Method and device for generating key of rfid system based on tag id
A key generation and system key technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, to achieve the effect of avoiding hidden safety problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
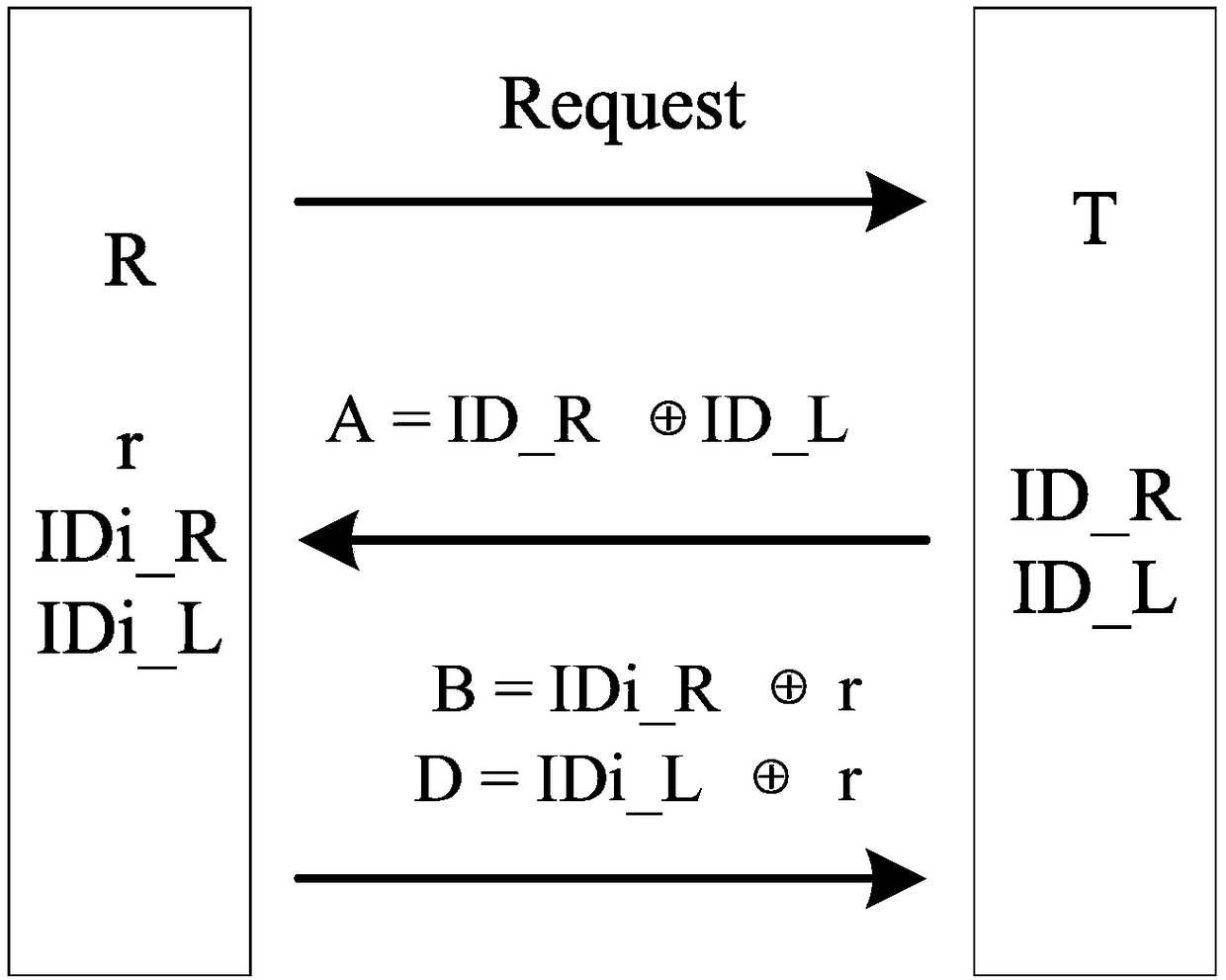
[0058] In the traditional RFID system, the shared key between the tag and the reader is pre-set and fixed during each reading and writing process, which is vulnerable to attacks and leaks. This embodiment discloses a tag ID-based RFID system key generation method. In the method, a reader / writer generates a shared key for a tag, that is, it is used to generate a single tag key.
[0059] Before describing the generation method in detail, the meaning of each symbol is given:
[0060] R: reader;
[0061] T: label;
[0062] r: random number generated by the reader (length is L bits);
[0063] k: the shared key between the reader and the tag (the length is L bits);
[0064] ⊕: XOR operation;
[0065] ||: AND operation;
[0066] [X] L : Take the first L bits of the operation result X;
[0067] ID_L: the value of the first half of the identifier (the value of the length of the first L bits);
[0068] ID_R: the value of the second half of the identifier (the value of the last L...
Embodiment 2
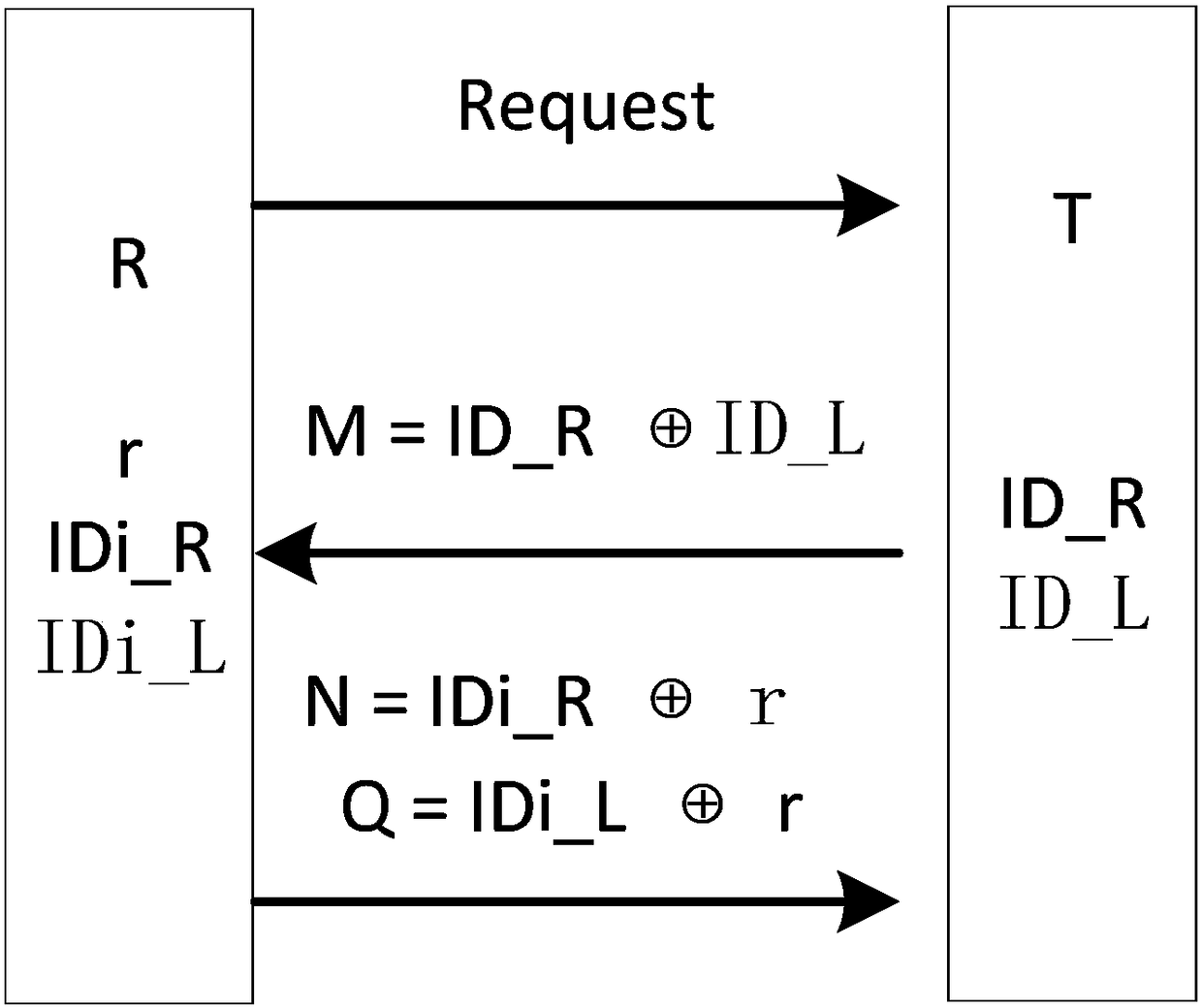
[0081] This embodiment has the same structure as Embodiment 1 except for the following features: this embodiment discloses a tag ID-based RFID system key generation method, in which the reader / writer generates different shared keys for a batch of tags , that is, for batch key generation.
[0082] The meaning of each parameter in the present embodiment is referring to embodiment 1, and its steps are as follows:
[0083] (1) The reader first broadcasts a key generation request command Request to the whole group of tags.
[0084] (2) After receiving the Request command, the tag first calculates M=ID_R⊕ID_L, and transmits the calculation result M to the reader.
[0085] (3) After the reader receives the M sent by the tag, it first calculates IDi_R⊕IDi_L through its stored IDi_R and IDi_L, and judges whether the calculation result is equal to the received M:
[0086] If they are equal, then the reader will immediately generate a random number r with a length of L bits, calculate ...
Embodiment 3
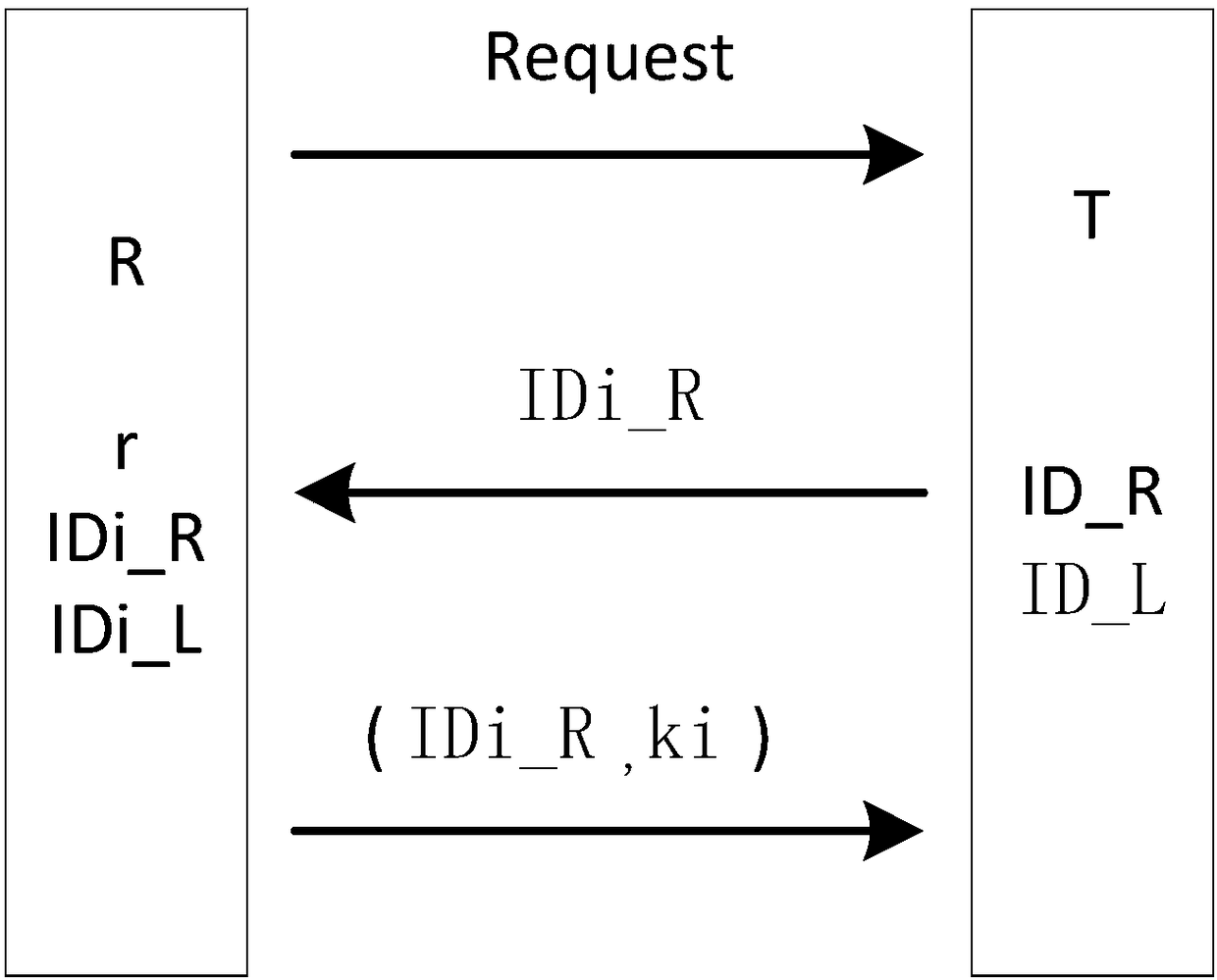
[0090] This embodiment has the same structure as Embodiment 1 except for the following features: this embodiment discloses a tag ID-based RFID system key generation method, in which the reader / writer generates a common group key for a group of tags , which is used for group key generation.
[0091] The meaning of each parameter in the present embodiment is referring to embodiment 1, and its steps are as follows:
[0092] (1) The reader first broadcasts a key generation request command Request to the whole group of tags, which is used to inform all tags to start group key generation.
[0093] (2) After the tag in the group receives the command, the tag Ti sends the IDi_R it stores to the reader.
[0094] (3) After the reader receives the reply from the tag, the reader will compare whether the received IDi_R is completely consistent with the information stored in itself. If not, it means that there is a tag that did not respond to the command. The writer will send the Request ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com