Multi-objective quantum Shuffled Frog Leaping Algorithm (SFLA) based water resource optimization and diversion method
A hybrid frog leaping algorithm and optimal scheduling technology, applied in computing, instrumentation, data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of algorithm optimization ability dependent on parameter settings, local optimal solutions, slow convergence speed, and poor initial population distribution. To achieve the effect of shortening the problem optimization process, maintaining population diversity, and increasing population diversity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention, should be understood that these embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, after having read the present invention, those skilled in the art will understand various equivalent forms of the present invention All modifications fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of the present application.
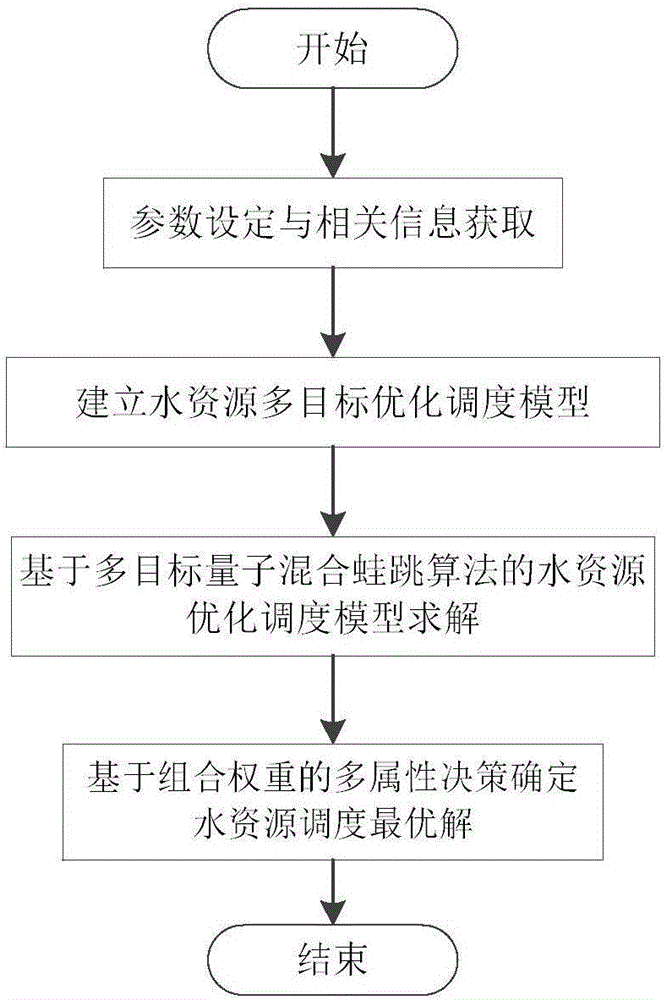
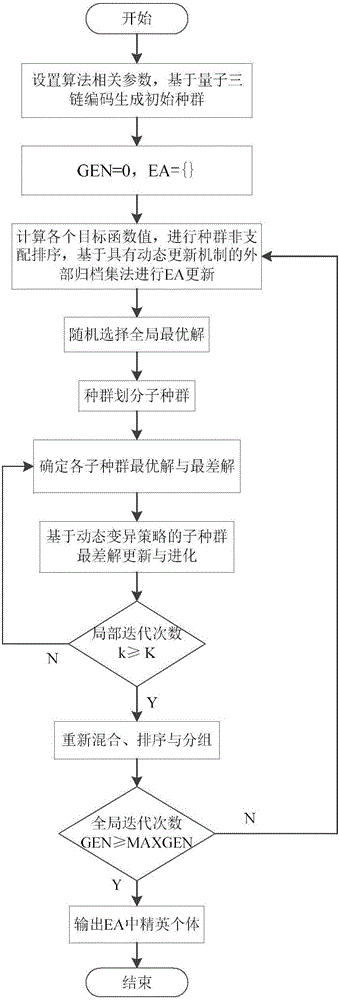
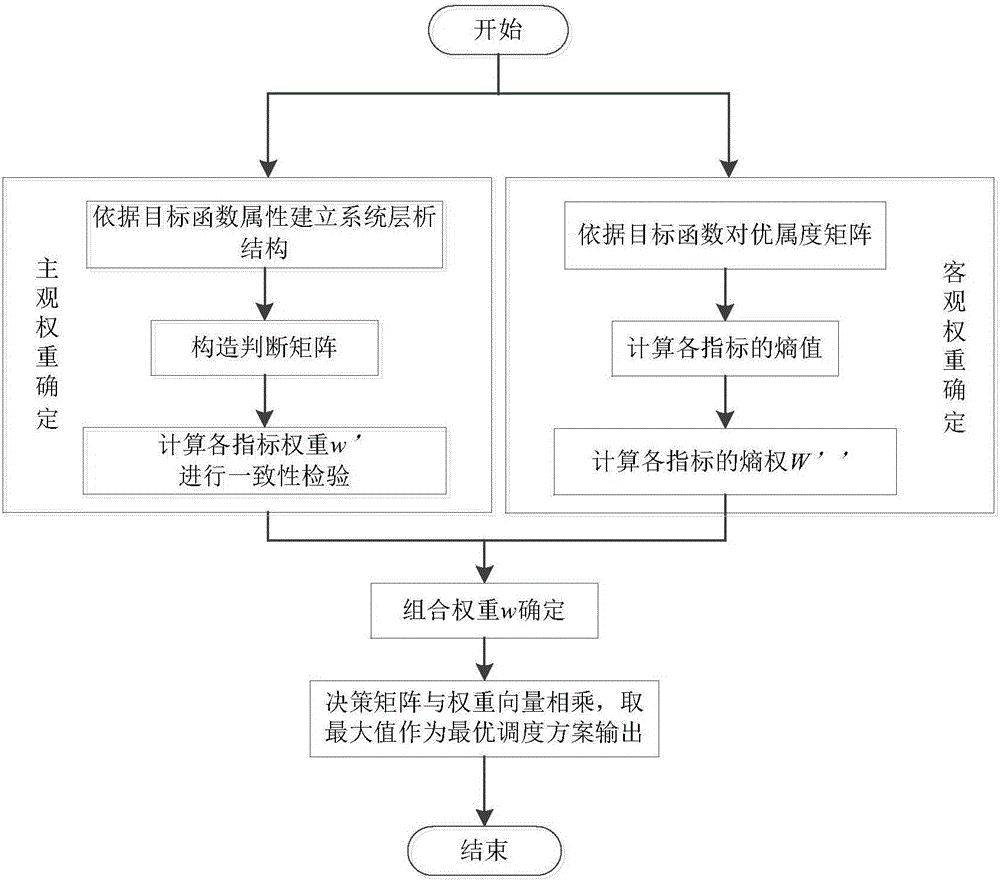
[0049] Aiming at the shortcomings of traditional SFLA such as slow convergence speed and falling into local optimal solutions, the present invention introduces quantum computing into SFLA in combination with the characteristics of quantum computing such as ergodicity, and provides a multi-objective quantum leapfrog algorithm (MQSFLA) based water resource scheduling method. This method uses quantum three-chain coding to generate the initial population, adopts the external archive set method of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com