Obstacle avoidance path optimal successive operation planning method for spatial multiplexing
A space multi-tasking, path-optimized technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, vehicle position/route/altitude control, non-electric variable control and other directions, can solve problems such as complex obstacle avoidance methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
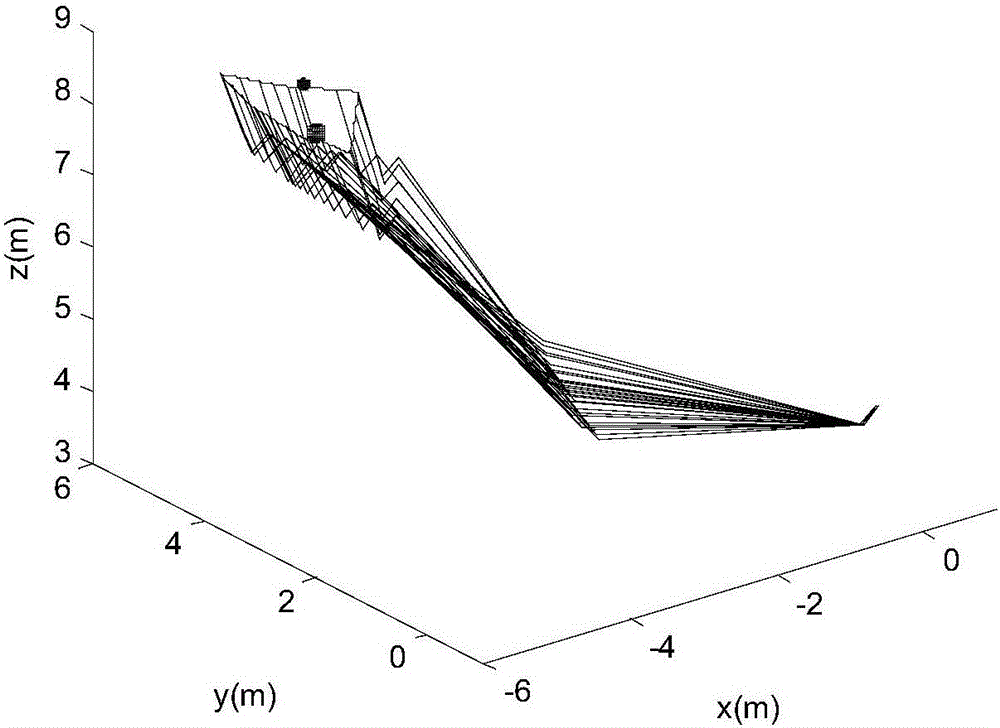
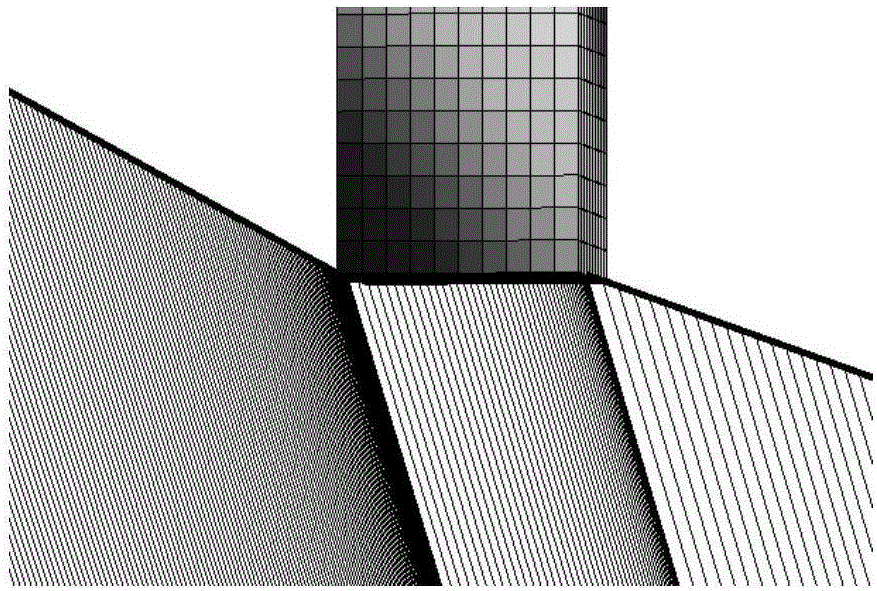
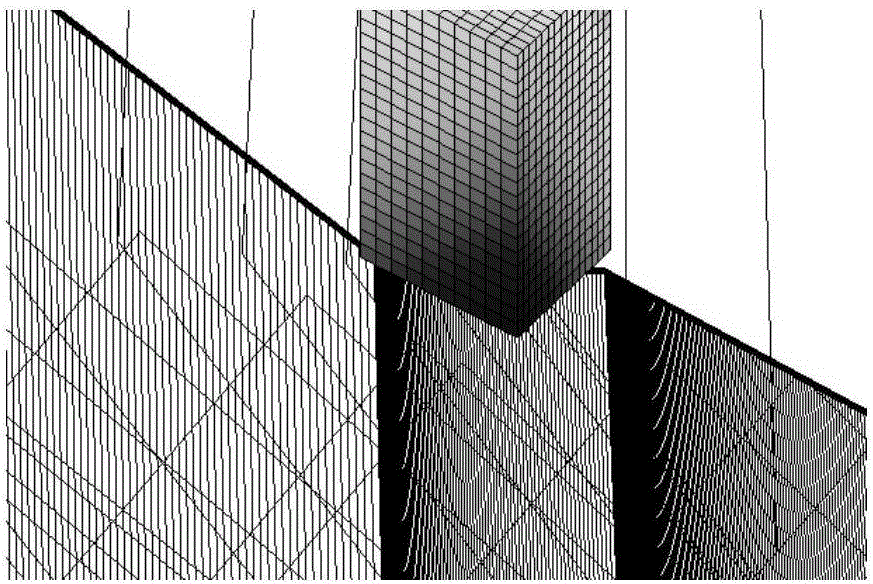
[0064] It is required that the end effector of the free-floating space robot system (see Table 1 for physical parameters) pass through four mission points (see Table 2 for position and attitude data), and there are irregular obstacles between adjacent mission points A and C, B and D See Table 3 for the optimal cube size surrounding irregular obstacles. The operating system needs to avoid obstacles and execute each task one by one. After completing the task, it returns to the initial task point. Excellent, and the attitude disturbance to the system body is zero.
[0065] Table 1 The positions and attitudes of the four task points
[0066]
[0067] Table 2 Optimal cube size surrounding irregular obstacles between mission points
[0068]
[0069] Table 3 Physical parameters of the free-floating space robot system
[0070]
[0071]
[0072] Figures 1 to 9 Schematic diagram of the path-optimized operation-by-operation planning for an operating system to perform task...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com