Parallel control method employing selective harmonic elimination pulse width modulation (SHEPWM) for multiple T-type three-level inverters
A technology of a three-level inverter and a control method, which is applied to electrical components, output power conversion devices, and AC power input into DC power output, etc., can solve the problem of hardware mismatch dead time control algorithm execution time, influence IGBT switch tube life, increase system loss and other issues, to achieve the effect of solving the problem of circulating current suppression, low harmonic content, and solving the problem of midpoint voltage balance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
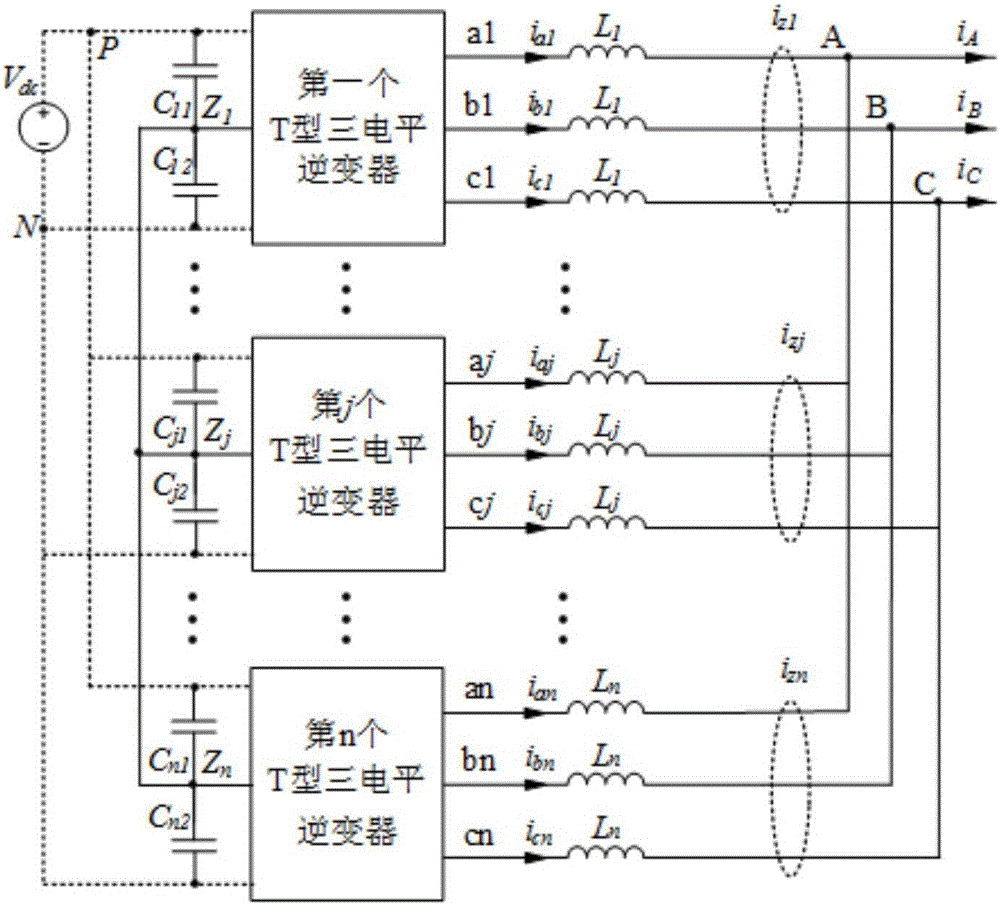
[0053] like figure 1 As shown, the topology diagram of the three-level inverter parallel system is as follows figure 1 As shown, multiple inverters share the AC and DC buses, P and N are the positive and negative buses of the parallel system; A, B, and C are the three-phase grid-connected points of the parallel system; aj, bj, and cj are the AC outputs of the inverters end, C j1 、C j2 It is two capacitors connected in parallel with the DC side, and the midpoint is Z j , the system uses an L filter, and the filter inductance is L i , the zero sequence current is i zj , i mj is the m-phase output current of the j-th inverter, m=a, b, c, j=1, 2,; i A i B i C is the grid-connected current of the system.
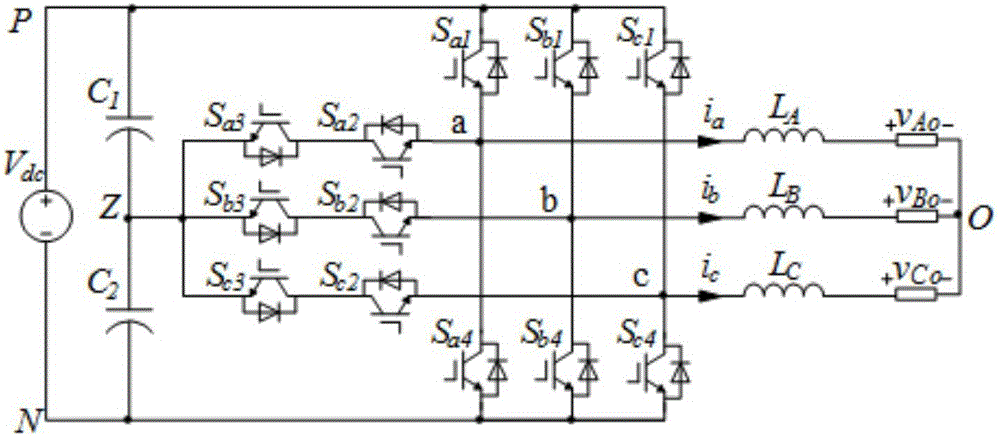
[0054] as figure 2 The single inverter structure shown illustrates the inverter control strategy. Two capacitors C are connected in series o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com