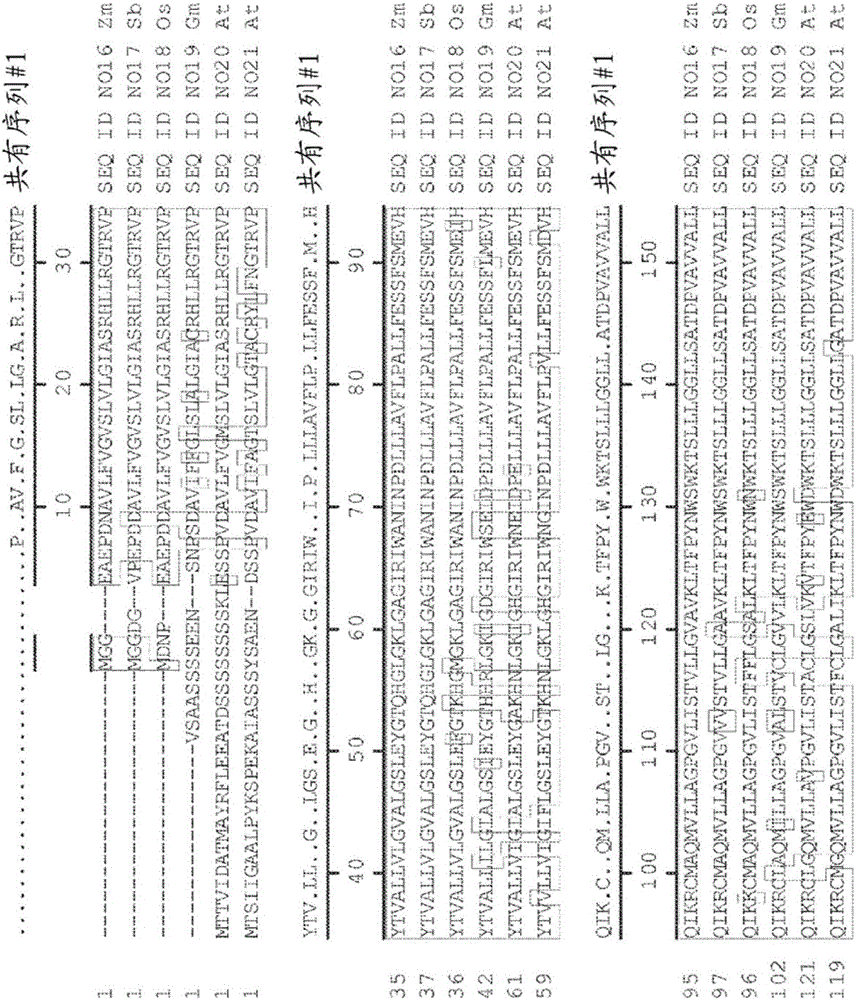
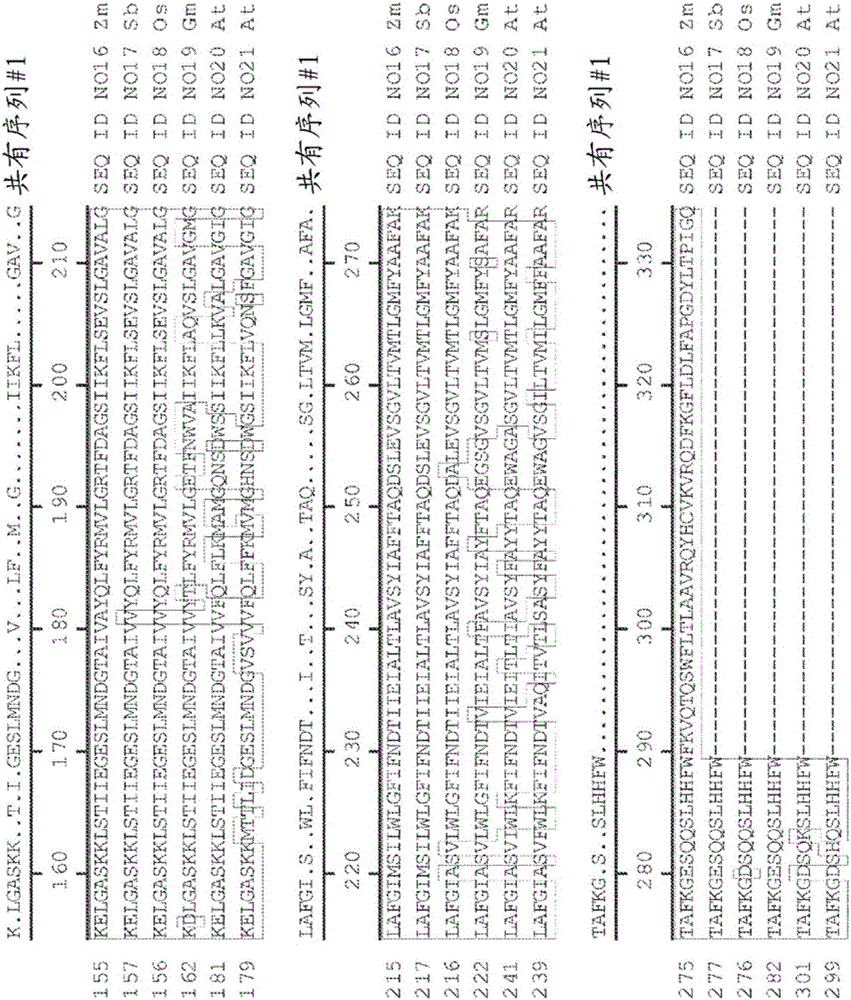
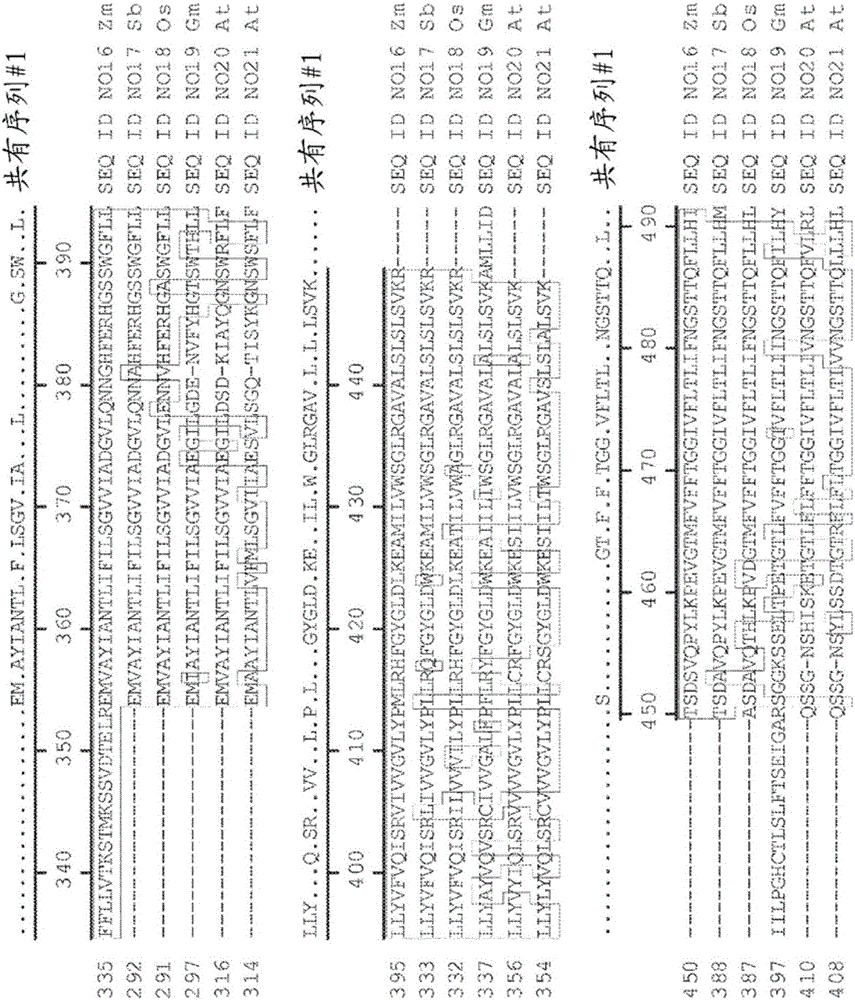
Genetic loci associated with response to abiotic stress
A related, genetic technology, applied in genetic engineering, biochemical equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in cultivating salt tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0247] association mapping analysis
[0248] One hundred and ten elite non-rigid stalk (NSS) lines were grown in the high soil salinity location of location 1, and seedling vigor, also called early growth (EGRWTH), was scored on a per row basis. Lines were genotyped at 56,000 SNP markers across the maize genome. Genome-wide association mapping was then performed to identify markers associated with the early growth (EGRWTH) phenotype in position 1. Phenotype and genotype scores for all individuals tested were input into individual association analyses.
[0249] The most prominent peak of the early growth phenotype was identified in the region of 142.6-156.0 cM of chromosome 1 on a single meiosis-based genetic map. One haplotype within this region (referred to herein as haplotype "A") was associated with lower early growth, with an average score of 3.8 on a scale of 1 to 9, with 9 being the best. The average score for all other haplotypes was between 6 and 6.6. Haplotype "...
Embodiment 2
[0257] QTL mapping using double haploid breeding populations
[0258] A biparental mapping population was generated by crossing two elite non-rigid stalk inbreds (referred to herein as inbred A and inbred B) and comparing the salt tolerance phenotype. F from the hybrid 1 Individuals produced 179 double haploid lines. The double haploid population was grown at position 1 in a field with high levels of soil salinity. Growth and flowering trait data were collected for the populations, including seedling vigor also known as early growth (EGRWTH), pollen release days (SHD), silking days (SLK), plant height (PLTHT) and ear height (EARHT). The EGRWTH trait is a visual score of early seedling health on a scale of 1 to 9, with 9 being optimal. QTL mapping was performed using composite interval mapping in WinQTL Cartographer and strong QTLs were observed on chromosome 1 from 145.1 cM to 169.6 cM (on a gene map based on a single meiosis obtained internally) for all five agronomic tr...
Embodiment 3
[0265] Early growth phenotypes shaped by differential salinity tolerance
[0266] A hydroculture study was performed with inbreds selected from the test panel used in Example 1 to validate a surrogate assay to be used for mapping gene clones for chromosome 1 QTL in a controlled environment. Nine inbreds with different responses to soil salinity at position 1 were selected for testing under high-salinity hydroponic conditions. Ten plants of each inbred were grown for four weeks under normal and 100 mM NaCl conditions. After four weeks, the plants were scored on a scale of 1 to 9, with 9 being the healthiest and largest plant and 1 being the smallest or dead plant. Ten plants of each inbred were averaged to give a single score (Table 5). There was a strong correlation between inbreds responding to the high soil salinity condition at position 1 and inbreds responding to the 100 mM salt condition in the hydroculture study. Inbreds with haplotype A showed considerably less see...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com