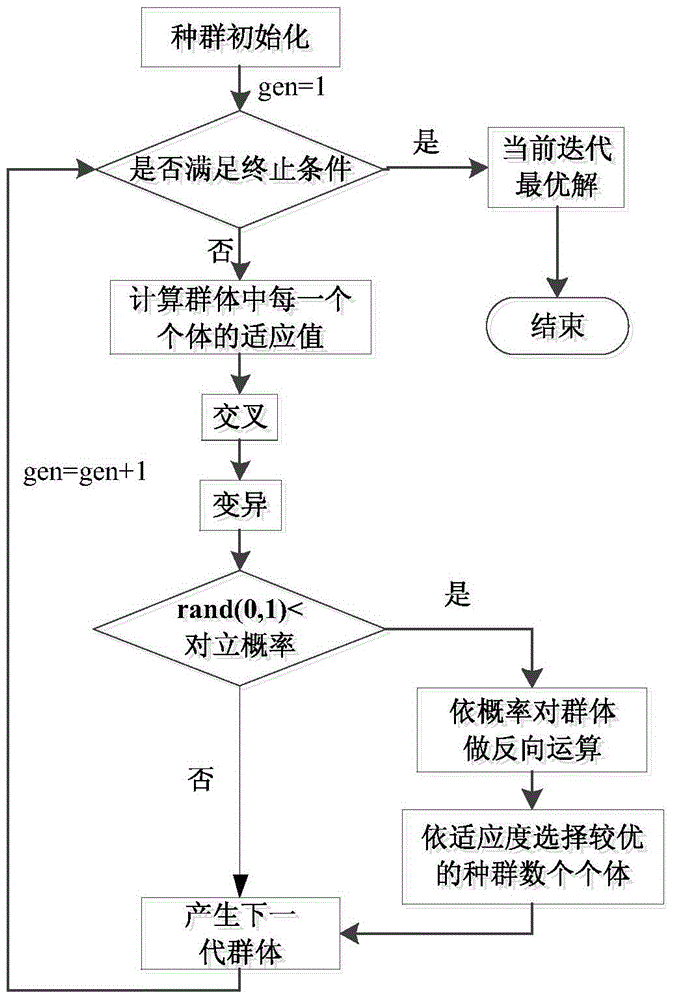
Multi-UCAV on-line striking target allocation method of opposition-based genetic algorithm(GA)
A technology of target assignment and genetic algorithm, applied in the field of aircraft mission planning, which can solve the problems of long time consumption and low convergence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
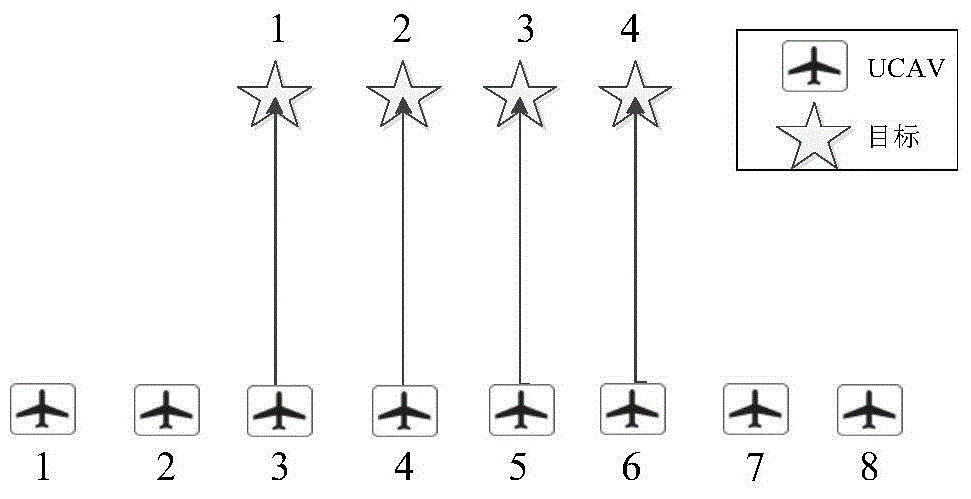
[0061] Suppose a flight formation has 8 UCAVs, attacking 4 known targets, and each UCAV can only attack one target at most. In the case of known theoretical optimal allocation results, the average number of model calls needed to obtain the optimal allocation results is calculated by using the genetic algorithm and the improved genetic algorithm based on the opposite idea respectively. The current coordinates of all UCAVs and targets are shown in Table 1, and the schematic diagram is shown in figure 2 As shown, the speed of UCAV is set to 1. From left to right, the numbers of UAVs are 1-8, and the numbers of targets are 1-4. Obviously, the optimal distribution of weapon targets is 4→1, 5→2, 6→3, 7→4, that is, the optimal individual is (3456).
[0062] The current position of UCAV and target in the first embodiment of table 1
[0063]
[0064] Using the improved genetic algorithm based on the opposite idea to deal with the multi-UCAV online target allocation problem, the ...
Embodiment 2
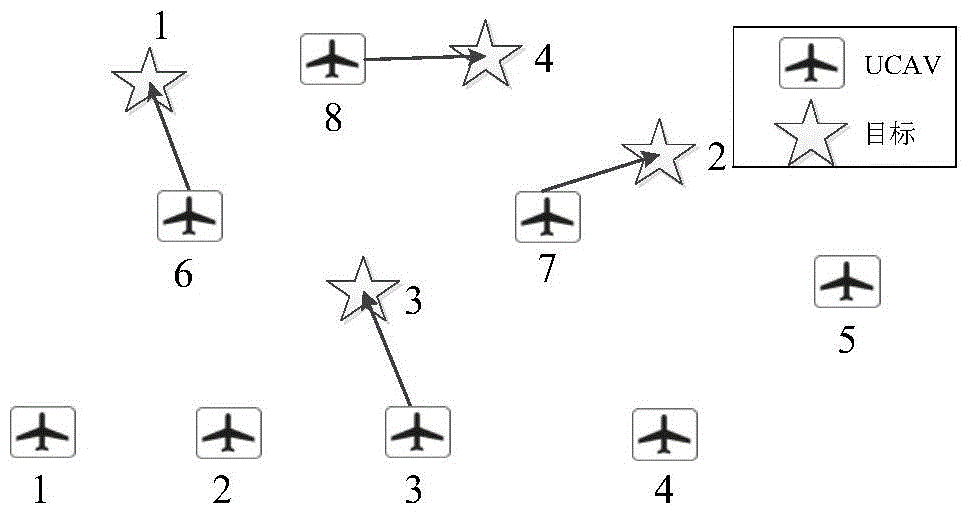
[0077] In real situations, it is very time-consuming to obtain the optimal allocation of weapon targets through theoretical calculations, and it is difficult to meet the real-time requirements of battlefield decision-making. Therefore, when the theoretical optimal allocation results are unknown, set the maximum model The number of calls is 2000 times. The method of the present invention and the customized GA are used to solve the multi-UCAV online target allocation problem respectively, and the calculation results of the two are compared. Assuming that a flight formation has 8 UCAVs and attacks 4 known targets, each UCAV can only attack one target at most. The current positions of UCAVs and targets are shown in Table 3.
[0078] The current position of UCAV and target in the embodiment two of table 3
[0079]
[0080] Using the improved genetic algorithm based on the opposite idea to deal with the multi-UCAV online target allocation problem, the specific implementation steps ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com