Interferometric sensor
A technology of sensors and detectors, applied in the direction of converting sensor output, instruments, and using optical devices to transmit sensing components, etc., can solve problems such as not performing phase measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
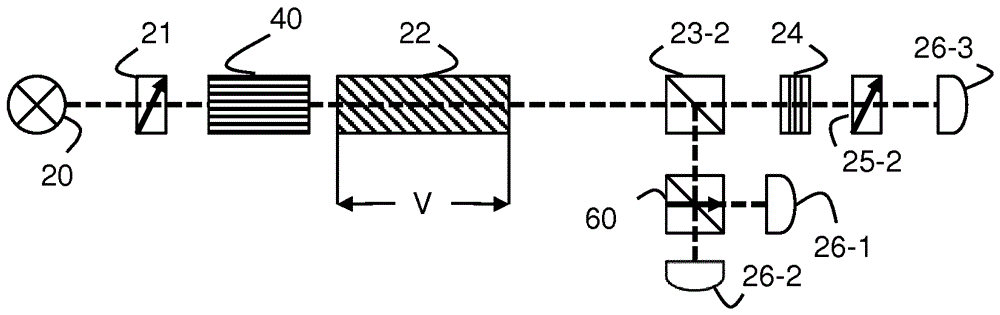
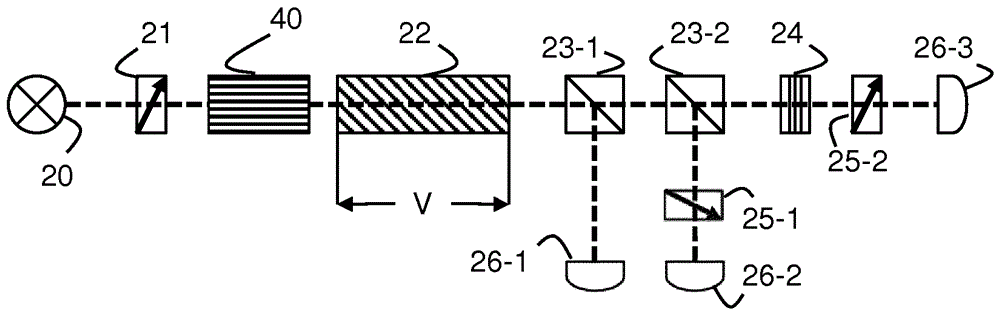
[0059] In the following, the example of an orthogonal polarization interferometer is used to describe the steps for signal manipulation or processing in the present invention. It should be noted that the basic principles of the described examples apply to many different types of interferometric sensors that otherwise suffer from period-wise ambiguities. Therefore, it can be applied to virtually any type of interferometer (Michelson, Mach-Zehnder, Fabry-Perot, Sagnac interferometer, etc.) with only minor differences in implementation or interpretation.
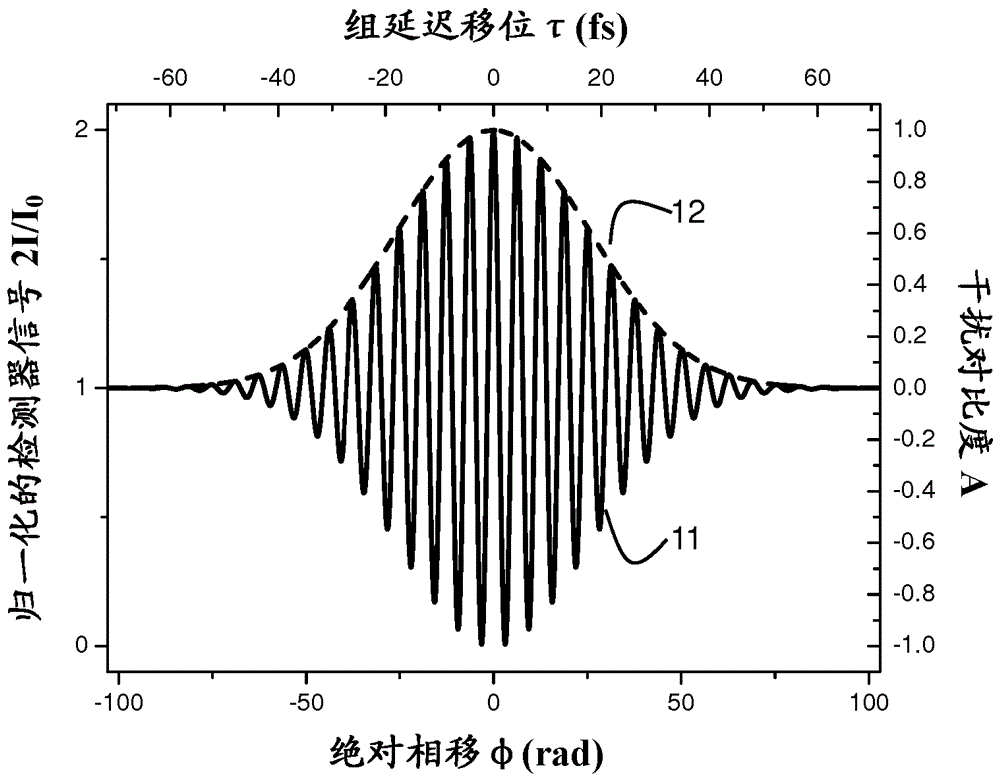
[0060] Typically, in an interferometer, the disturbed optical detector signal can be written as the sum of a fundamental term proportional to the output power of the light source and a sinusoidal term that varies as between phase shift of And change. In addition, the interference of non-monochromatic waves further introduces an additional modification of the temporal coherence of the waves to the detector signal . This ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com