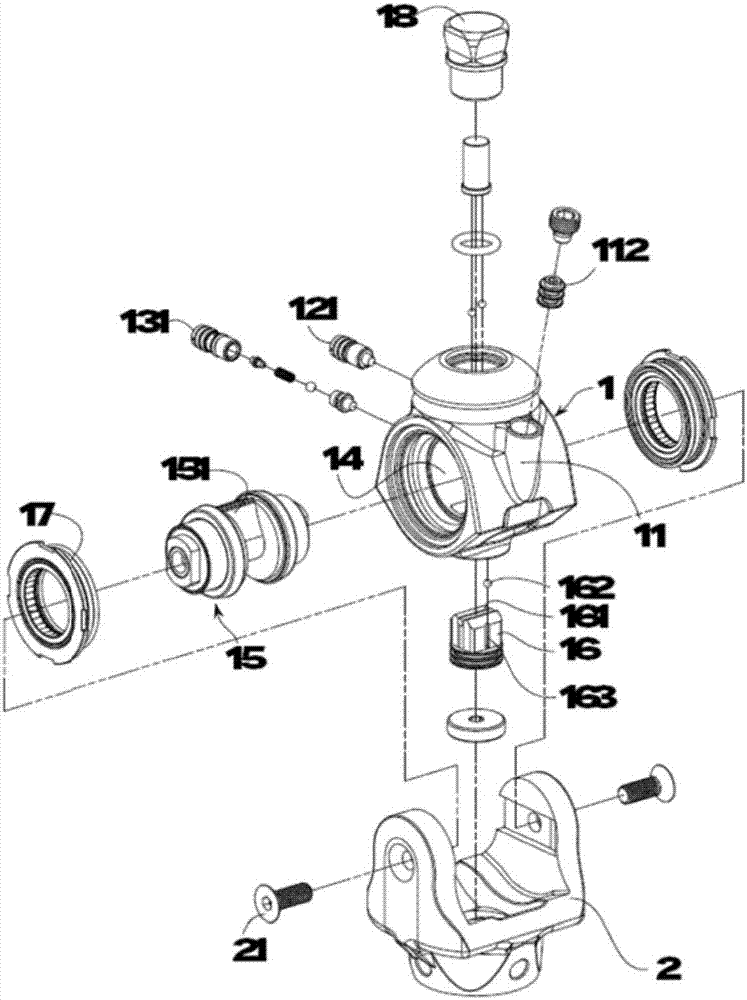
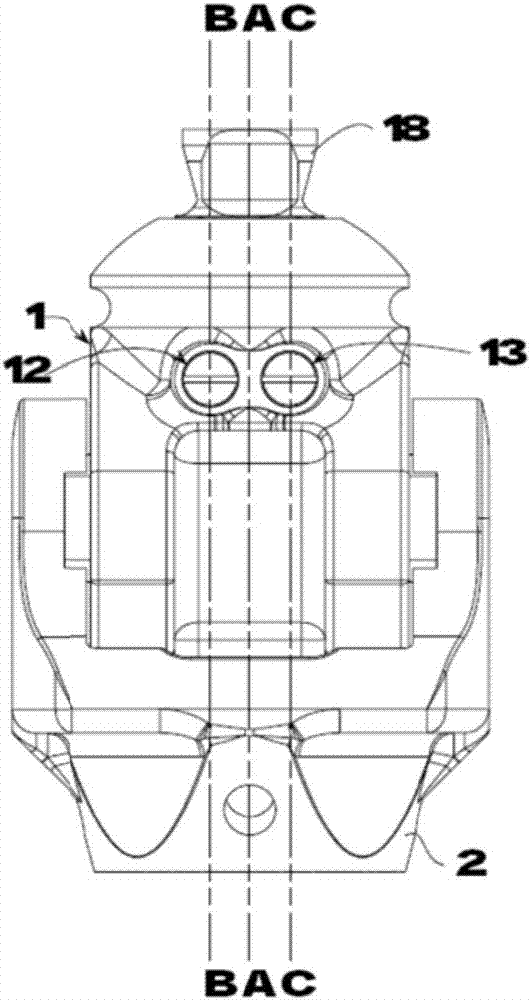
Owner:北京市康复辅具技术中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com