Method for joining structural material, joining sheet, and joint structure
A technology of structural materials and joining methods, applied in the direction of welding/cutting media/materials, welding media, welding equipment, etc., can solve problems such as high-priced equipment, and achieve the effect of improving strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach 》
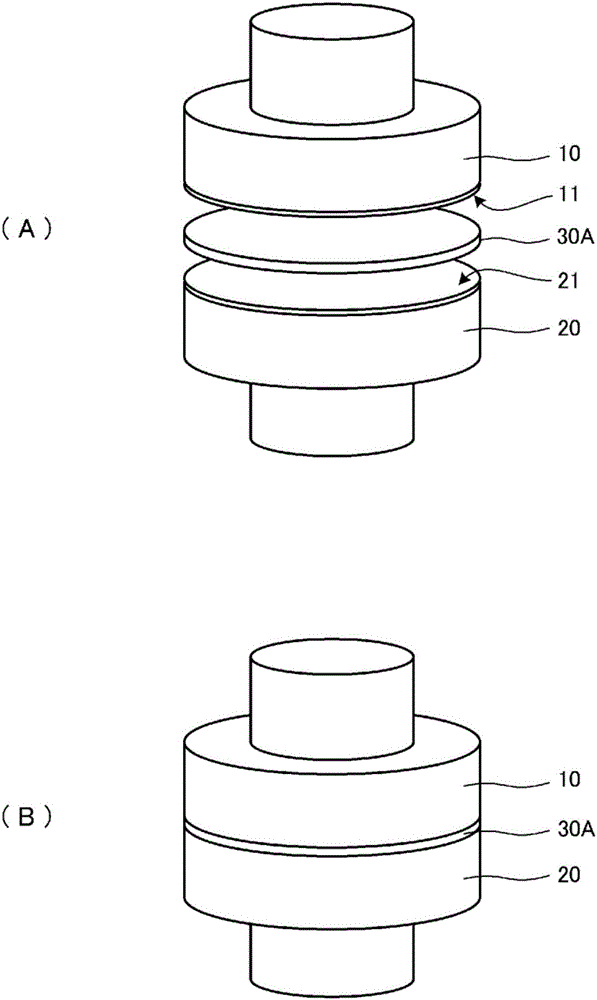
[0031] refer to Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 The structural material joining method, joining material, and joining structure of the first embodiment will be described.
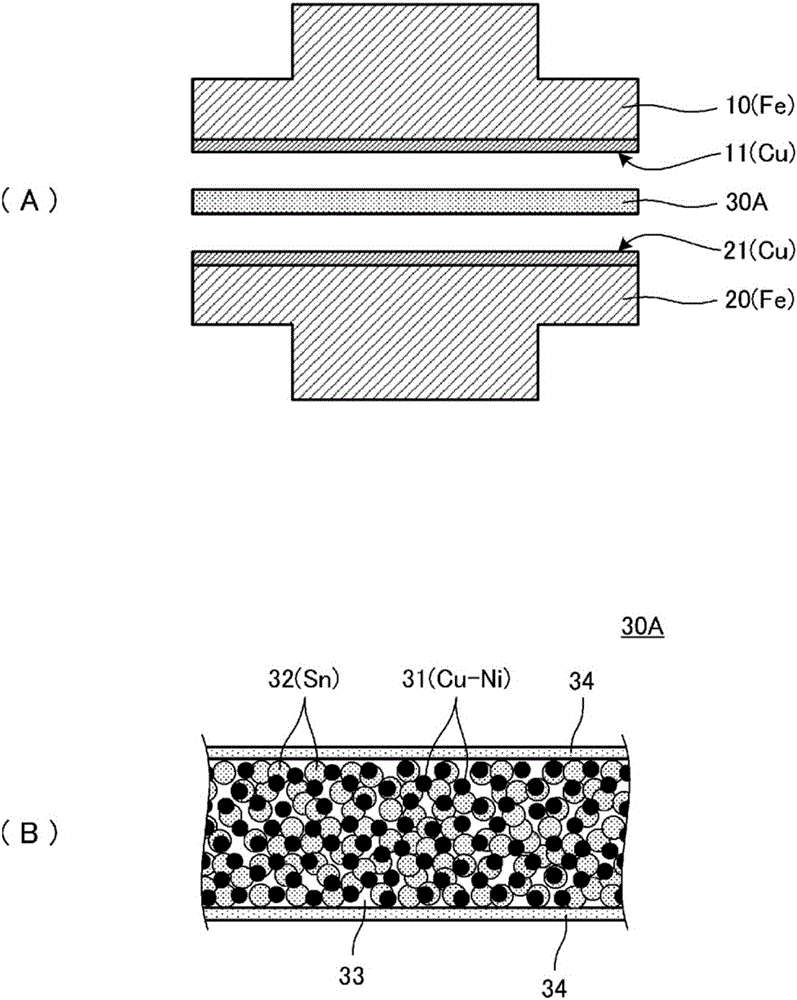
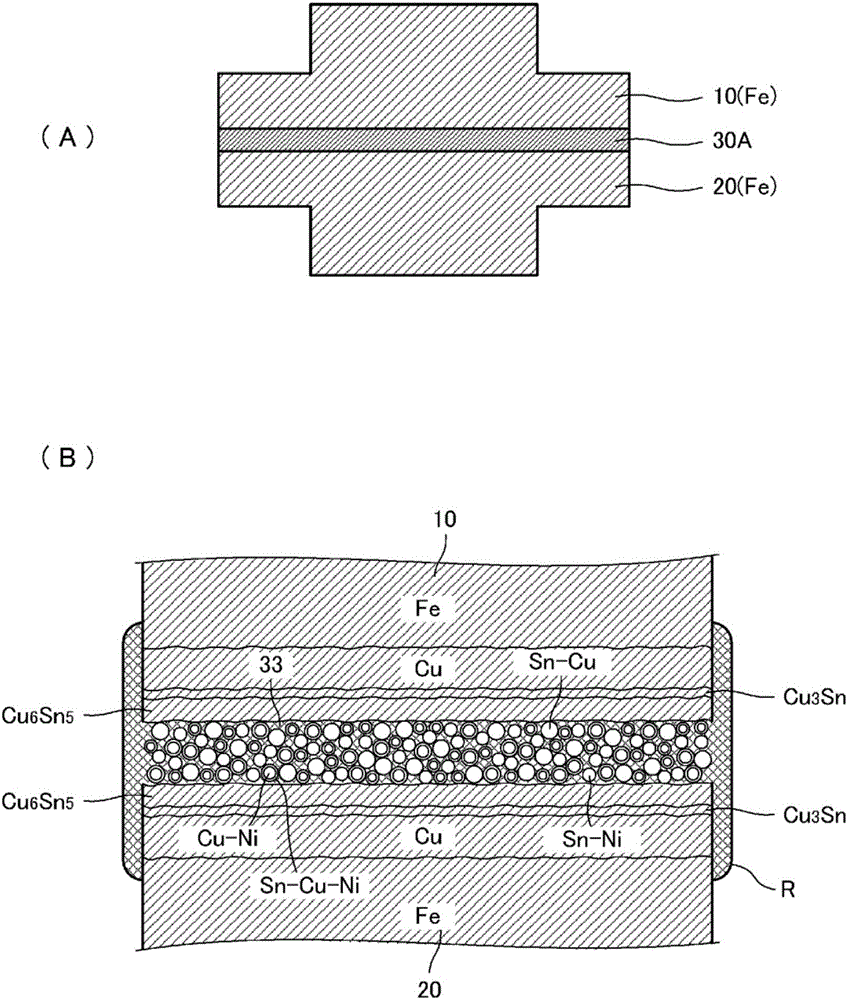
[0032] figure 1 (A) is a perspective view showing the state before joining of the first structural material 10 , the second structural material 20 , and the joining material 30A to be joined. figure 1 (B) is a perspective view showing the state after joining. figure 2 (A) is a cross-sectional view showing a state before joining the first structural material 10 , the second structural material 20 , and the joining material 30A to be joined. figure 2 (B) is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the bonding material. image 3 (A) is a cross-sectional view showing a state after bonding of the first structural material 10 , the second structural material 20 , and the bonding material 30A. image 3 (B) is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the junction.
[0033] Each structural material is, for example, a frame materi...
no. 2 Embodiment approach 》
[0056] refer to Figure 5 , Image 6 The structural material joining method, joining material, and joining structure of the second embodiment will be described.
[0057] Figure 5 (A) is a cross-sectional view showing a state before bonding of the first structural material 10 , the second structural material 20 , and the bonding material 30B to be bonded. Figure 5 (B) is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the bonding material. Image 6 (A) is a cross-sectional view showing a state after bonding of the first structural material 10 , the second structural material 20 , and the bonding material 30B. Image 6 (B) is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the junction.
[0058] The first structural material 10 is, for example, a steel material, and a plated film 12 of Cu—Ni alloy, which is a refractory metal, is formed on the joint surface. Similarly, the second structural material 20 is, for example, a steel material, and a Cu—Ni alloy plating film 22 is formed on the joint su...
no. 3 Embodiment approach 》
[0073] refer to Figure 7 , Figure 8 The structural material joining method, joining material, and joining structure of the third embodiment will be described.
[0074] Figure 7 (A) is a cross-sectional view showing a state before bonding of the first structural material 10 , the second structural material 20 , and the bonding material 30C to be bonded. Figure 7 (B) is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the bonding material. Figure 8 (A) is a cross-sectional view showing a state after bonding of the first structural material 10 , the second structural material 20 , and the bonding material 30C. Figure 8 (B) is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the junction.
[0075] The first structural material 10 is, for example, a steel material, and a Sn plating film 13 that is a low melting point metal is formed on the bonding surface. Similarly, the second structural material 20 is, for example, steel, and a Sn plating film 23 is formed on the bonding surface. It should be ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com