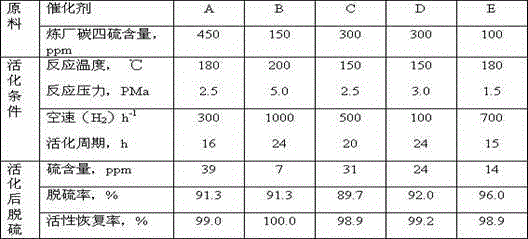
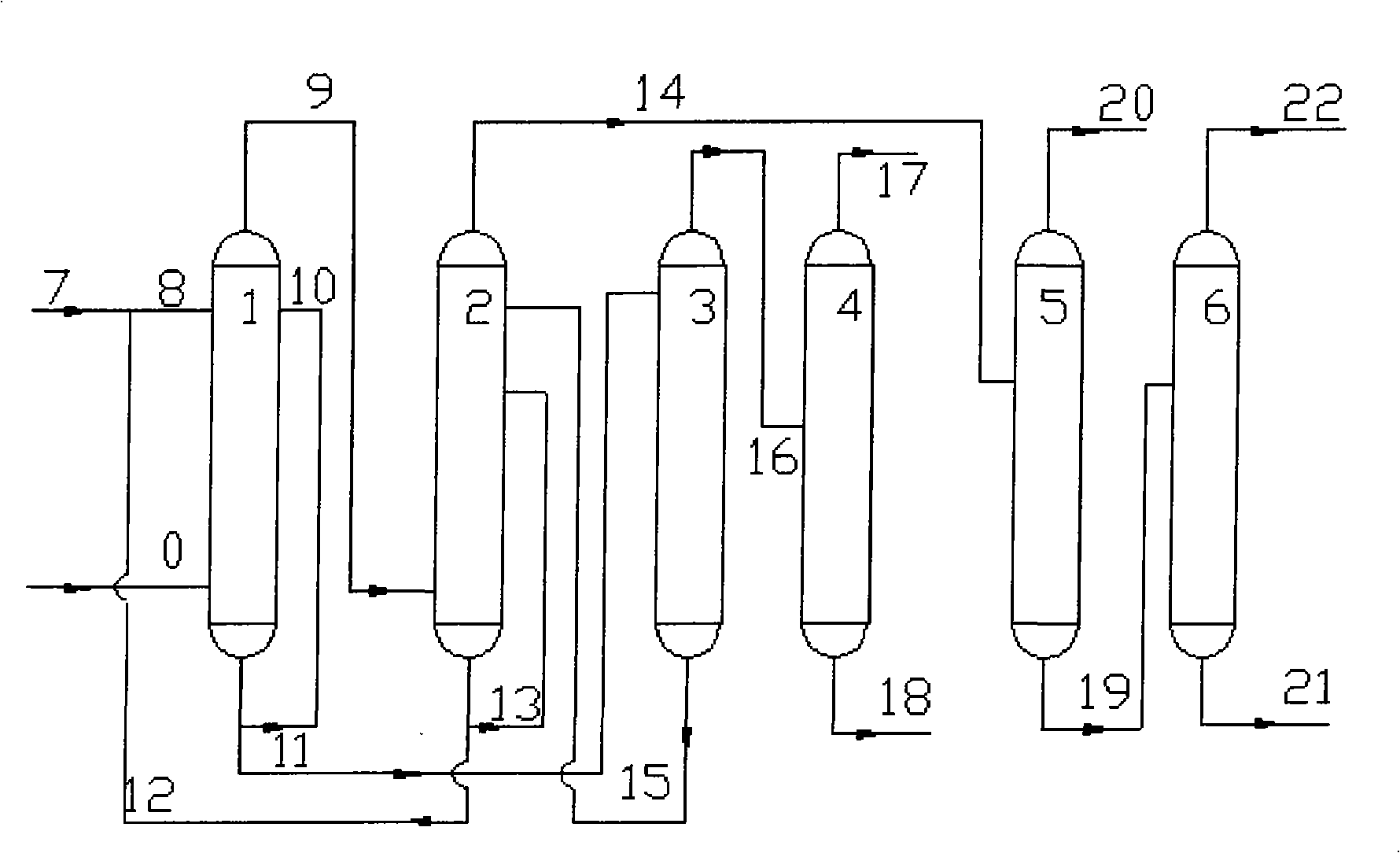
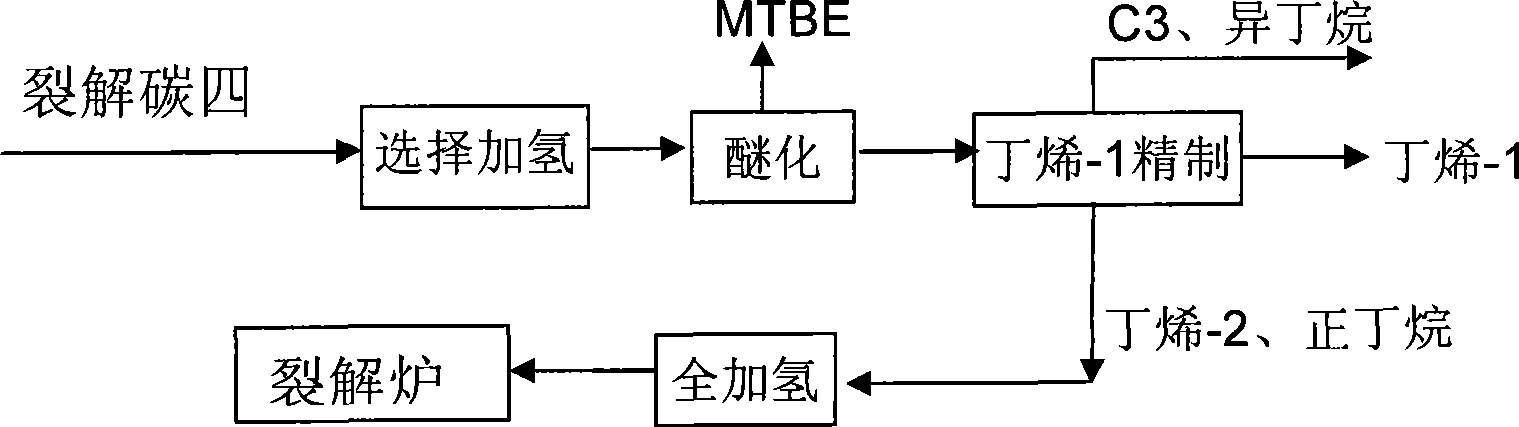
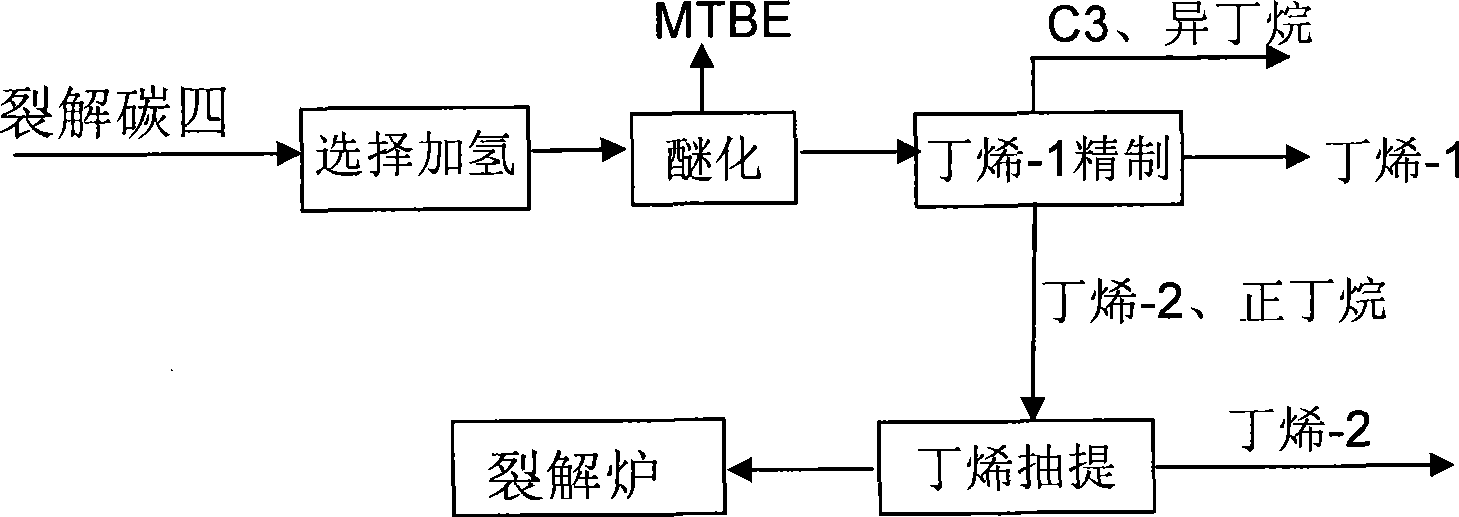
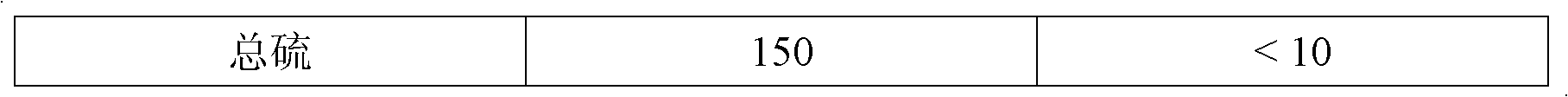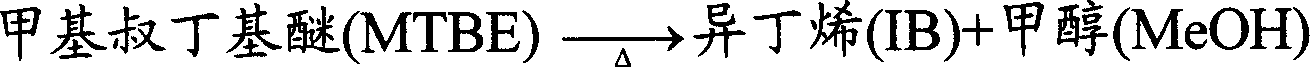Patents
Literature
662 results about "Methyl tert-butyl ether" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE), also known as tert-butyl methyl ether, is an organic compound with a structural formula (CH₃)₃COCH₃. MTBE is a volatile, flammable, and colorless liquid that is sparingly soluble in water. It has a minty smell vaguely reminiscent of diethyl ether, leading to unpleasant taste and odor in water. MTBE is a blending component of gasoline, used as an oxygenate to raise the octane number and to replace lead. Its use is controversial in some parts of the world, such as the US, because of contamination of groundwater, which was followed by legislation favoring ethanol. However, worldwide production of MTBE has been constant owing to growth in Asian markets.
Fuel for jet, gas turbine, rocket and diesel engines
InactiveUS20050023188A1Hydrocarbon purification/separationSolid fuelsAromatic moietyComponents of crude oil
A fuel or fuel blendstocks for jet, gas turbine, rocket, and diesel engines, particularly jet and rocket engines utilizing components of conventional petroleum not currently utilized for jet, gas turbine, rocket, and diesel fuels, such as benzene, butanes, butanes, and methyl tert butyl ether (MTBE) alklyated with aromatic moieties to make monoaromatics used in jet and diesel fuels. Additionally, a fuel having such monoaromatics has multiple desired properties such as higher flash point, low pour point, increased density, better lubricity, aerobic degradability, reduction in toxicity, and additionally can deliver benefits in blendstocks.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Process and apparatus for purifying methyl tert-butyl ether contaminated water
There is provided an efficient and effective method and apparatus for purifying methyl-tert butyl ether contaminated water by bubbling into the water an oxidizing gas and then stripping the oxidizing gas and MTBE from the water. A pressurized container is used to create microbubbles and to promote oxidation.
Owner:WASINGER ERIC M
Method for desulphurizing methyl tertiary butyl ether with high sulphur content
InactiveCN101643392ASimple processAdvanced technologyEther separation/purificationPolymer scienceSulfur product
The invention relates to a method for desulphurizing MTBE with high sulphur content, belonging to the field of the refining of methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE). The methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) with high sulphur content is placed into a distillation tower and heated by a reboiler, the temperature of a tower kettle is kept between 90 DEG C and 120 DEG C, the pressure of the tower kettle iskept at 0.08+ / -0.02 MPa, the temperature of a tower top is kept between 69 DEG C and 75 DEG C, and the pressure of the tower top is kept at 0.06+ / -0.02 MPa so that a finished product is distilled outof the tower top, a reflux ratio is kept from 1 to 10, and a sulfur product is recycled from a tower bottom. The invention has the advantages of simple process, advanced technology, easy and convenient control operation, little investment, low cost and no three-waste pollution.
Owner:SHANDONG YUHUANG CHEM CO LTD
Cleaning gasoline with alcohol ether base
InactiveCN1597873AMeet power requirementsIncrease oxygen contentLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCleansing AgentsNuclear chemistry
The invention discloses a clean alcohol ether-base gasoline, prepared of alcohol-base fuel mixed solution, naphtana etherified liquid, C-5 and cleaning agent; and its components in weight percent (wt%): alcohol-base fuel mixed solution 40-50, C-5 10-20, naphtana etherified liquid 30-45, cleaning agent 0.1. The alcohol-base fuel mixed solution is composed of methanol, acetone, hydrogen peroxide, ferrocene-benzene solution and camphor powder. The naphtana etherified liquid is prepared by etherifying naphtana, methyl-tert-butyl ether and isopropyl ether. The finished oil has rich HO molecular groups, high oxygen content and can fully burn. After it is used, the indexes of various harmful matters in the discharged tail gas from engines are obviously lower than those of ordinary gasoline and environmental protection.
Owner:于雷
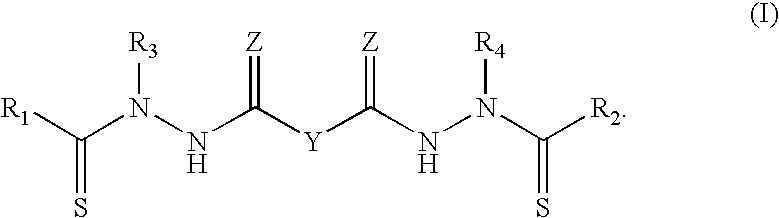
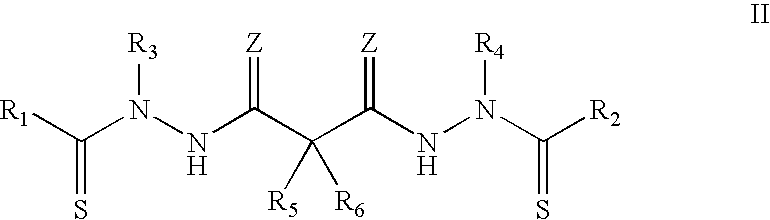
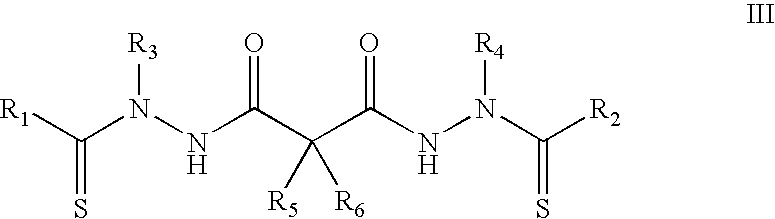
Synthesis of bis(thio-hydrazide amide) salts
InactiveUS20060270873A1Easy to disassembleLower levelOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationThio-Potassium hydroxide
A method of preparing a bis(thio-hydrazide amide) disalt includes the steps of combining a neutral bis(thio-hydrazide amide), an organic solvent and a base to form a bis(thio-hydrazide amide) solution; and combining the solution and methyl tert-butyl ether, thereby precipitating a disalt of the bis(thio-hydrazide amide). In some embodiments, a method of preparing a bis(thio-hydrazide amide) disalt includes the steps of combining a neutral bis(thio-hydrazide amide) and an organic solvent selected from methanol, ethanol, acetone, and methyl ethyl ketone to make a mixture; adding at least two equivalents of a base selected from sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium methoxide, potassium methoxide, sodium ethoxide and potassium ethoxide to the mixture, thereby forming a solution; and combining the solution and methyl tert-butyl ether to precipitate the disalt of the bis(thio-hydrazide amide). The disclosed methods do not require lyophylization and the solvents used in the process can be more readily removed to low levels consistent with pharmaceutically acceptable preparation.
Owner:SYNTA PHARMA CORP
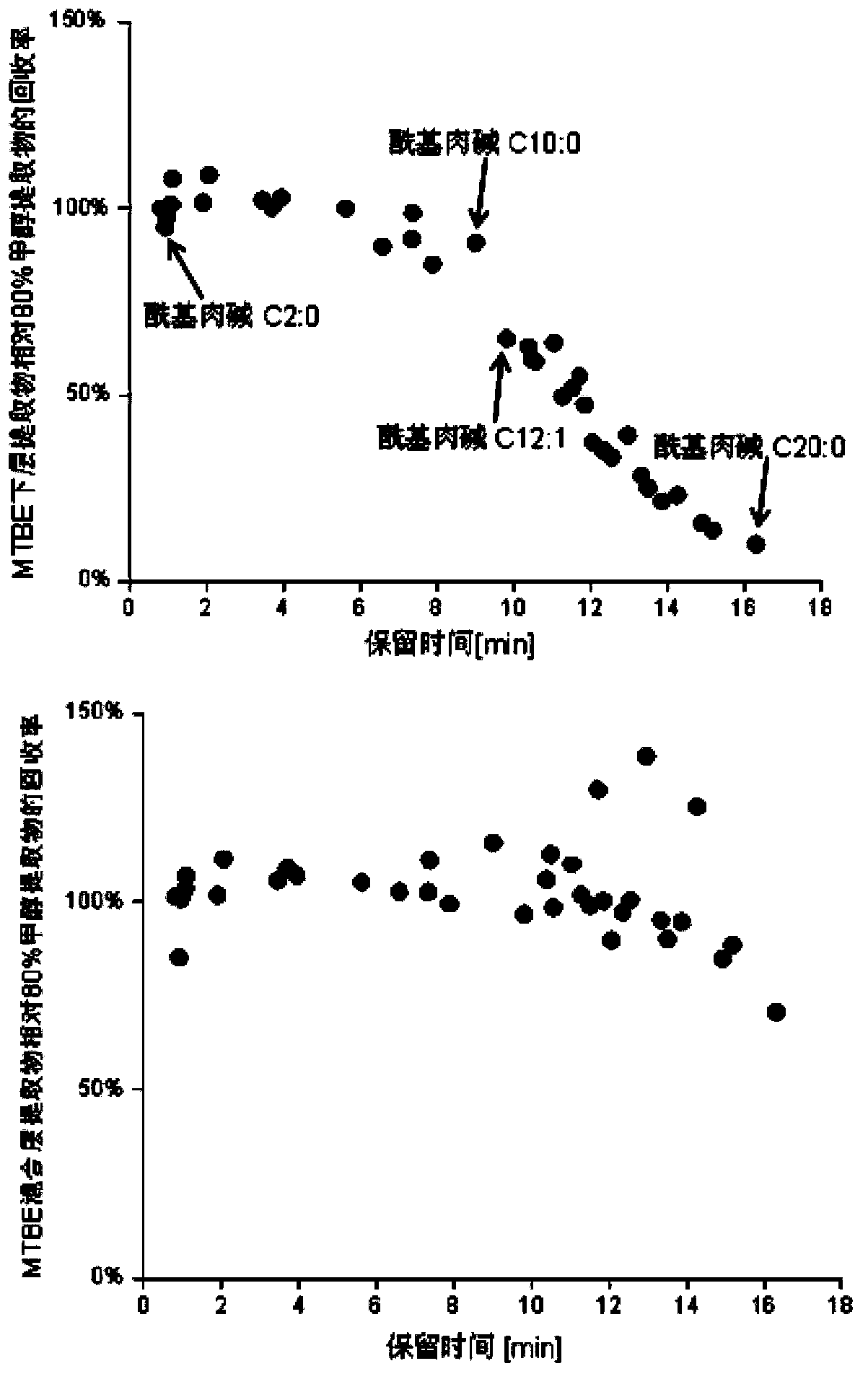
Method for simultaneous extraction and analysis of metabolite group and lipid group in microtissue
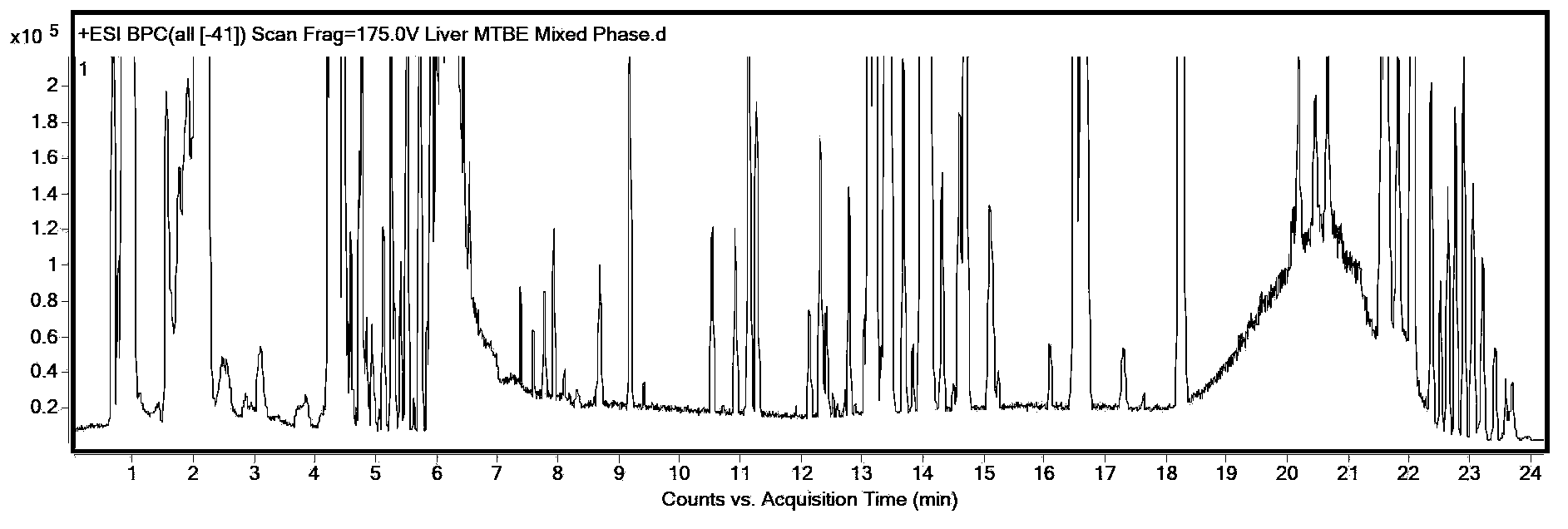
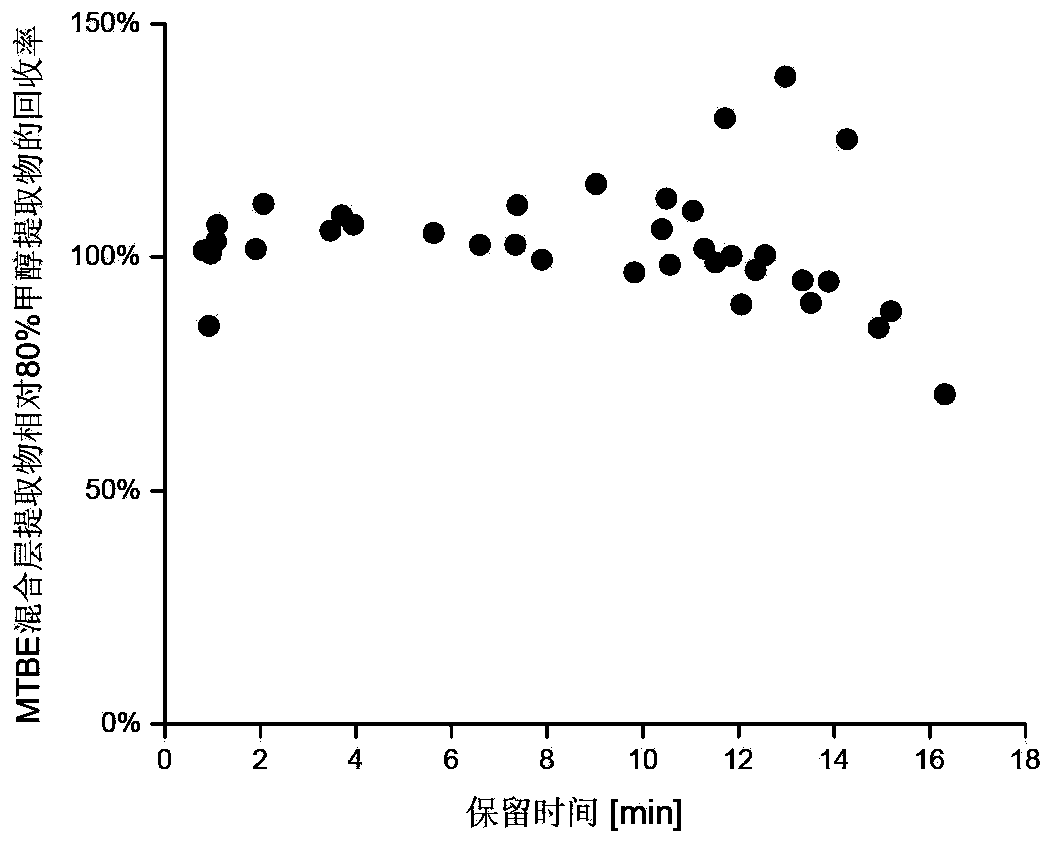
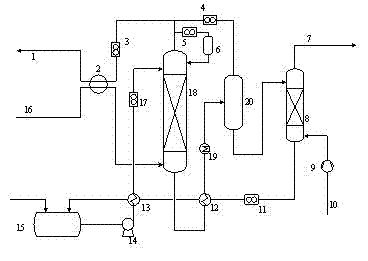
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous extraction and analysis of a metabolite group and a lipid group in microtissue. The method comprises the following steps: freeze drying to-be-analyzed microtissue, accurately weighing 1 to 25 mg of the freeze-dried microtissue and adding solvents like methanol (MeOH), methyl tert butyl ether (MTBE) and water in certain proportion for extraction; allowing a solution obtained after completion of extraction to be divided into two layers, wherein an upper layer mainly contains nonpolar metabolites and lipids, and the lower layer mainly comprises polar and medium-polar metabolites; and subjecting the upper-layer solution and the lower-layer solution to mixing in proportion and freeze-drying, then carrying out redissolving and then metabonomical analysis based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, subjecting the upper-layer solution to freeze-drying and then to redissolving and carrying out lipidomical analysis based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method has the following advantages: metabolites and lipids are extracted as many as possible through one extraction of a small amount of tissue, and through metabonomical and lipidomical analysis, the amount of a tissue sample is saved, which benefits other biochemical analysis of the tissue sample.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
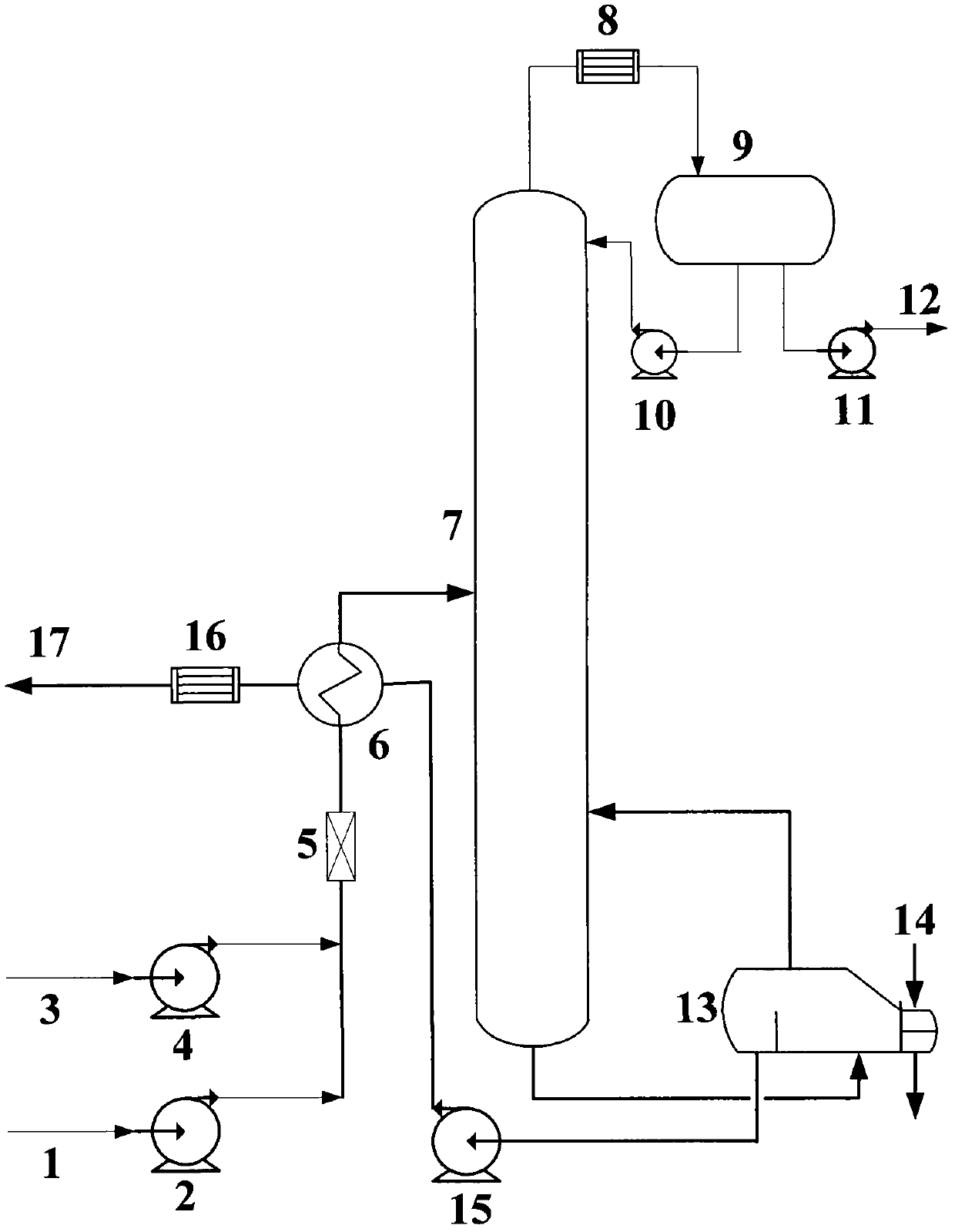
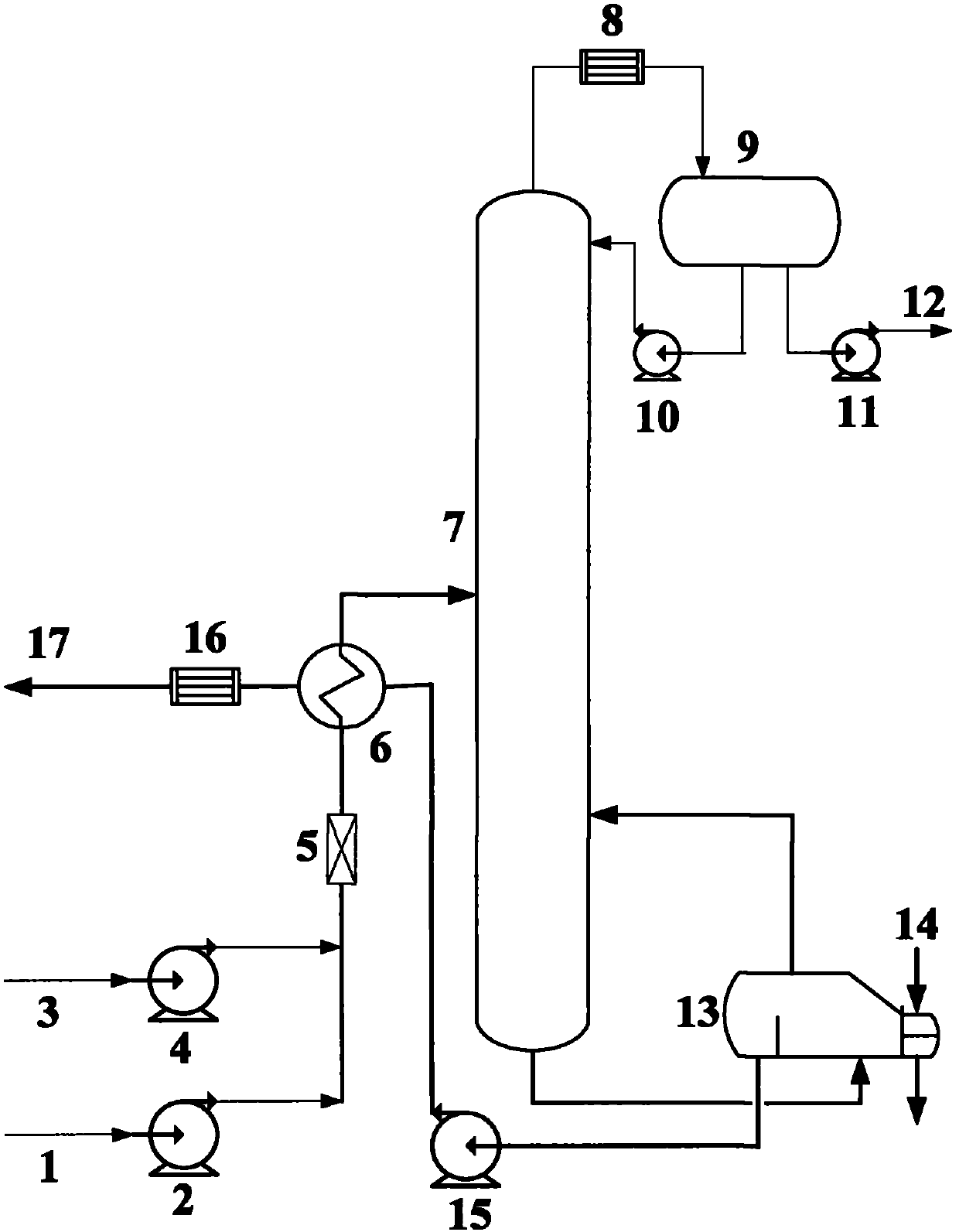
Method and device for removing organic sulfur in methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE)
InactiveCN102381945AHigh yieldHigh desulfurization rateEther separation/purificationTowerMethyl tert-butyl ether
The invention relates to a method and a device for removing organic sulfur in methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE). The method and the device are utilized for high-sulfur content MTBE refinement. The method and the device realize normal-pressure low-temperature extraction rectification desulphurization of a high-sulfur content MTBE product. A technical scheme of the invention comprises the following steps that 1, a sulfur-containing MTBE product is heated by a heat exchanger and then is fed into a rectifying tower from a lower part of the rectifying tower; 2, an extractant is fed into the heat exchanger, is heated and then is fed into the rectifying tower from an upper part of the rectifying tower, wherein a rectifying tower temperature is in a range of 70 to 80 DEG C and the heated sulfur-containing MTBE product and the heated extractant countercurrently contact with each other so that countercurrent contact extraction desulphurization is realized; 3, the desulfurated MTBE product is output from the top of the rectifying tower, is subjected to cooling condensation to form liquid in the heat exchanger and then is output; and 4, the sulfur-containing extractant obtained by the step 2is output from the bottom of the rectifying tower, is heated by the heat exchanger, is fed into a flash tank, is distilled at a temperature of 80 to 85 DEG C so that the residual desulfurated MTBE product is distilled off, then is fed into an actifier column, and countercurrently contacts with dry air in the actifier column so that countercurrent contact gas stripping regeneration is realized. Through the method and the device, good desulphurization effects are realized; a high product yield is obtained; and an extractant can be regenerated for recycle. The method is convenient for operation,has low costs and low energy consumption, and can be utilized for high-sulfur content MTBE product refinement.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Catalyst for preparing isobutene by methyl tert-butyl ether cracking, preparation method, and application thereof
ActiveCN102451674AImprove pressure resistanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWater vaporHigh pressure
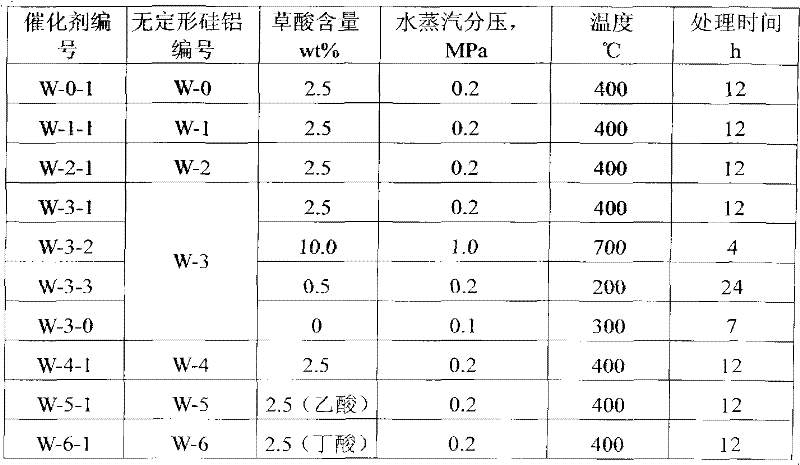
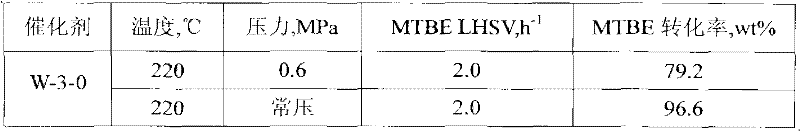
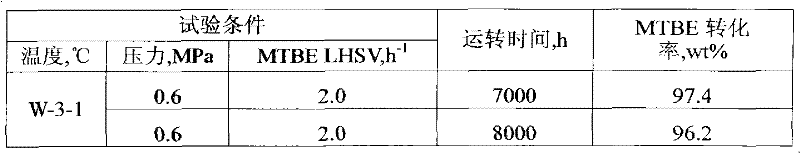
The present invention discloses a catalyst for preparing isobutene by methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) cracking, a preparation method, and an application thereof. According to the method, amorphous silicon-aluminum is subjected to a hydrothermal treatment by using water vapor containing oxalic acid to obtain the catalyst. According to the present invention, when the catalyst is adopted for preparing the isobutene by the MTBE cracking, the reaction can be completed at high pressure; the product isobutene flows into a following separation system with the self-pressure, and a compressor is not required to press the product isobutene into the liquid phase, such that the operating cost is saved, and the conversion rate of the MTBE and the selectivity of the isobutene are high.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for extracting dihydro-quercetin from larch
InactiveCN1844095AGood technical effectImprove stabilityOrganic chemistrySolventMethyl tert-butyl ether
The invention provides a method of extracting dihydroquercetin from eastern larch, this method using water as extractant, extracting xingan eastern larch contains dihydroquercetin, liquid-liquid extracting the produced aquosity extract, adsorption decolouring methyl tert-butyl ether tobacco extract by activated char or active clay, stripping the dissolvant of decolourized methyl tert-butyl ether tobacco extract in vaccum, the grease thing of water stripped is crystallization purified by water and getting rude product of dihydroquercetin. According to need, the getted rude product of dihydroquercetin can be recrystallization purified by water and getting elaboration product of dihydroquercetin. The method of this invention has prominant technique effect, not only the yield is as high as 1.69%-2.0%, but also the getted rude product of dihydroquercetin's purity is as high as 95%-96%, the purified elaboration product of dihydroquercetin can reach the purity of 99%.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Catalysts for production of unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid and a process for producing unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid using the catalysts
InactiveUS6583316B1High yieldGuaranteed uptimeOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsGas phaseCerium
Improved catalysts for use in vapor phase oxidation of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of propylene, isobutylene, t-butanol and methyl-t-butyl ether with molecular oxygen or a molecular oxygen-containing gas to produce the corresponding unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid are provided. The improved catalysts are compositions comprising (A) a complex oxide containing as essential components molybdenum, bismuth and iron, which is known per se as a catalyst for said reaction and (B) a complex oxide containing cerium and zirconium as the essential components. When the improved catalysts are used, the production operation of unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid can be continued stably for over prolonged period.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
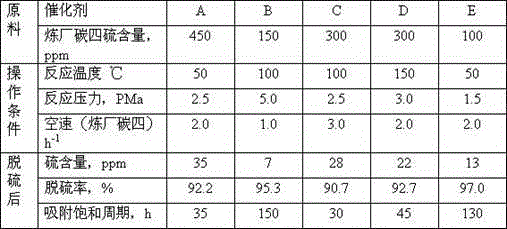
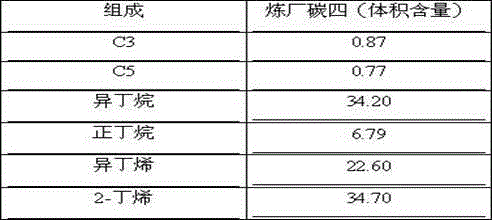
Deep desulfurization method of refinery C4
InactiveCN104557388APromote regenerationCause changeHydrocarbonsAdsorption purification/separationHydrogenActive component
The invention discloses a deep desulfurization method of refinery C4, which comprises the following steps that at least two fixed bed reactors are adopted; a C4 fraction is subjected to adsorption desulfurization by the action of an adsorbent loaded with a hydrogenated active component; the C4 fraction is switched to another reactor for the adsorption desulfurization after adsorption saturation; hydrogen is supplied to the adsorption saturated fixed bed reactor for a hydrogenated desulfurization reaction; and the adsorbent loaded with the hydrogenated active component is regenerated. Refinery C4 desulfurized by the method can directly serve as a raw production material of MTBE (methyl tert-butyl ether), and isobutylene in the C4 fraction is sufficiently protected and utilized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
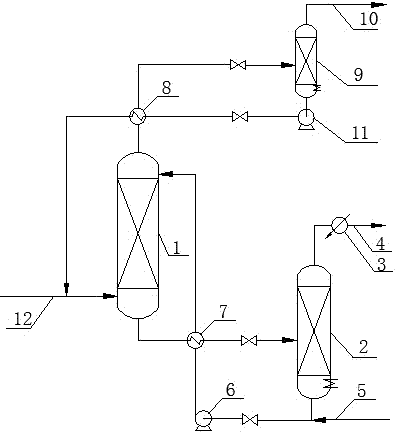
Refining device for preparing high-pure isobutene by cracking methyl tertiary butyl ether and technique thereof
InactiveCN101260016AHigh purityImprove mass transfer efficiencyHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsWater dischargeTower
The invention discloses a refining device and a technical method used to make high-purity isobutene through the cracking of methyl tert-butyl ether. The technical method contains a six-tower continuous rectification technical process, and comprises a cooling absorption double tower system, a methanol dehydrating tower system, a methanol refining tower system, an isobutene light fraction-removal tower system and an isobutene heavy fraction-removal tower system, wherein the water discharged from the methanol dehydrating tower system is cooled down and then is returned to a cooling absorption tower to undergo cooling absorption operation once again; therefore, the refining process realizes zero release of cooling absorption water; moreover, the internal top of a cooling absorption tower 2 is provided with a foam destroyer which catches the liquid droplets carried in gas, thereby ensuring the purity of isobutene product. All internal parts of each rectification tower device adopt efficient regular filler and multi-row hole distribution, which ensures that the purity of high-purity isobutene product is more than 99.7 percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for comprehensive utilization of cracking C4
ActiveCN101475429ATake advantage ofIncrease productionHydrocarbon by hydrogenationDistillation purification/separationHydrogenation reactionEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively utilizing cracking carbon four. The method comprises: firstly, the cracking carbon four is subjected to selective hydrogenation reaction so that acetylene hydrocarbon and diene in the cracking carbon four are subjected to selective hydrogenation to generate mono-olefine; secondly, isobutene in the cracking carbon four reacts to generate methyl tertiary butyl ether by an etherification device; a methyl tertiary butyl ether product and a material mainly comprising butylene-1, butylene-2 and butane are obtained through separation; the materialcomprising the butylene-1, butylene-2 and butane is introduced to a butylene-1 refining system to obtain a butylene-1 product, a material containing carbon three and isobutene and a material mainly containing butylene-2 and n-butane through separation; the material mainly containing the butylene-2 and n-butane is treated to remove the butylene-2 so as to obtain a material containing the n-butane;and the material containing the n-butane is returned to a cracking furnace and is used as raw material. The method adopts selective hydrogenation, full hydrogenation, etherification, rectification, extraction and other combined technologies to fully utilize each component of the cracking carbon four, thereby obtaining largest economic benefit.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for deeply desulfurizing methyl tertiary butyl ether
ActiveCN102557888AReduce sulfur contentMeet the requirements of motor gasolineEther separation/purificationDistillationAutomotive gasoline
The invention provides a method for deeply desulfurizing methyl tertiary butyl ether. The method is characterized in that the sulfur-containing methyl tertiary butyl ether is mixed with light oil to form a mixture; the mixture enters a distillation column for distillation, so as to remove sulfur compounds in the sulfur-containing methyl tertiary butyl ether; and the column reactor temperature of the distillation column is 70 DEG C to 120 DEG C, the column top temperature is 50 DEG C to 60 DEG C, the pressure is 0.01 MPa to 0.15 MPa, the theoretical column plate number is 3 to 20 and the reflux ratio is 0.25 to 10. By adopting the method, the total sulfur content of the methyl tertiary butyl ether can be reduced from more than 1000 Mug*g-1 to less than 1000 Mug*g-1, and the distilled methyl tertiary butyl ether can well satisfy the requirement of mixing automotive gasoline of a production country IV or a production country V.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Catalyst for cracking methyl tert-butyl ether to prepare isobutylene and its prepn
InactiveCN101020142AHigh catalytic activityHigh selectivityCatalyst carriersHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsPolymer scienceAqueous solution
The present invention discloses one kind of catalyst for cracking methyl tert-butyl ether to prepare isobutylene and its preparation process. The catalyst includes carrier and supported bisulfate in the amount of 1.5-30 % carrier weight accounting in the bisulfate radical. It is prepared through soaking the carrier in water solution of bisulfate for 0.5-24 hr, filtering, drying at 100-130 deg.c for 1-8 hr and baking at 150-900 deg.c for 2-12 hr. The catalyst has high catalytic activity, high methyl tert-butyl ether converting rate at low temperature, high methanol and isobutylene selectivity and other advantages.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for removing sulfides in methyl tertiary butyl ether by using activated carbon
InactiveCN102757316AReduce sulfur contentEfficient removalEther separation/purificationReaction temperatureFixed bed
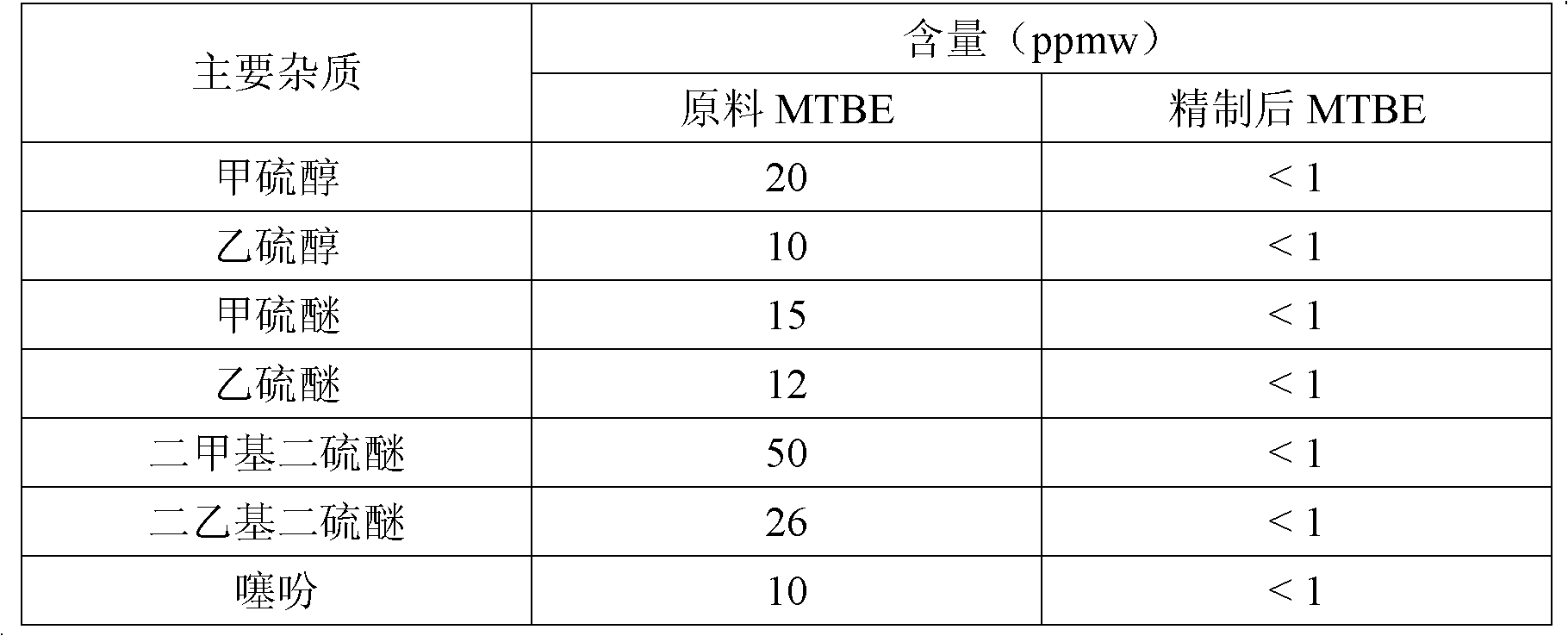
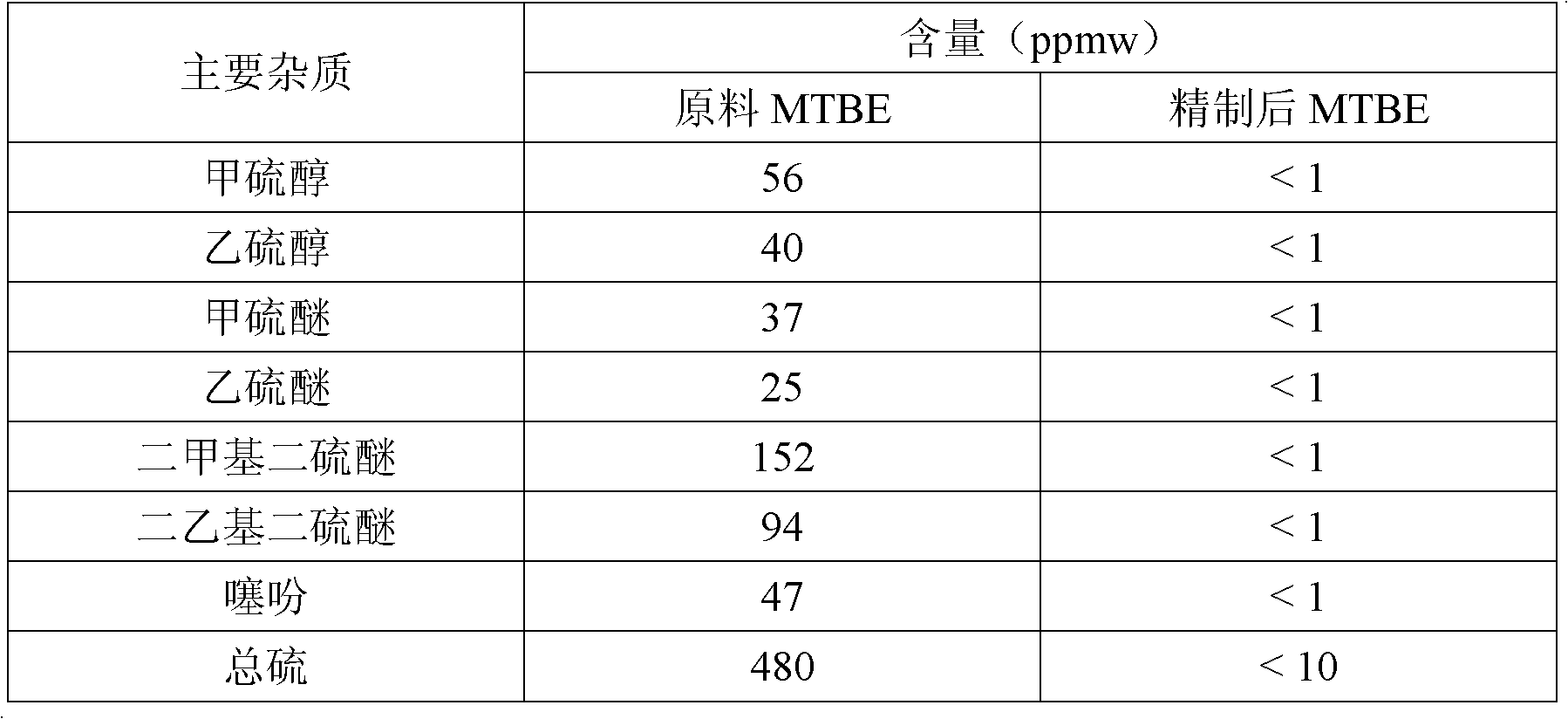
The invention relates to a method for removing sulfides in methyl tertiary butyl ether by using activated carbon. The method includes enabling a methyl tertiary butyl ether raw material containing the sulfides to contact with the activated carbon to obtain a methyl tertiary butyl ether product; performing an intermittent reaction process for purification, adding the activated carbon with the volume accounting for 0.4-10% of that of the methyl tertiary butyl ether raw material into a reaction kettle filled with the methyl tertiary butyl ether raw material, performing room-temperature reaction for 0.5-4 hours under protection of nitrogen, and extracting the methyl tertiary butyl ether after the reaction stops; or performing a continuous reaction process by the aid of a fixed bed for purification, filling the activated carbon in a reactor of the fixed bed, controlling the reaction temperature to range from 20 DEG C to 80 DEG C and purifying the methyl tertiary butyl ether by continuous reaction. In the continuous reaction process, the liquid hourly space velocity of the methyl tertiary butyl ether raw material ranges from 1.0h-1 to 10h-1, and the pressure ranges from the atmospheric pressure to 1.0MPa. By the aid of the method, the sulfur content of the methyl tertiary butyl ether can be reduced to be lower than 10ppmw, and the disulfide content is lower than or equal to 2ppmw.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
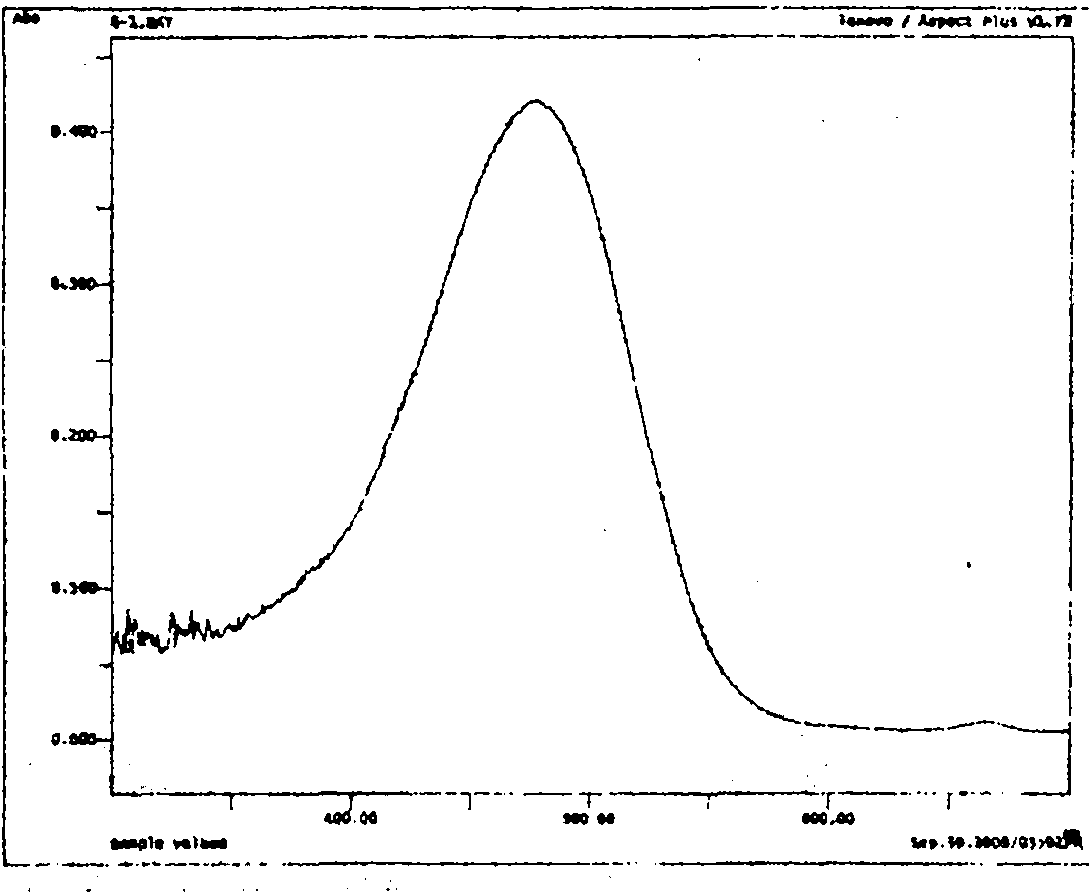
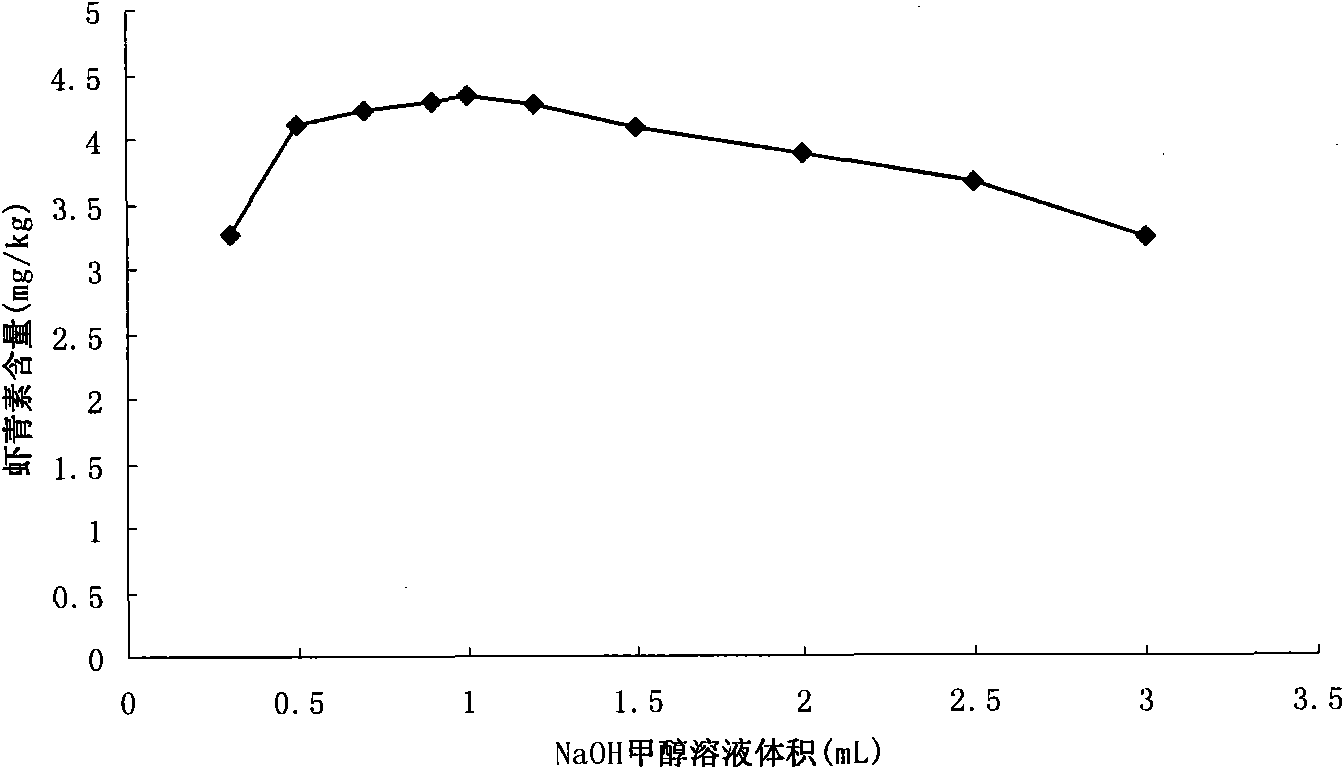
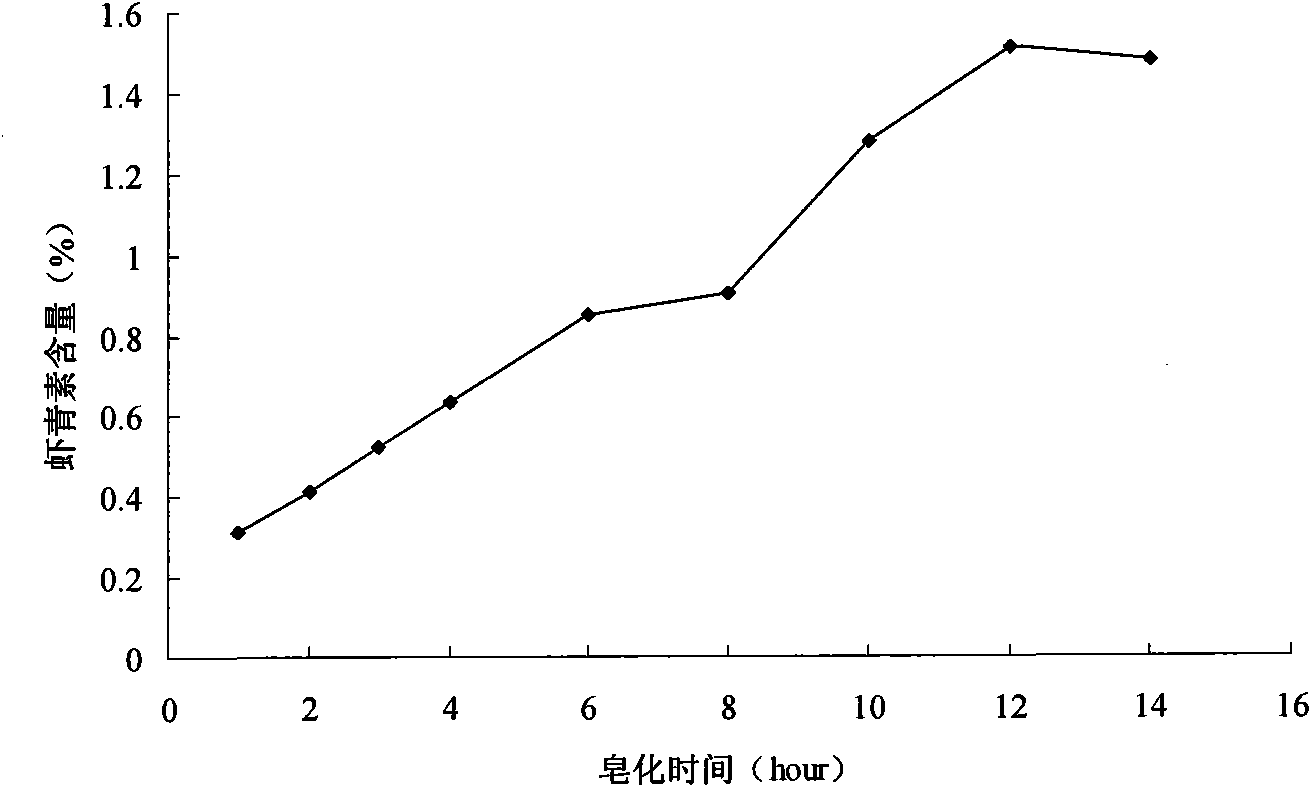
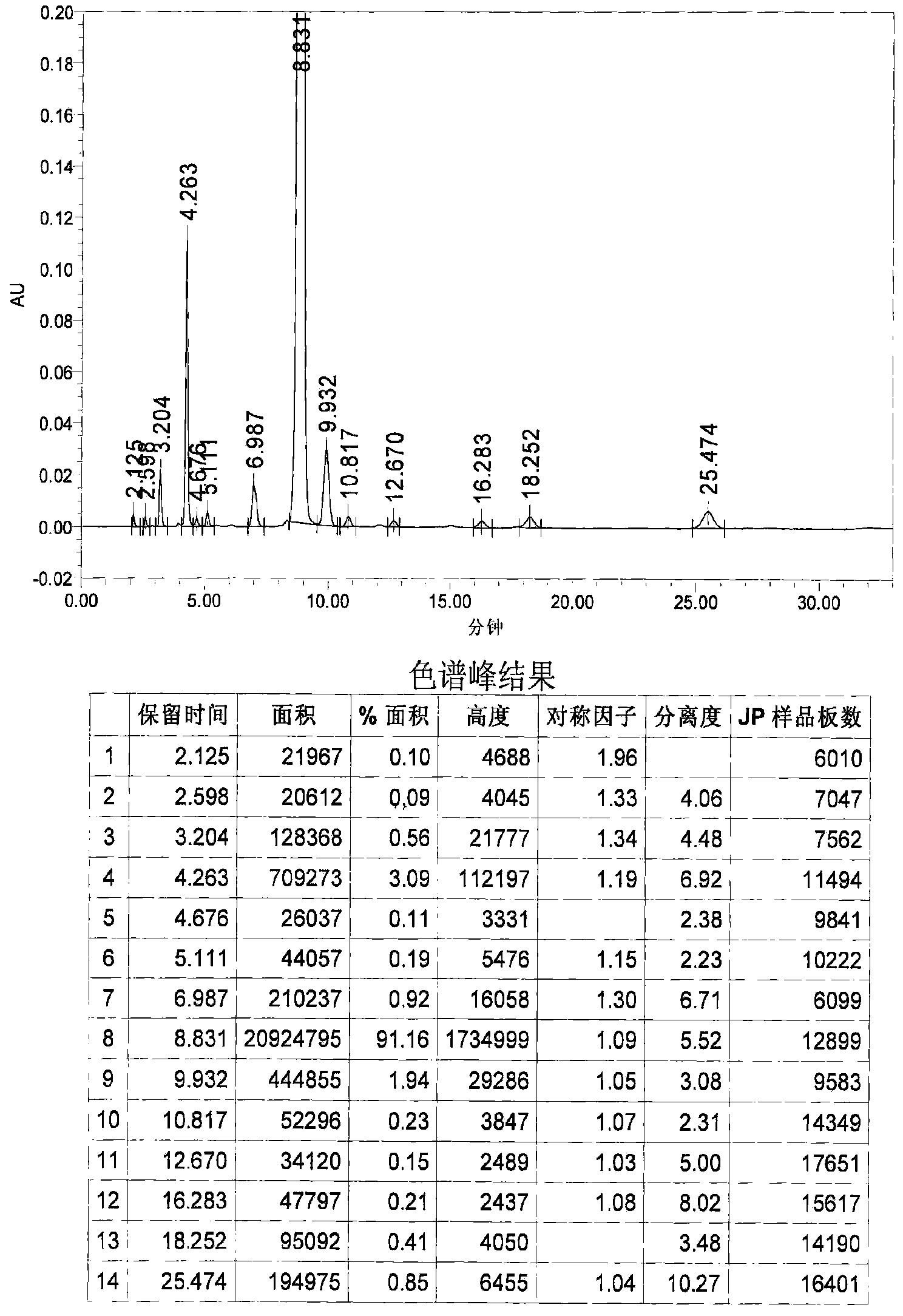
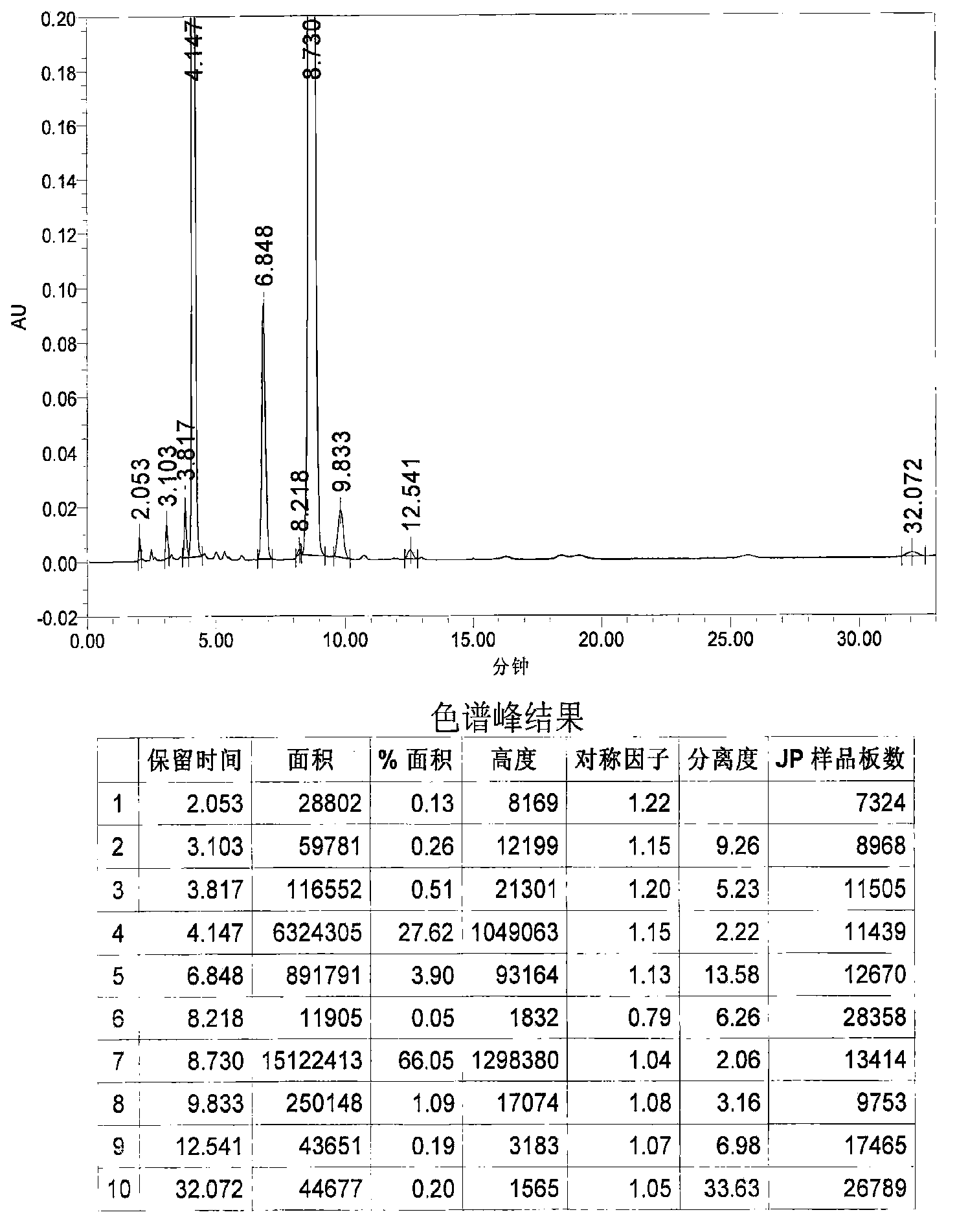
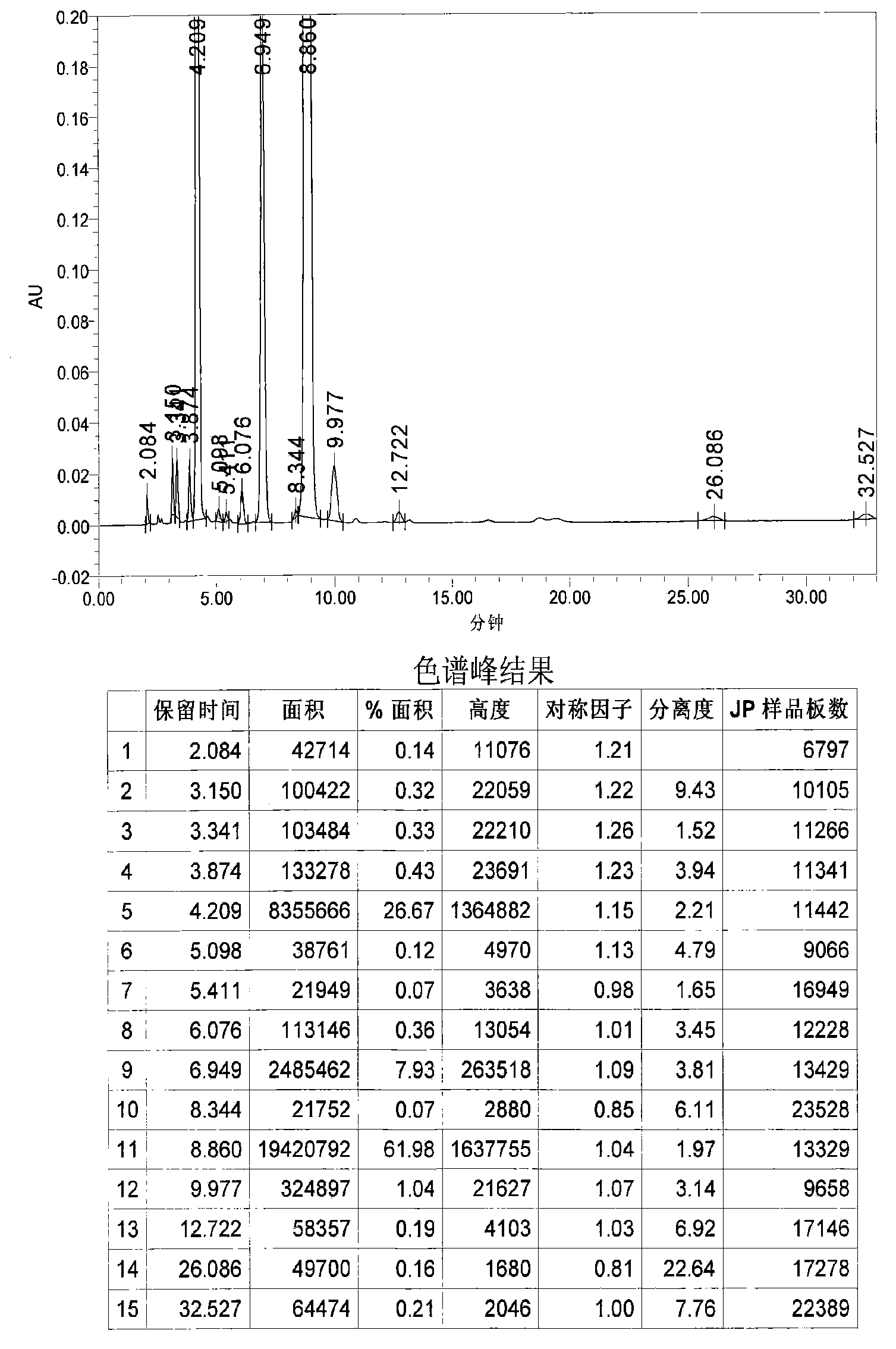
Method for determining content of astaxanthin in antarctic krill oil by chromatography
The invention relates to a method for determining the content of astaxanthin in antarctic krill oil by chromatography, which comprises the steps of adopting a gel purification column with a BIO-3X packing, taking ethyl acetate and cyclohexane as eluant according to the proportion of 1:1, and collecting a fractions at 7.48-12.60min; carrying out low-temperature saponification in a solvent formed by methylene dichloride and methanol after purification, and completely converting astaxanthin esters to free astaxanthin; adopting a YMC-Carotenoid C30 chromatographic column; carrying out gradient elution by taking water solution of the methanol, methyl tert-butyl ether and 1% of phosphoric acid as a mobile phase; leading the flow rate to be 1.0mL / min, using an ultraviolet detector as the detector, and leading the detecting wavelength to be 474nm; and determining three isomers of the astaxanthin and adopting the sum of three peak areas for quantifying. The gel chromatographic column can better separate fat from the astaxanthin in the antarctic krill oil, and the adoption of the C30-reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography can accurately determine the content of the astaxanthin, thereby objectively and truly evaluating the quality of the antarctic krill oil.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Methanol gasoline and its compounding process
InactiveCN1487060AReduce usageSolve the problem that mechanical stirring cannot be usedLiquid carbonaceous fuelsZinc peroxideMethyl tert-butyl ether
Methanol gasoline is compounded with lead-free gasoline 15-80 wt%, methanol 15-80 wt%, and acetone 1-10 wt%, and some of the following material(s) may be also added: zinc peroxide, ethyl ether, fat activitor, dimethoxy methane, methyl tert-butyl ether, ocatne and light gasoline. Methanol and gasoline are miscible, and using the methanol gasoline can obtain ever high driving force and 0.7-3.6% lowered oil consumption, and reduce CO in tail gas by over 95% and oxycarbide by over 85%. In addition, the methanol gasoline may be used with gasoline alternately.
Owner:季子善
Method of producing isobutene joint producing dimetylether and dipolyisobutene
InactiveCN1493552AImprove conversion rateLess investmentOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsSolid acidReaction temperature
A process for preparing isobutylene along with dimethylether and dipolyisobutylene includes cracking reaction of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) in the reactor containing solid acid catalyst at 230-270 deg.c, dewatering part of resultant methanol to obtain dimethylether, and further polymerizing part of isobutylene to obtain dipolyisobutylene.
Owner:中国石油化工股份有限公司北京燕山分公司研究院
Additive of M50 methanol gasoline
The invention relates to an additive of fuel, in particular to an additive of high-proportion methanol gasoline, such as M50 methanol gasoline. The additive is characterized in that the additive in the total volume ranging from 2% to 5% is added into the methanol gasoline and consists of 60% to 70% of mutual solvent formed by compounding alcohols, alcohol ethers, esters and acetones according to optional proportion, 24.4% to 30% of ignition agent formed by compounding fatty hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons and methyl tertiary butyl ether according to optional proportion, 4% to 6% of combustion improver formed by compounding nitryls and nitrate esters according to optional proportion, 1% to 3% of corrosion inhibitor formed by compounding phenols and grease according to optional proportion, and catalyst and anti-oxidant stabilizer in proper quantity. By the aid of the additive, the service life of a gasoline tank can be prolonged evidently, methyl alcohol system of the gasoline can be effectively guaranteed against being deteriorated and layered easily, and the problems of poor startability and power performance and the like can be solved effectively. The additive is rich in raw material sources, simple in production process and procedures and convenient in use and popularization.
Owner:HEBEI JICHUN CHEM CO LTD
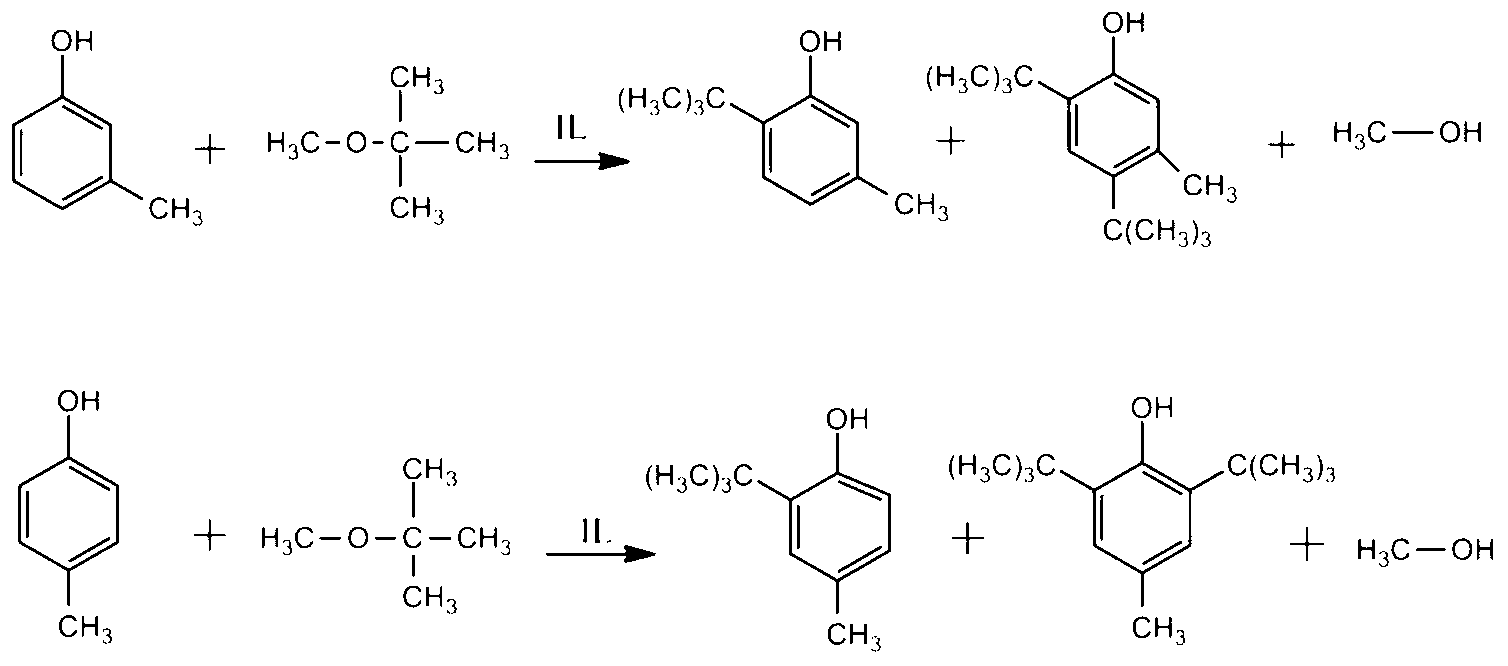
Catalyst for alkylation separation of m-cresol and p-cresol and separation method
InactiveCN103212438ALess corrosiveDoes not affect activityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHydrogen SulfateButylated hydroxytoluene
The invention relates to a novel catalyst for alkylation separation of m-cresol and p-cresol and a separation method. Imidazole type ionic liquid 4-(3-methyl-1-imidazol)-1-butyl sulfonic acid hydrogen sulfate with the purity of 99% is taken as the catalyst for alkylation reaction of cresol. A cresol mixture and an alkylation reagent, namely methyl tert-butyl ether perform hydrocarbyl substitution reaction to generate di-tert-butyl substitutes (4, 6-di-tert-butyl-m-cresol and 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol) of m-cresol and p-cresol with greater boiling point difference. The di-tert-butyl substitutes are separated by utilizing a rectification method according to the boiling point difference between the two, and then tert-butyl groups in the di-tert-butyl substitutes of the cresol are removed to obtain pure m-cresol and p-cresol so as to achieve the purpose of separating the m-cresol and the p-cresol. The transformation rate of the m-cresol after the reaction is 85-89%, the transformation rate of the p-cresol is 78-81%, and alkylation products are 6-tert-butyl-m-cresol, 2-tert-butyl-p-cresol, 4, 6-di-tert-butyl-m-cresol and 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol.
Owner:天津北洋国精科技有限责任公司
Method for removing sulfide in methyl tertiary butyl ether through double-solvent extractive distillation
InactiveCN103922900AGuaranteed low sulfur contentReduce energy consumptionEther separation/purificationChemical industryExtractive distillation
The invention relates to a method for removing sulfide in methyl tertiary butyl ether through double-solvent extractive distillation in a refinery plant or chemical industry, which can deeply remove sulfide in methyl tertiary butyl ether. The method comprises the following steps of mixing an organic sulfur extraction agent with a sulfur-containing MTBE raw oil and inputting the mixture from the lower part of an extraction tower, simultaneously, inputting an MTBE extraction agent from the upper part of the extraction tower, contacting the two fluids in countercurrent manner to be extracted in the extraction tower; extracting MTBE into the MTBE extraction agent and outputting from the bottom of the extraction tower, inputting into a distillation tower A from the lower part for distilling the MTBE product, evaporating and recycling the refined MTBE from the top of the tower, outputting the MTBE extraction agent from the bottom of the tower, and recycling; extracting the sulfide into the organic sulfur extraction agent and outputting from the top of the extraction tower, inputting into a distillation tower B from the middle part for distillation, discharging the sulfide from the top of the tower and entering sulfide to a recycling device, discharging the organic sulfur extraction agent from the bottom of the tower and desulfurizing circularly. The method has good desulfurizing effect, is simple and convenient to operate, and has low energy consumption, and the product has stable quality and high yield.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Preparation method of butoconazole nitrate intermediate suitable for industrial production
ActiveCN103880596AHigh yieldReduce bumpsPreparation by OH and halogen introductionMagnesium organic compoundsGrignard reactionEthyl Chloride
The invention provides a method for industrial production of a butoconazole nitrate intermediate, that is 1-chloro-4-p-chlorophenyl-2-butanol (a compound in formula II). The method of the invention comprises: 1. a Grignard reaction, that is, adopting p-chlorobenzyl chloride as a raw material, and performing a Grignard reaction with magnesium powder in a mixed solvent of methyl tertiary butyl ether and tetrahydrofuran; 2. a condensation reaction, that is, continuing reaction by adding epichlorohydrin to obtain the compound II which is an important intermediate for preparing butoconazole nitrate. According to the method, the raw materials are cheap and easily available, the reaction solvent is safer, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG ACADEMY OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
Device and process for preparing isobutylene by dehydrogenating isobutane
ActiveCN103232312AGood for coking reactionLow costHydrocarbonsHydrocarbon preparationPlatinumWater vapor
The invention relates a process for preparing isobutylene by dehydrogenating isobutane. The process is characterized in that H2 and steam are adopted and used as diluents, a loaded platinum dehydrogenation catalyst is adopted and used for performing dehydrogenation reaction on the isobutane in a static bed adiabatic reactor; after being subjected to heat exchange and cooling, a reaction product is separated and purified; the unreacted isobutane returns to a dehydrogenation reactor; in separating and refining of the product, light components, namely, H2 and C1-C3, are separated by the copious cooling method; the isobutane and the isobutylene are separated by the method of catalyzing and distilling to generate methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE); and then the obtained MTBE is cracked to obtain the isobutylene. By adopting the process, H2 with purity more than 98% and a high-purity isobutylene product can be obtained; simultaneously, the consumption of raw materials can be effectively reduced, and the equipment investment and operation cost are decreased.
Owner:青岛京齐新材料科技有限公司 +1
Refinement method of methylamino abamectin benzoate
ActiveCN103497226ASuitable for preparationHigh puritySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationBenzoic acidPhosphate
The invention relates to a refinement method of methylamino abamectin benzoate. The refinement method comprises the following steps: carrying out dissolved clarification on methylamino abamectin serving as a raw material in a polar solvent A, then adding phosphoric acid, devitrifying in methylbenzene so as to obtain methylamino abamectin phosphate, dissolving with water, adding an ester solvent B, adjusting the pH value, standing still, layering, carrying out vacuum concentration so as to obtain high-quality methylamino abamectin free alkali, salifying the high-quality methylamino abamectin free alkali and benzoic acid in a methyl tertiary-butyl ether, thus obtaining the high-content methylamino abamectin benzoate. The refinement method is simple in process and can be used for realizing industrial large-scale production; and the product has high purity and is used for preparing high-end preparations.
Owner:QILU SYNVA PHARMA
Apparatus and method to produce isooctane by indirect alkylation technique
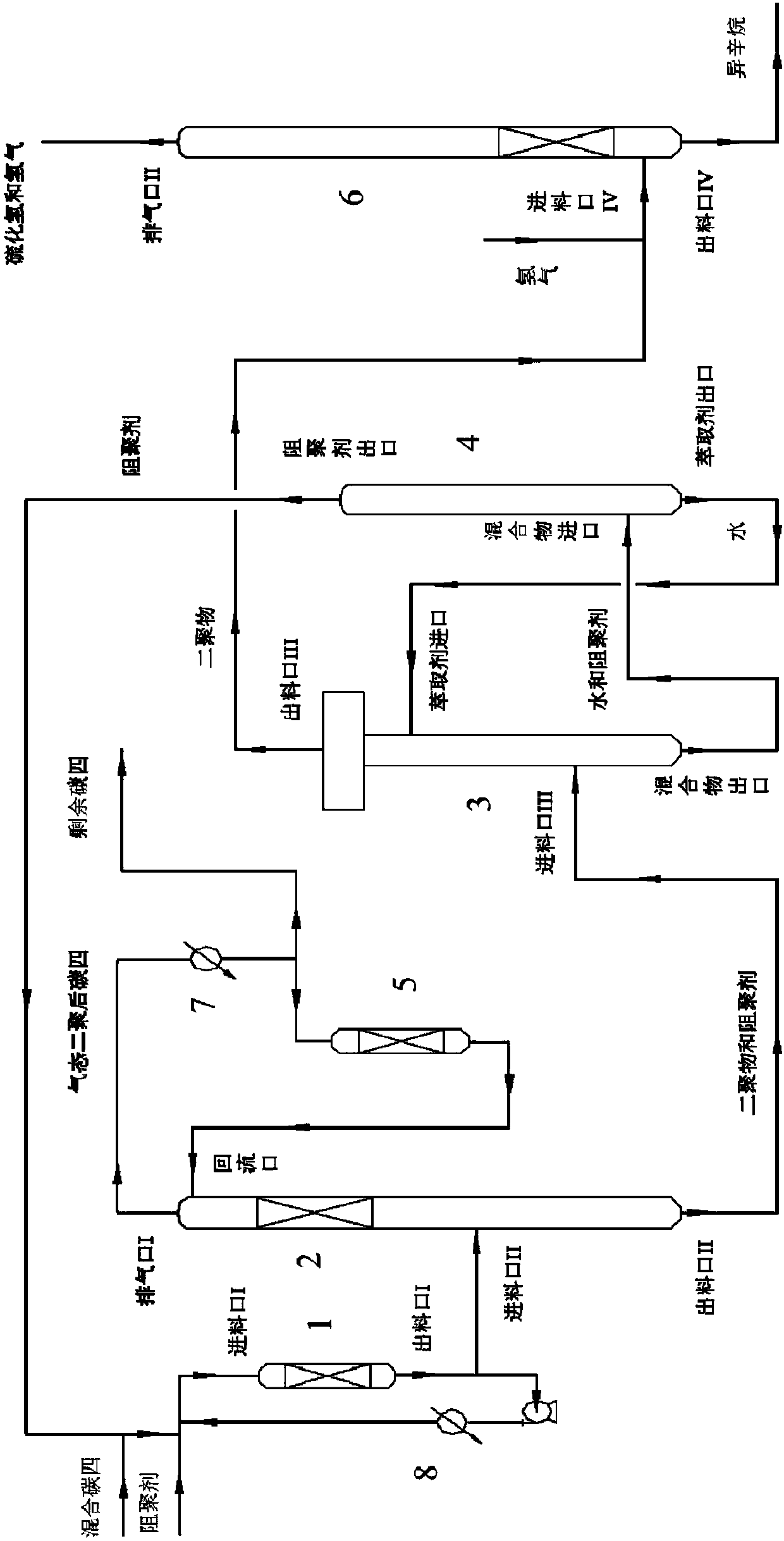
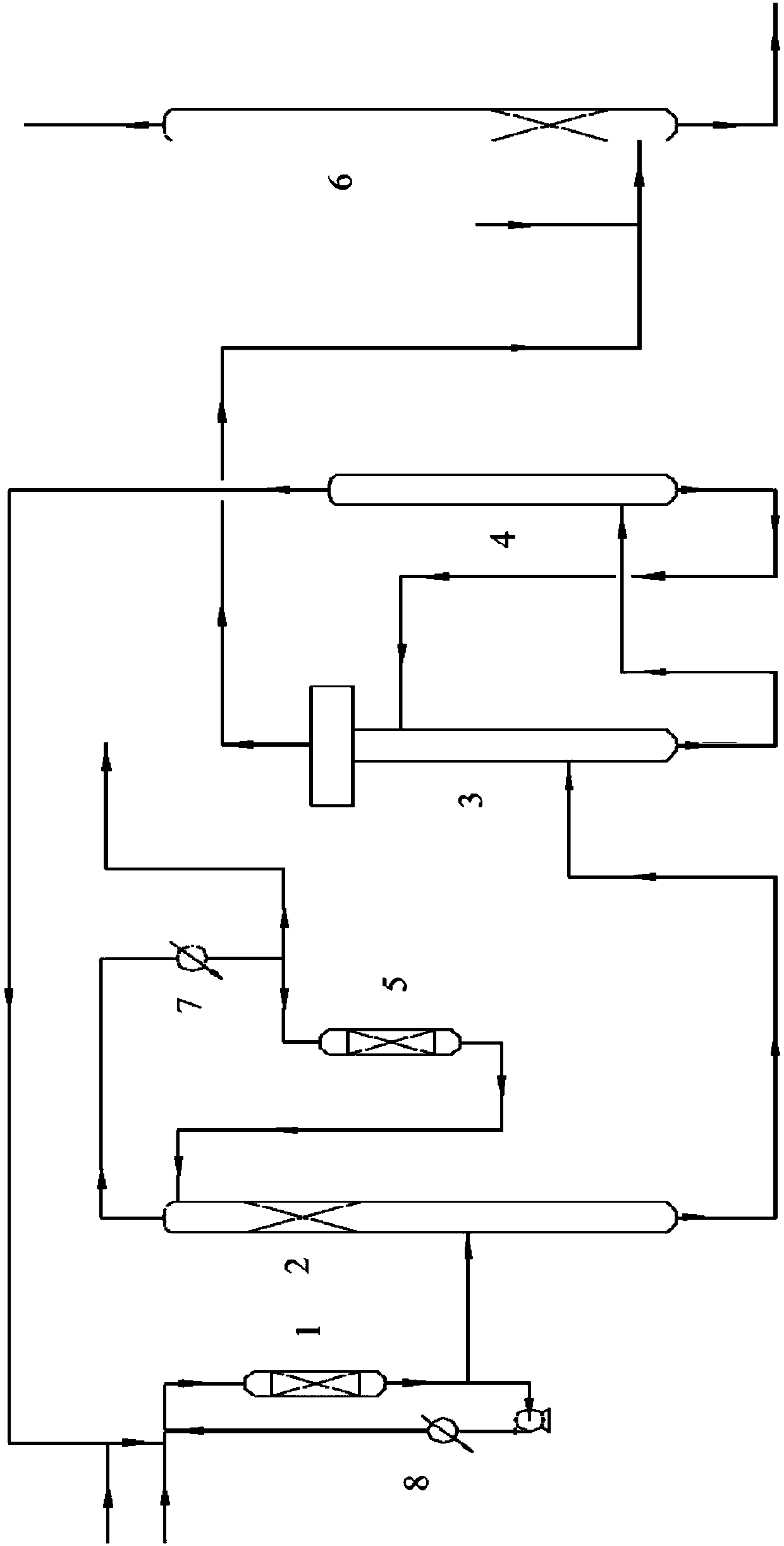
PendingCN107827694ATemperature controlImprove conversion rateHydrocarbon by hydrogenationChemical industryAlkyl transferHydrogen
The invention discloses an apparatus and method to produce isooctane by an indirect alkylation technique. The apparatus comprises fixed-bed reactor I, a catalytic distilling column, an extracting column and a recycling column which are connected in sequence. The method comprises: allowing mixed C4 and a polymerization inhibitor to react in reactor I, feeding part of the product into the catalyticdistilling column, and removing reaction heat from the other part by a heat exchanger before returning; after catalytic distillation, feeding the overhead product into fixed-bed reactor II, reflowingafter reacting, and feeding the bottom product into the extracting column; after extracting, feeding overhead biopolymer into a desulfurizing column, and feeding the bottom product into the recyclingcolumn; after recycling, returning an extracting agent into the extracting column and the polymerization inhibitor to the reactor I; subjecting the biopolymer and hydrogen to hydrodesulfurization in the desulfurizing column to obtain isooctane that may act as a gasoline blend component. Existing MTBE (methyl tert-butyl ether) production equipment is modified into isooctane production equipment; the produced isooctane may act as an ethanol-gasoline blend component; byproducts of the isooctane may also act as other materials for reuse.
Owner:KAIRUI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Method for analyzing distribution of sulfur in methyl tert-butyl ether, sulfide qualitative analysis database, and use of database
ActiveCN104807895AReduce dosageSimple methodComponent separationSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis dataQualitative analysis
The invention provides a method for qualitatively / quantitatively analyzing distribution of sulfur in a methyl tert-butyl ether product through using a gas chromatography / sulfur chemiluminescence detector. The qualitative / quantitative analysis method can be used to identify most sulfur compounds with different structure types in the methyl tert-butyl ether product and quantitatively analyze all sulfides in order to make real time adoption of a suitable desulphurization means in the production field convenient and guarantee the quality of the product. The invention also provides a sulfide qualitative analysis database based on the gas chromatography / sulfur chemiluminescence detector, and an application thereof.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Method for preparing flavonoids compounds in camellia seed shells by high-speed counter-current chromatography
InactiveCN104861019ASugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChromatographic separationAcetic acid
A method for preparing flavonoids compounds in camellia seed shells by high-speed counter-current chromatography comprises the following steps: camellia seed shells are taken as raw materials which are crushed and then extracted with ethanol, the extracting solution is collected and purified by D-101 macroporous resin, and after that, the materials of water, n-butyl alcohol, methyl tert-butyl ether, acetonitrile and glacial acetic acid at the volume ratio of 6: 3: 1:1: 0.001 serve as a high-speed counter-current solvent system to conduct high-speed counter-current chromatography on the camellia seed shell extract to prepare two flavonoids compounds. The method is simple and convenient, and excellent in reproducibility, can be used for large-scale preparation of compounds and lays a material basis for further study on activity.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Depth purification method for isobutene
InactiveCN102942436AHigh activityImprove conversion rateAdsorption purification/separationMolecular sievePurification methods
The invention relates to a depth purification method for isobutene. The method comprises that the isobutene which is generated through schizolysis of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) serving as a raw material is in contact with a molecular sieve, the water in the isobutene is removed till the content is no more than 10 ppmw, an oxygenated chemical adsorbent is used for removing methanol, dimethyl ether, the MTBE and thiobarbituric acid (TBA) of the isobutene until the content is no more than 10 ppmw and the depth purification is completed. By the aid of the method, the sigma S of the isobutene containing sigma S4-7 ppmw, the methanol of 100-150 ppmw, the dimethyl ether of 200-300ppm, the MTBE of 10-50 ppmw, the TBA of 10-20 ppmw and H2O of 100-150 ppmw is removed through the absorption of a dry sorbent, a desulfurization sorbent and a de-oxygenates agent till the content is no more than 1 ppmw, the methanol, the dimethyl ether, the MTBE and the TBA are removed till the content is no more than 10 ppmw, the H2O is removed till the content is no more than 10 ppmw, and the depth purification is achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
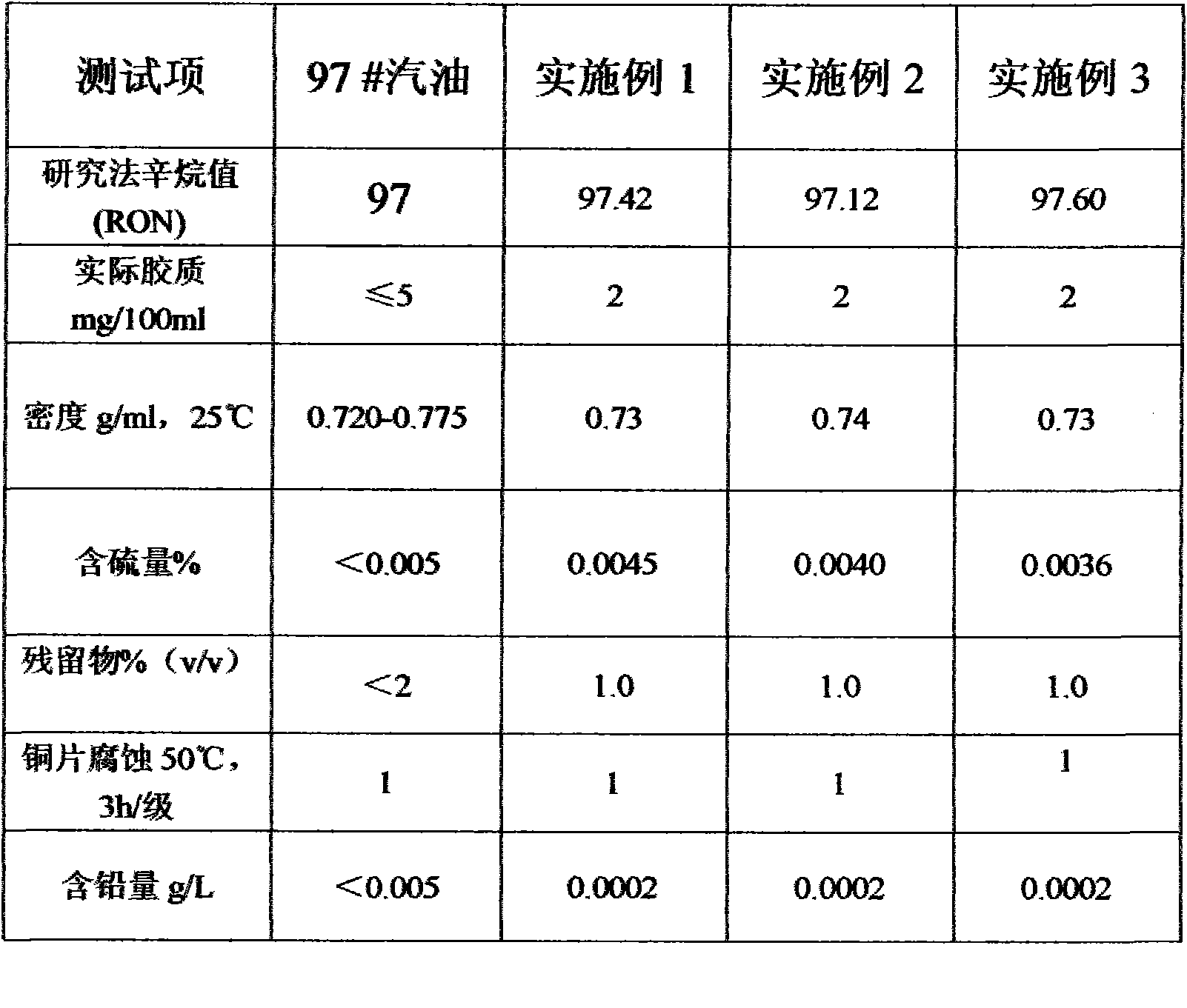
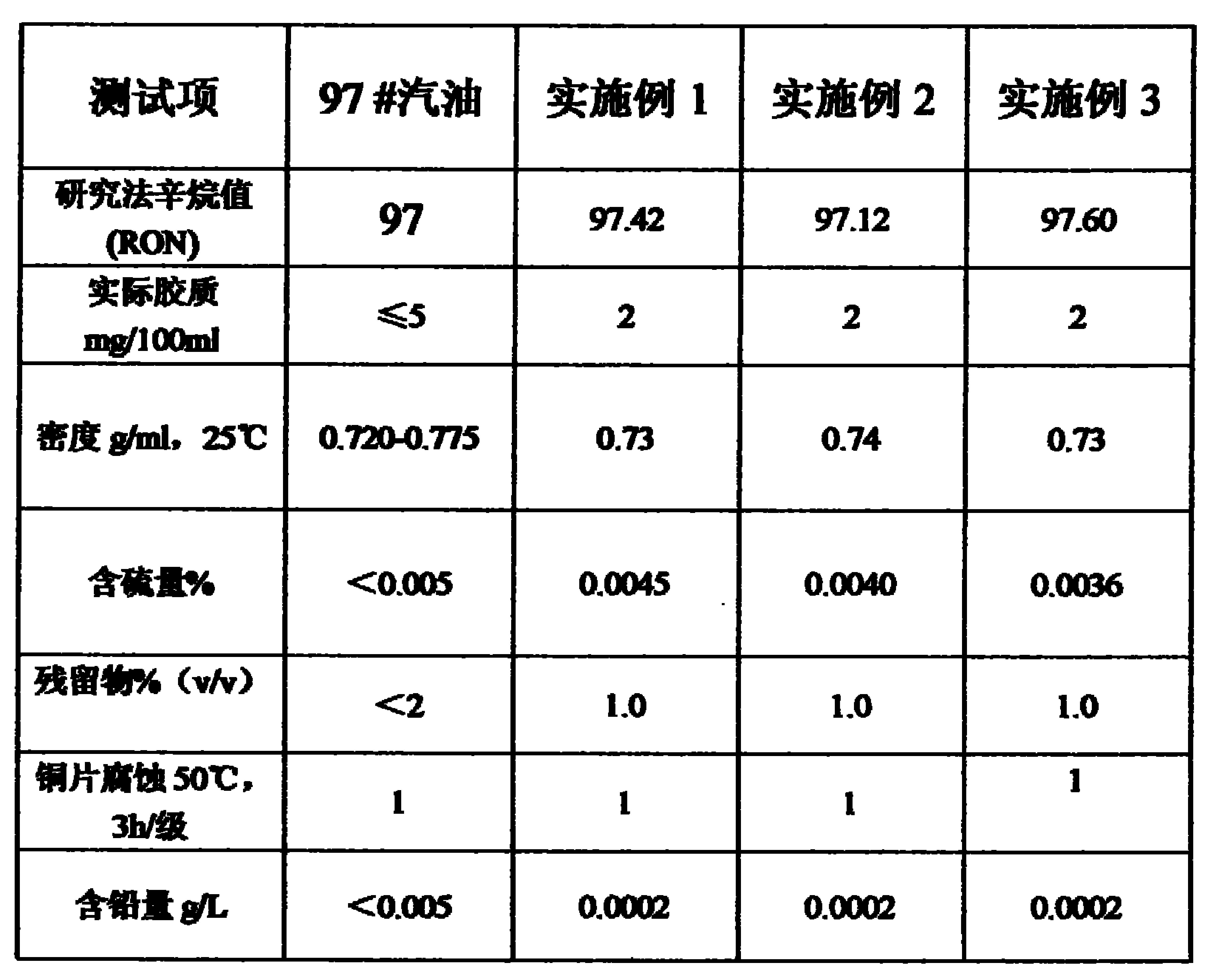
High-cleanness blended gasoline and its preparation method
InactiveCN102373102AGood ignition performanceExcellent ignition performanceLiquid carbonaceous fuelsNaphthaGasoline
The invention relates to high-cleanness blended gasoline and its preparation method. The blended gasoline is characterized by comprising the following components by weight: 35-45% of arene; 25-35% of naphtha; 6-10% of MTBE (methyl tert-butyl ether); 1-3% of an antiknock additive; 6-10% of heavy C5; and 10-15% of light C5. Specifically, the antiknock additive is prepared by the steps of: adding raw material 1#, raw material 2# and raw material 3# uniformly into a small tank according to a batching ratio, conducting stirring and blending for 2-3h, then leaving the mixture to stand for 8h. In the gasoline blending process, raw materials are mixed according to the ratio of the above formula in a blending tank for blending till blended uniformly, and then the mixture is left to stand for 8h. The blended gasoline of the invention has the advantages of good ignition startup performance, high flame resistance, strong stability, good intersolubility, strong driving force, good environmental protection property, and advanced blending technology. 6-8h is needed for refining a tank of gasoline in an oil refinery, while only 2h is needed for blending a tank of gasoline by the method of the invention. The antiknock additive in the invention can effectively enhance gasoline quality and RON (research octane number), reduce or eliminate peroxides.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER DELTA XUZHOU GASOLINEEUM TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com