Artificial noise-based cooperative network power allocation method for main channel and cooperative channel under non ideal channel estimation condition
A channel estimation and artificial noise technology, applied in the field of information technology security, can solve the problems of reducing the signal-to-interference-noise ratio of legitimate receivers, unreasonable assumptions, and influences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
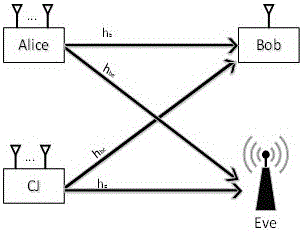
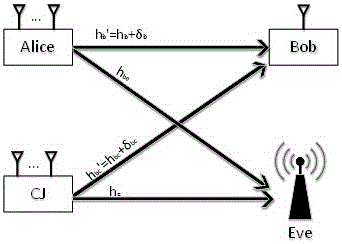
[0043] The transmission power allocation method in the cooperative network based on artificial noise under the condition of non-ideal channel estimation of the main channel and the cooperative channel, such as figure 1 As shown, suppose that the transmitting source Alice transmits a secret message to the legal receiver Bob, and there is a passive eavesdropping node Eve in the system to eavesdrop the message, and another node CJ acts as a cooperative jammer to transmit a signal to cause interference to the eavesdropping node Eve. The transmitting source Alice transmits the information of the legal communication channel (the communication channel between Alice and Bob, also known as the main channel) information combined with the non-ideal channel estimation, and performs the optimal power allocation signal between the useful signal and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com