A social network information dissemination method based on the law of forgetting
A technology of social network and information dissemination, applied in the field of social network information dissemination based on the law of forgetting, it can solve the problems of not considering influence and different reactions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
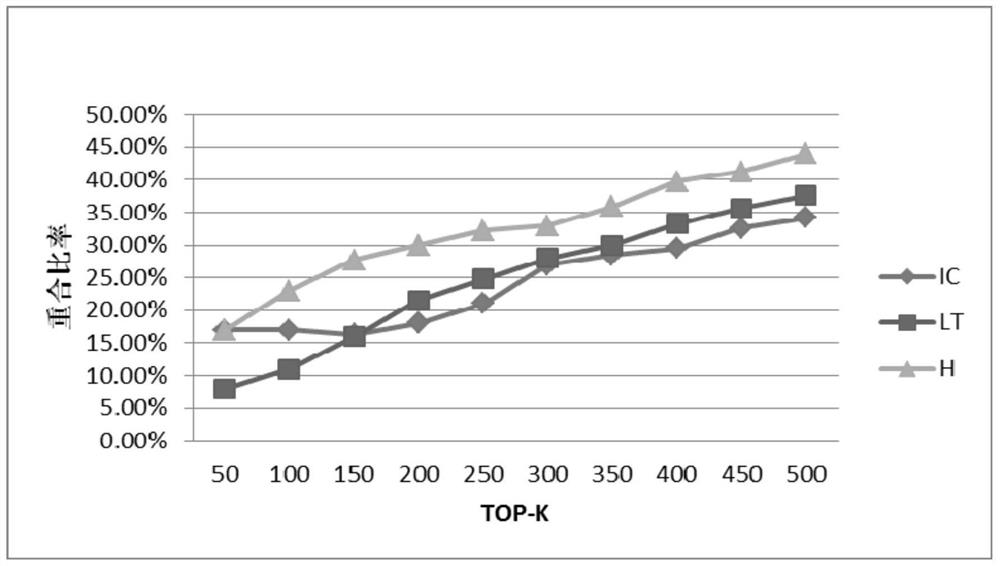
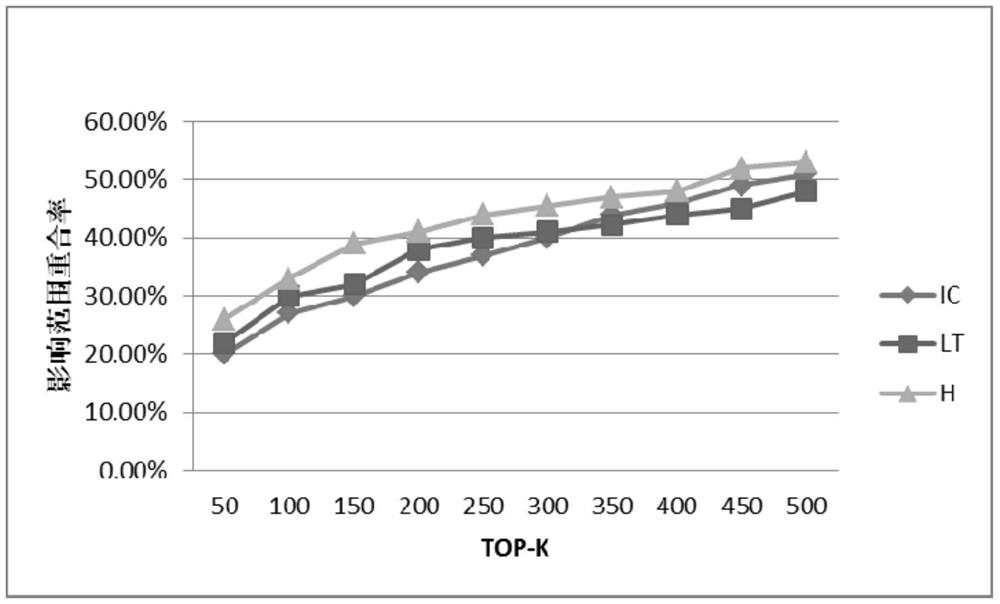
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
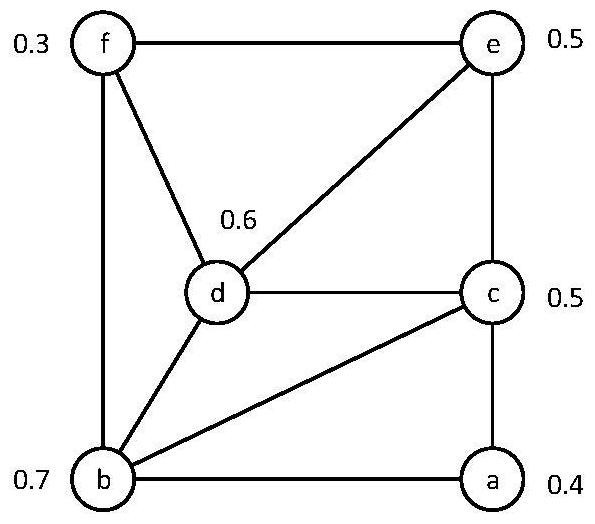
[0031] Specific implementation mode one: a method for disseminating social network information based on the law of forgetting in this implementation mode is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0032] Step 1: Set the initial active node set S;
[0033] Step 2: At time t x When , the active node in the network activates the inactive neighbor node v in the network;
[0034] Step 3: If the inactive neighbor node v is activated successfully, then at t x+1 At time, the inactive neighbor node v changes to the active state, and tries to activate its adjacent inactive node x;
[0035] Otherwise, the inactive neighbor node v at t x+1 The state does not change at all times;
[0036] Step 4: Repeat step 2 and step 3 until there are no undiffused active nodes in the network, and the propagation process ends.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0037] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: as described in step two, at time t x When , the active node in the network activates its inactive neighbor node v; the specific process is:
[0038] Any node in the network can only be in two states: active or inactive; active nodes (or activated nodes) have influence on inactive nodes (or inactive nodes). Influence will make the node in the inactive state change to the active state, and this state change of the node is one-way, that is, it can only change from the inactive state to the active state;
[0039] The influence includes the random influence for the first time and the fixed influence after the first time;
[0040] Random Influence: The influence that an inactive node receives when it is first activated by an adjacent activated node is randomly generated.
[0041] Fixed influence: According to a specific algorithm (such as buv=1 / d in ou...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0055] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the concrete process of described formula (4) is:
[0056]
[0057] In the formula, e is the natural base.
[0058] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com