Phytophthora root rot resistance gene and application
A technology for Phytophthora sojae and root rot, applied in the directions of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of no gene of Phytophthora sojae root rot found, no soybean, and low efficiency of variety screening.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1 Reagents used in the experiment
[0036] 1) Reagents for extracting soybean RNA
[0037] TRIzolReagent was purchased from Invitrogen Company; M-MLV reverse transcriptase, RNase-freeDNaseI, RNasin, Taq enzyme, dNTP, Oligo (dT), and DTT were purchased from TaKaRa Company; DEPC was purchased from Sigma Company; agarose (Agarose) for electrophoresis The reagents were imported from Spain; QuantiFastSYBRGreenPCRKit was purchased from QIAGEN.
[0038] 2 Genomic RNA extraction method
[0039] Preparation:
[0040] (1) DEPC (0.1%) water preparation: 1mLDEPC was added to 1000mL deionized water, and magnetically stirred for 24h.
[0041] (2) Put the mortar, tweezers, beaker, measuring cylinder, glass rod, etc. into the oven, and dry heat sterilization at 180°C for more than 6 hours.
[0042] (3) Put the centrifuge tube, pipette tip, etc. into the reagent bottle that has been sterilized by dry heat, fully soak it with the prepared DEPC (0.1%) water, seal the bottle mouth with...
Embodiment 2
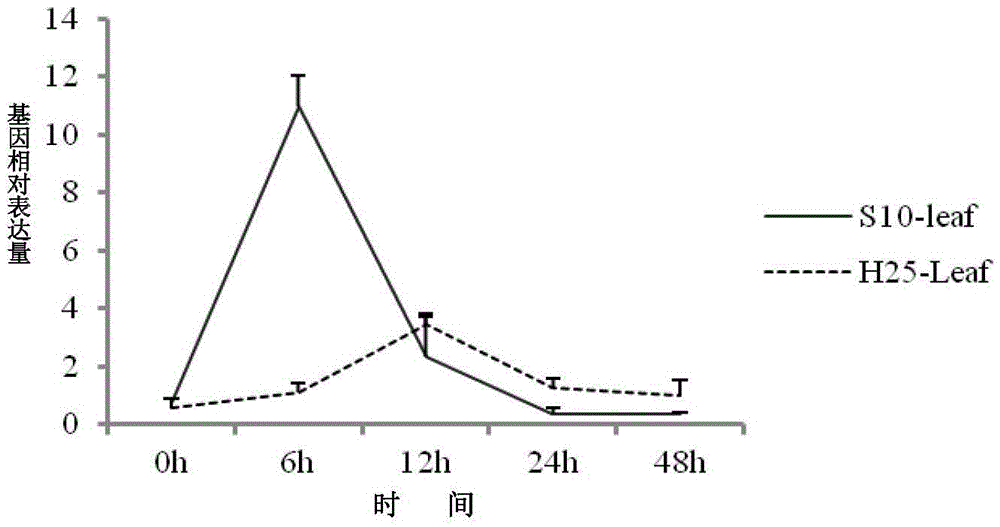
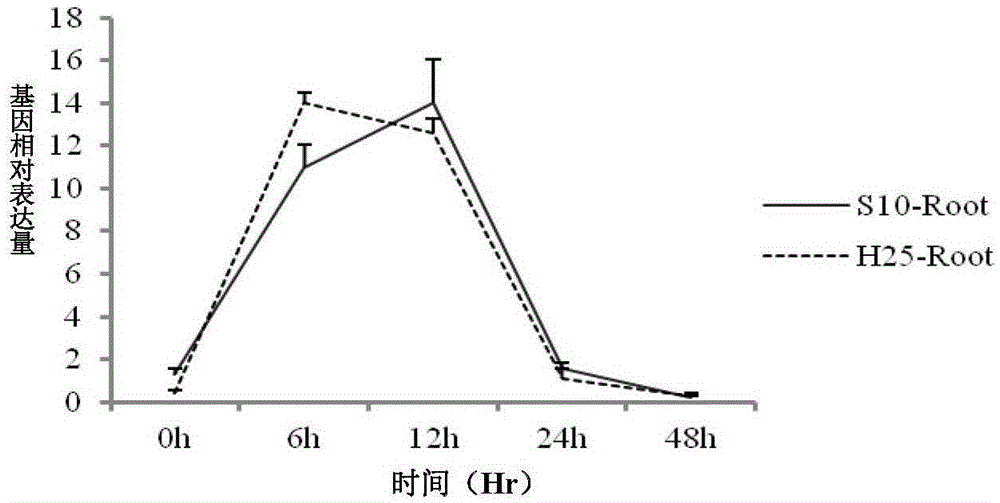
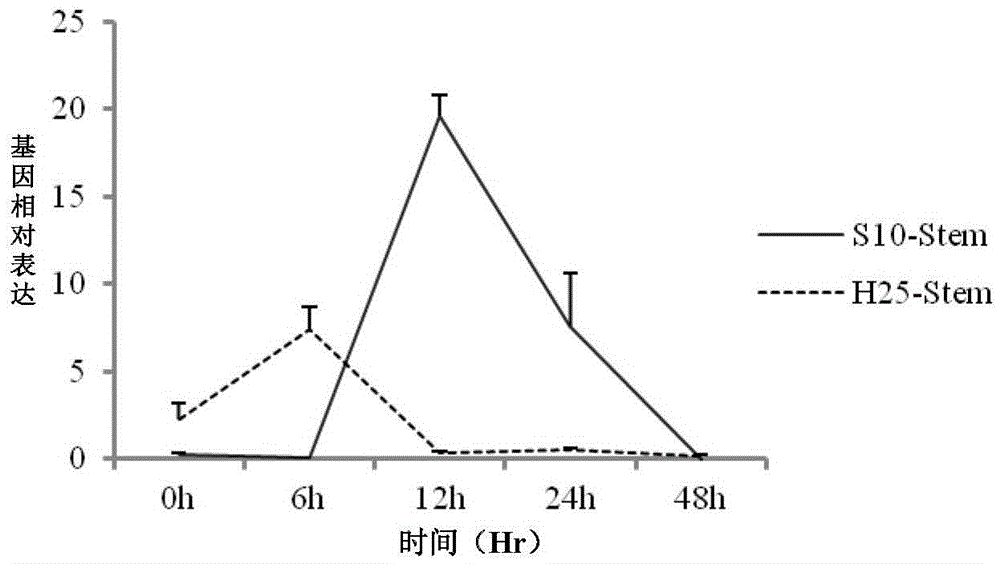
[0080] Real-time quantitative analysis was performed on the control and treated RNA extracted from the different tissues of the resistant variety Suinong 10 and the susceptible variety Hefeng 25 at different times. The expression levels of all changed (results Such as Figure 1-3 shown). Among the resistant varieties: the reaction time of the stem is the longest, and the reaction of the leaf is the most sensitive; among the susceptible varieties: the reaction of the stem is the most sensitive. In the middle leaves of the disease-resistant variety Suinong 10, the expression peak was reached at 6 hours, and the expression level was 12 times, while in the susceptible variety Hefeng 25, there was only a slight up-regulation at 12 hours, and the expression level was not high, about 3 times, Such as figure 1 ; In the resistant variety Suinong 10, the roots and stems responded slowly, reaching the peak at 12 hours, and the expression levels reached 14 times and 18 times respect...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Real-time quantitative analysis was performed on the control and treated RNA extracted from the different tissues of the resistant variety Jiusan H05-23 and the susceptible variety Baojiao 06-6046 at different times, and it was found that the GmDRR gene in the resistant variety soybean GmDRR gene in each tissue from 0h to 48h expression levels have changed. In the disease-resistant variety Jiusan H05-23, the response of leaves is the most sensitive, reaching the peak expression at 6 hours, and the expression level is 8 times. The reaction of roots and stems is slower than that of leaves, reaching the peak at 12 hours, and the expression level is 11 times and 7 times, the change trend was consistent with the change trend of the gene in Suinong 10 after being inoculated with Phytophthora soybean No. The amount is 14 times and 4 times respectively ( Figure 4 with Figure 5 ), the expression level in the roots was relatively low, which was slightly different from the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com