Patents
Literature
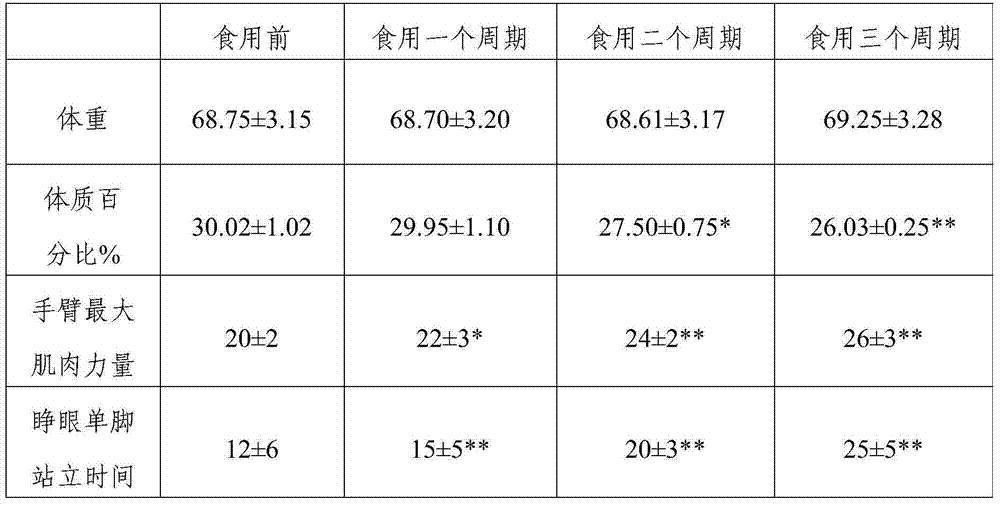
111 results about "Muscle power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
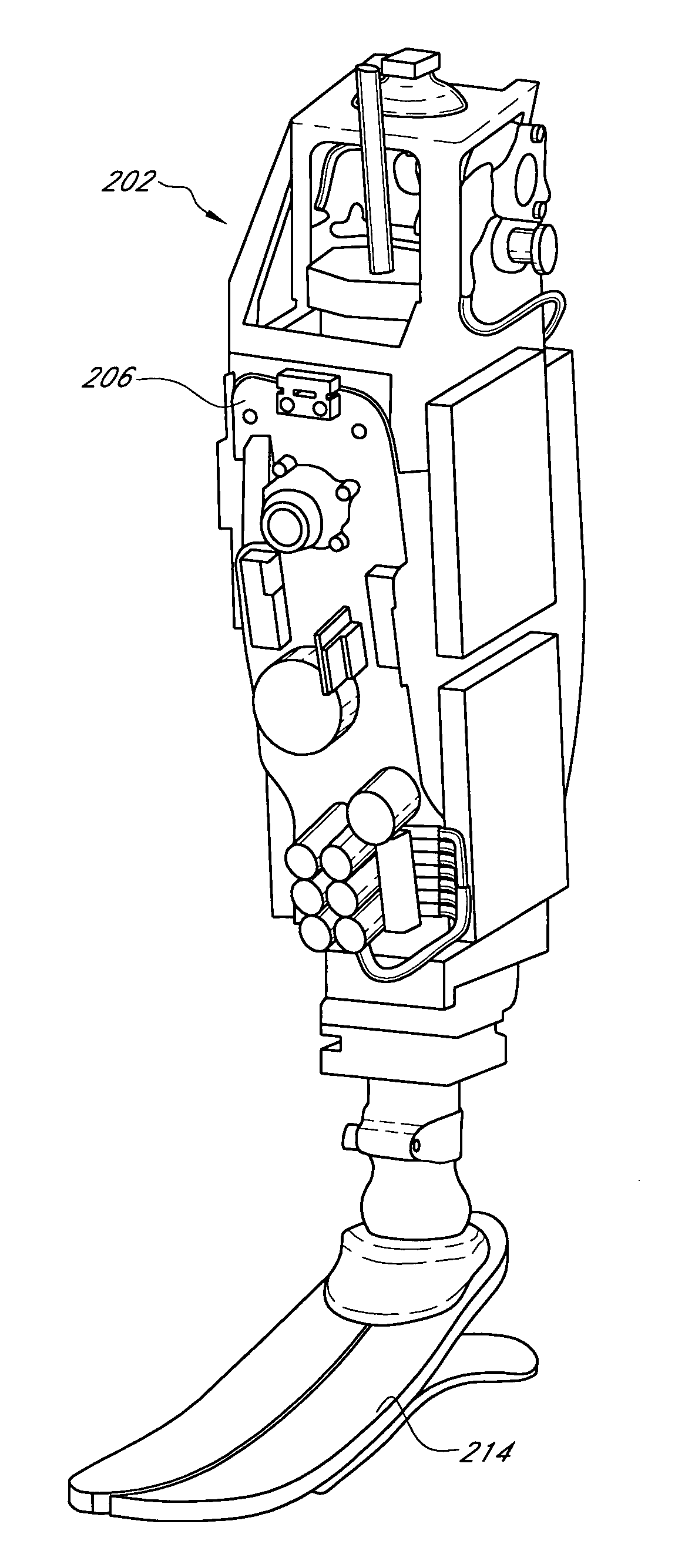
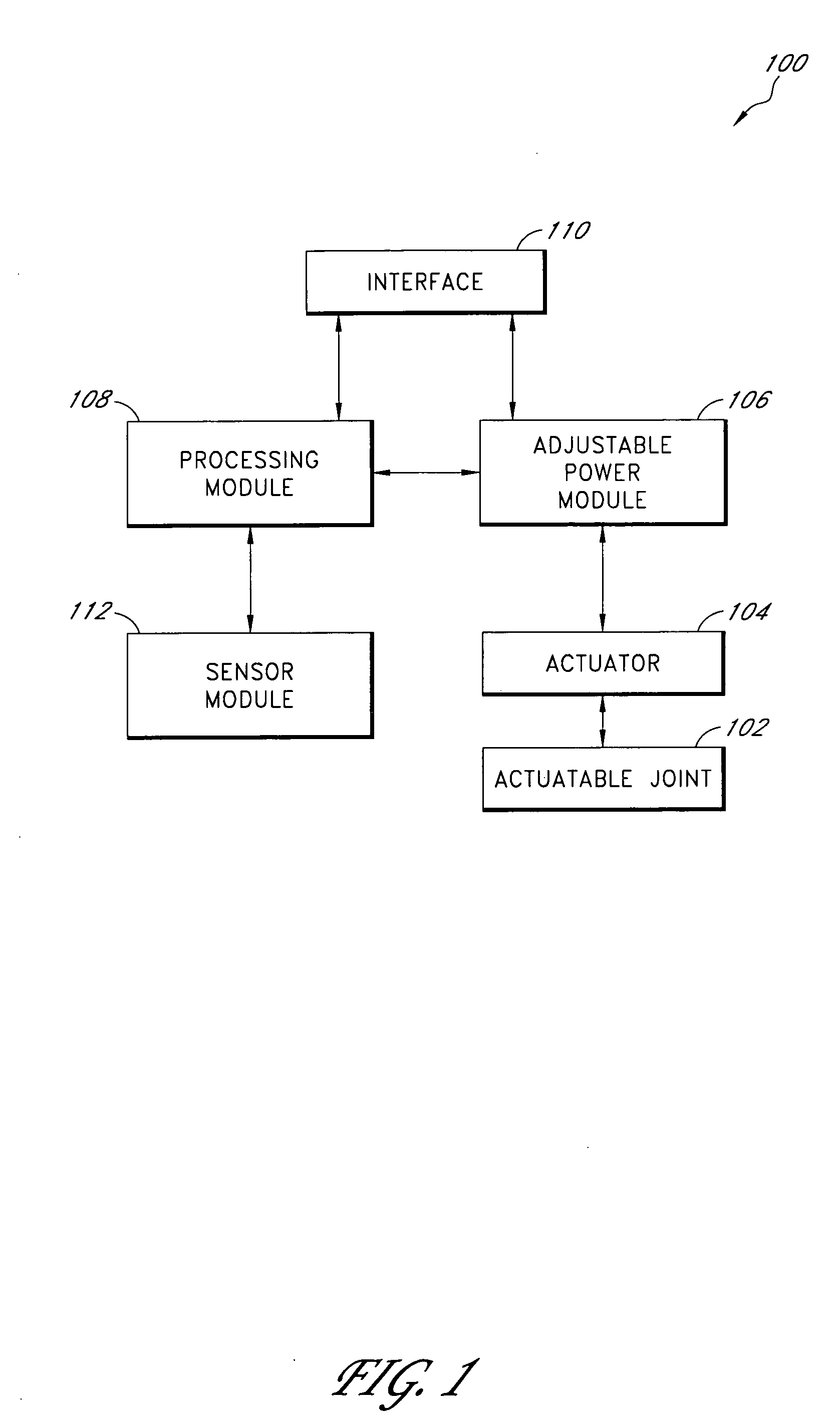
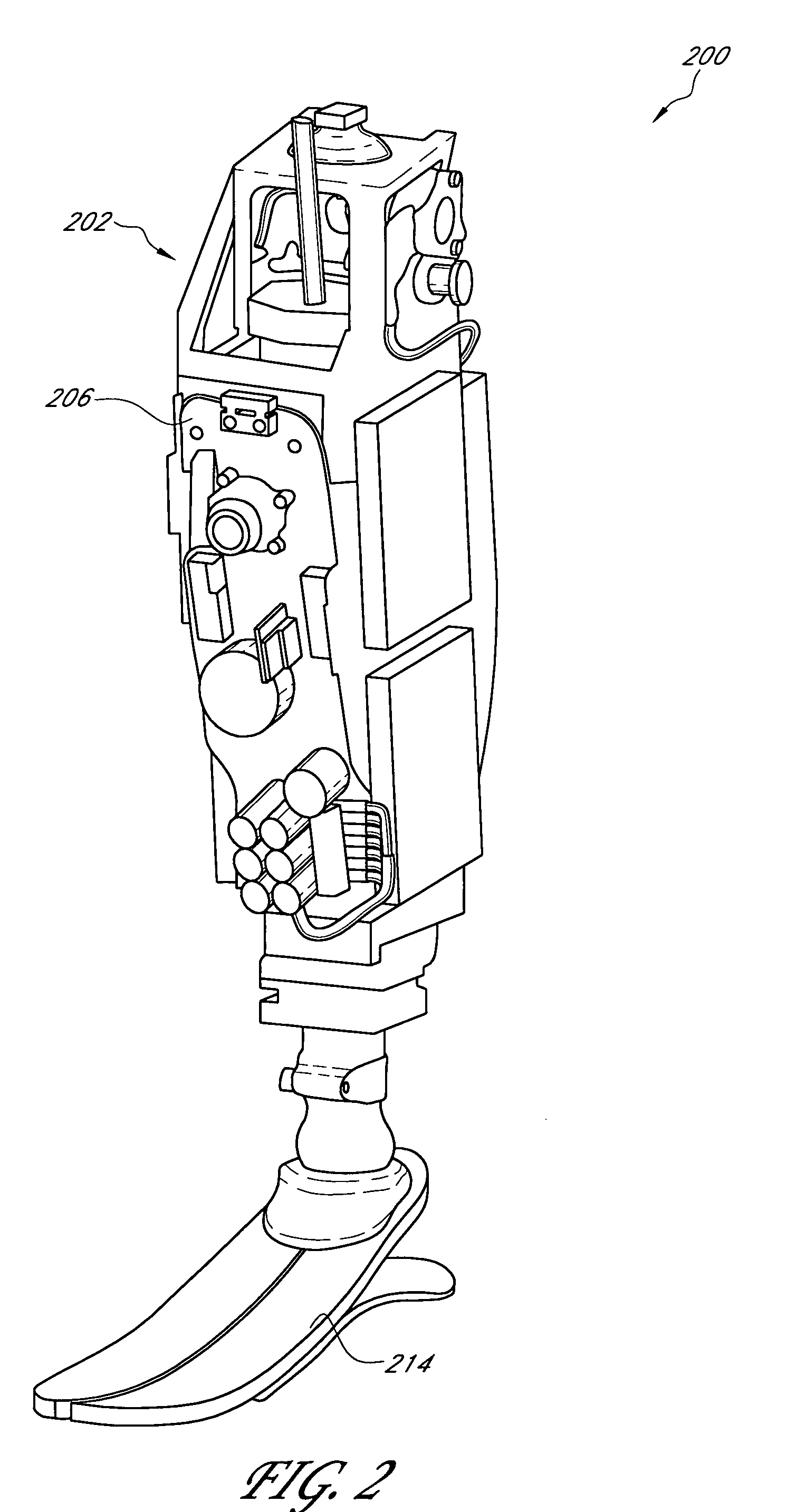
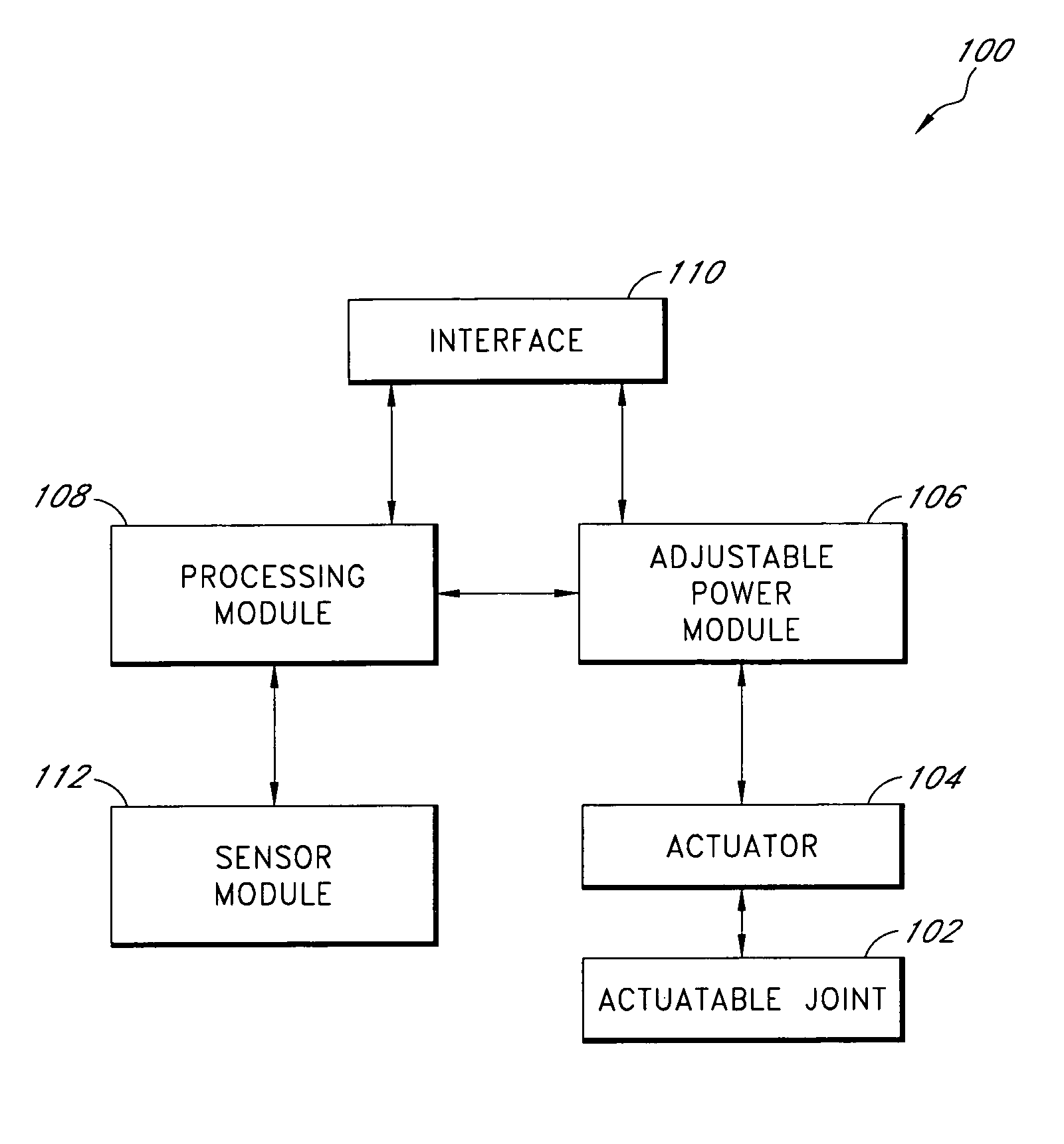
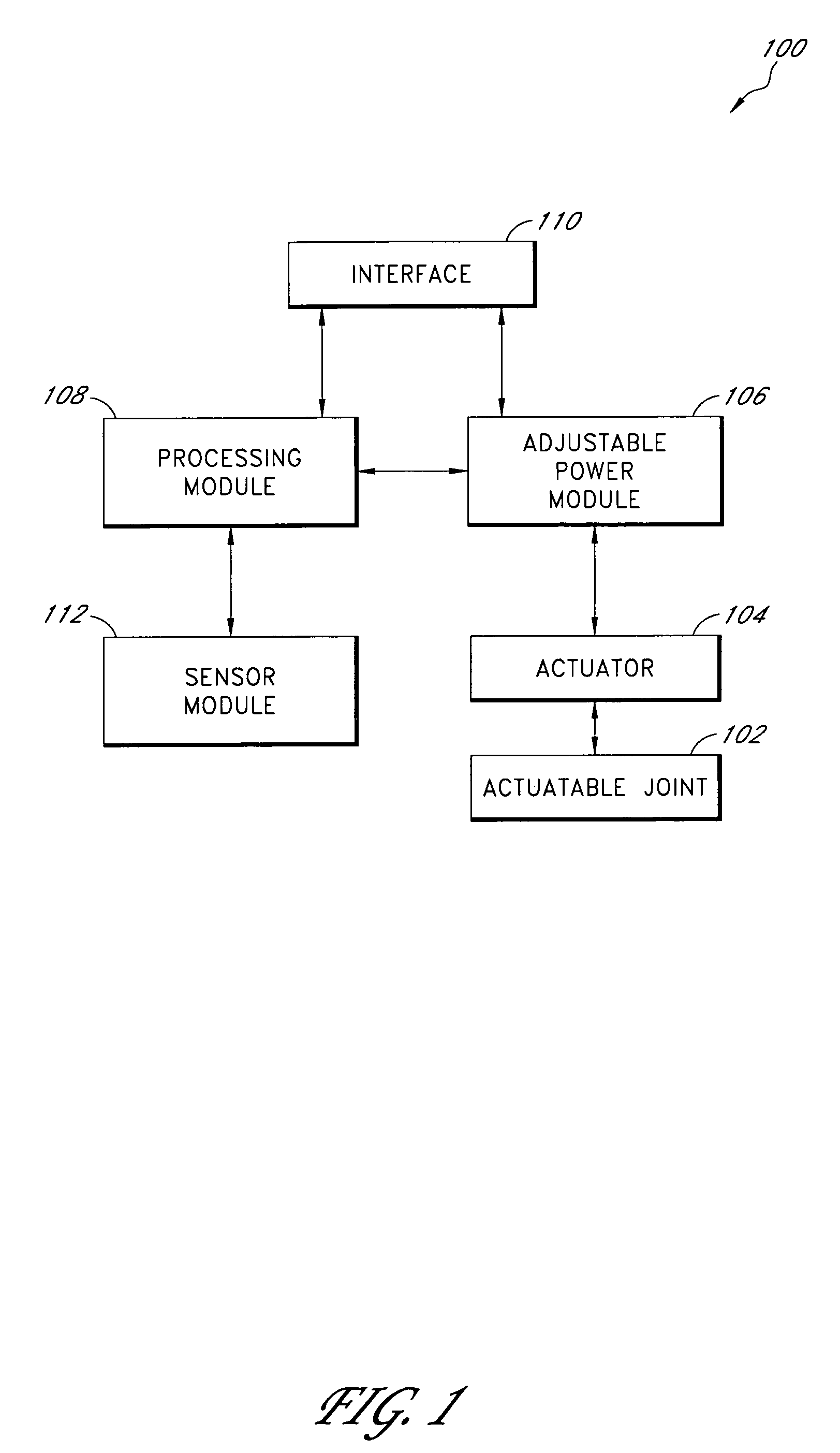
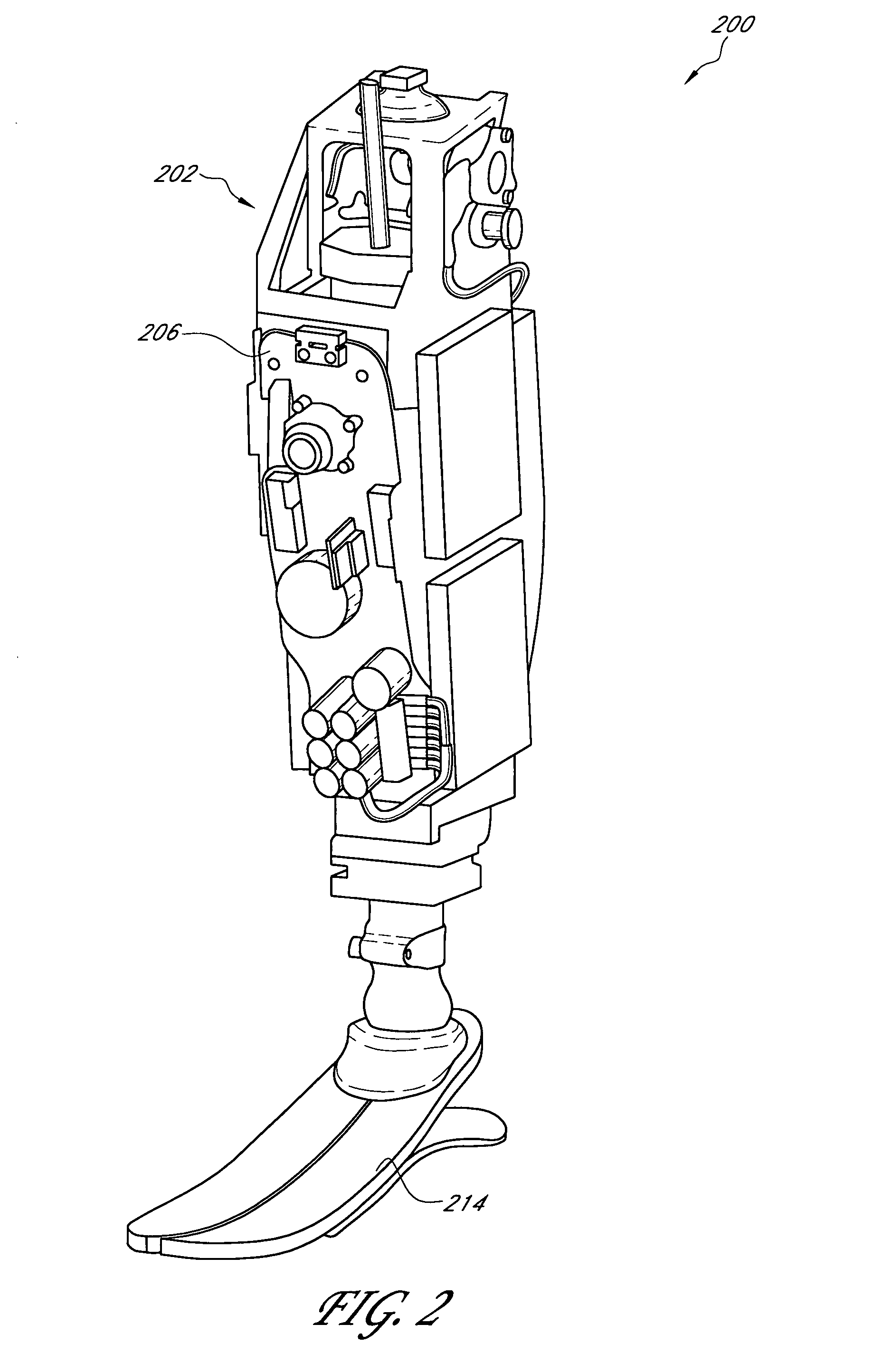
Prosthetic and orthotic systems usable for rehabilitation
ActiveUS20060173552A1Smooth rotationReduce energy consumptionSurgeryChiropractic devicesDevice prostheticMuscle power
Disclosed are adjustable powered rehabilitation devices and methods for using the same to rehabilitate and / or train a user. The rehabilitation devices preferably have a plurality of selectable power settings that correspond to one or more rehabilitation-oriented actions or functions of the rehabilitation devices. For example, the power of the rehabilitation device may be selected based on a need, ability, muscle-power and / or physiological characteristics of the user. For instance, a rehabilitation device may be operated at a relatively low power setting to allow a patient to use his or her own muscle power when moving with the rehabilitation device. The rehabilitation device may also include an adjustable sensitivity level that corresponds to a user difficulty in triggering a particular rehabilitation-oriented action. The powered rehabilitation device may also temporarily be used to train a user in interacting with a passive or more conventional prosthetic device.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Prosthetic and orthotic systems usable for rehabilitation
ActiveUS8048007B2Smooth rotationReduce energy consumptionSurgeryChiropractic devicesProsthesisDevice prosthetic
Disclosed are adjustable powered rehabilitation devices and methods for using the same to rehabilitate and / or train a user. The rehabilitation devices preferably have a plurality of selectable power settings that correspond to one or more rehabilitation-oriented actions or functions of the rehabilitation devices. For example, the power of the rehabilitation device may be selected based on a need, ability, muscle-power and / or physiological characteristics of the user. For instance, a rehabilitation device may be operated at a relatively low power setting to allow a patient to use his or her own muscle power when moving with the rehabilitation device. The rehabilitation device may also include an adjustable sensitivity level that corresponds to a user difficulty in triggering a particular rehabilitation-oriented action. The powered rehabilitation device may also temporarily be used to train a user in interacting with a passive or more conventional prosthetic device.
Owner:OSSUR HF
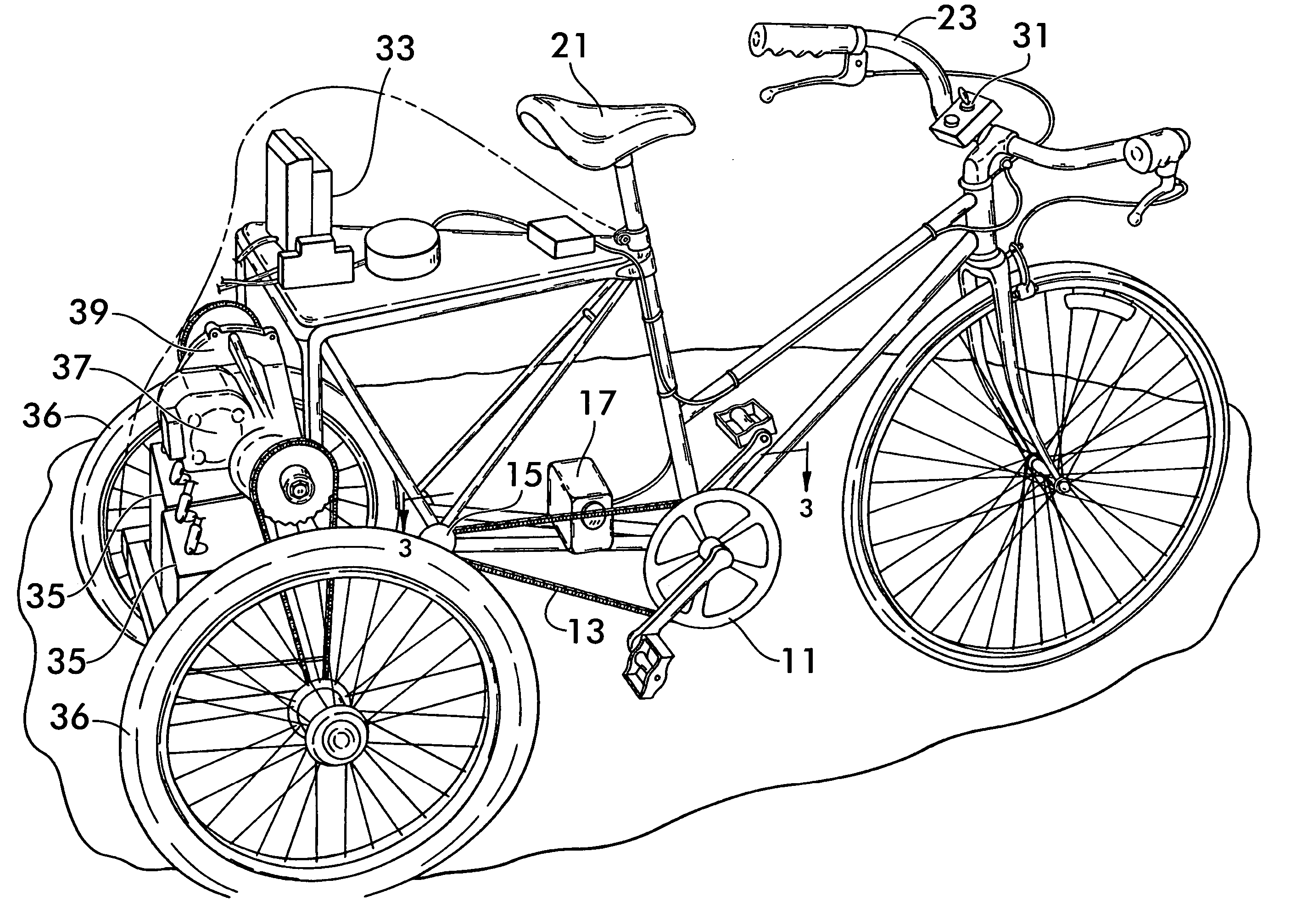
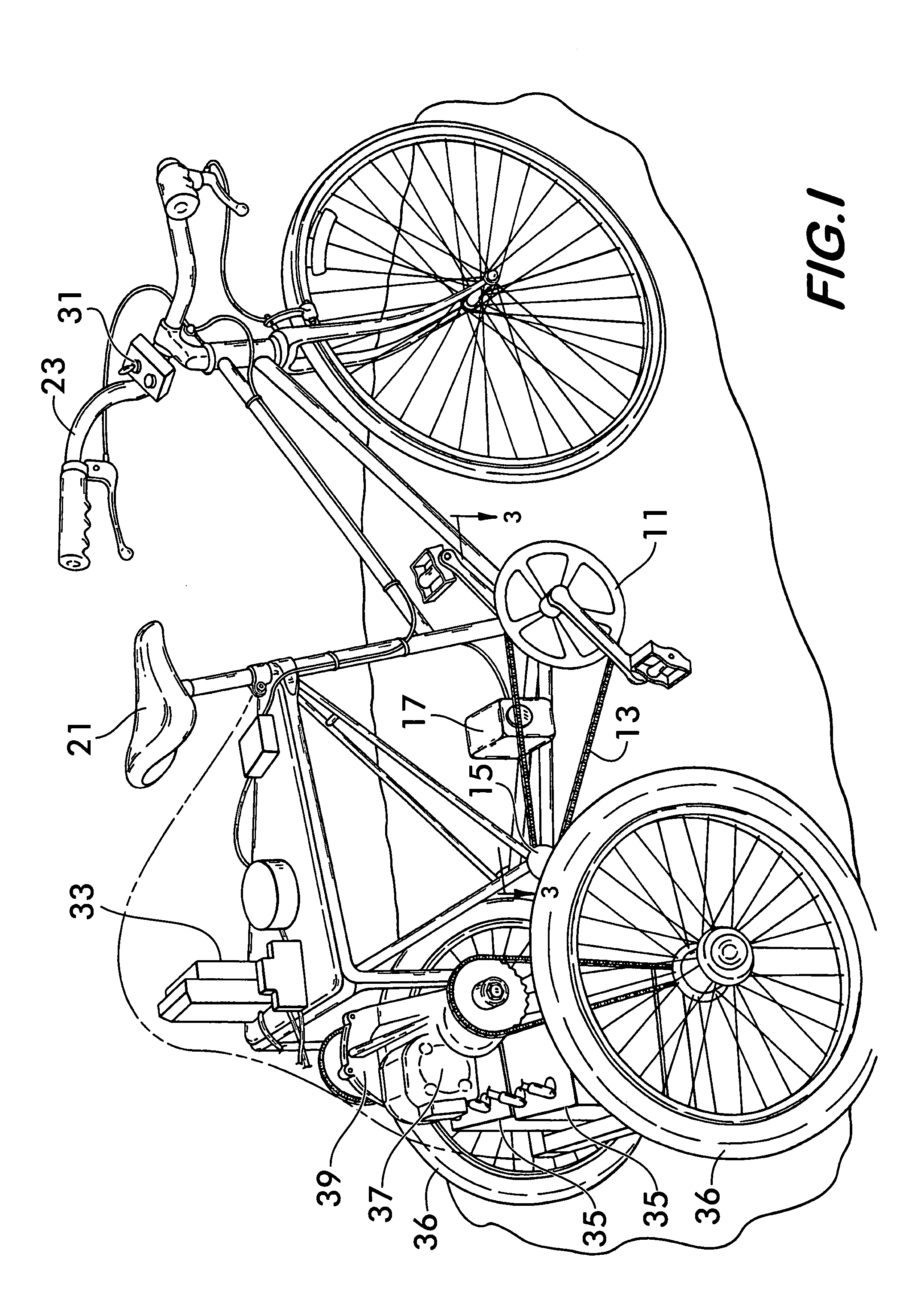
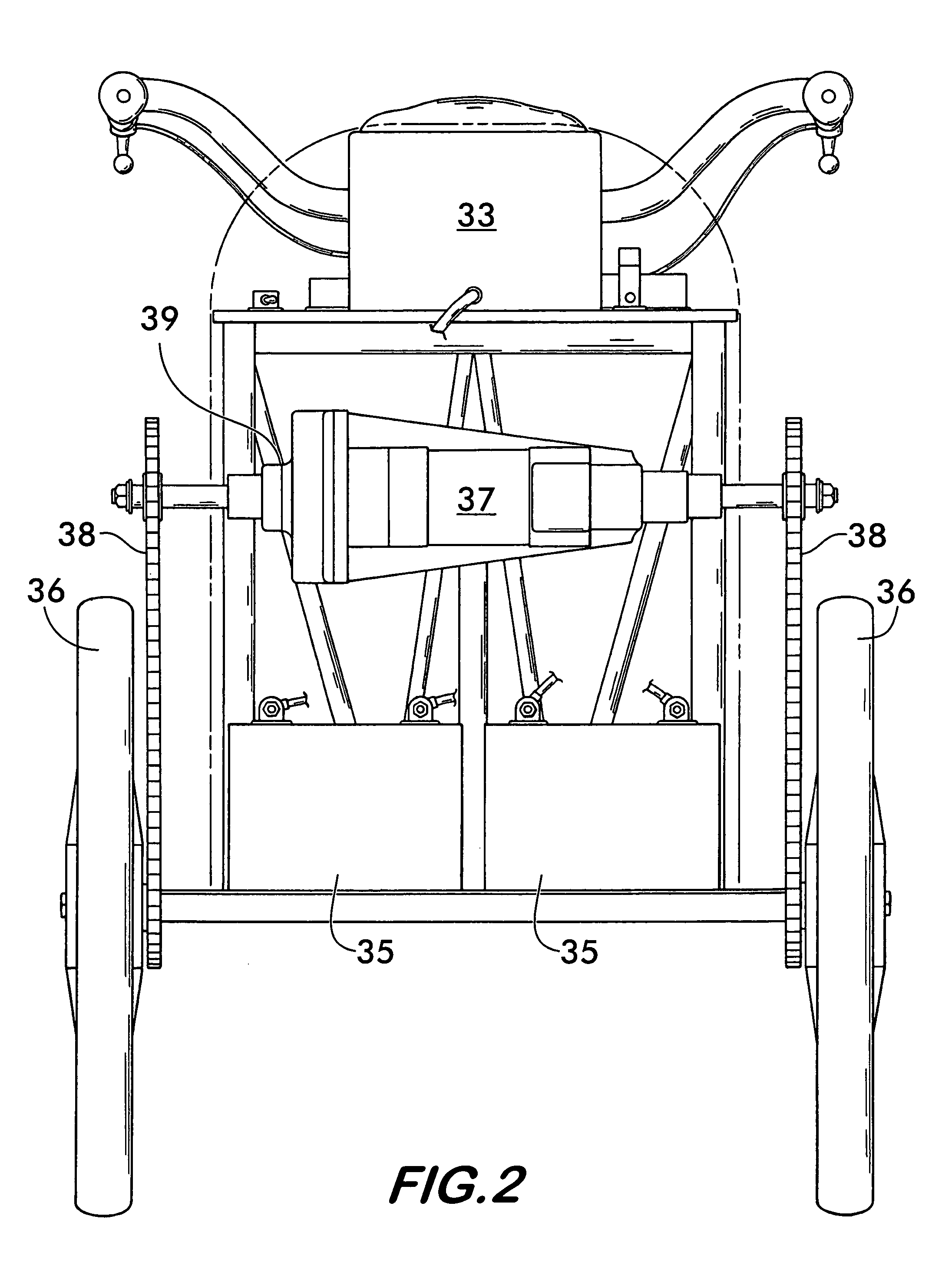
Hybrid drive mechanism for a vehicle driven by muscle power, with an auxiliary electric motor
InactiveUS6286616B1High speedEasy to assembleElectric propulsion mountingVehicle transmissionDrive wheelControl theory
A hybrid drive mechanism for a wheel-driven vehicle. The drive mechanism has an electromotor with a rotor and a stator as a first drive source, with a first speed and a first torque, and a pedal drive as a second drive source, with a second speed and a second torque. The stator of the electromotor is positioned on an axle or shaft of the drive train between the pedal crank and the drive wheel, preferably on a wheel axis, in such a way that it can rotate. The stator can be coupled mechanically with the second drive source so that the stator is driven by the second drive source, and the rotor of the electromotor has a speed which corresponds to the sum of the first speed of the first drive and the second speed of the second drive.
Owner:KUTTER MICHAEL
Cherry and tomato composite beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104312859AComprehensive and balanced nutritionEvenly ruddy colorAlcoholic beverage preparationThirstNutrient solution
The invention discloses a cherry and tomato composite beverage and a preparation method thereof. The cherry and tomato composite beverage is prepared from the following raw materials, by weight, 30-45 parts of cherry, 15-20 parts of tomato, 10-15 parts of guava, 10-14 parts of pitaya peel, 10-15 parts of buckwheat, 14-18 parts of red glutinous rice, 1-3 parts of stevioside, 2-3 parts of very precious flower in Plateau Snow Mountain, 2-4 parts of ginseng fruit, 3-5 parts of grapefruit flower, 1-2 parts of flower of Intermediate peashrub, 1-2 parts of Japanese metaplexis, 12-18 parts of setose abelmoschus, a proper amount of rose wine, and 8-10 parts of a nutrient solution. The cherry and tomato composite beverage prepared in the invention maximally reserves nutritional components of cherry and tomato, has the characteristics of red and uniform color, aroma, sweet and delicious taste, smooth mouthfeel, abundant and balanced nutrition, and simple and feasible technology, has the efficacies of body fluid production promoting, thirst quenching, stomach strengthening, food digesting, pressure reducing, lipid lowering, heat clearing, detoxifying, toxin expelling and face nourishing through the synergistic effect with health care components of traditional Chinese medicines, and can promote digestion, enhance muscle power and improve the oxidation resistance of human bodies through long term drinking.
Owner:徐九山
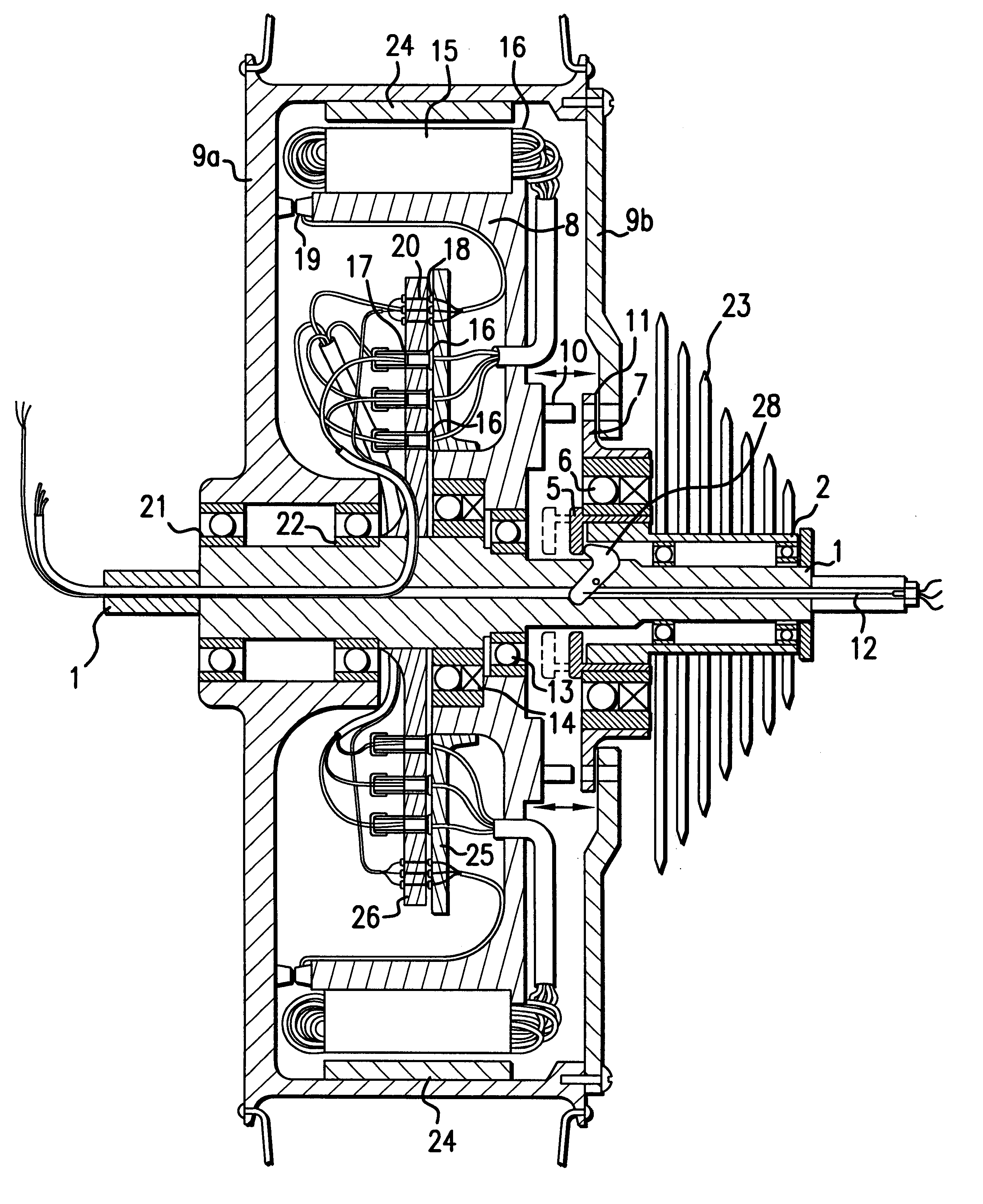
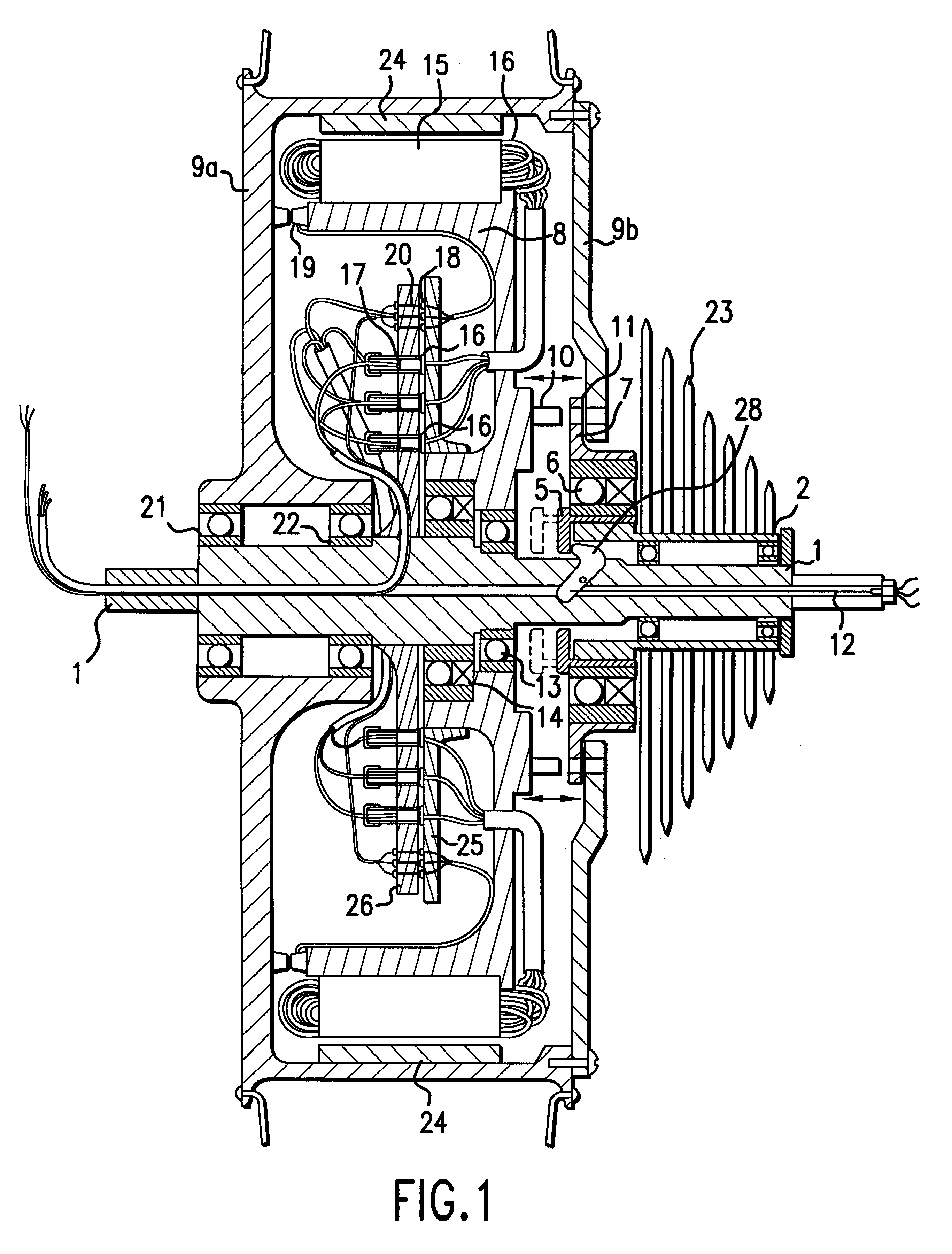
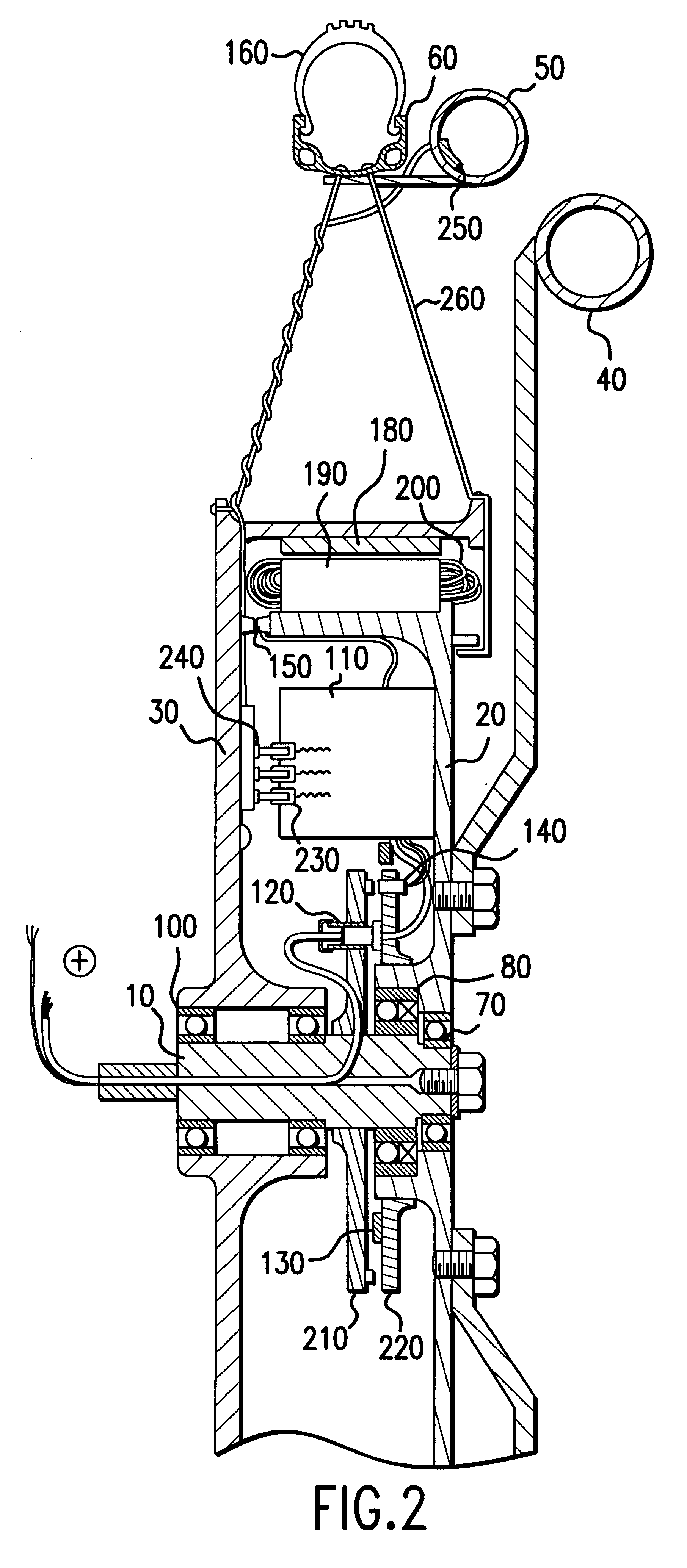
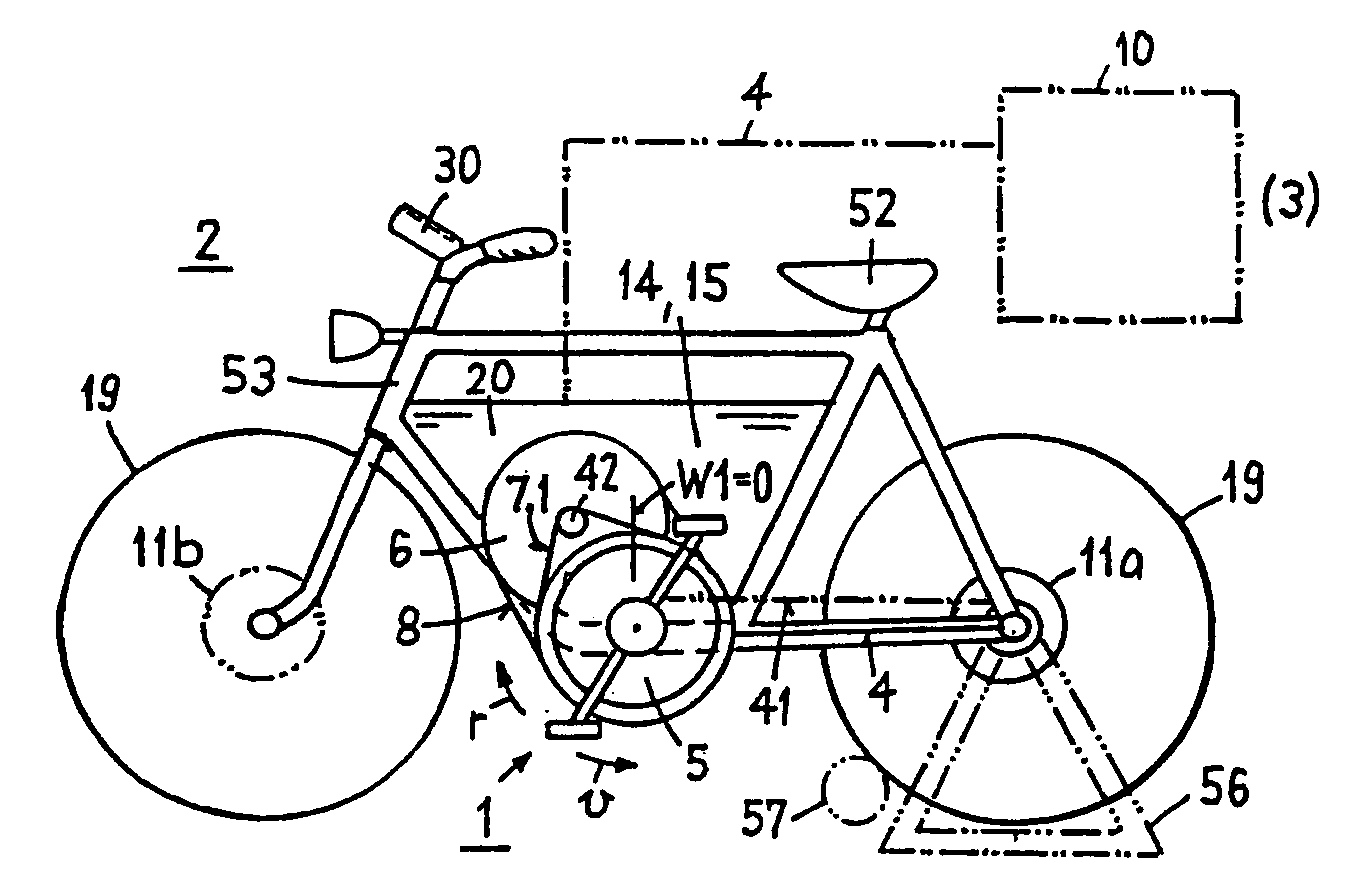
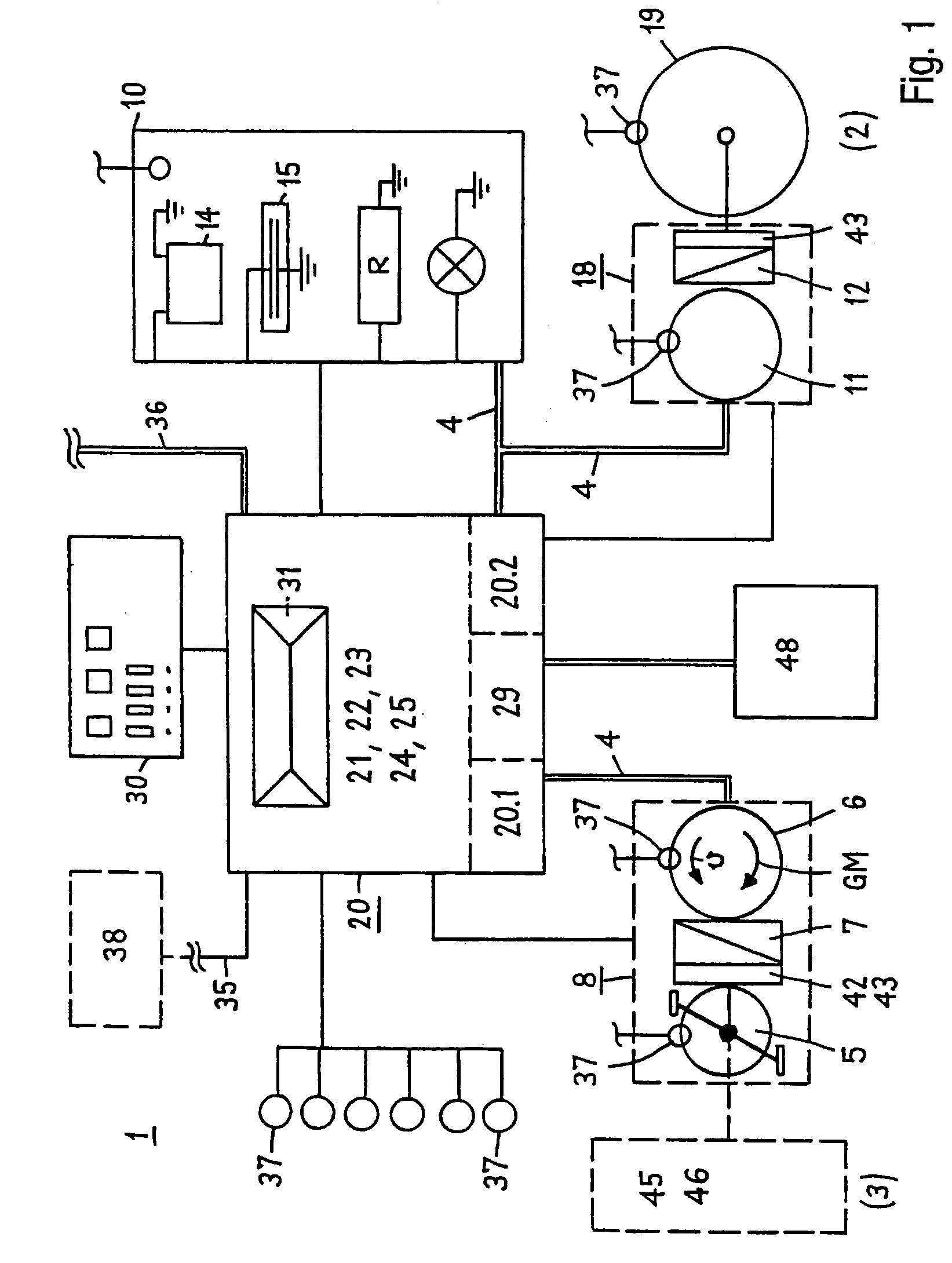
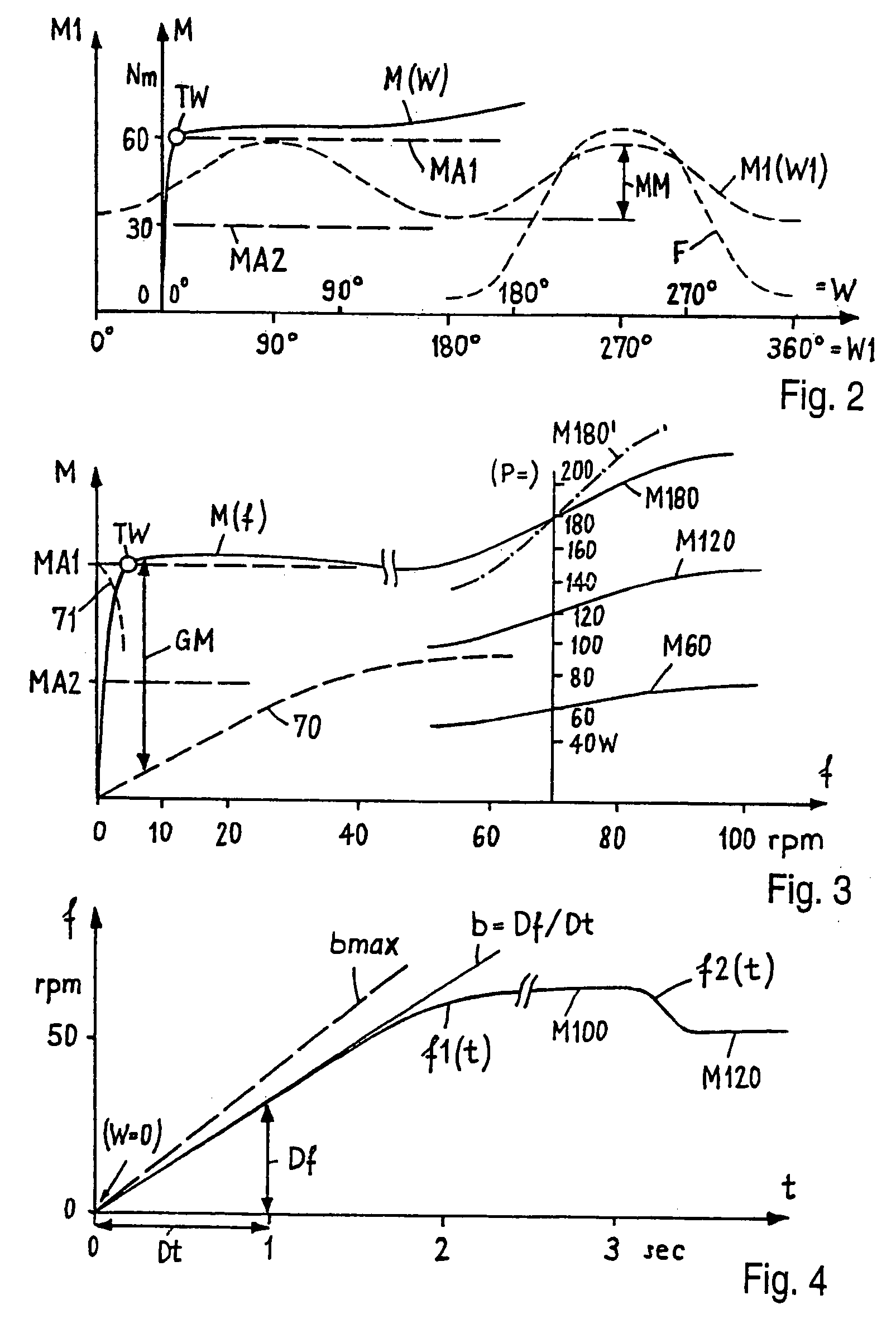
Drive system operated by muscle-power
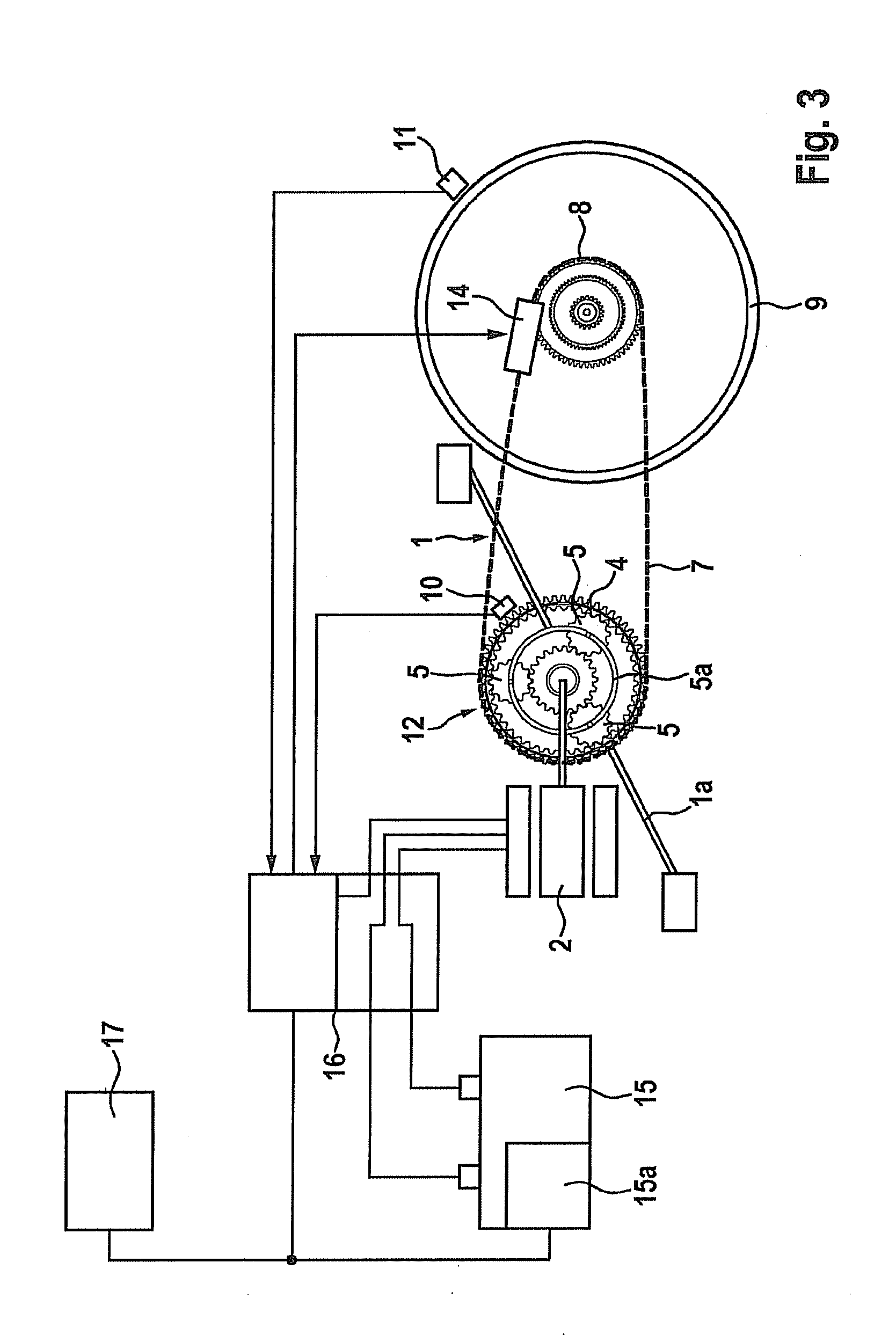
An electric drive system (1) operated by muscle power for a vehicle (2) includes a foot pedal (5) and a mechanical generator (6) mechanically connected to the foot pedal. The drive system also includes an electric transmission (4) and an electric control system (20) with a control program (21) of the generator, which is able to generate a counter or load moment (GM). The drive system also includes a starting control system (22) for the generator, by means of which a standstill pedal resistance (TW) and a high starting moment (MA) is produced at the foot pedal. When used in a stationary training apparatus (3), the drive system includes a motor operation control system (23) with a bi-directional converter (31), by means of which the generator is also able to be operated as a motor.
Owner:SWISSMOVE
Device and system to measure and assess superficial muscle contractile characteristics
InactiveUS20190022388A1Inertial sensorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerMuscle contraction
The present invention relates to a device and system to measure and assess superficial skeletal muscle mechanical and neuromuscular contractile characteristics, and interpret the results to provide metrics with quantifiable and qualitative descriptors relating to muscle function. The present device provides a further type of mechanomyography and a new use for acceleromyography by measuring the mechanical muscle movement of an involuntary stimulated muscle from an automated electro-stimulation protocol to determine muscle contractile properties. Muscle twitch response during the latent, contraction and relaxation phase is measured using an array of multiple accelerometers on a sensor pad to assess and diagnose muscle. function from various measurements. This information is processed using algorithms to determine muscle function abnormalities, muscle activation patterns, muscle symmetry of lateral muscle pairs, muscle synchronization of antagonist muscle, muscle force, muscle acceleration, muscle speed, muscle tone, muscle fatigue, muscle power / torque and muscle efficiency.
Owner:QUANIMUS INC
Combined muscular multi-directional bending flexible joint
The present invention relates to a combinatory muscle type flexible joint capable of bending toward several directions. It can be used as various joints of robot and artificial limb. Said flexible joint adopts the axial expasion of elastic corrugated pipe after which is forced by fluid pressure as muscle power, several artificial muscle components are formed into said flexible joint. It adopts plate spring or plate hinge as flexible joint skeleton capable of bending toward two directions, and adopts bar spring and ball universal joint or cross universal joint as flexible joint sekelton capable of bending toward several directions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
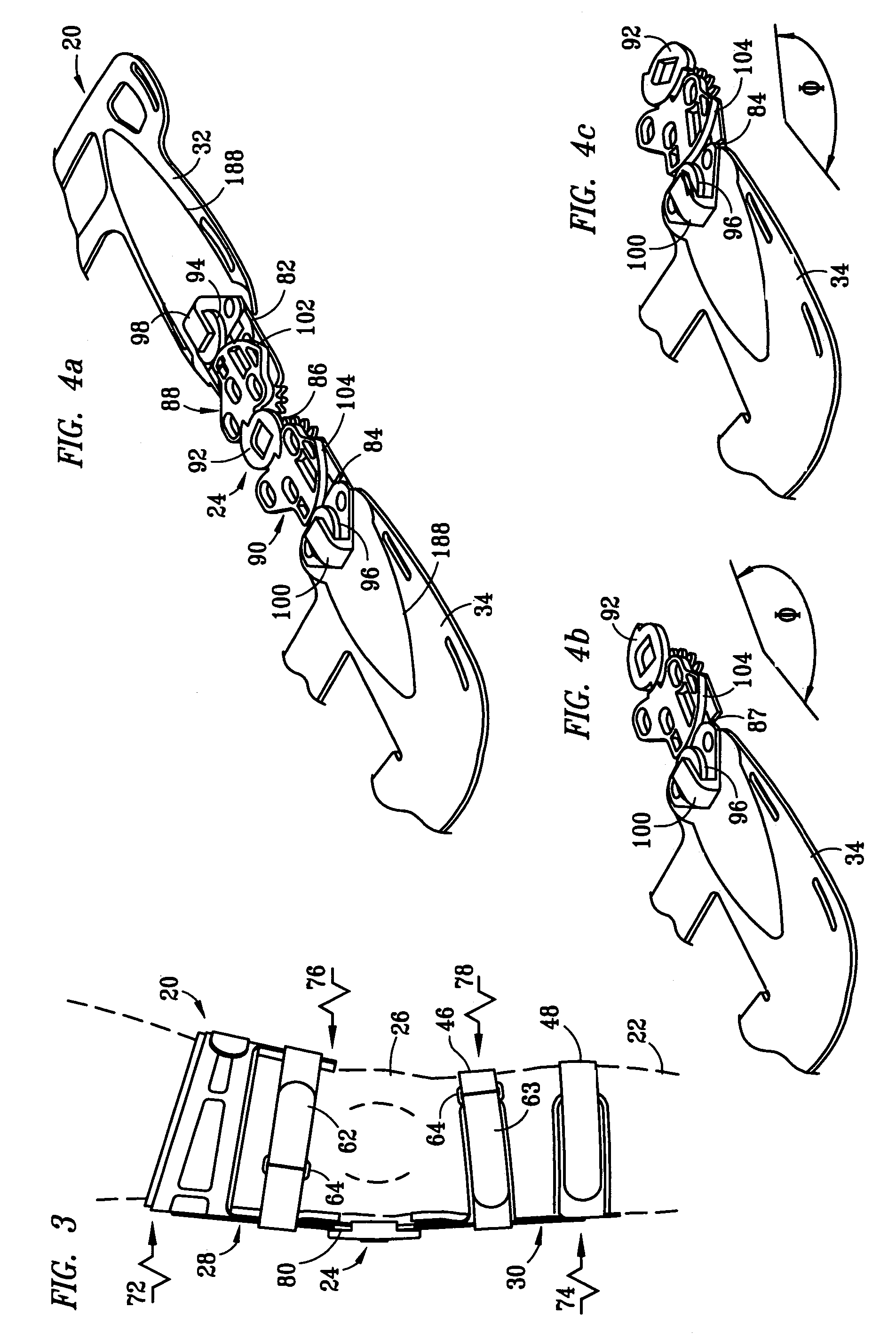
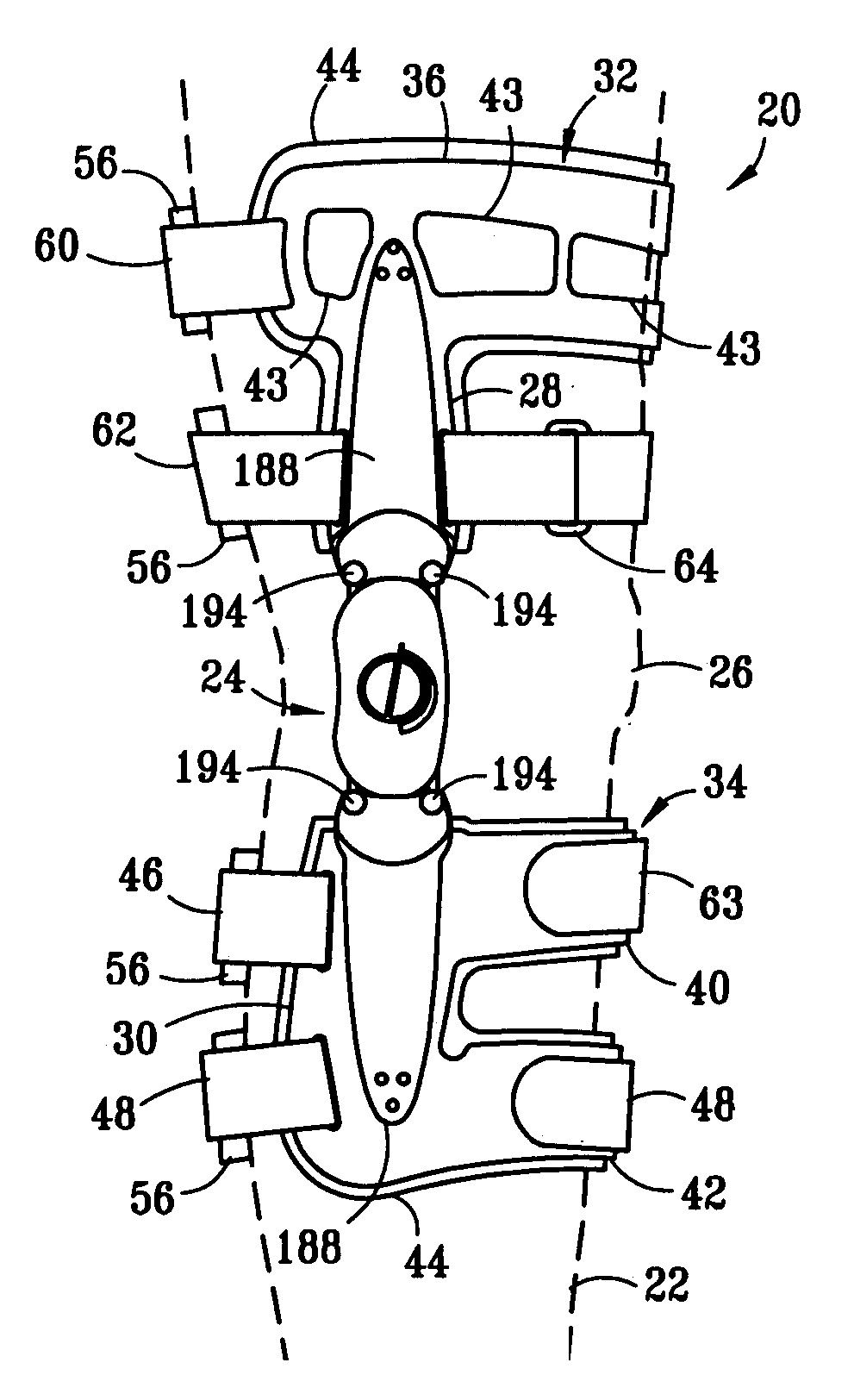
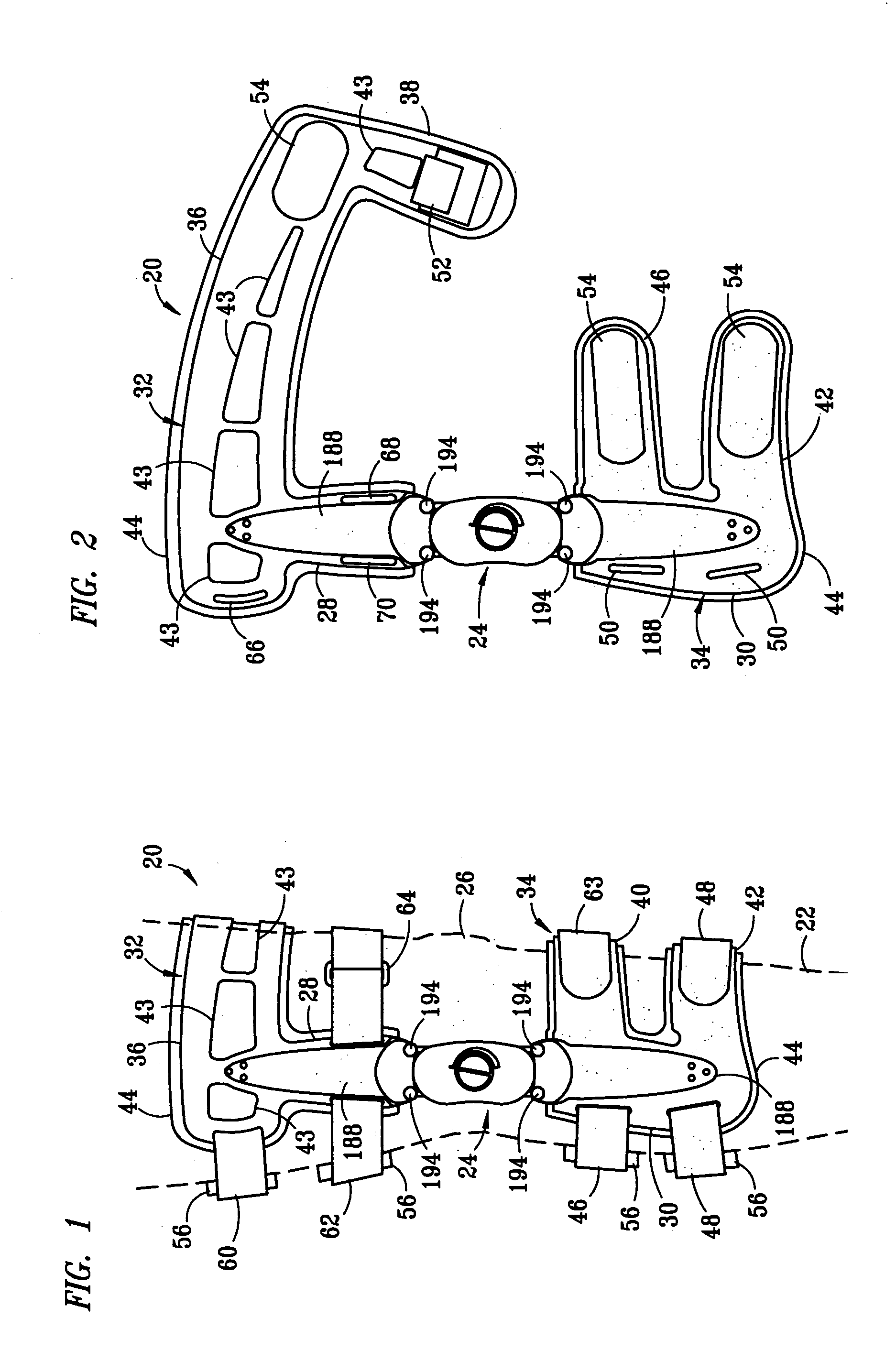
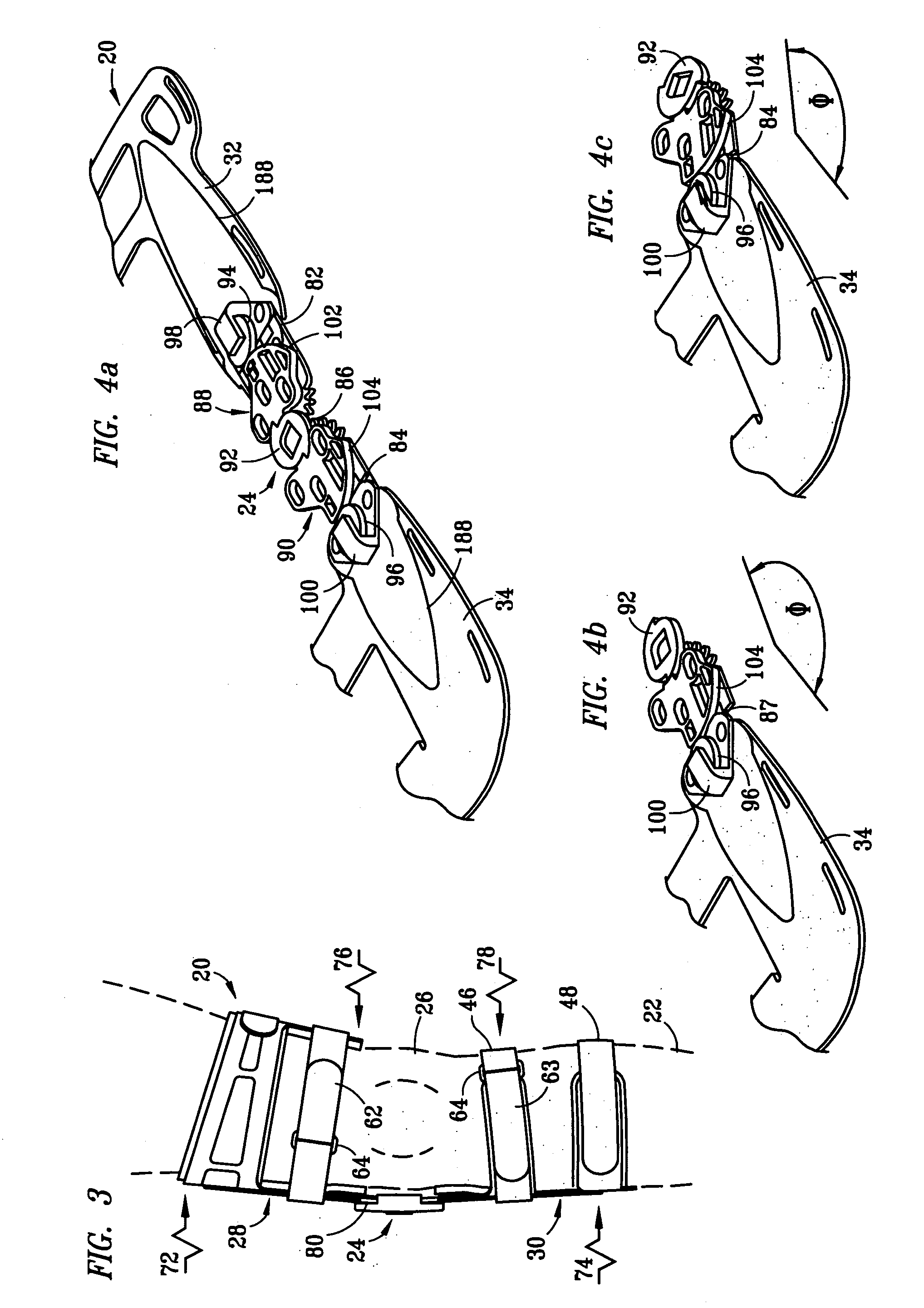
Muscle powered dynamic knee brace
A dynamic knee brace that can be used to apply a bending force across the knee. Two brace arms are connected together by a central joint that allows the knee to pivot. A joint in each brace arm allows the brace arm to be inclined toward the leg. A cam assembly is present to actively incline each brace arms toward the leg as the knee moves to full extension. An adjustment mechanism for the cam assemblies provides control over the maximum amount of inclination each brace arm achieves. Preferably, the adjustment mechanism adjusts the cams equally so that both brace arms are inclined by the same amount.
Owner:BREG
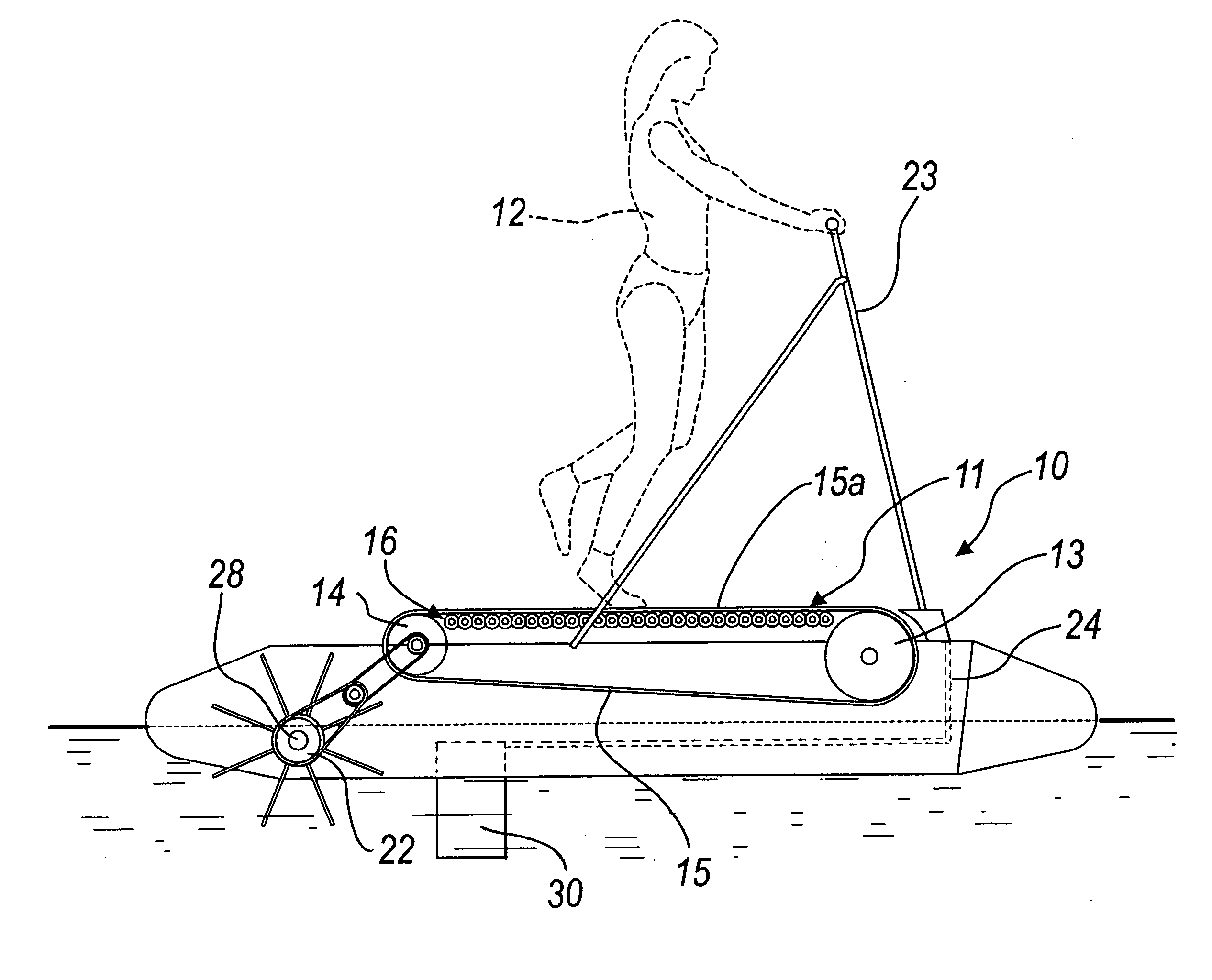
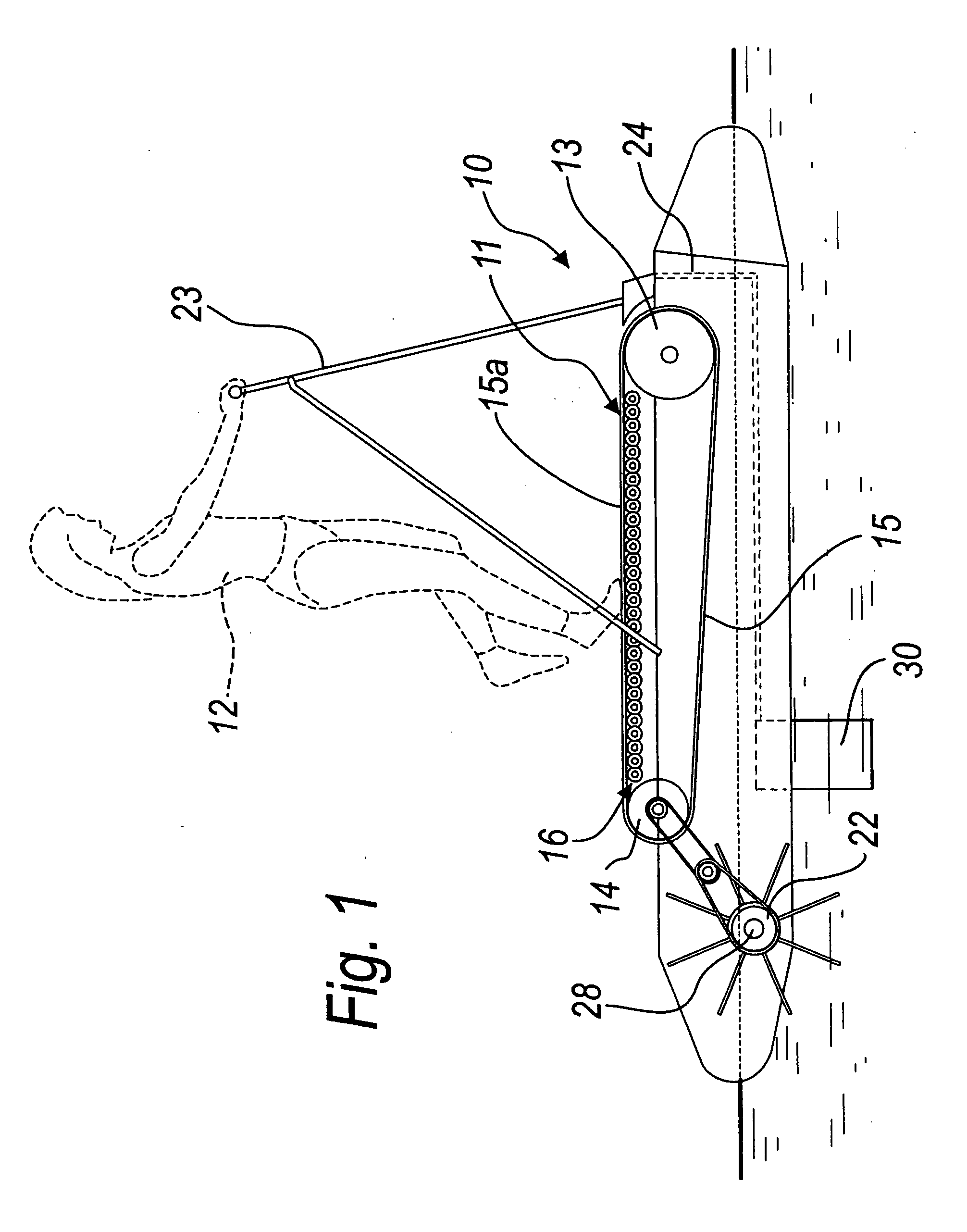
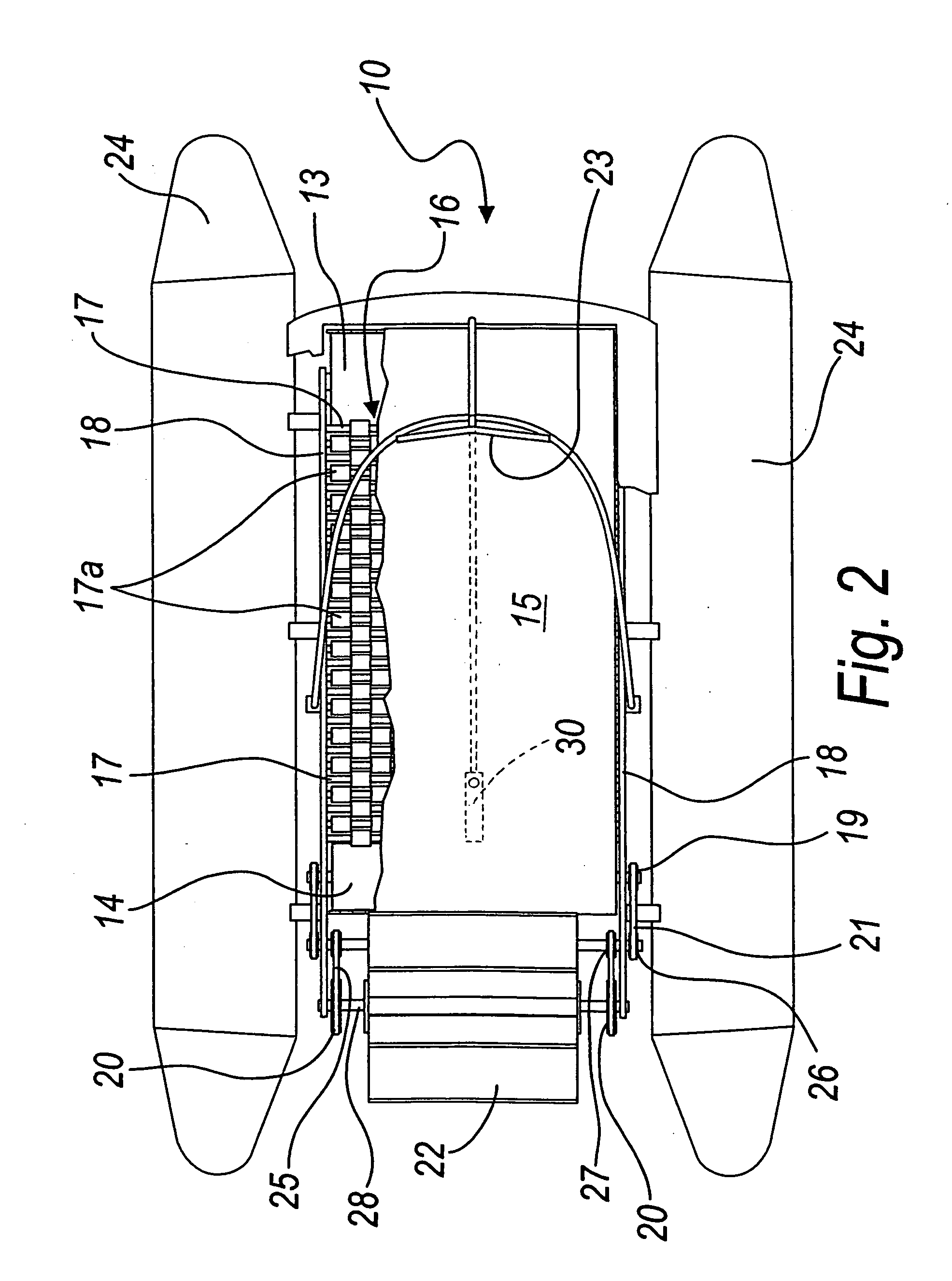
Muscle-powered vehicle
InactiveUS20060287165A1Promote circulationImprove efficiencyPropulsive elements of rotary typeMuscle power acting propulsive elementsEngineeringMuscle power
A muscle-powered vehicle, comprising a treadmill, which is supported by a chassis and is adapted to be actuated by the thrust of the feet and legs of at least one user who walks or runs thereon; a system for travel over land or on water functionally connected to the treadmill by way of motion transmission means; and a steering system for directing the travel.
Owner:PASQUALIN GIORGIO GIULIANO
Shooting action training method
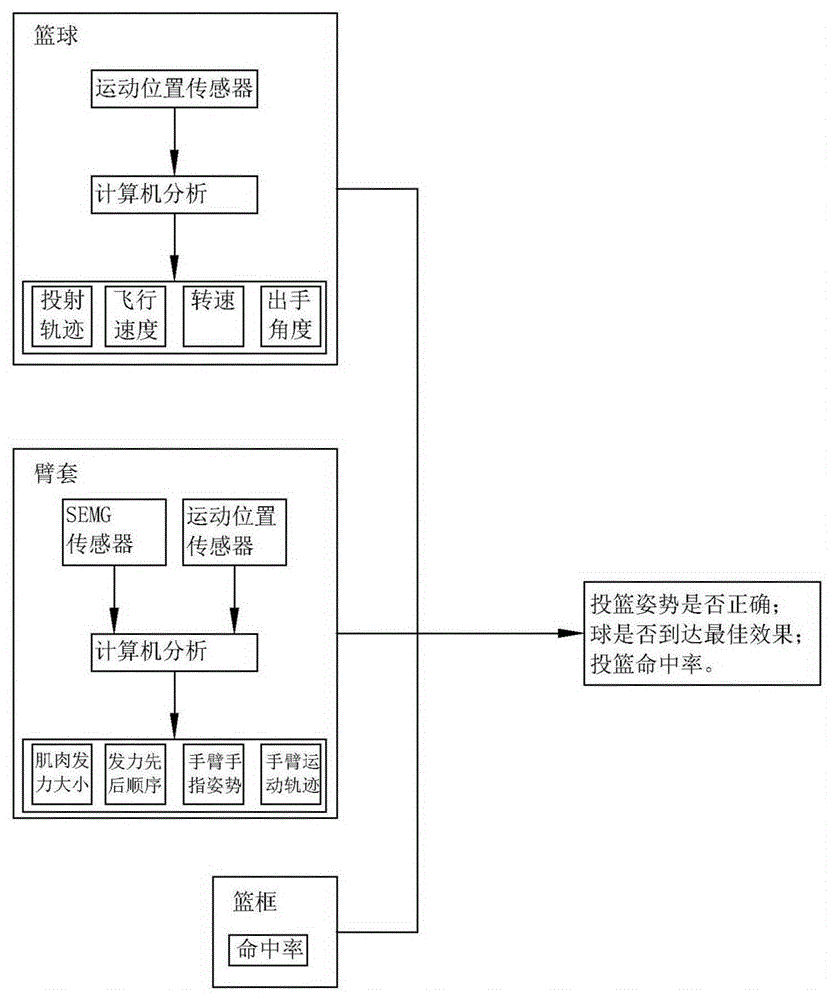
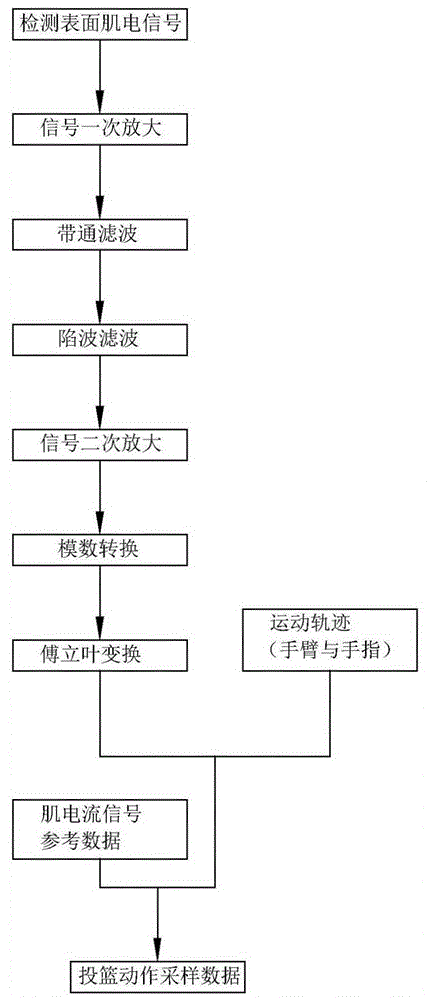
The invention relates to a shooting action training method. The shooting action training method comprises the following steps: obtaining the shooting association data of a shooting action and a basketball moving state as well as shooting average by combining the basketball moving state information which is fed back by a basketball, the shooting actions of arms which are fed back by arm sleeves when the basketball is shot, and the shooting average which is fed back by a basket; comparing the shooting association data with a preset shooting action model which serves as a training standard, and finding and feeding back the difference between the shooting association data and the shooting action model to obtain training data, wherein the basketball moving state information comprises shooting trajectory, flying speed, rotating speed, and shooting angle; the shooting action comprises muscle power strength, power generating order, the postures of arms and fingers, and the action trajectory of the arms. The method is used for analyzing the coherent postures and muscle effectiveness of a basketball player in a shooting practice exercise, and giving posture correction and muscle power generation suggestions.
Owner:福建奇迹运动体育科技有限公司
Hybrid drive for an electric bicycle
ActiveUS20110303474A1Balanced and pleasant driving behaviorMore cost-effectivelyWheel based transmissionChain/belt transmissionElectricityEngineering
A bicycle includes an electrical auxiliary drive, including an electric motor, a battery for storing electrical energy, which battery is connected to the electric motor, a crank mechanism having pedal cranks, which are mounted on a pedal crankshaft disposed about a crank axis, so as to be able to rotate, and a planetary gear for driving the bicycle both by the electric motor and by the muscle power of a driver, the planetary gear and the electric motor being disposed about the pedal crankshaft of the crank mechanism.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Muscle powered dynamic knee brace
A dynamic knee brace that can be used to apply a bending force across the knee. Two brace arms are connected together by a central joint that allows the knee to pivot. A joint in each brace arm allows the brace arm to be inclined toward the leg. A cam assembly is present to actively incline each brace arms toward the leg as the knee moves to full extension. An adjustment mechanism for the cam assemblies provides control over the maximum amount of inclination each brace arm achieves. Preferably, the adjustment mechanism adjusts the cams equally so that both brace arms are inclined by the same amount.
Owner:BREG
Acteoside and acteoside-rich plant extracts for increasing athletic performance in humans
InactiveUS20110144040A1Improve athletic performanceRaise the ratioBiocideAntipyreticBiotechnologyHuman use
The present invention relates to increasing the athletic performance of humans using acteoside. This may be in the form of a pure compound, or plant extracts containing at least 10% acteoside by weight. Application of this invention provides increased strength, muscle power, endurance, muscle protein content, and reduced fatigue.
Owner:MN INTPROP CORP
Drive Mechanism for a Vehicle Propellable by Muscle Power and Vehicle
InactiveUS20100320718A1Less complexLess prone to failureRider propulsionFriction gearingsDrive shaftEngineering
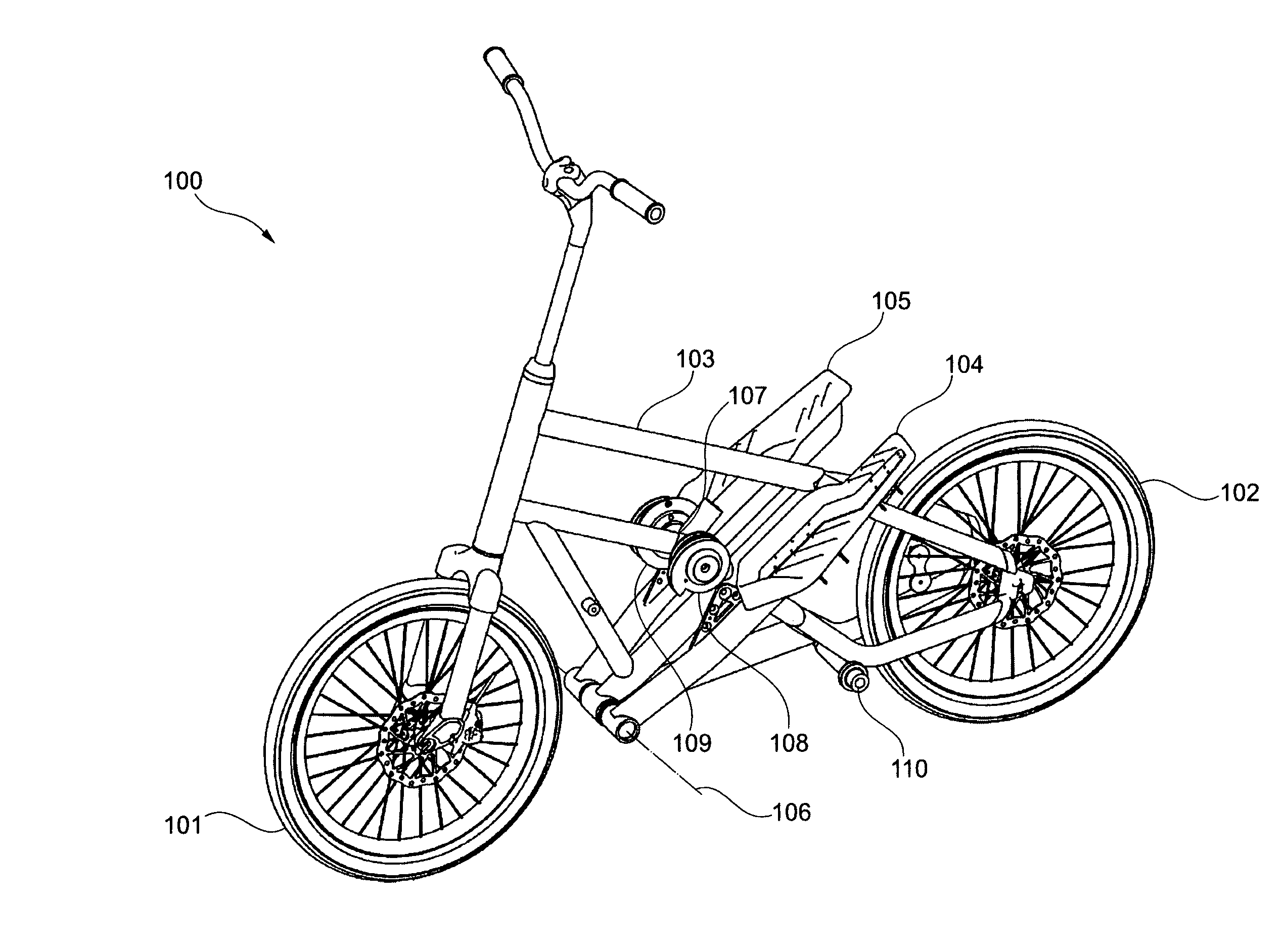
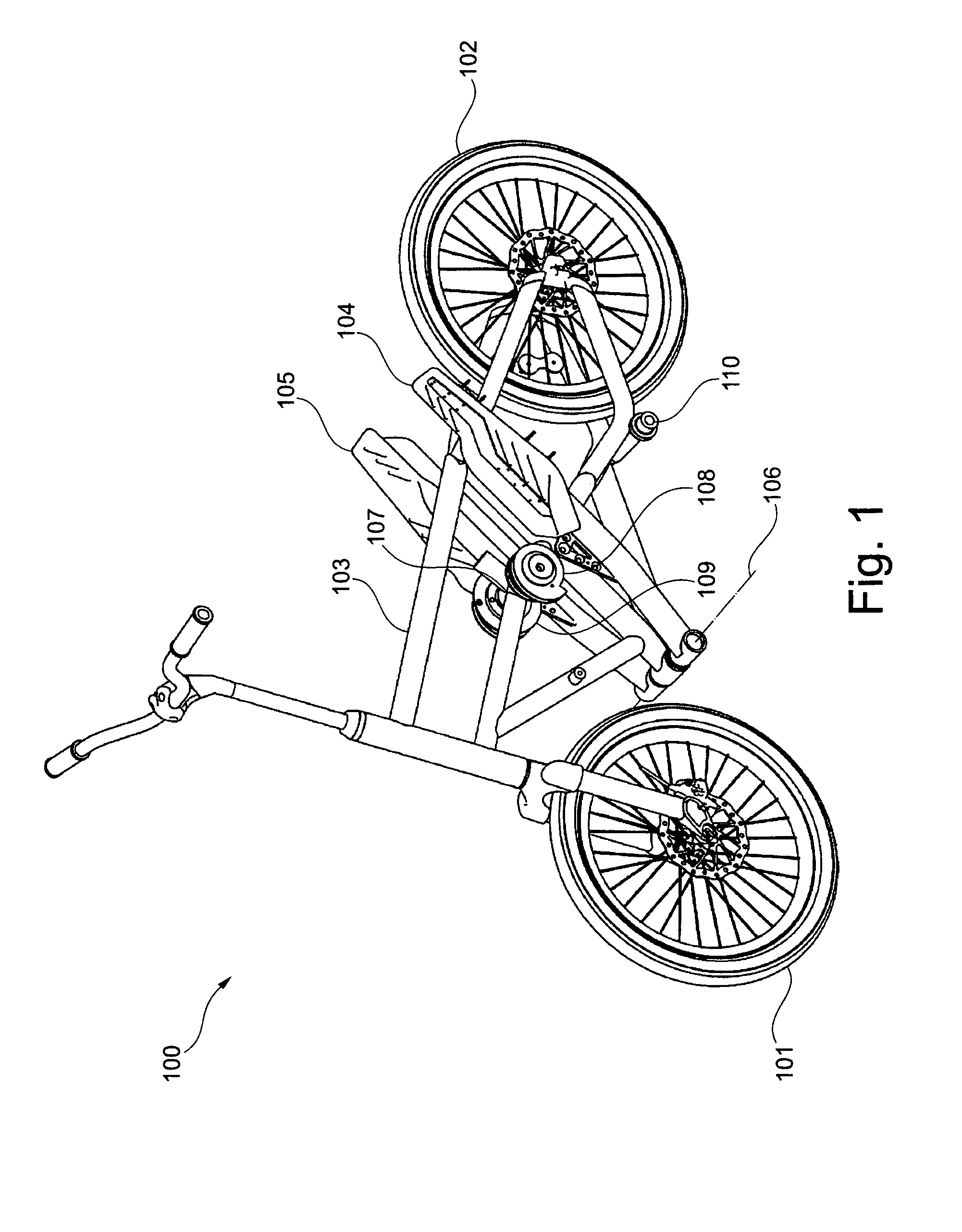
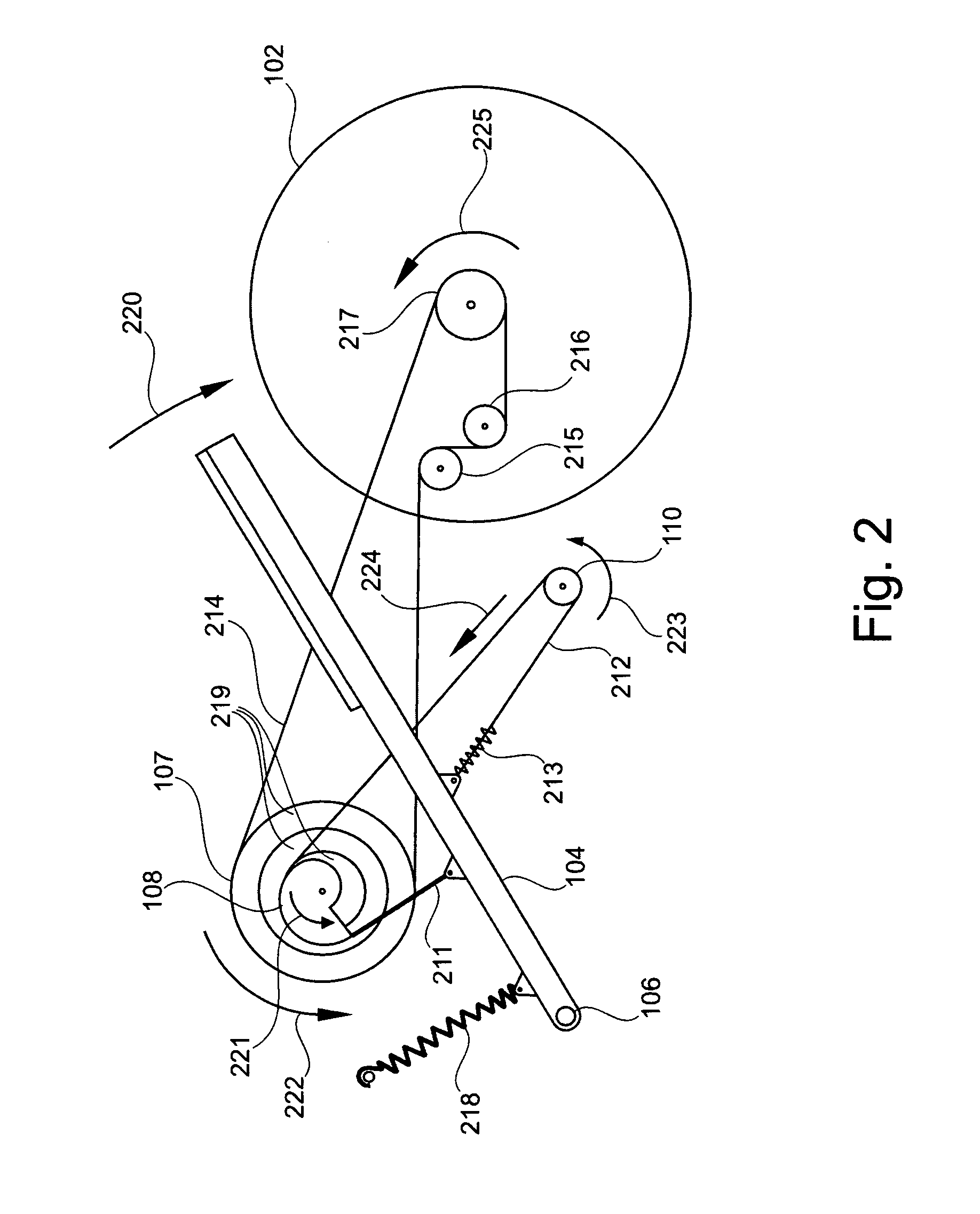
A drive mechanism for a vehicle propellable by muscle power is provided, wherein the drive mechanism comprises a first actuating element (104) which is moveable by a stroke along a movement path, a first driving element (211), a first gearing comprising a driving shaft (107), and first returning element (212), wherein the first driving element (211) is coupled between the first actuating element (104) and the driving shaft (107) in such a way that actuating element stroke induces a movement of the driving shaft in a first direction, and wherein the returning element (212) is coupled between the first actuating element (104) and the driving shaft (107) in such a way that it induces a movement of the driving shaft in a second direction opposite to the first direction.
Owner:GRADITECH ENTWICKLUNGS
Composition with muscle building function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103766696AWeakened gastrointestinal functionHigh activitySugar food ingredientsVitamin food ingredientsIntestinal structureLife quality
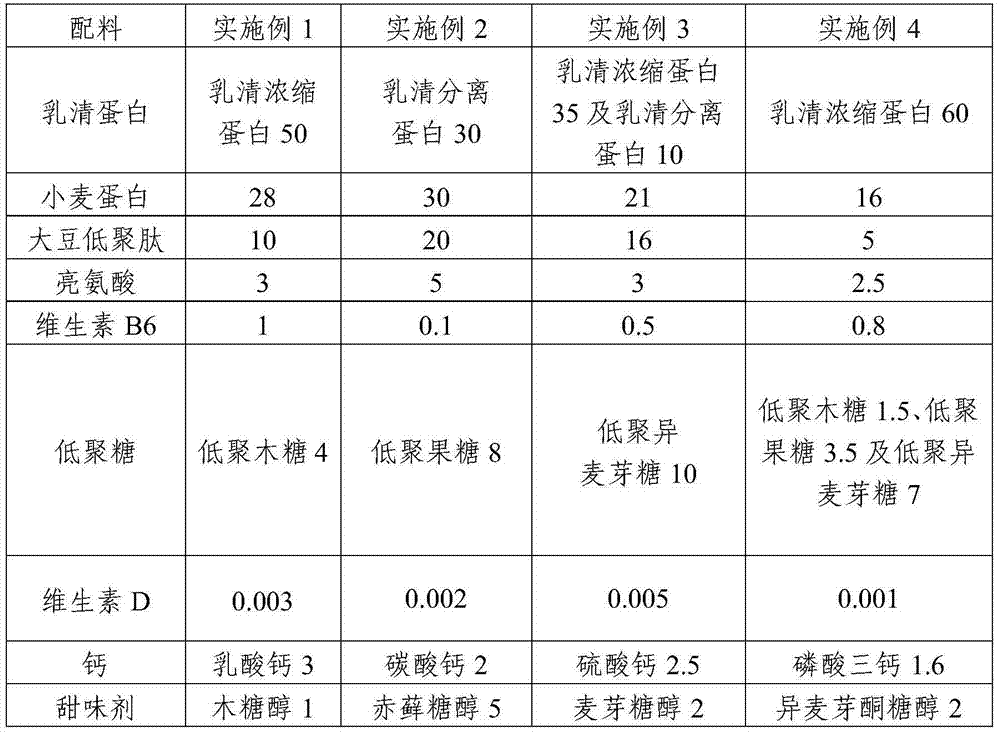
The invention provides a composition with a muscle building function. The composition comprises following components in parts by weight: 30-60 parts of whey protein, 10-30 parts of wheat protein, 5-20 parts of soybean oligopeptide, 1-5 parts of leucine, 0.1-1 part of vitamin B, 0.001-0.005 part of vitamin D and 0.35-0.8 part of calcium. According to the composition, the design of the product considers the characteristics that the intestines and stomach functions of old people are weakened and the absorption utilization rate of proteins is low, and the combination of high-quality proteins and a reasonable formula are selected, so that the product can have a reasonable aminogram and the digestion absorption rate of the protein is improved; the composition is good for absorption and utilization of the protein by the old people and the synthesis of muscle is promoted; and the muscle weakening caused by age dependency is reduced. The quality and the capability of the muscle of the old people are enhanced and certain muscle power is kept, so as to meet the common activities in daily lives and improve the living capability and the living quality of the old people.
Owner:BEIJING COMPETITOR SPORTS SCI & TECH
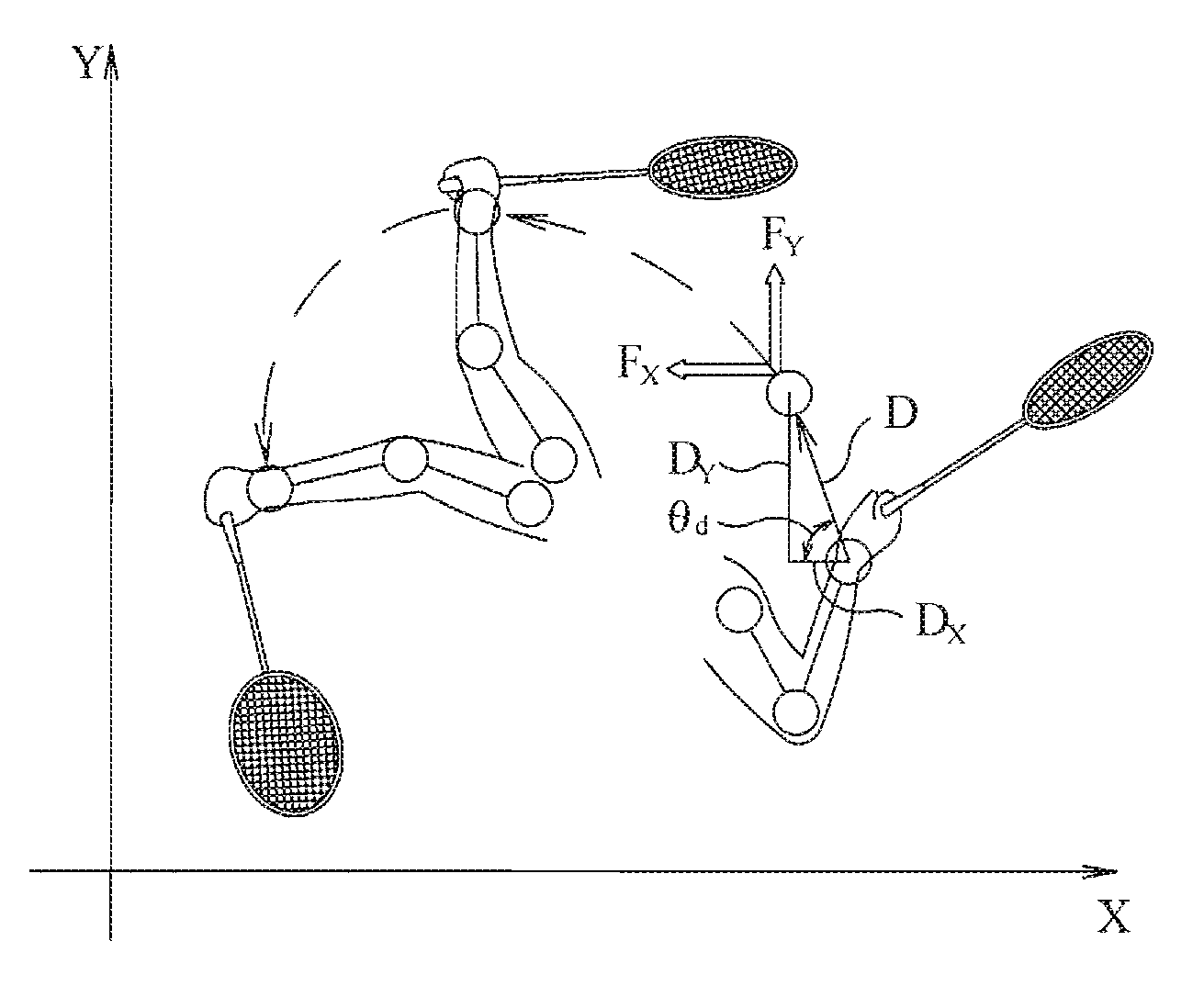
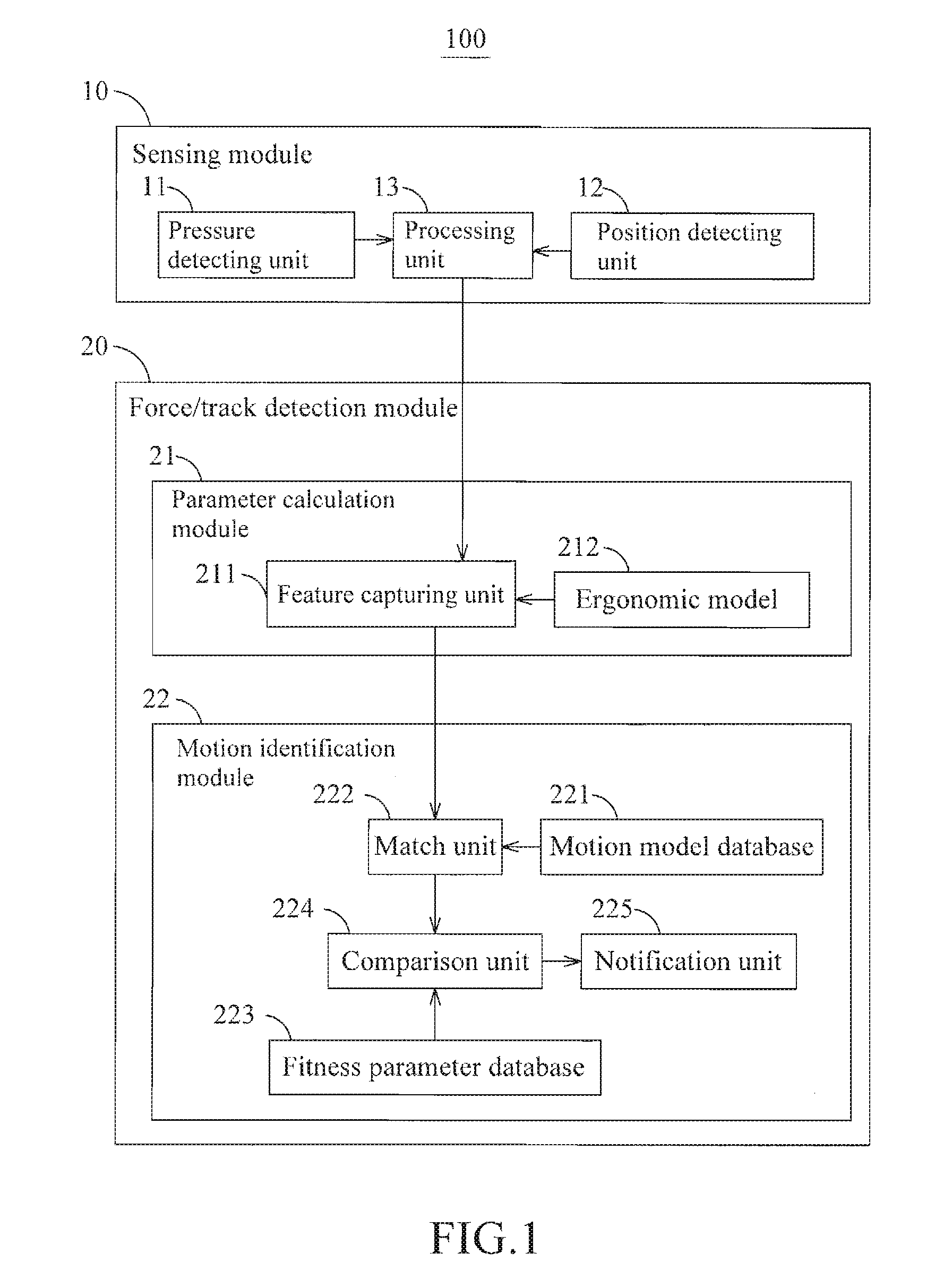
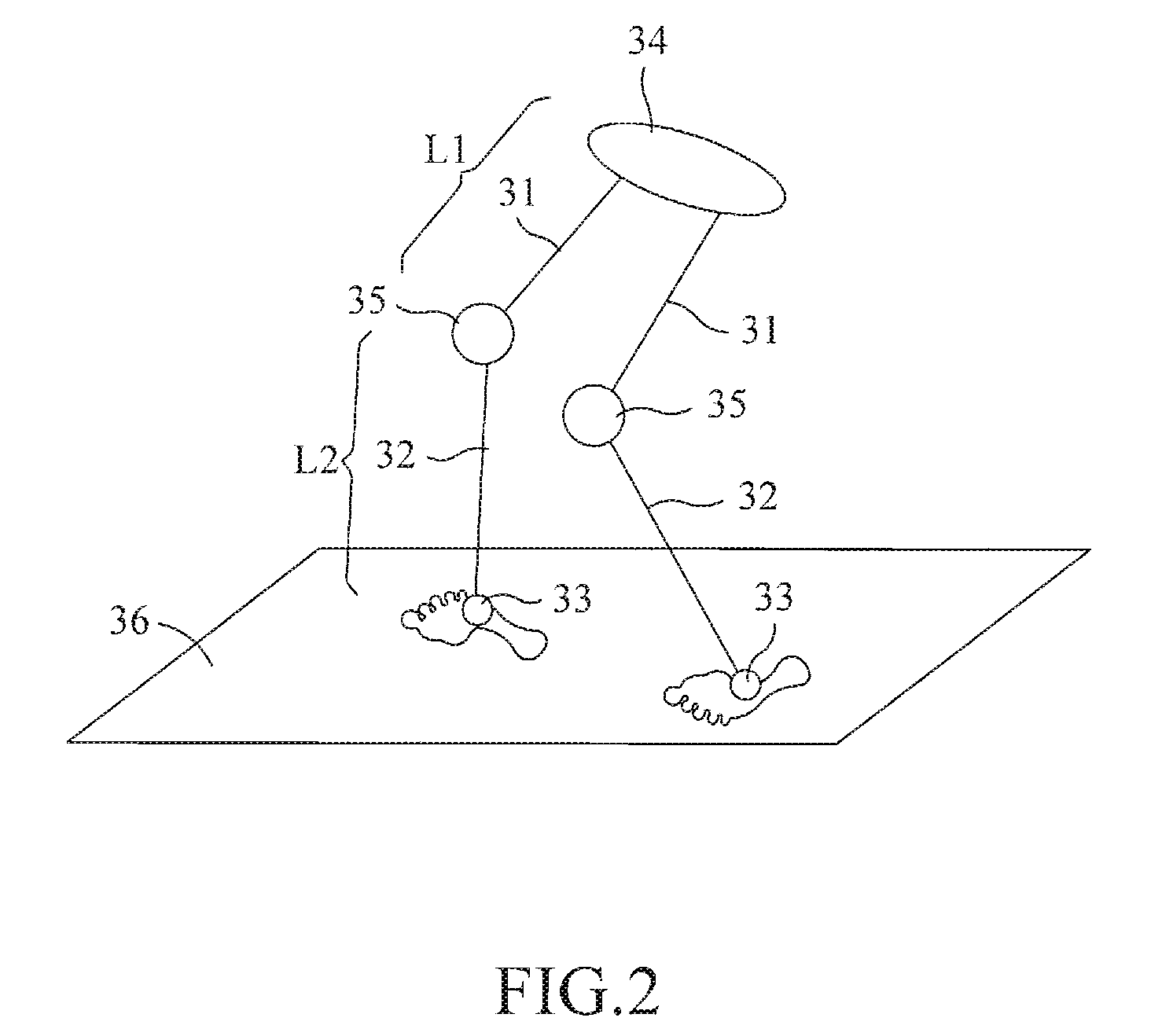
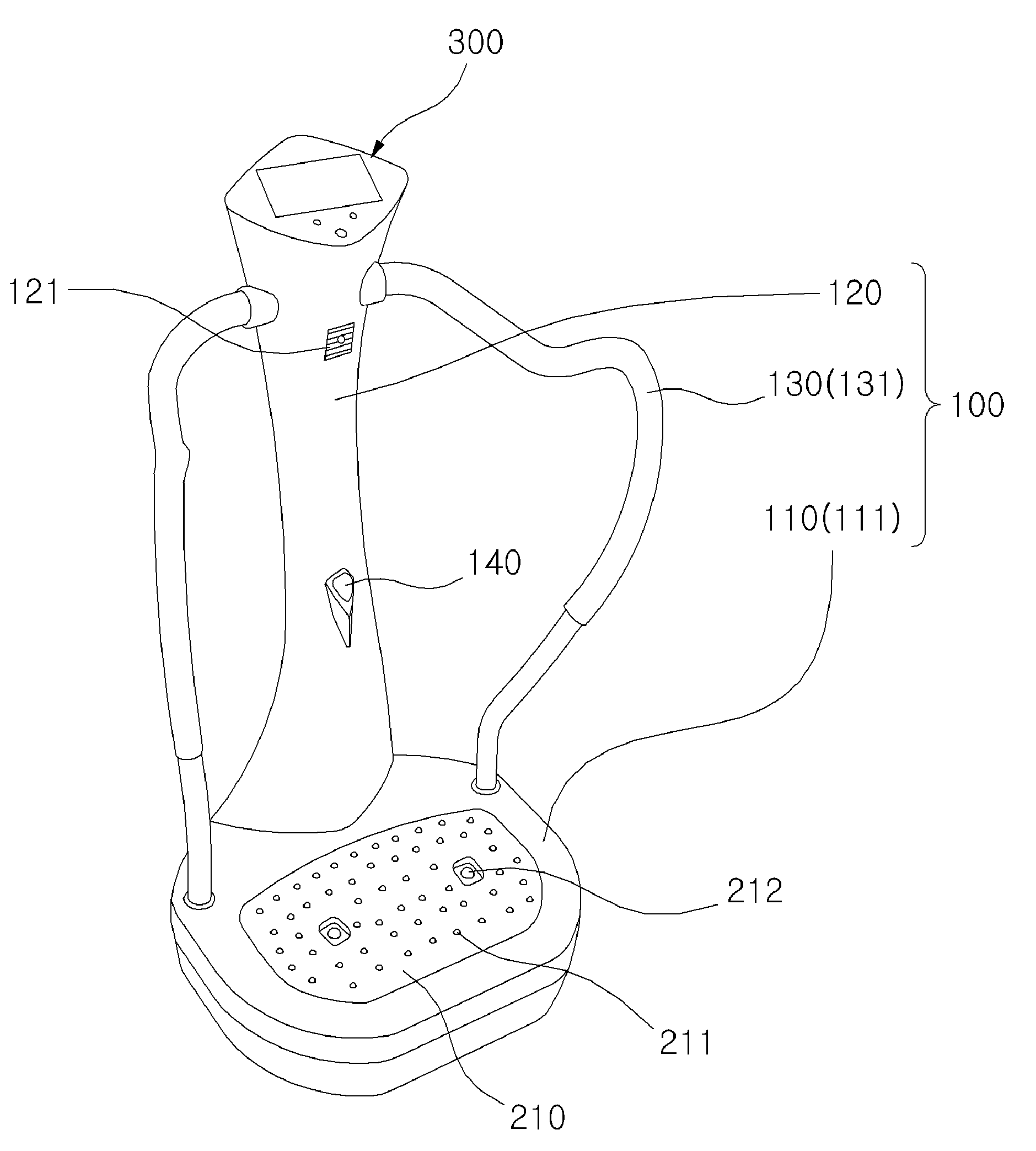
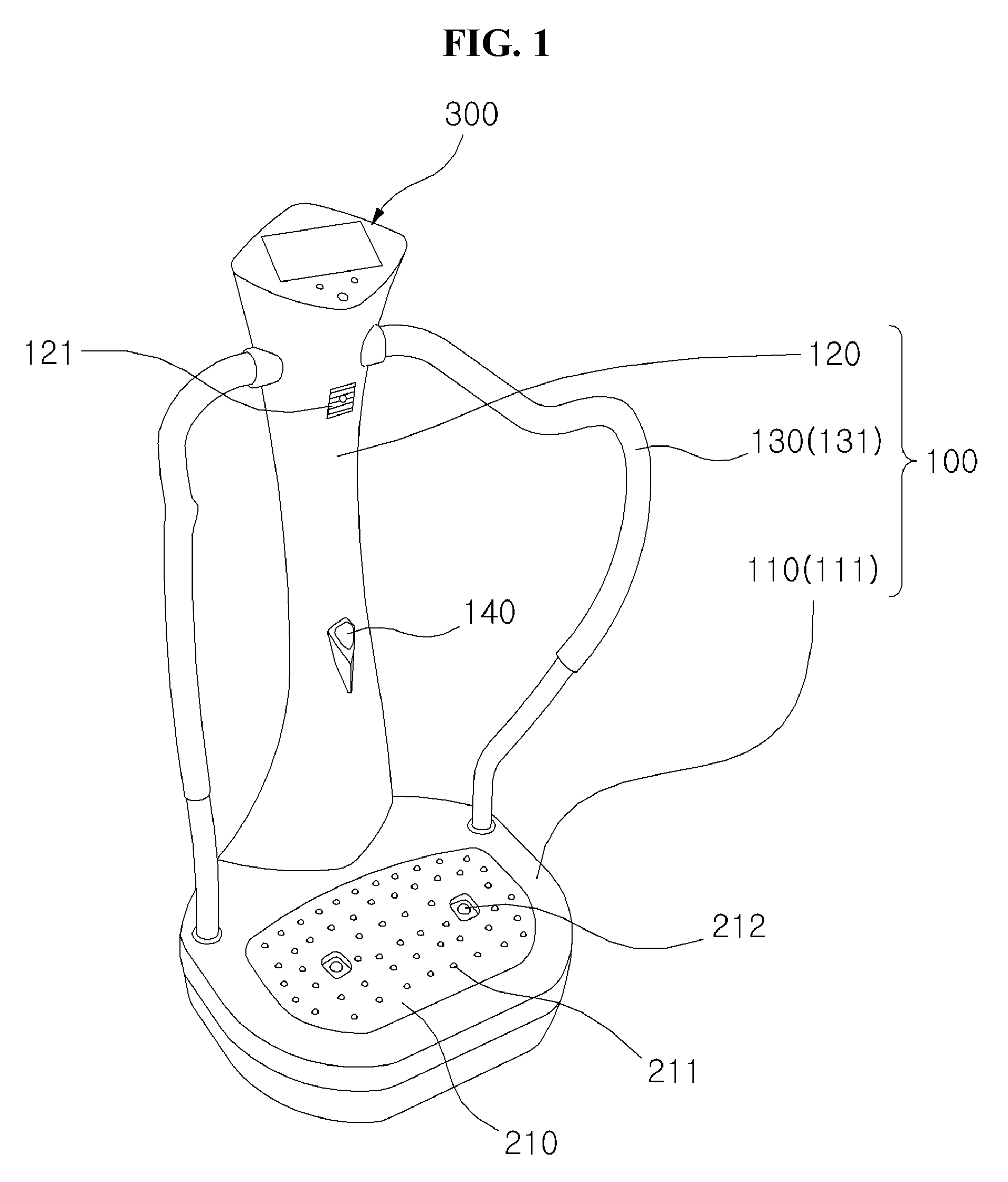
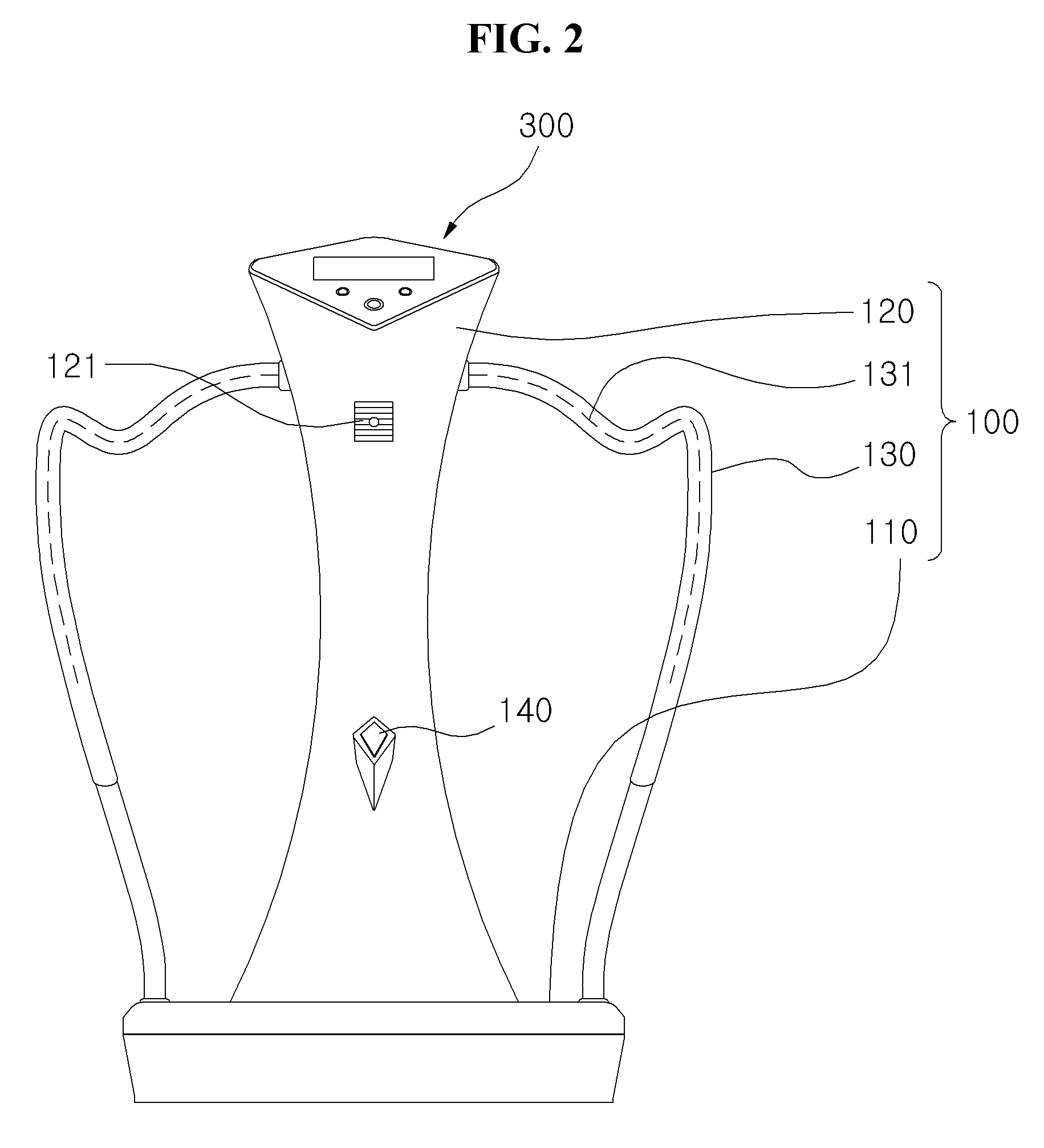
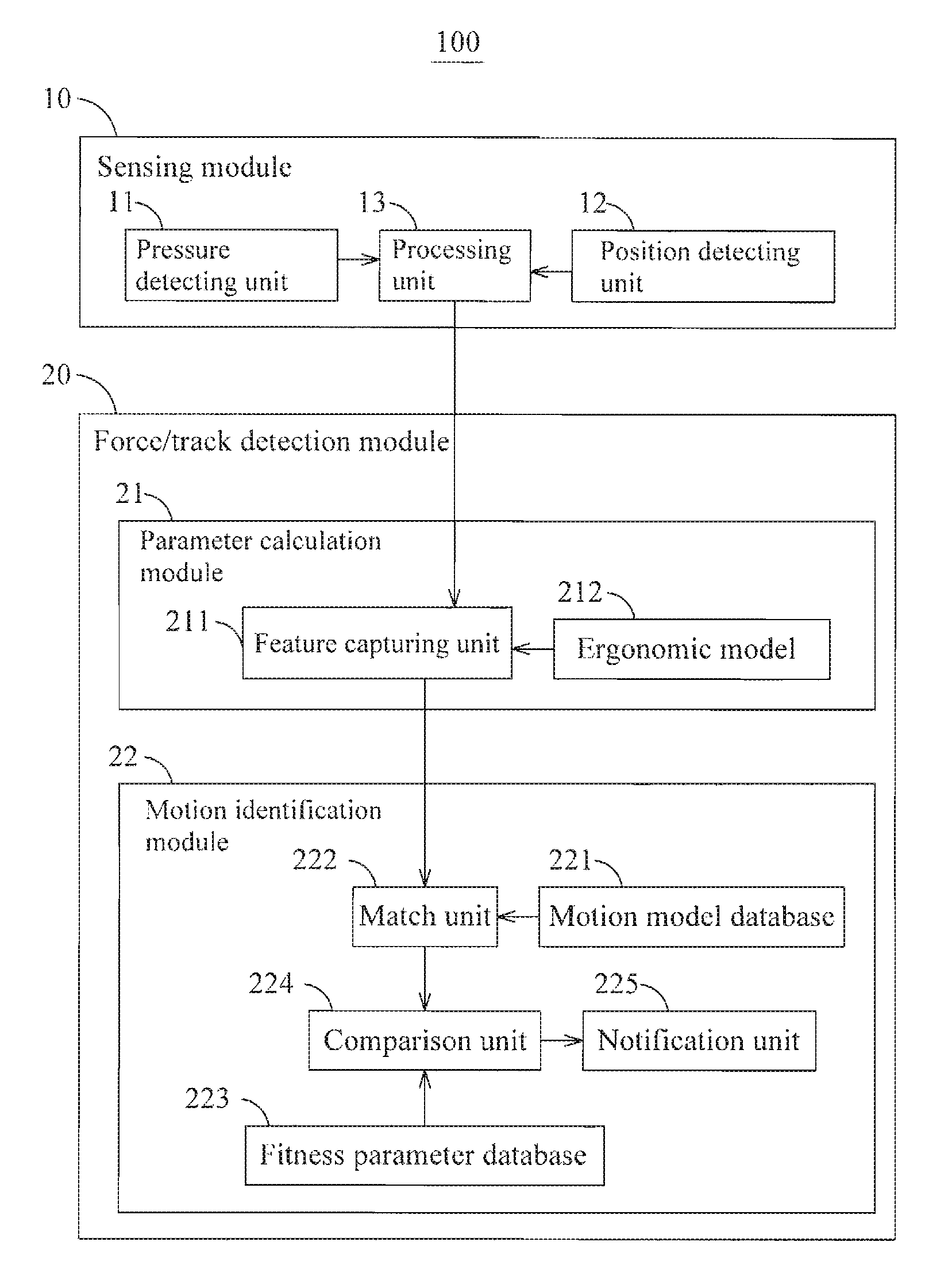
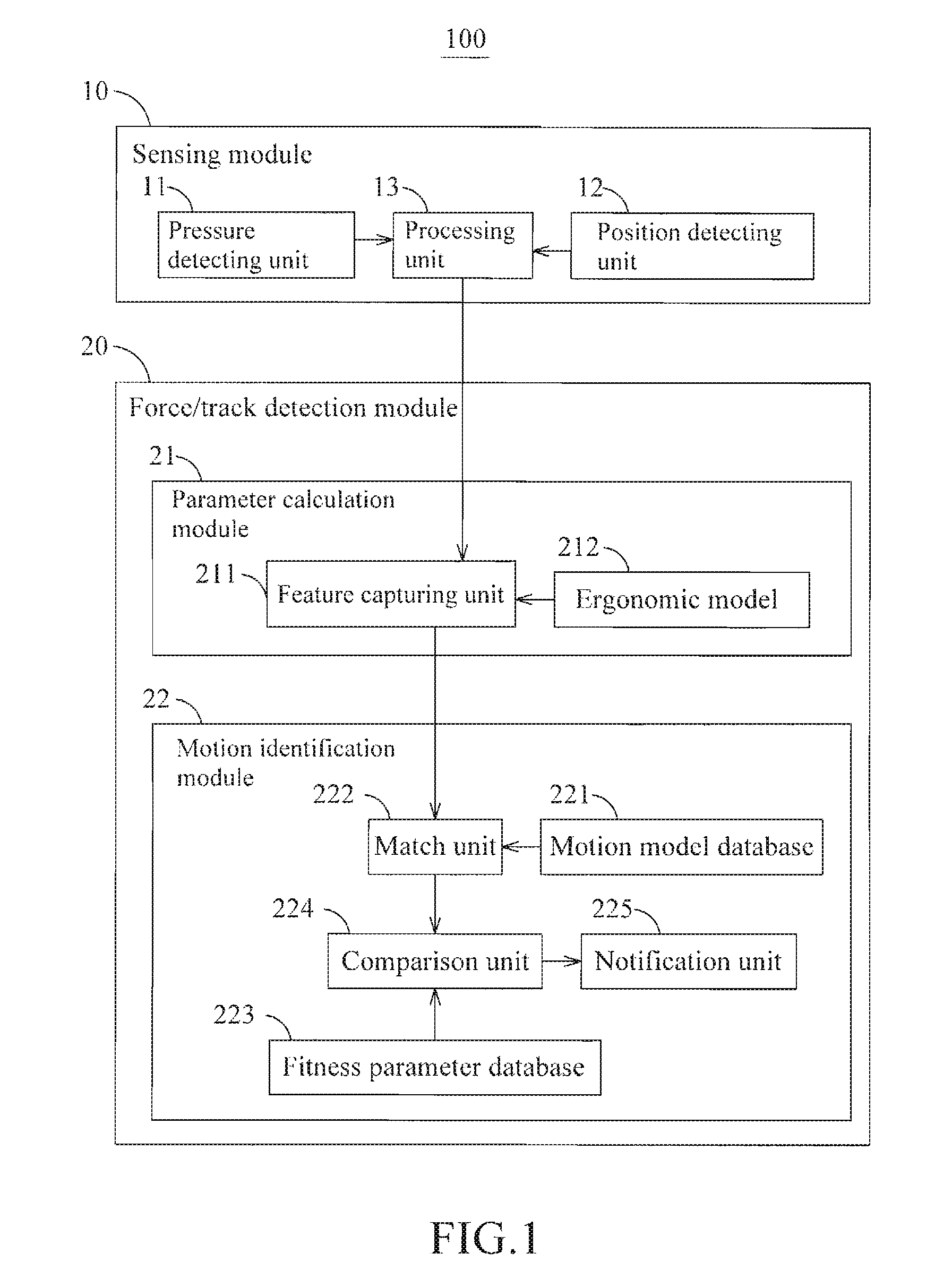
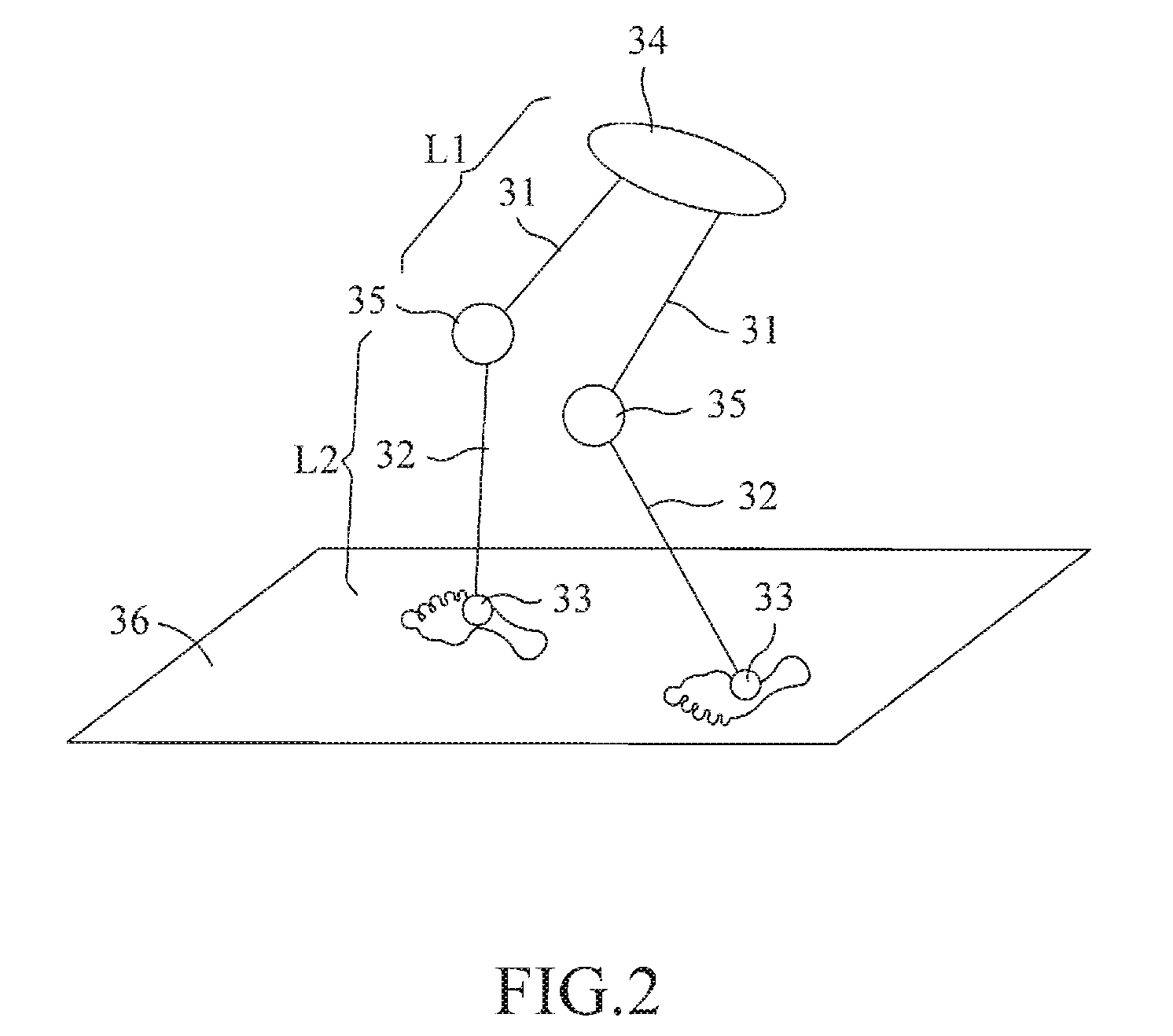
Method and system for monioring sport related fitness by estimating muscle power and joint force of limbs
The present invention relates to a method and system for monitoring sport related fitness by estimating muscle power and joint force of limbs, in which the system comprises a sensing module and a force / track detection module, wherein sensor values from the sensing module are fed to the force / track detection module to be used as base for estimating feature parameters and classifying a motion series relating to muscle power and joint force of limbs so as to obtain skill-related fitness parameters corresponding to the sensing of the sensor module.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Composition having muscle power fatigue alleviating and anoxic tolerance improving effects, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104026563AEasy to manufactureImprove the taste of takingFood ingredient functionsFood preparationVitamin CPhysiology
The invention relates to a composition having muscle power fatigue alleviating and anoxic tolerance improving effects. The composition is prepared by using L-arginine, L-citrulline, taurine, vitamin C, vitamin E powder and folic acid according to a prescribed ratio. Animal function tests prove that the composition can obviously prolong the weight bearing swimming time of mice, prolong the viability time of the mice under normal pressure anoxic conditions, obviously reduce the urea nitrogen and blood lactic acid content of serum of post-exercised mice, and increase the liver starch content of mice during exercise; and results of human feeding tests show that the composition can improve the maximum oxygen consumption of subjects, reduce the blood lactic acid rise after exercise and increase the exercise tolerance of bodies. The composition has muscle power fatigue alleviating and anoxic tolerance improving effects.
Owner:SHANDONG MINGREN FURUIDA PHARMA
Muscle-powered continuously variable drive system and apparatus having same
A muscle-powered continuously variable drive system, and apparatus having same, is disclosed. The system employs dual actuator levers pivoted at one end. The free pedal ends of the levers reciprocate through an arcuate range of motion via application of muscle power by the user, rather than cycling through complete revolutions of a small-radius circle, such as is common for conventional bicycles. The reciprocating motion of the levers initiated by the user generates a force that is translated into rotational motion of a drive wheel via a drive tether. The drive tether is attached to the actuator levers and runs around three idler pulleys mounted to the apparatus' frame. Two chain segments of the tether engage respective dual sprockets at the hub of the drive wheel. The geometry of the transmission enables a light, simple, system of continuously-variable torque multiplication, which eliminates the need for conventional derailleurs and multiple sprockets, or internal gear hubs.
Owner:LINEARC
Stepper with wave type vibrator
InactiveUS20080171639A1Improvement in base metabolic rateReduce the body fatChiropractic devicesLight therapyDrive motorConveyor belt
The present invention relates to a stepper with a wave type vibrator, which enables a user to aerobically exercise his / her feet or other parts requiring training to harden the parts or reduce the body fat thereof, using both strong wave type vibrating motion of a step board and an improved multi-level control system, thus increasing the base metabolic rate of the user's body and realizing effective body fat reduction and an increase in muscle power. The stepper includes a stepper frame, a drive unit and a control unit. The stepper frame is composed of a box-shaped stand, a central column securely standing on the stand, and a handle arm extending outwards from each of left and right sides of the central column to an associated position on the stand. The drive unit is composed of a step board installed in the depression of the stand, with a plurality of acupressure protrusions and two far-infrared lamps, a drive motor mounted to the bottom wall of the step board, a drive belt wrapped around the output shaft of the drive motor, a driven pulley connected to the output shaft of the drive motor by the drive belt, a rotating shaft rotated by the driven pulley and divided into left and right shaft parts based on the driven pulley, and a vibrating bracket having an actuating link to be actuated in conjunction with rotation of the rotating shaft. The control unit is composed of a course setting unit for commanding the drive unit to execute four different vibrating motions and controlling power supply for the drive unit, and a far-infrared lamp controller for controlling a preset temperature and a preset operating time period of the far-infrared lamps.
Owner:HAHN SANG WON
Method and system for monitoring sport related fitness by estimating muscle power and joint force of limbs
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Novel Wearable Vibration Device
ActiveUS20160175187A1Increase muscle strengthPhysiological effect is goodBlood stagnation preventionChiropractic devicesLED displayHigh energy
The present invention provides a novel wearable vibration device. According to an embodiment, the novel wearable vibration device delivering high energy vibration deep in to the muscles and soft tissues for muscle treatment comprising an upper soft fabric foam covered case encompassing at least a vibration motor a lithium ion battery, a control PCB, a control switch with LED display and a lower fabric covered case. The wearable vibration device delivers high energy vibration to the chosen muscle group and thereby, penetrates deep in to the muscle and to the soft tissues. The upper soft fabric foam covered case and lower fabric covered cases are fixed together by gluing or stitching. The control PCB drives vibration motor to set frequencies for vibration motor activations. Vibrations for the device are tuned at frequencies in the range of 30-50 Hz to increase muscle power and for other beneficial physiological effects.
Owner:MYOVOLT
Mechanical arm with tremble inhibiting function
InactiveCN108582155AChange biomechanical propertiesReduced tremor movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsDamping factorBiomechanics
The invention discloses a mechanical arm with a tremble inhibiting function. The mechanical arm with the tremble inhibiting function is characterized in that a damping coefficient of a magnetorheological damper is changed to realize the adjusting of joint damping and inertia coefficients of an elbow joint, thus the biomechanical characteristic of a man-machine system is changed, and as a result, the purpose of reducing the tremble movement of the legs can be achieved; an electromyographic signal sensor is used for picking up a bio-electricity signal of arm muscle, filtering the electricity signal, recognizing non-intentional movement component in the movement information, and controlling a power source to supply power to realize active tremble inhibition. The mechanical arm comprises a bigarm, a forearm a wrist joint, the magnetorheological damper, a gear and a motor; the human elbow muscle power applying mode is simulated at the elbow joint; the elbow part is driven to move throughthe motor; the stroke of the motor can be limited to realize the bending and stretching movement of the elbow; the forearm is inwards and outwards rotated under the transmission of the gear; the wristjoint is bent and stretched through a small hydraulic rod; all supports clinging to the human arm are of arc-shaped structures which fit the sizes of arms of most of people.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method used for bleeding a hydraulic vehicle brake system
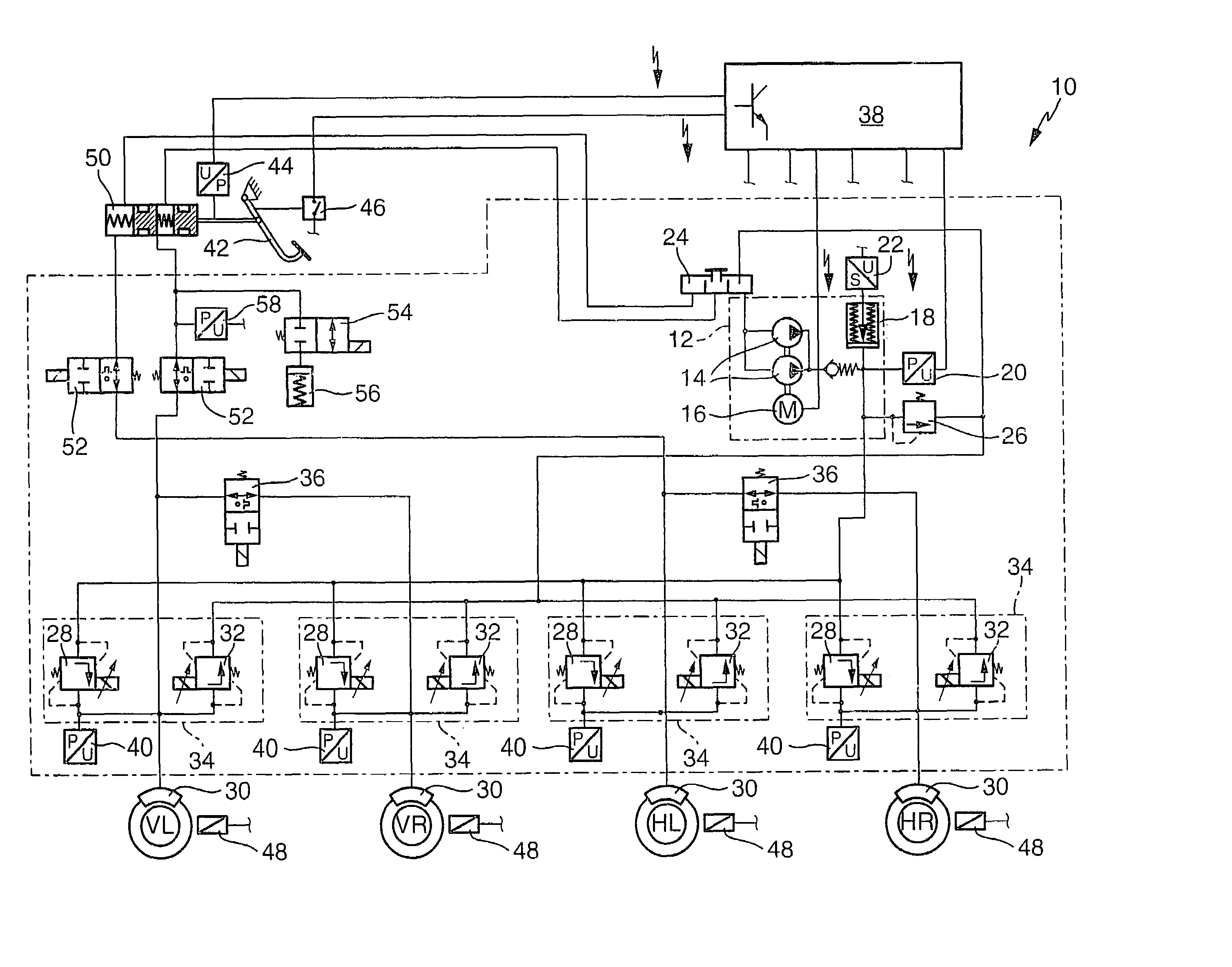
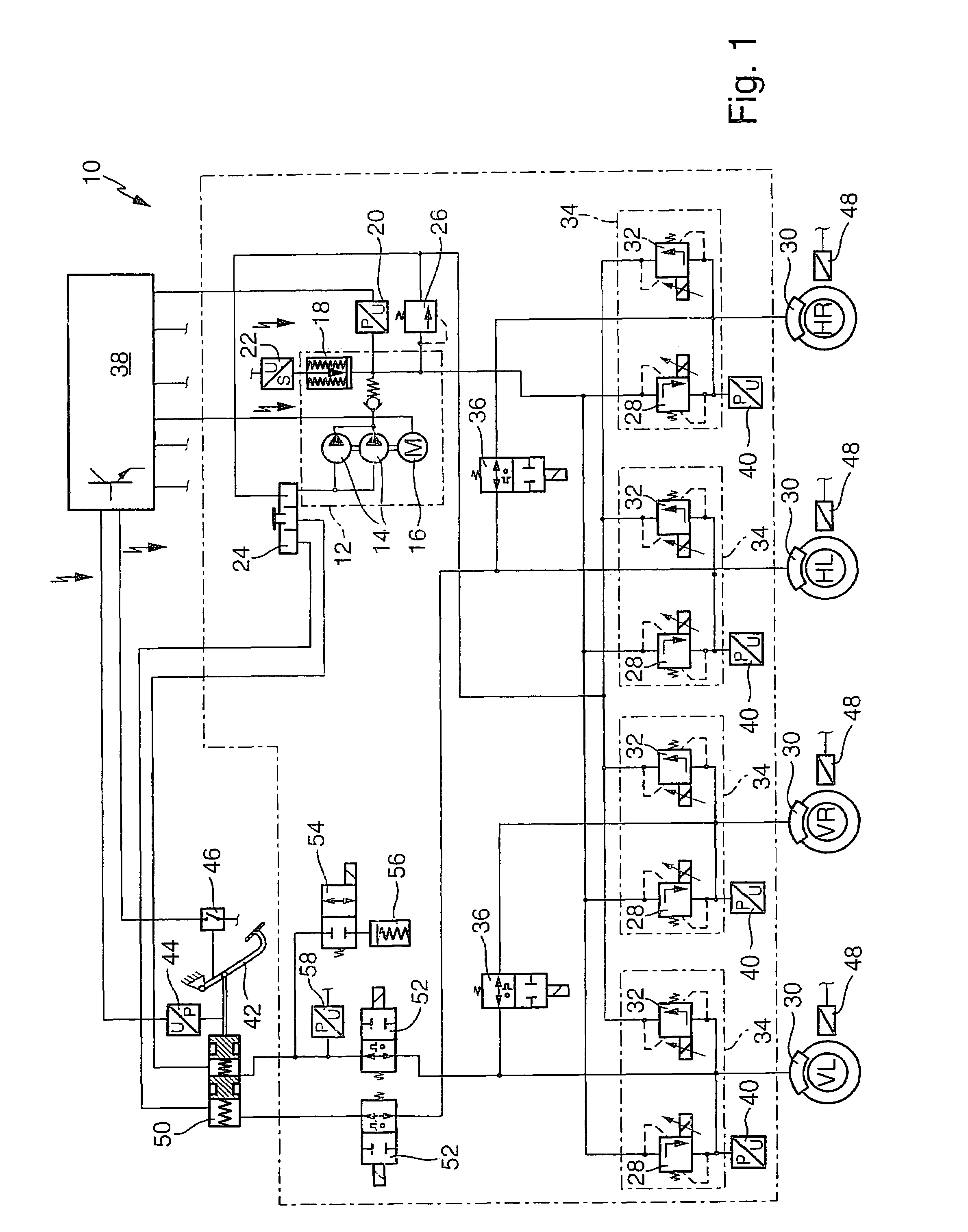
InactiveUS7344206B2Fluid braking transmissionApplication and release valvesMaster cylinderEngineering
The invention relates to a method for degassing a hydraulic vehicle brake system that has an external-force service brake system and a muscle-powered auxiliary brake system. For the degassing, brake pressure buildup valves are opened, preferably successively, so that brake fluid flows through the brake pressure buildup valves, disconnection valves and a master cylinder and reaches a brake fluid reservoir. The brake fluid positively displaces any brake fluid containing gas from the vehicle brake system into the brake fluid reservoir, where gas bubbles can escape from the brake fluid. Compressibility of the brake fluid from gas bubbles is avoided.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Portable oxygen production apparatus
The invention relates to a portable oxygen production apparatus, which is characterized in that the inner part of the portable oxygen production apparatus is separated to an upper solvent chamber and a lower substrate chamber by an interface layer, a rubber membrane is provided in the solvent chamber, a solvent and a catalyst are filled in the rubber membrane, a compression molding oxygen production substrate is filled in the substrate chamber, a tunnel of the interface layer is communicated to an upper chamber body and a lower chamber body, and an oxygen channel is composed of the tunnel and a bottle cap, a firing pin button and an air filtering cotton are attached outside the solvent chamber, a gravity valve is attached in the substrate chamber, and the upper part of the substrate chamber is combined with the bottle cap in a sealing mode. A heat absorption substance is not required by the apparatus, and solvent amount accounts for less than 30% of volume and weight of the whole apparatus. After the rubber membrane is impaled by the firing pin button, the solvent and a catalyst are released to the substrate chamber, is contacted to the oxygen production substrate to generate oxygen, and then oxygen is discharged by a gas-guide tube. The oxygen production apparatus has the characteristics of passive portable performance, light weight and small volume, and can be widely used for first aid, high altitude anoxia, and recovery and health care after violent muscle power consumption.
Owner:迈奇曼德(北京)科技有限责任公司
Vehicle propelled by muscle power, in particular step scooter
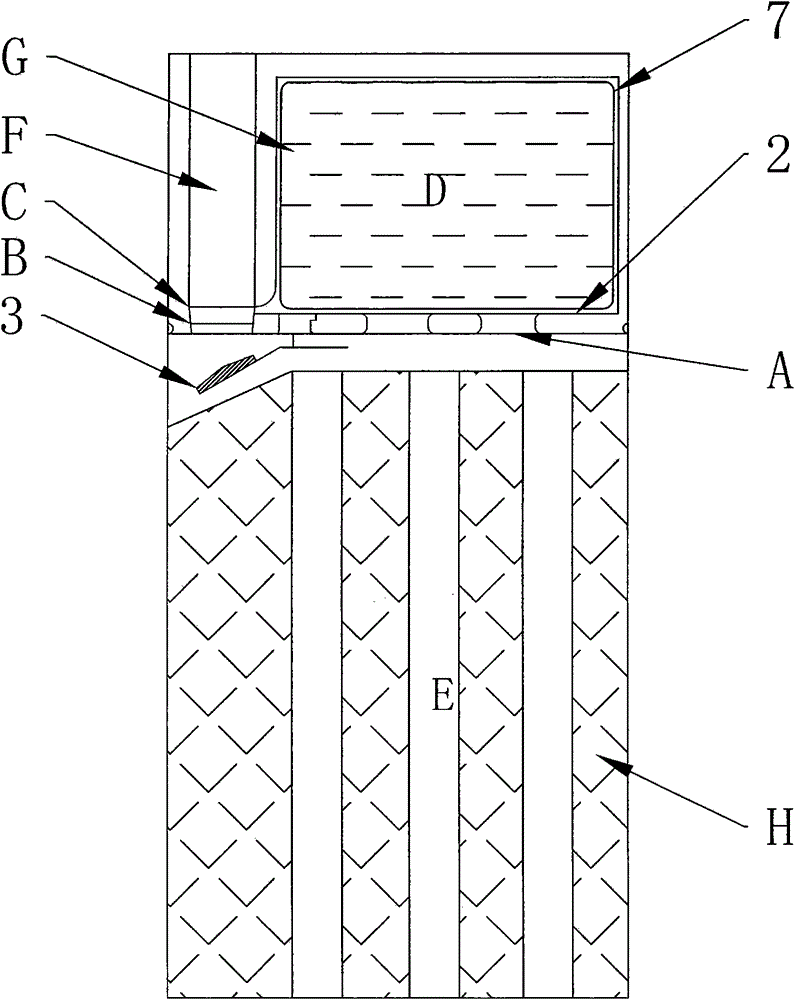
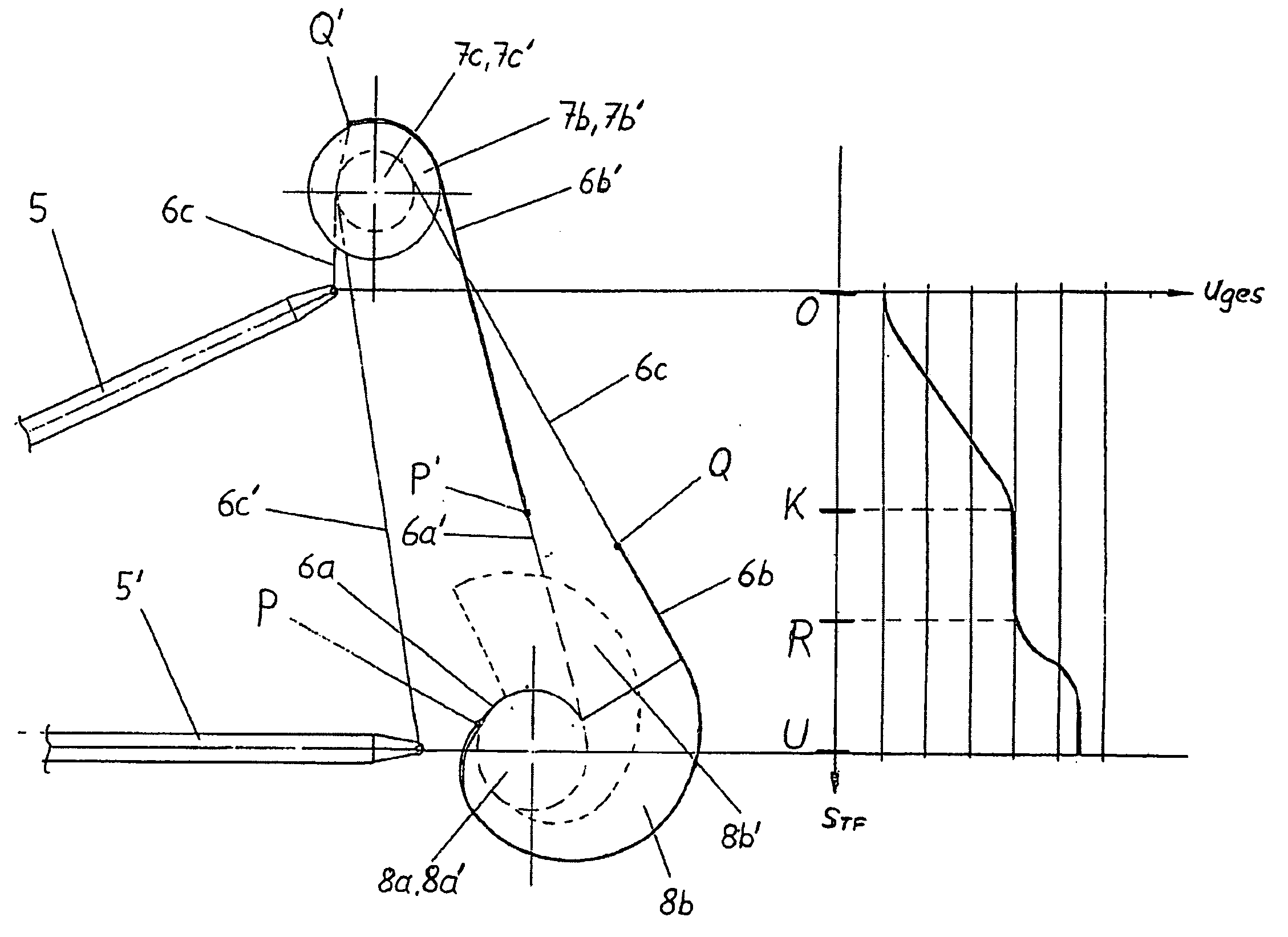
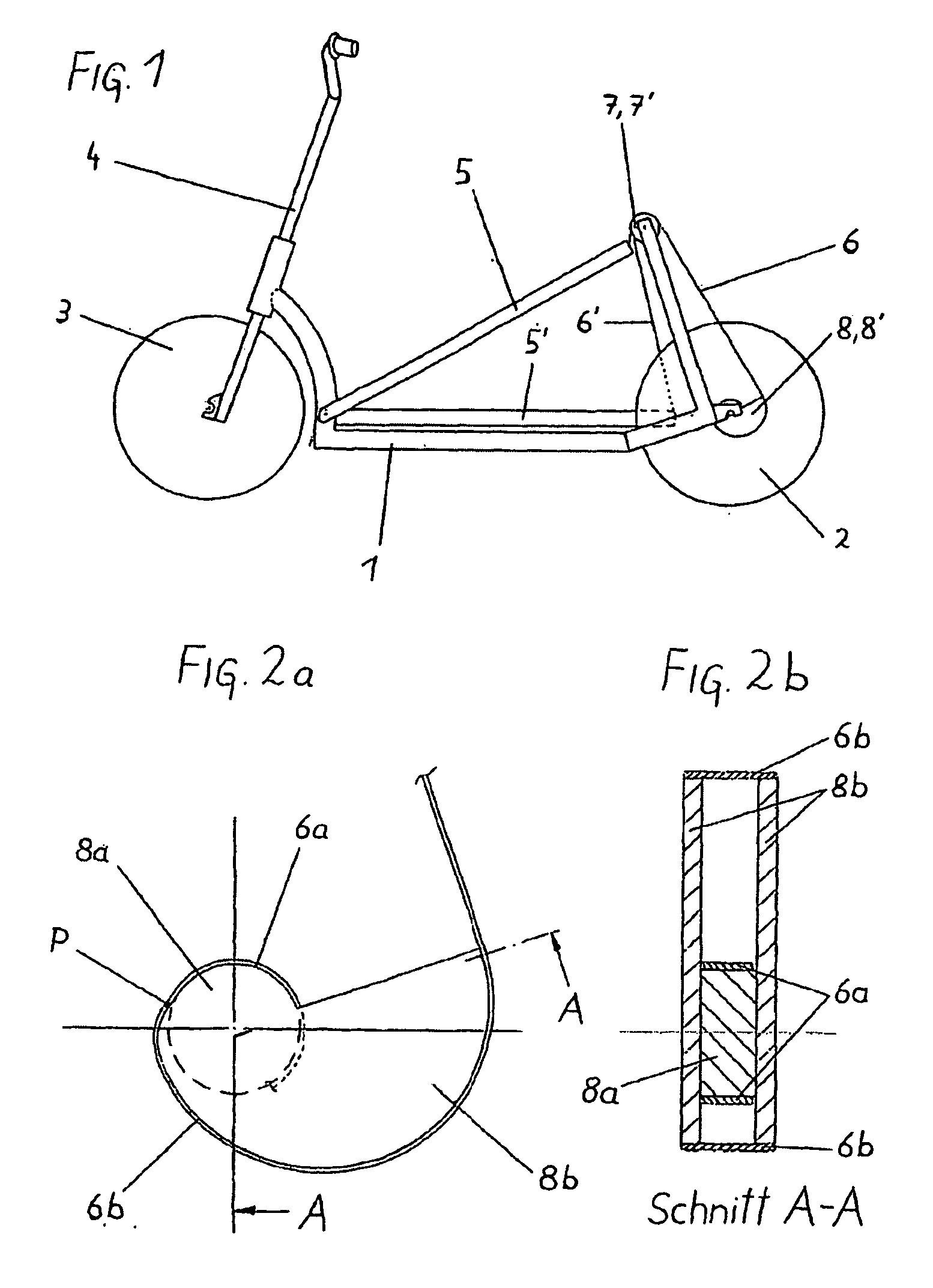
Vehicle propelled by muscle power, in particular scooter, with at least one driving wheel and at least one tread surface (5, 5′) which is movable via a tread surface stroke, wherein the force transmission from the at least one tread surface (5, 5′) to the at least one driving wheel takes place by means of a driving element (6, 6′) which is guided with a nonpositive fir via a drive shaft (8, 8′) which is coupled to the driving wheel via a freewheeling mechanism, wherein the drive shaft (8, 8′) and / or preferably at least one deflecting roller (7, 7′) is / are divided into at least two axial regions (7b, 7c; 7b′, 7c′, 8a, 8b; 8a′; 8b′) with radii which differ from one another or are variable, and the driving element (6, 6′) is divided into partial sections with different cross sections which are designed in such a manner that the partial sections (6a, 6b 6c; 6a′, 6b′ 6c′) of the driving element (6, 6′) are guided within the tread surface stroke (O-U) on the respectively corresponding axial region of the drive shaft (8, 8″) and / or deflecting roller (7, 7′). As a result, the overall transmission ratio (uges) of the vehicle can be configured within the tread surface stroke (O-U) within wide limits, wherein, in particular, the drive shaft (8, 8′) which is designed according to the invention can undertake a plurality of revolutions without colliding with a driving element.
Owner:GRADITECH ENTWICKLUNGS
Training equipment to improve the ability of cognition and memory and the muscle power of upper and lower limb and training method thereof
ActiveUS20200206567A1Increase muscle strengthLow powerVideo gamesTeaching apparatusUpper limb muscleVirtual space
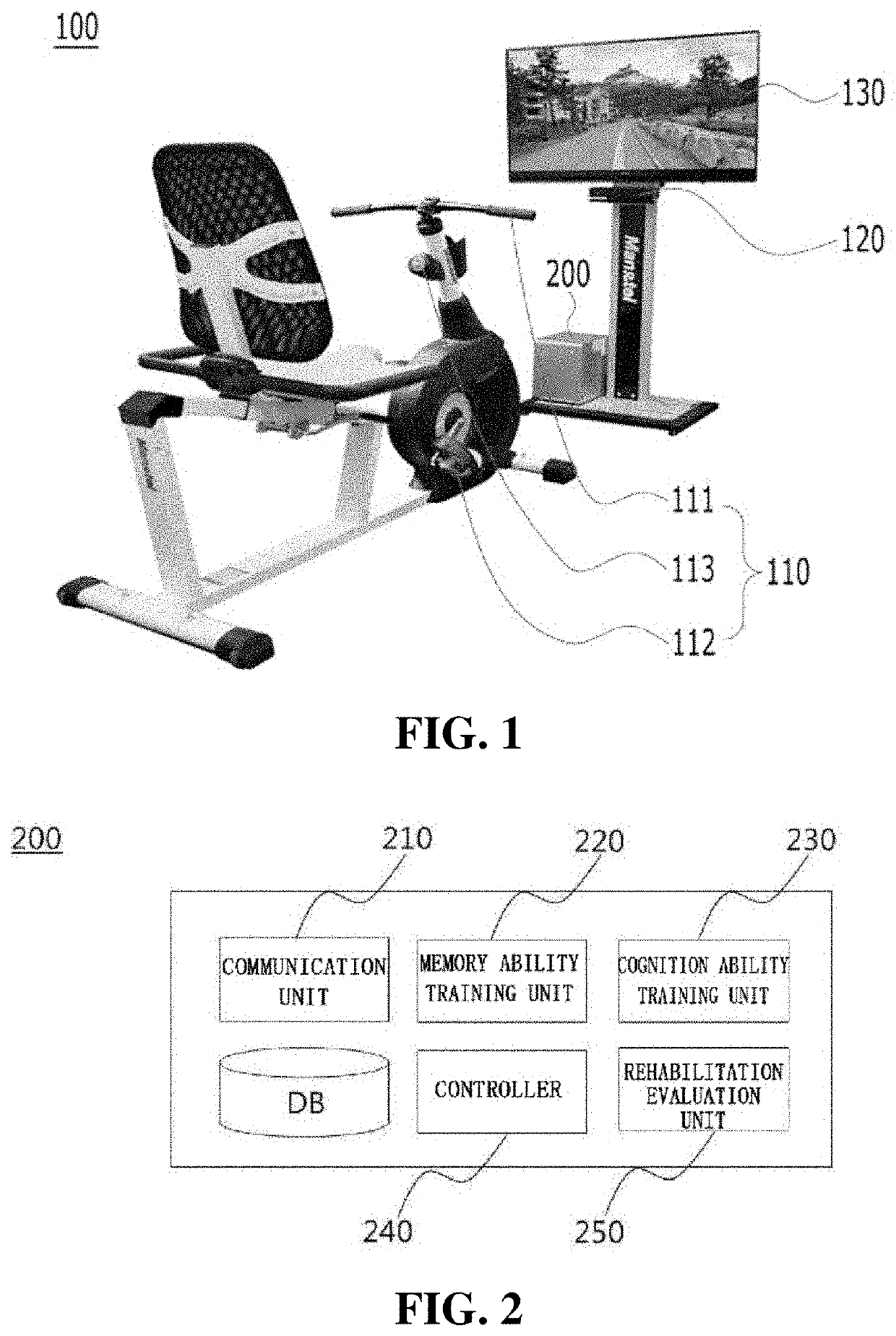
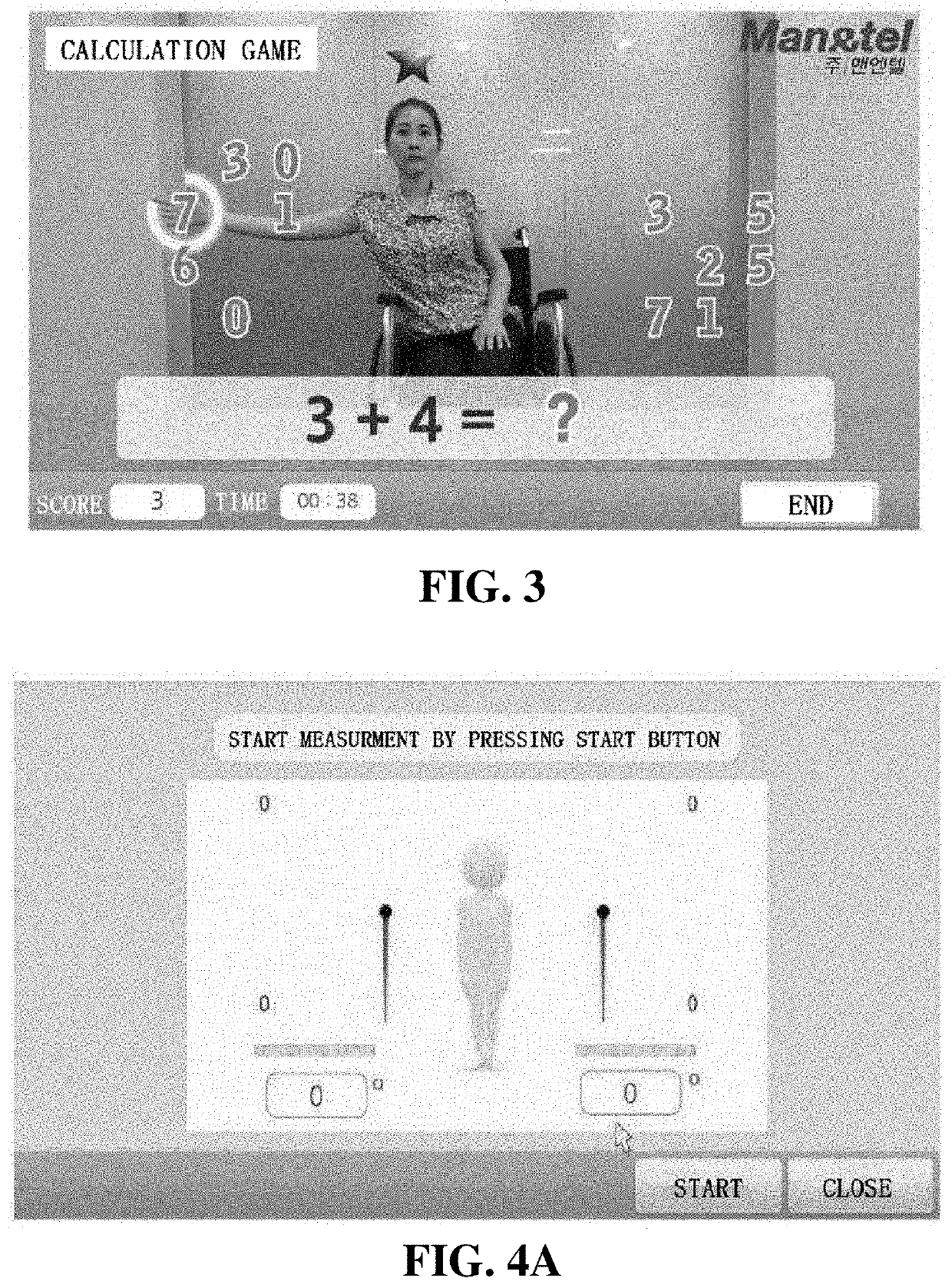
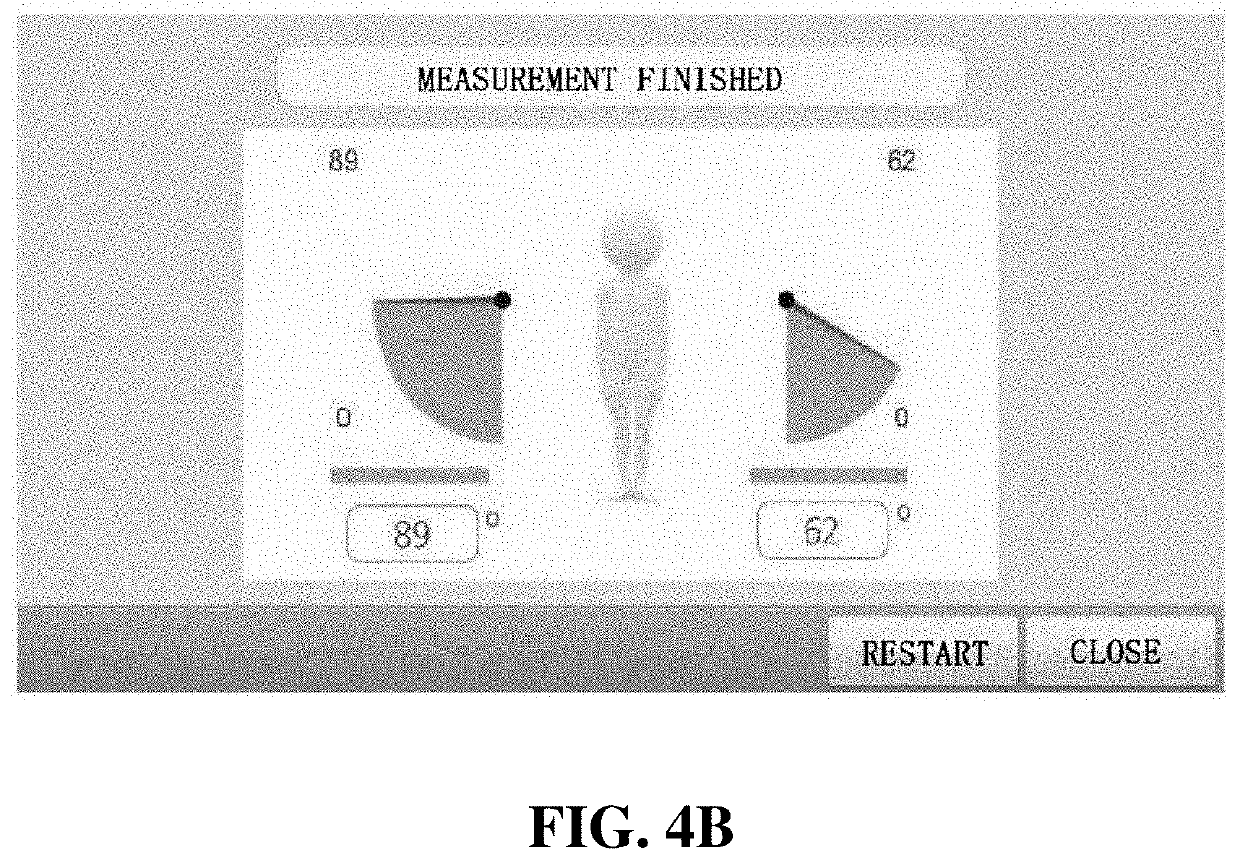
The present invention relates to training equipment for improving the ability of memory and cognition, and muscle power, and a training method using the training equipment. In particular, the present invention relates to training equipment for improving the ability of memory and cognition, and muscle power (upper and lower limb muscle power), the training equipment including: a lower limb muscle power exercise module that includes pedals for strengthening the muscle power of user's lower limbs and / or a handle for steering; a display that implements traveling in a virtual space for memory ability training of the user; and a training unit that improves cognition ability and / or muscle power of the user on the basis of driving data of the lower limb muscle power exercise module, thereby being able to complexly support memory ability training, lower limb muscle power exercise, and upper limb muscle power exercise of rehabilitation patients, patients with dementia, and / or patients with cognitive impairment.
Owner:MAN&TEL
Composition for enhancing muscle power and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106262938AImprove absorption rateRelieve or eliminate exercise fatigueFood ingredient functionsSide effectTert-leucine
The invention provides a composition for enhancing muscle power and a preparation method thereof. Functional components of the composition comprise the following components in parts by weight: 10-500 parts of soybean oligopeptides, 10-100 parts of L-leucine, 10-100 parts of L-isoleucine, 10-100 parts of L-valine, and 2-10 parts of oligosaccharides; and the composition is obtained by mixing the components. The composition employs soybean oligopeptides as a functional nutrient with extremely low sensitization and extremely high absorptivity, specific amino acids and oligosaccharides are compounded with mutual synergistic effects, so that the composition has substantial effects for alleviating or eliminating sport fatigue and mental fatigue, and good mouthfeel without any side effects; the preparation method is simple and is suitable for needs of large scale industrial production.
Owner:乐康珍泰(天津)生物技术有限公司
Speed controller for a vehicle
A kinematic speed controller for a vehicle requires the constant deliberate movement of a rotary apparatus which is physically independent from the vehicle drive system. It does not require substantial operator muscle power since there is no direct mechanical connection between the kinematic controller and the vehicle drive system. The rotary apparatus which controls the vehicle speed may be a foot pedal and crank assembly. Additionally, the invention may include a variable degree of resistance to the rotary input device to enhance operator control or to provide muscle exercise for the operator if desired. Furthermore, the invention may include the variable setting of the relationship between the speed of the rotary input device and the amount of power provided to drive the vehicle and hence the speed of the vehicle. The components of the invention may be arranged to visually simulate a bicycle-type mechanical chain drive. The speed controller is preferably connected to an electrical generator which through appropriate circuitry controls the amount of power delivered to a drive motor from batteries. A simple electrical key switch may be utilized to completely disable the operation of the vehicle.
Owner:EDMONDS JR RICHARD F
Next to skin garments manufactured from a fabric coated with a composite material based on metal oxides and ainorganic material
A non compression garment and specially “next to skin” articles based on a fabric coated with a composite material on the basis of metal oxides and inorganic material emitting in the far infrared range which comprises a composite material including a polymer matrix with embedded particles of an inorganic material capable of emitting far-infrared radiation, a fabric surrounding a body part of the user and having at least a part or the whole of it covered with the said composite material which comprises metal oxides and inorganic material, where the fabric is printed with the composite material for forming a pattern, and surrounds any body part of the user, such as arms, throat, torso, thigh, or calf for increasing of the temperature of the skin, improving blood circulation to the microcapillaries thereunder, to the upper and lower limbs, improving the muscle power, decreasing the lactic acid in the muscles and the free radicals, and for reducing the appearance of cellulite.
Owner:PSIPSIKAS GEORGE +1
Elbow joint training adaptation element, rehabilitation training equipment and training control method thereof
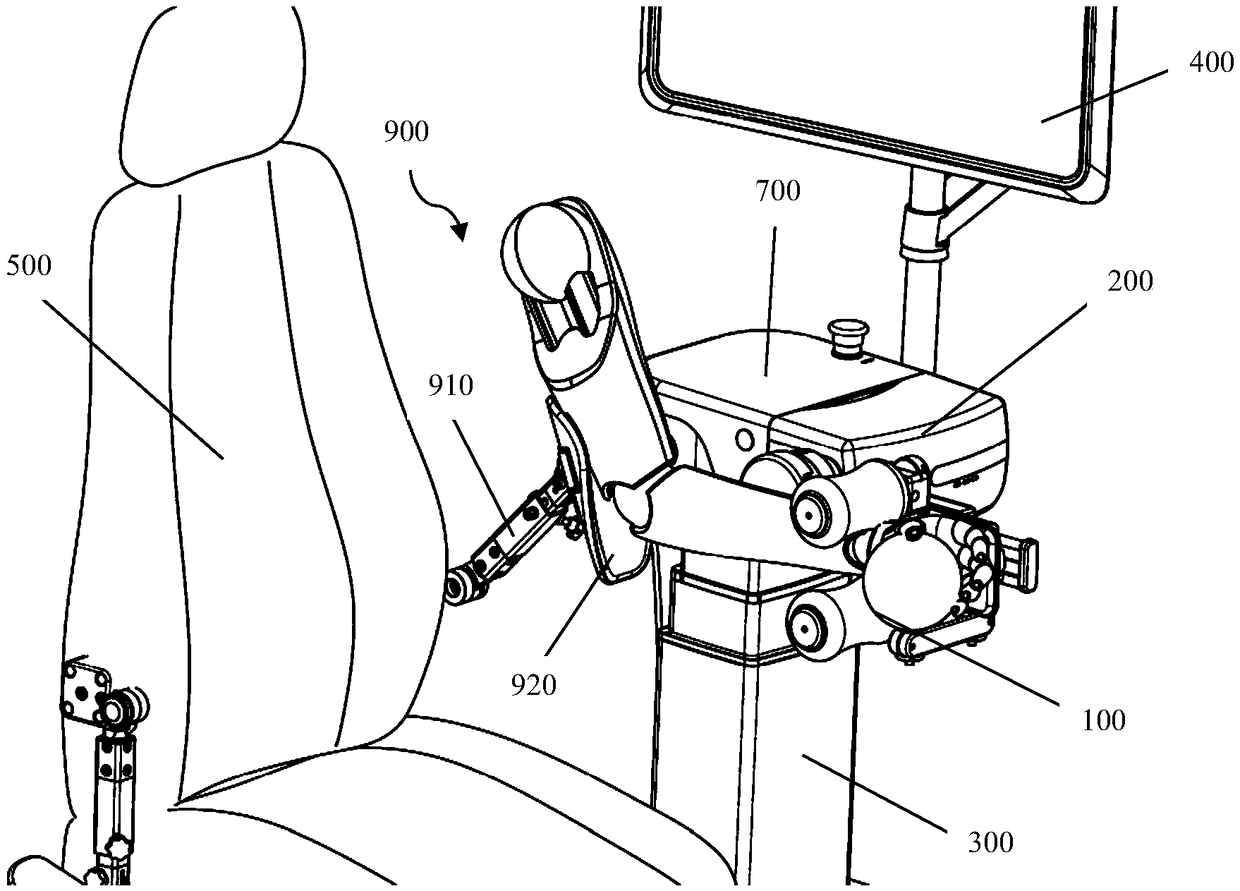
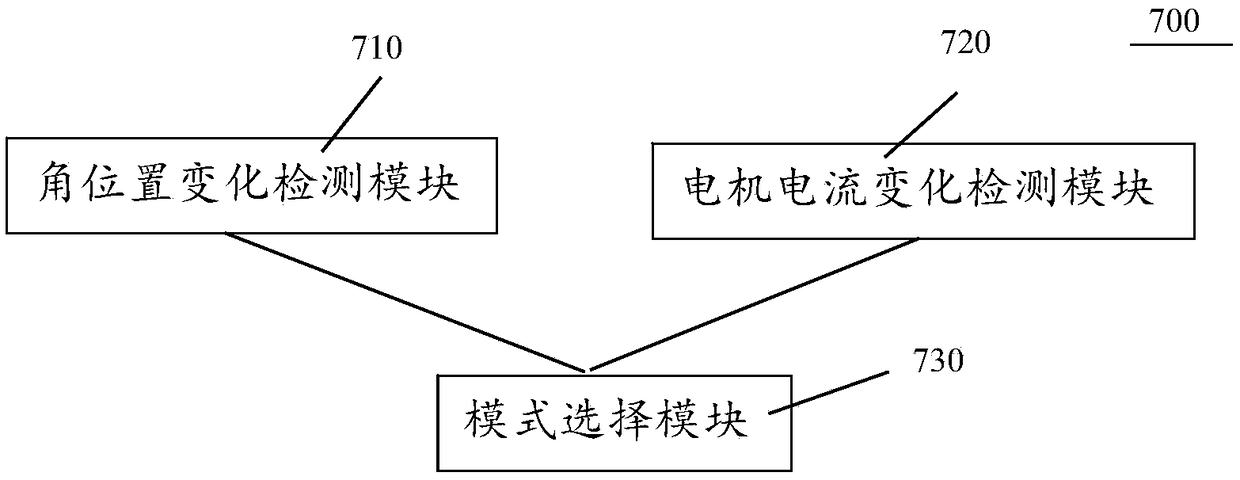
PendingCN109276407AEasy to useSmall volumeChiropractic devicesMuscle exercising devicesEngineeringDrive motor
The invention discloses an elbow joint training adaptation element, elbow joint rehabilitation training equipment and a training control method thereof. The elbow joint training adaptation element comprises an elbow joint adaptation device and a motion control host, wherein the elbow joint adaptation device comprises a regulator, a position regulating mechanism and a joint fixing element; the joint fixing element is connected onto the regulator in a way capable of being regulated through the position regulating mechanism; the motion control host comprises a driving motor and a control module;the regulator is connected with a driving motor and can rotate relative to an output shaft of the driving motor; the control module is connected with the driving motor; and the control module comprises an angle position change detection module, a motor current change detection module and a mode selection module. The elbow joint training adaptation element, the elbow joint rehabilitation training equipment and the training control method provided by the invention can be used for effectively helping a patient do joint training, so that the muscle power is improved; the joint activity is improved; and the stiff joint can be relaxed through traction.
Owner:HANGZHOU EXTREME MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com