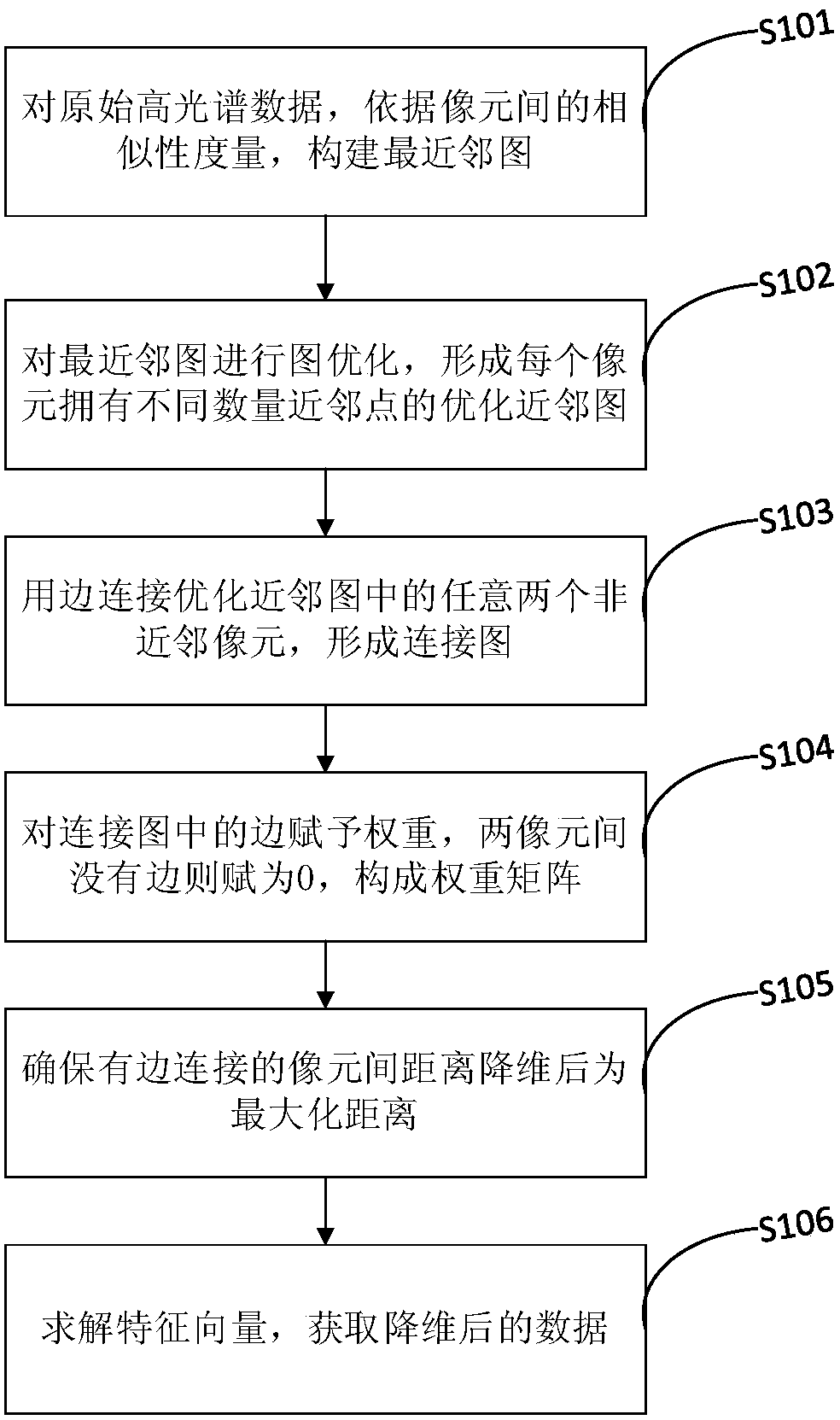
A Hyperspectral Dimensionality Reduction Method Based on Optimal Graph Theory
A hyperspectral and dimensionality reduction technology, applied in the field of remote sensing, can solve the problems of not considering the difference of non-nearest neighbors, the dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral data relying on local neighbor information, and the classification accuracy is not significantly improved, etc., to achieve enhanced separation and improved accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
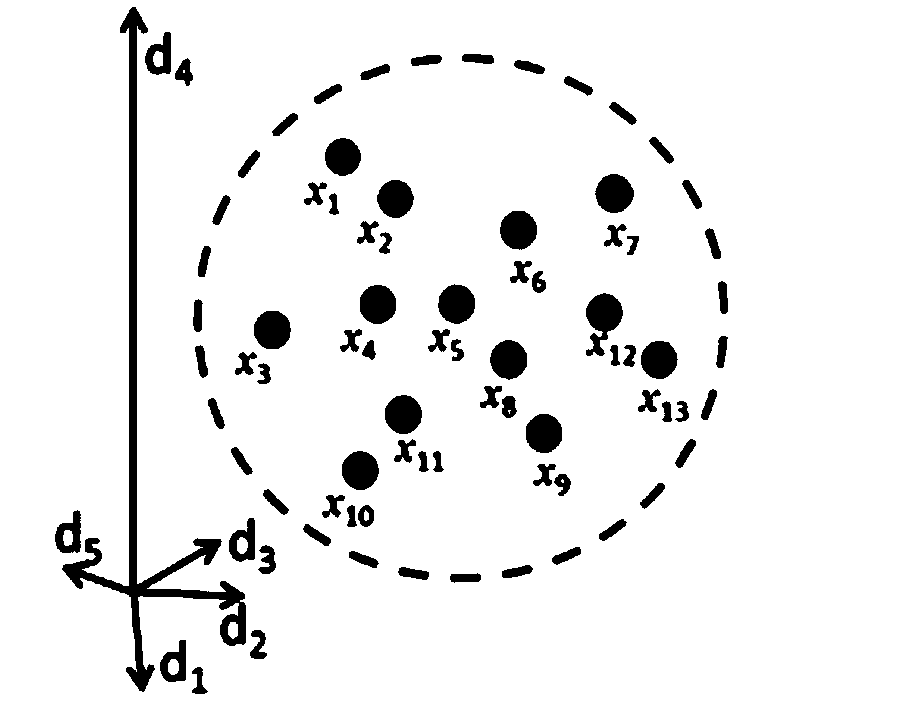
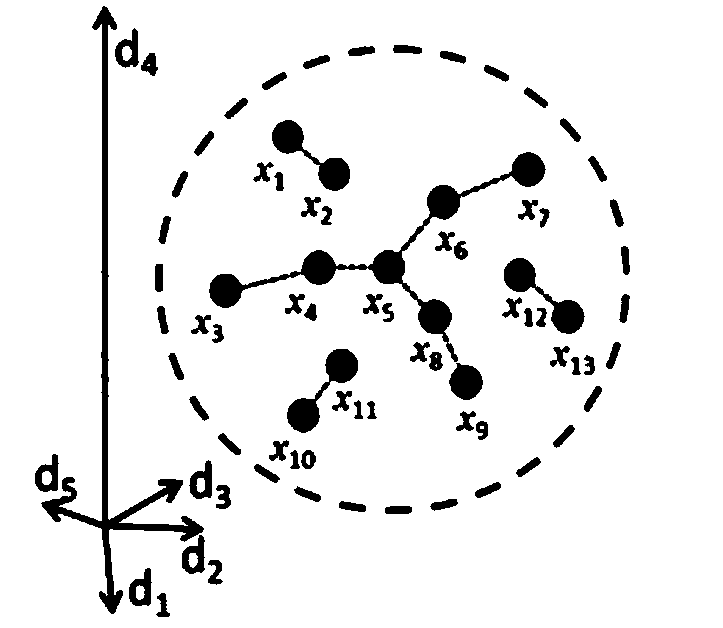
[0073] The original data in this embodiment is the image of Northwestern Indiana, USA in 1992 acquired by the AVIRIS sensor, which contains 220 bands, the spatial resolution is 20 meters, and the image size is 145 pixels*145 pixels. Three categories (soybean-notill, soybean-mintill, and corn-notill) of 100 pixels each were selected from the image. The original spectral curve as image 3 As shown, the two-dimensional scatter plot (bands 21 and 54) as Figure 4 As shown, the scatter diagram of the first two bands after dimensionality reduction by this method is as follows Figure 5 Shown: vs. Figure 4 and Figure 5 , we can see that the separation between different categories is greatly enhanced by this method, which facilitates the subsequent classification of hyperspectral images and greatly improves the classification accuracy.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com