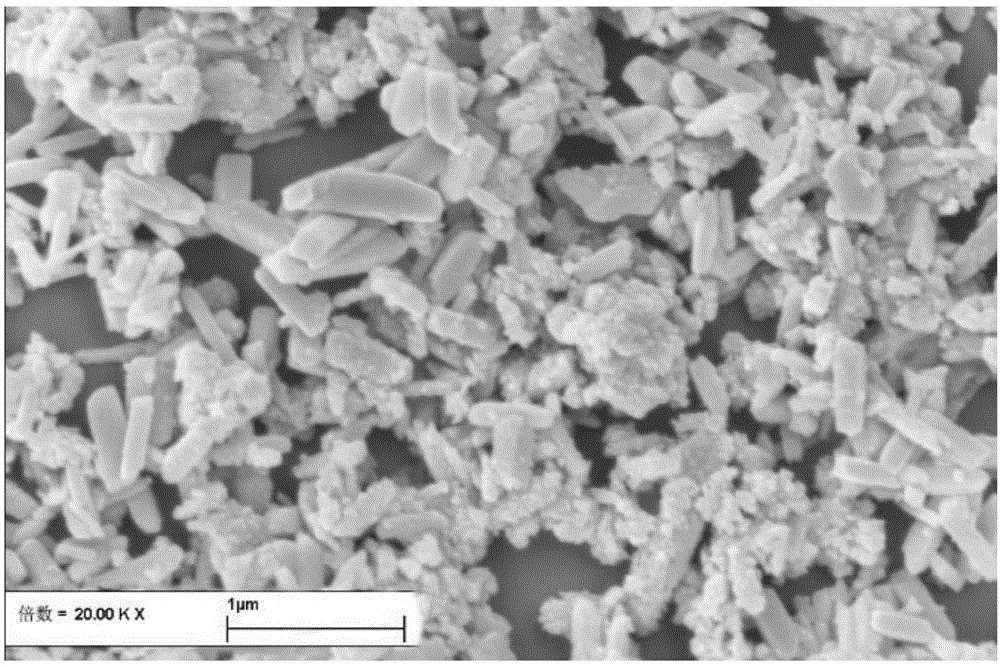
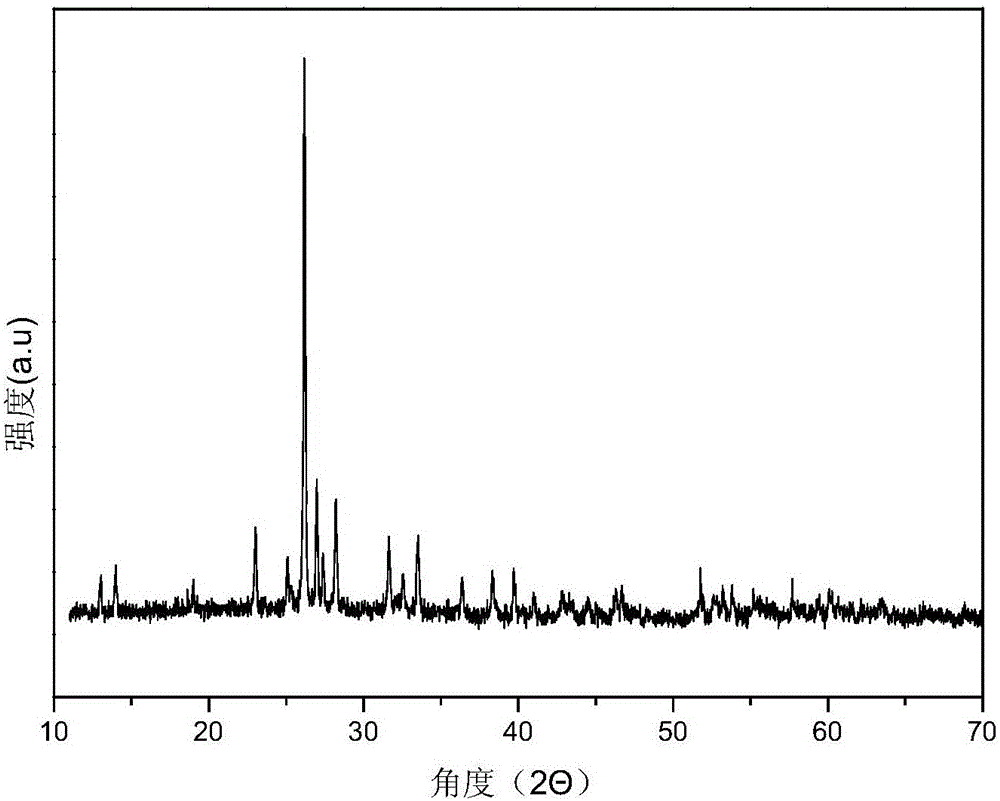
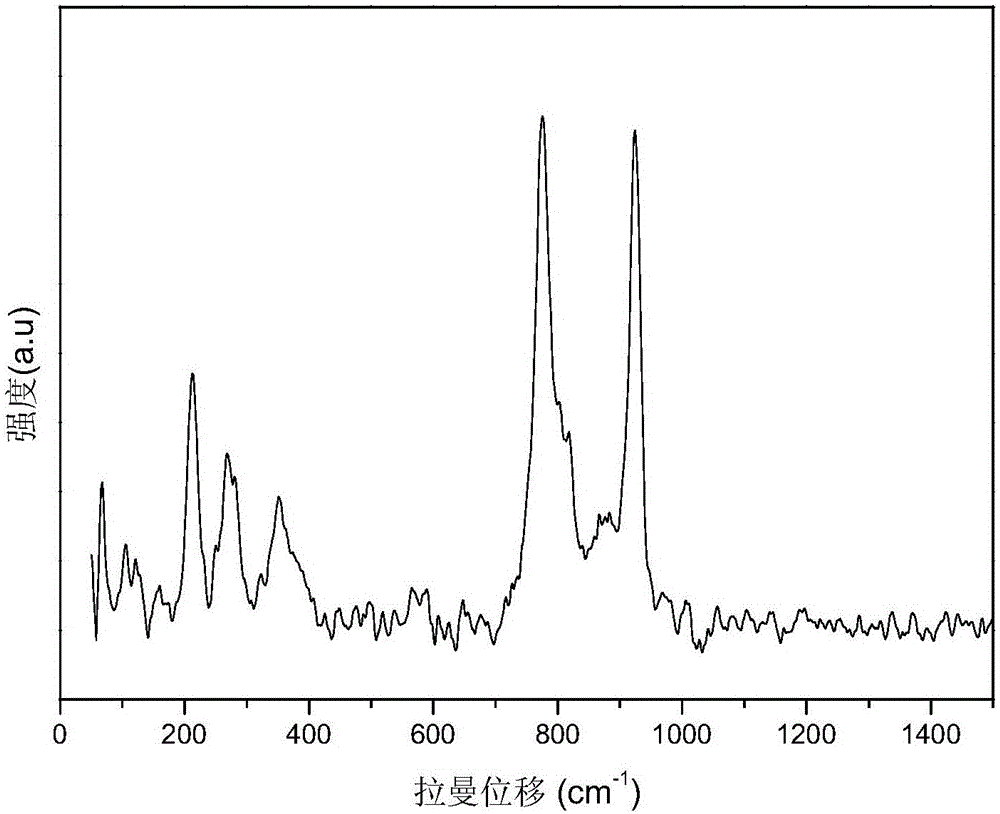
Method for degrading organic wastewater through excitation of peroxysulphate under effect offerrous molybdate
A technology for activating persulfate and organic wastewater, applied in chemical instruments and methods, special compound water treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc. Application prospect and cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 1) Add sodium persulfate to 100mg / L orange G dye waste water to obtain a waste water solution, and adjust the pH value of the waste water solution to 3.0 with sulfuric acid;
[0038] 2) add ferrous molybdate in waste water solution again, the concentration of sodium persulfate in waste water solution is 1400mg / L, and the concentration of ferrous molybdate in waste water solution is 200mg / L;
[0039] 3) Put the waste water solution after adding the ferrous molybdate into the constant temperature shaking table and stir, and react at normal temperature, and the decolorization rate of the dye is 94.6% after 30 minutes.
[0040] Comparative experiment 1: only sodium persulfate was added to the dye wastewater, the pH of the wastewater solution was adjusted to 3.0, and the decolorization rate was only 2.0% after the same time.
[0041] Comparative experiment 2: only ferrous molybdate was added to the dye wastewater, the pH of the wastewater solution was adjusted to 3.0, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 1) Add sodium persulfate to 20mg / L orange G dye waste water to obtain a waste water solution, and adjust the pH value of the waste water solution to 3.0 with sulfuric acid;
[0044] 2) add ferrous molybdate in waste water solution again, the concentration of sodium persulfate in waste water solution is 1000mg / L, and the concentration of ferrous molybdate in waste water solution is 200mg / L;
[0045] 3) Put the waste water solution after adding ferrous molybdate into a constant temperature shaker and stir, and react at normal temperature, and the decolorization rate of the dye is 96% after 30 minutes.
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1) Add sodium persulfate to 20mg / L orange G dye waste water to obtain a waste water solution, and adjust the pH value of the waste water solution to 1.5 with sulfuric acid;
[0048]2) add ferrous molybdate in waste water solution again, the concentration of sodium persulfate in waste water solution is 1000mg / L, and the concentration of ferrous molybdate in waste water solution is 200mg / L;
[0049] 3) Put the waste water solution after adding the ferrous molybdate into the constant temperature shaking table and stir, and react at normal temperature, and the decolorization rate of the dye is 95% after 15 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com