Nonvolatile memory control device and nonvolatile memory control method
一种非易失性、控制装置的技术,应用在仪器、输入/输出到记录载体、计算等方向,能够解决缩短非易失性存储器寿命等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0035] [1. Explanation of structure]
[0036] Hereinafter, specific aspects of the present invention will be described using the drawings. However, the scope of the invention is not limited to the illustrated examples.
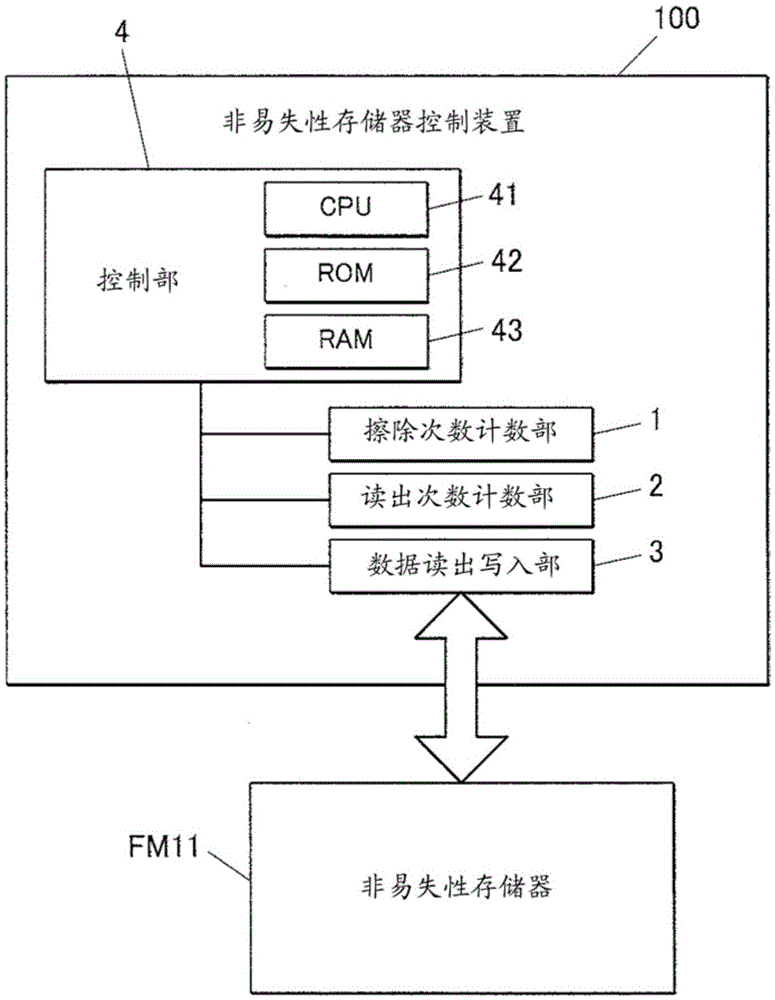
[0037] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the nonvolatile memory control device 100 according to the embodiment of the present invention.
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, the nonvolatile memory control device 100 of the present embodiment appropriately selects partitions of the nonvolatile memory FM11 into which data is written, and equalizes the number of erasures of each partition of the nonvolatile memory FM11 .
[0039] Specifically, the nonvolatile memory control device 100 of the present embodiment includes an erasure count unit 1 , a read count unit 2 , a data read / write unit 3 , a control unit 4 , and the like.
[0040] The number of erasing count unit 1 counts the total number of times of erasing for each par...
Deformed example 1
[0071] [4. Multiple partitions that meet the conditions]
[0072] In the description of the embodiment, the control unit 4 of the nonvolatile memory control device 100 has a predetermined number of times of erasing or more in a specific partition, and there is a case where the number of times of erasing is smaller than that of a specific partition, and the number of times of reading is large. In the case of a certain partition, the data of the partition is swapped with the data of the specific partition, but when there are multiple partitions satisfying such a condition, the data of the partition that has been read the most times may be swapped.
Deformed example 2
[0074] [5-1. Change of the value of the predetermined number of times]
[0075] In the description of the embodiment, the control unit 4 of the nonvolatile memory control device 100 handles the predetermined number of times compared with the number of times of erasing as one predetermined value, but a plurality of values may be set in advance. For the specified number of times, change the value of the specified number of times according to the condition.
[0076] For example, when the erasing count of the partition in which the data to be updated has been stored is greater than or equal to the previously set predetermined count, the control unit 4 may change the value of the predetermined count to be larger than the erasing count of the partition. value.
[0077] In this case, since the predetermined number of times can be gradually increased, the number of erasing times of each partition can be finely balanced, and the life of the nonvolatile memory can be extended.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com