Impact-resistant polypropylene material with high melt strength
A polypropylene material and high melt strength technology, applied in the field of polypropylene materials, can solve problems such as insufficient rigidity, toughness or impact resistance, and achieve the effects of high melt strength, good rigidity and toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] The propylene polymerization reaction is carried out on a polypropylene unit, and the main equipment of the unit includes a prepolymerization reactor, a first loop reactor, a second loop reactor and a third gas phase reactor. The polymerization method and steps are as follows.
[0068] (1) Prepolymerization reaction
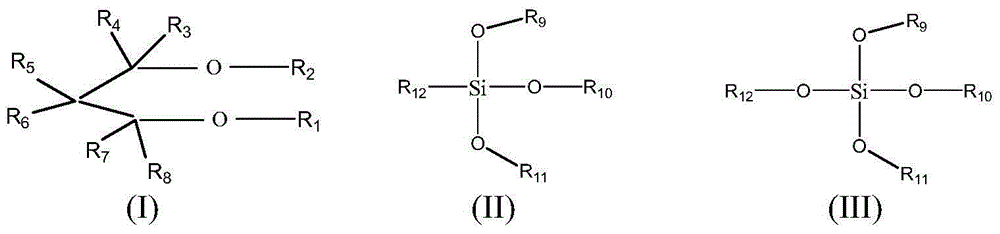
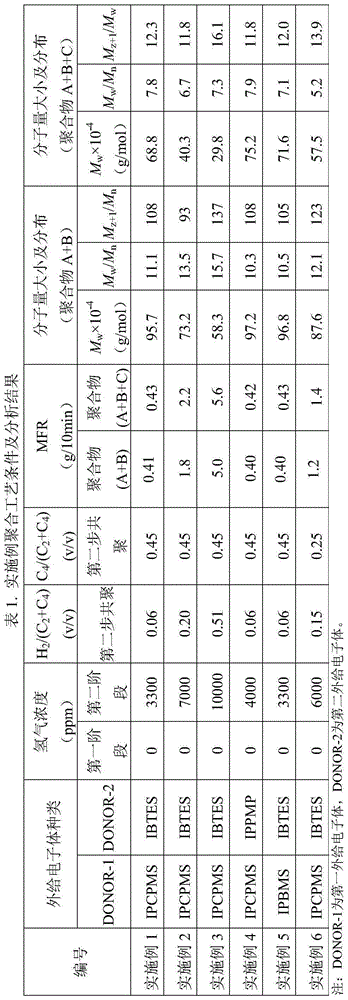
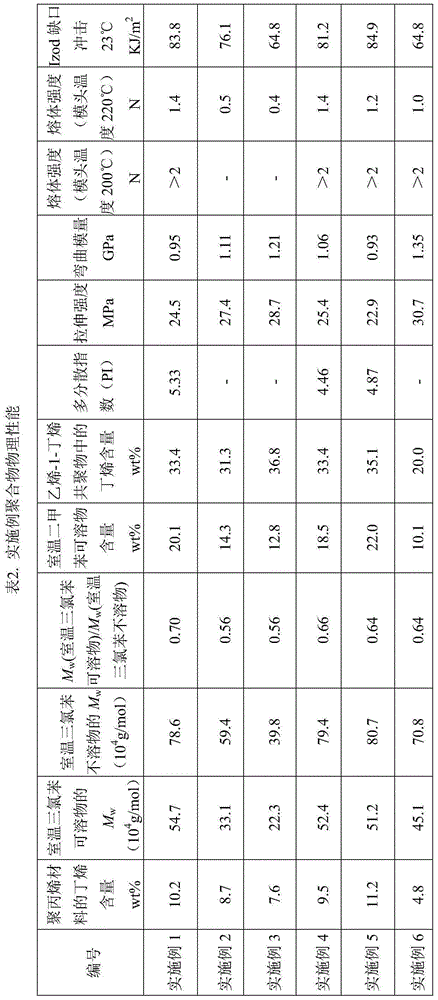
[0069] The main catalyst (DQC-401 catalyst, provided by Beijing Aoda Branch of Sinopec Catalyst Company), co-catalyst (triethylaluminum), and the first external electron donor (isopropylcyclopentyldimethoxysilane, IPCPMS) were After pre-contacting at 6°C for 20 minutes, it is continuously fed into a continuous stirred tank prepolymerization reactor for prepolymerization. The flow of triethylaluminum (TEA) entering the prepolymerization reactor is 6.33g / hr, the flow of isopropylcyclopentyldimethoxysilane is 0.3g / hr, the flow of main catalyst is 0.6g / hr, TEA / IPCPMS The ratio is 50 (mol / mol). The pre-polymerization is carried out in the bulk environment of...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The catalyst used in embodiment 2, pre-complexation, polymerization process conditions and auxiliary agent formula and add-on are the same as embodiment 1. The difference with Example 1 is: the amount of hydrogen in the second reactor becomes 7000ppm in the second stage, and the H in the second step gas phase reactor 2 / (C 2 +C 4 ) adjusted to 0.20 (v / v). The obtained polymer analysis results and polymer physical properties are listed in Table 1 and Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0079] The catalyst used in embodiment 3, pre-complexation, polymerization process conditions and auxiliary agent formula and addition are the same as embodiment 1. The difference with Example 1 is: the amount of hydrogen in the second reactor becomes 10000ppm in the second stage, and the H in the second step gas phase reactor 2 / (C 2 +C 4 ) adjusted to 0.51 (v / v). The obtained polymer analysis results and polymer physical properties are listed in Table 1 and Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com